- How to restart the networking service?
- 18 Answers 18
- For Desktops
- For Servers
- For Servers
- How To Start, Stop, Restart Networking On Linux?
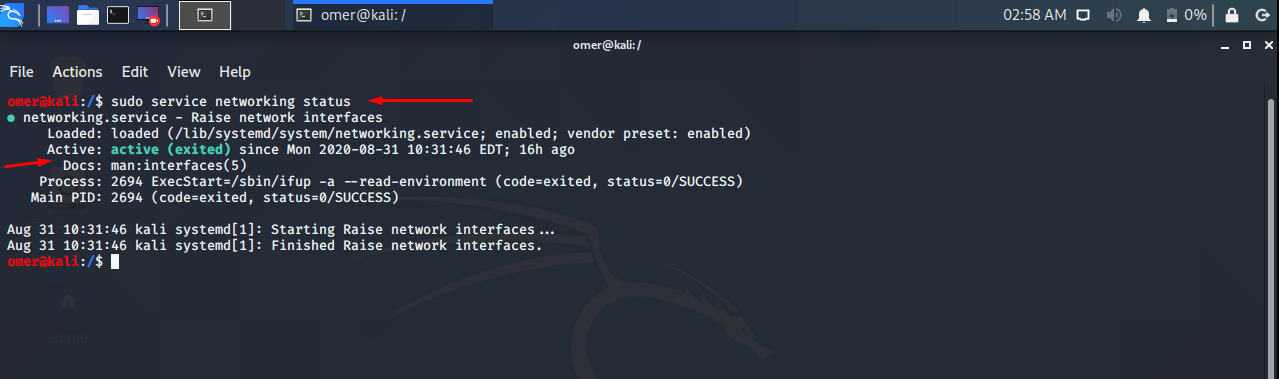
- Get Status Of Network Service
- Debian, Ubuntu, Kali
- Fedora, CentOS
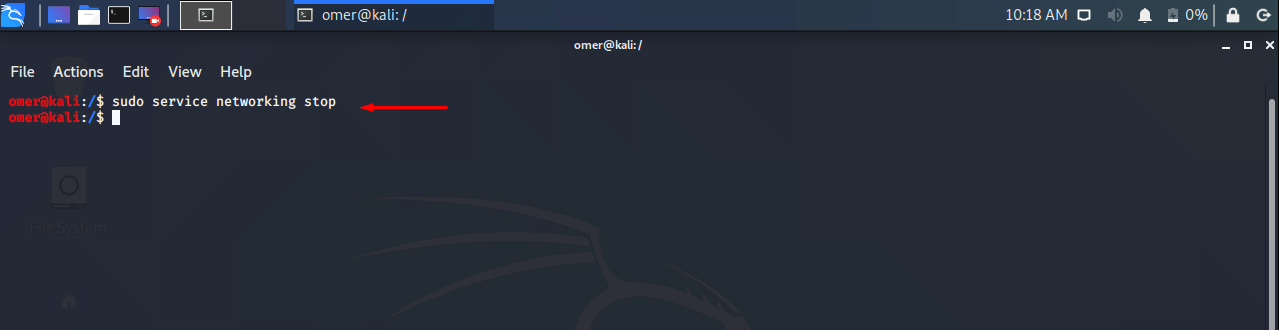
- Stop Network Service
- Ubuntu, Debian, Kali
- Fedora,CentOS
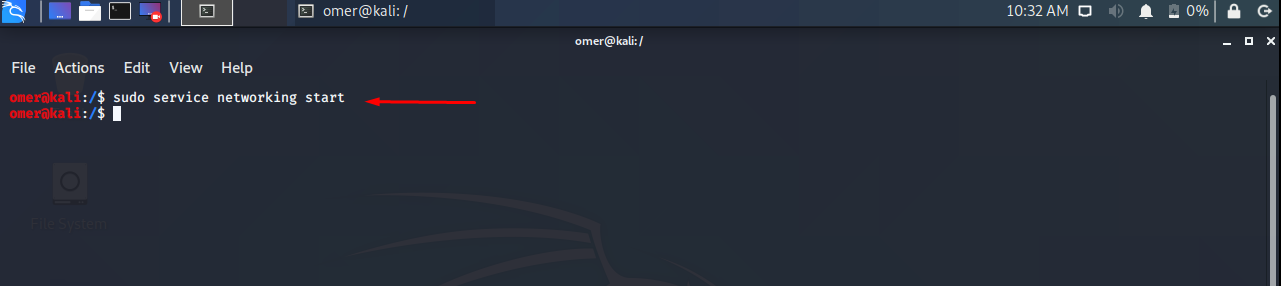
- Start Network
- Ubuntu, Debian, Kali
- Fedora,CentOS
- Restart Network
- Ubuntu, Debian, Kali
- Fedora,CentOS
- Restarting, Starting, Stopping, Checking the Status of the Network Service in Linux
- Network Operations
- Stop Network Service
- Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
- Fedora and CentOS
- Start Network Service
- Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
- Fedora and CentOS
- Status Network Service
- Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
- Fedora and CentOS
- Restart Network
- Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
- Fedora and CentOS
- How To start/Stop/Restart Network Service on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- Starting Network Service in Ubuntu
- Stop Network Service in Ubuntu
- Restart Network Service in Ubuntu
- Checking Status of Networking Service
- Enabling Netowrk Service in Ubuntu
- Disabling Network Service in Ubuntu
- Conclusion
How to restart the networking service?
