- Запускаем диспетчер задач в Linux
- Открываем диспетчер задач в терминале
- Запускаем графический диспетчер задач
- Ищем системный вариант
- Загружаем системный монитор из графической оболочки Gnome
- linux task manager console
- What is the standard console Task Manager in Linux?
- How do I open Task Manager in Ubuntu?
- What is the Linux equivalent of Ctrl Alt Del?
- Does Linux have a task manager?
- How do you kill a task in Linux?
- How do I open Task Manager?
- How do I see CPU usage on Linux?
- How do I see running processes in Linux?
- How do I kill a process in Ubuntu?
- Is there a Ctrl Alt Delete for Ubuntu?
- How do I unfreeze Ubuntu?
- How to open task manager in Linux?
- Linux task manager
- How to open the GUI task manager in Linux?
- How to access the command-line task manager on Linux?
- How to use the Ctrl+Alt+Del shortcut to launch task manager?
- Yadullah Abidi
- Диспетчер задач в Ubuntu
- Диспетчер задач Ubuntu
Запускаем диспетчер задач в Linux
Несмотря на более высокую отказоустойчивость Linux в сравнении с Windows, случается так, что нужно получить доступ к диспетчеру задач, чтобы «убить» какой-то процесс или просто отследить его поведение (избыточное потребление ресурсов или некорректную работу).
Открываем диспетчер задач в терминале
Отследить запущенные в Linux процессы можно с помощью текстовой утилиты htop. Она довольно наглядно отображает всю необходимую информацию. В ней есть удобный поиск конкретных процессов и взаимосвязи между запущенными программами. Также в программе можно посмотреть код PID процесса для его завершения через командную строку. В общем, это полноценный диспетчер задач, только jy работает в терминале и управляется не так, как мы привыкли в графической оболочке.
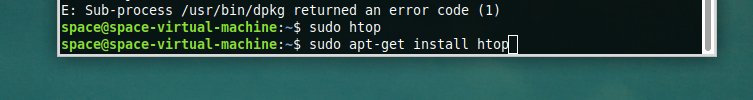
По умолчанию этого диспетчера задач нет в большинстве дистрибутивов. Поэтому придется скачать его. Благо он доступен в популярных репозиториях. Скорее всего, получится установить htop одной командой sudo название менеджера пакетов install htop.
Например, в Ubuntu (или в его дериватах типа Linux Mint и Elementary OS) — sudo apt-get install htop В Fedora — __sudo dnf install htop__
В openSUSE — sudo zypper install htop
Вот как будет выглядеть процесс установки на примере Linux Mint:
Загружаем утилиту в систему с помощью стандартного менеджера пакетов
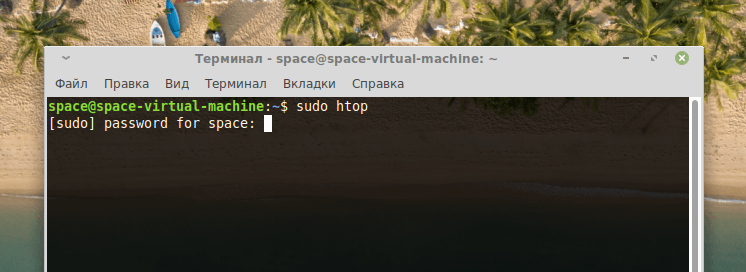
При вводе пароля набираемые символы могут не отображаться. Придется вписывать их вслепую
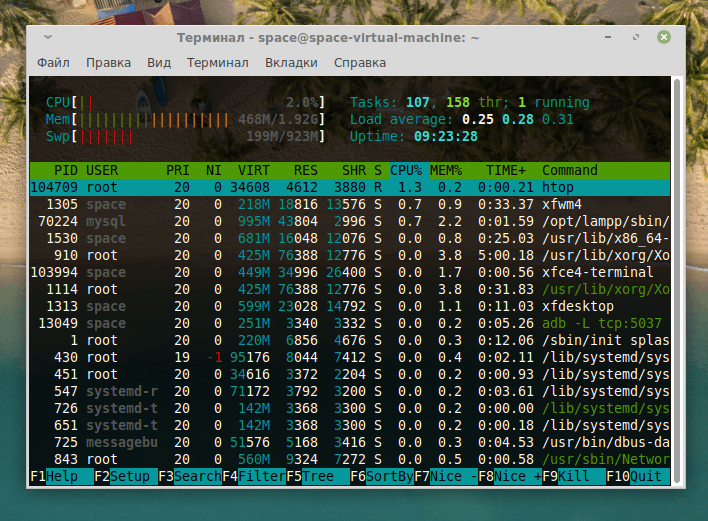
На этом все. Теперь остается разобраться с тем, как работает диспетчер задач. Элементы управления расположены в нижней части окна и закреплены за клавишами F1-F9.