Note that you might reanimate your keyboard, if you unplug and replug it — and it is hot pluggable, i.e. USB.
I also faced similar issue on Gnome 3 on Ubuntu 13.03. Screen disorted as top bar gone. Short keys not worked. As no menu/Activies shown I get no way to operate the system. Luckily console was opened already. So reboot command can be typed.
if you are looking for GUI method just open dash, type «Network» and select that. now press «On/Off» button to turn off and again click to on. your networking is restarted now.
18 Answers 18
For Desktops
sudo service network-manager restart Or on recent Ubuntu versions:
sudo systemctl restart systemd-networkd Ubuntu uses network-manager instead of the traditional Linux networking model. so you should restart the network-manager service instead of the network service. Or use ifup/down.
For Servers
hmm, strange that restarting just networking breaks the system. Does it happen to you too or is it just me?
For Servers
Restarting networking on a desktop machine will cause dbus and a bunch of service to stop and never be started again, usually leading to the whole system being unusable.
As Ubuntu does event based network bring up, there quite simply isn’t a way to undo it all and redo it all, so a restart just isn’t plain possible. The recommended way instead is to use ifdown and ifup on the interfaces you actually want to reconfigure:
sudo ifdown --exclude=lo -a && sudo ifup --exclude=lo -a @waspinator the bug is marked fixed as of march of this year: bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/dbus/+bug/1072518
Worked on Ubuntu Server 16.04.1. Ubuntu Server doesn’t appear to include Network Manager, so askubuntu.com/a/230751/13756 doesn’t work.
How To Start, Stop, Restart Networking On Linux?
I have changed my network configuration and want to restart to make changes effective. Or there are some problems with my network and I think restarting it will solve my problems. Here we will look at how to restart networking service in various network distributions like Ubuntu, Debian, Fedora, CentOS.
Get Status Of Network Service
We will get status of network with the following command.
Debian, Ubuntu, Kali
For deb based distributions we will use init.d system. We will provide status option to the networking script.
$ /etc/init.d/networking statusAs we cab see that networking service is active from given date. Its PID is 897 .
Fedora, CentOS
For distributions like CentOS, RedHat, Fedora we will use systemctl command. We will provide the options status and network which is the networking service.
Stop Network Service
We can stop network like below. Bu keep in mind for remote connection it can be create problems with ssh
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali
We will use stop option with networking command in order to stop network services in Ubuntu, Debian, Kali, Mint etc.
$ sudo /etc/init.d/networking stopFedora,CentOS
We will use systemctl again with stop option which will stop network services. We also require root privileges that will beget with sudo command.
$ sudo systemctl stop networkStart Network
We can start network like below.
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali
We will provide start option in order to start network services in deb based distributions.
$ sudo /etc/init.d/networking startFedora,CentOS
We will use start network option in order to start network services in rpm based distributions.
$ sudo systemctl start networkRestart Network
Now we can restart our network or network services.