Вот как выглядит наш диспетчер задач
Запускаем графический диспетчер задач
Если разбираться в терминале не очень хочется, то можно воспользоваться одним из доступных графических диспетчеров задач или загрузить какой-нибудь на свой вкус. Я рассмотрю диспетчер задач, встроенный в графическую оболочку XFCE, а также загружу аналогичную утилиту из рабочего стола Gnome.
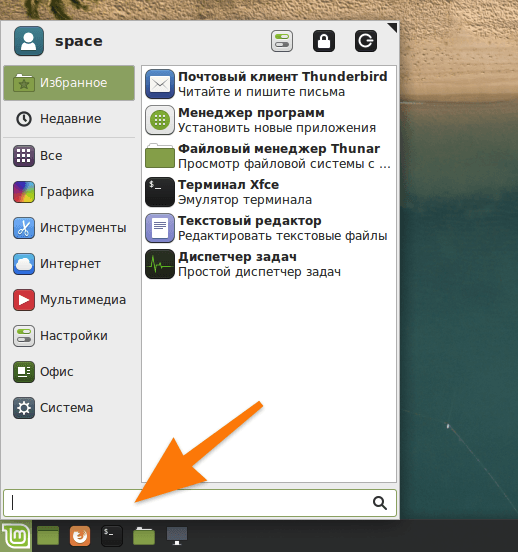
Ищем системный вариант
Когда нет каких-то особых предпочтений в выборе программ, сначала стоит попробовать отыскать в системе уже имеющийся диспетчер задач.
В оболочке XFCE меню располагается в левом нижнем углу (как и в KDE). А в GNOME 3 оно отображается в верхнем левом углу
- Прописываем в поиск название программы (обычно она так и называется, «Диспетчер задач» или «Системный монитор»).
Ищем подходящее приложение
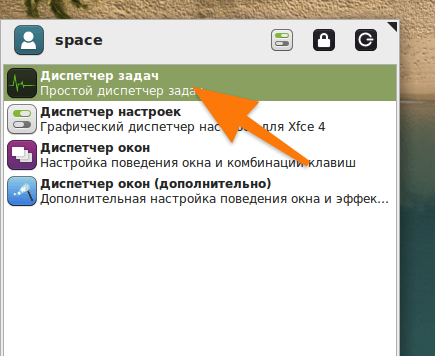
И, собственно, все. В моем примере используется графическая оболочка XFCE со встроенным диспетчером задач. Диспетчер довольно минималистичен и не так функционален, как его аналоги. Но это дело вкуса.