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali
$ /etc/init.d/networking restartFedora,CentOS
$ systemctl restart networkRestarting, Starting, Stopping, Checking the Status of the Network Service in Linux
In Linux-based operating systems, information about network operations such as network settings, network commands or network configuration is included. In Linux operating systems, as everything is a file, network settings are also kept in files. The settings can be edited with any text editor or by various tools.
Network settings are located in the following files and directories.
/ etc / sysconfig / network file / etc / sysconfig / network-scripts directory / etc / hosts /etc/resolv.conf /etc/nsswitch.conf / etc / services
Each of the settings files is used for different operations. The files in the network-scripts directory are used for network settings. Network settings are eth0, eth1, etc. according to the network card in files starting with ifcfg. kept by names.
Inside the network settings;
DEVICE - Name of the network card. ONBOOT - The state that the network is activated at startup. BOOTPROTO - How to set network settings (static, dhcp, bootp). IPADDR - IP address. NETMASK - Network mask. BROADCAST - Broadcast address. GATEWAY - Specifies the gateway address.
It also has various settings such as MAC address, Network type. When you want to get IP using DHCP , it will be sufficient to write the DEVICE, BOOTPROTO and ONBOOT settings.
Network Operations
In Linux systems, we can use the following commands to examine the Stop, Start, Restart and Status of our Network services.
Stop Network Service
You can stop the network service as follows. Check before stopping the service. There will be a problem with your connection. We recommend that you try it in your test environment.
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali, Mint etc. We will use the networking stop command to service networking stop.
sudo service networking stop
Fedora and CentOS
Fedora and CentOS etc. We will use the networking stop command to systemctl stop network.target.
systemctl stop network.target
Start Network Service
You can start the network service as follows.
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali, Mint etc. We will use the networking start command to sudo service networking start.
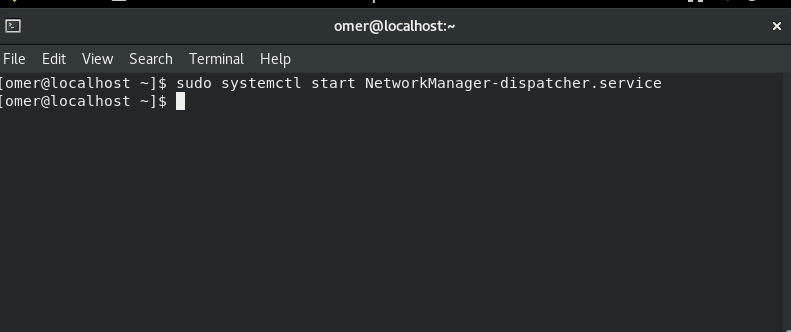
sudo systemctl start NetworkManager-dispatcher.service
Fedora and CentOS
Fedora and CentOS etc. We will use the networking stop command to sudo systemctl start NetworkManager-dispatcher.service.
sudo systemctl start NetworkManager-dispatcher.service
Status Network Service
You can status the network service as follows.
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali, Mint etc. We will use the networking start command to sudo service networking status.
sudo service networking status
Fedora and CentOS
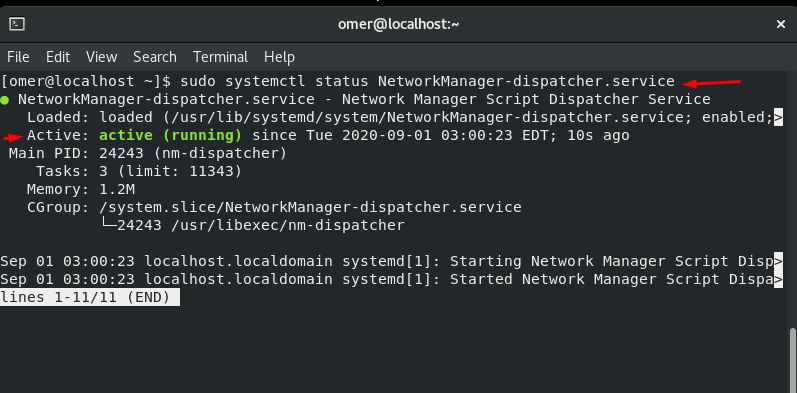
Fedora and CentOS etc. We will use the networking stop command to sudo systemctl status NetworkManager-dispatcher.service.
sudo systemctl status NetworkManager-dispatcher.service
Restart Network
You can restart the network service as follows.
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
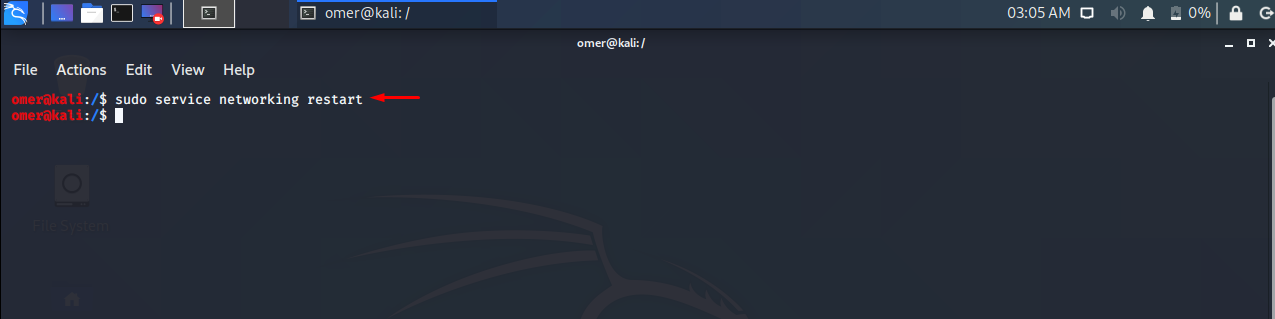
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali, Mint etc. We will use the networking start command to sudo service networking restart.
sudo service networking restart
Fedora and CentOS
Fedora and CentOS etc. We will use the networking stop command to sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager-dispatcher.service.
sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager-dispatcher.service
How To start/Stop/Restart Network Service on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
If you are working on a Ubuntu Linux system, and you may be need to set IP address for a given enternet interface or you need to change network settings by modifying networking configuration file called interfaces located in the /etc/network directory using your vim text editor. or you can use cat command to dispaly the content of the current networking configuration file, type:
$ sudo vim /etc/network/interfaces
devops@devops:~$ cat /etc/network/interfaces # interfaces(5) file used by ifup(8) and ifdown(8) auto lo iface lo inet loopback auto enp0s3 iface enp0s3 inet dhcp Starting Network Service in Ubuntu
If your network service daemon is stopped, and you may be need to start it by using the following command:
$ sudo systemctl start networking.service
$ sudo /etc/init.d/networking start
Stop Network Service in Ubuntu
If you wish to stop a network service in your Ubuntu or Debian Linux, and you can type the following comand:
$ sudo systemctl stop networking.service
$ sudo /etc/init.d/networking stop
Restart Network Service in Ubuntu
If you modified networking configuration in your Ubuntu system, and you need to restart its service by using the following command:
$ sudo systemctl restart networking.service
$ sudo /etc/init.d/networking restart
Checking Status of Networking Service
If you need to check the current status of networking service in your Ubuntu system, and you can issue the following command:
$ sudo systemctl status networking.service
$ sudo /etc/init.d/networking status
devops@devops:~$ sudo systemctl status networking.service networking.service - Raise network interfaces Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/networking.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (exited) since Tue 2019-10-08 02:59:03 EDT; 18min ago Docs: man:interfaces(5) Main PID: 1158 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Tasks: 0 (limit: 1121) CGroup: /system.slice/networking.service Oct 08 02:58:59 devops systemd[1]: Starting Raise network interfaces. Oct 08 02:59:03 devops systemd[1]: Started Raise network interfaces. Enabling Netowrk Service in Ubuntu
If you want to enable your network service at system boot on your Ubuntu system, and you can run the following command:
$ sudo systemctl enable networking.service
devops@devops:~$ sudo systemctl enable networking.service Synchronizing state of networking.service with SysV service script with /lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install. Executing: /lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install enable networking Disabling Network Service in Ubuntu
If you want to diable network service at system boot, just using the following command:
$ sudo systemctl disable networking.service
Conclusion
You should know that how to start/stop/restart/enable/disalbe network service in your Ubuntu or Debian L Linux system.