Вот как выглядит диспетчер задач в XFCE
Загружаем системный монитор из графической оболочки Gnome
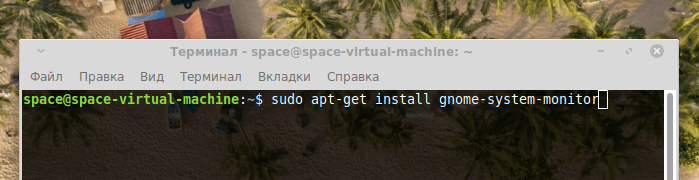
Большим спросом пользуется диспетчер задач из графической оболочки Gnome. Он относительно современный и отображает более подробную информацию о процессах, протекающих в системе. Тем, кто привык к работе с GUI, он точно понравится. Чтобы начать с ним работать:
- Просто скачиваем диспетчер задач с помощью команды sudo apt-get install gnome-system-monitor
Загружаем нужный компонент из базового репозитория
Открываем диспетчер задач из терминала. При желании можно найти соответствующий ярлык в списке установленных программ
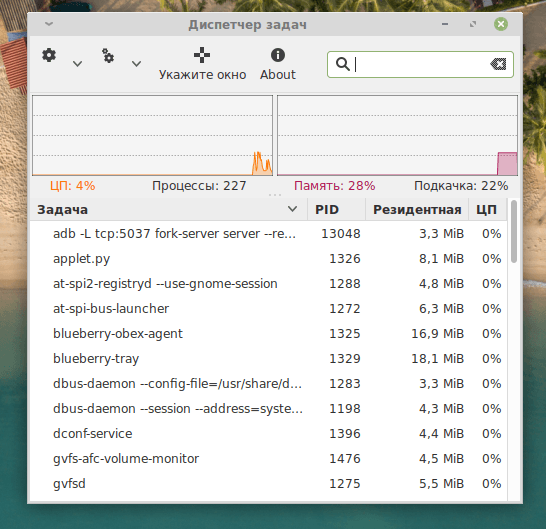
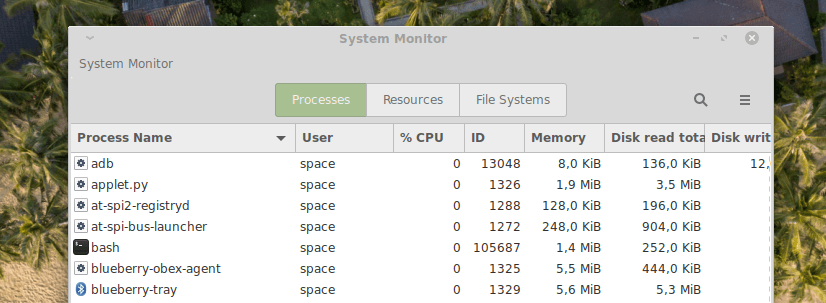
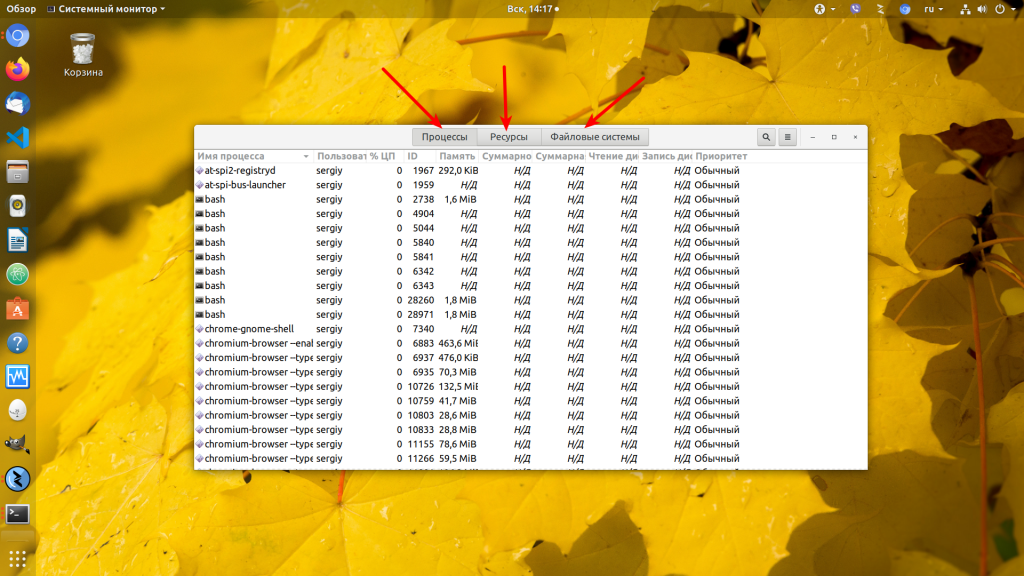
Интерфейс Gnome System Monitor делится на три части. В первой вкладке отображается список запущенных процессов, имя пользователя, который их запустил, и количество ресурсов, которое потребляют действующие программы.
Здесь можно управлять всеми запущенными программами. Есть удобный поиск по задачам
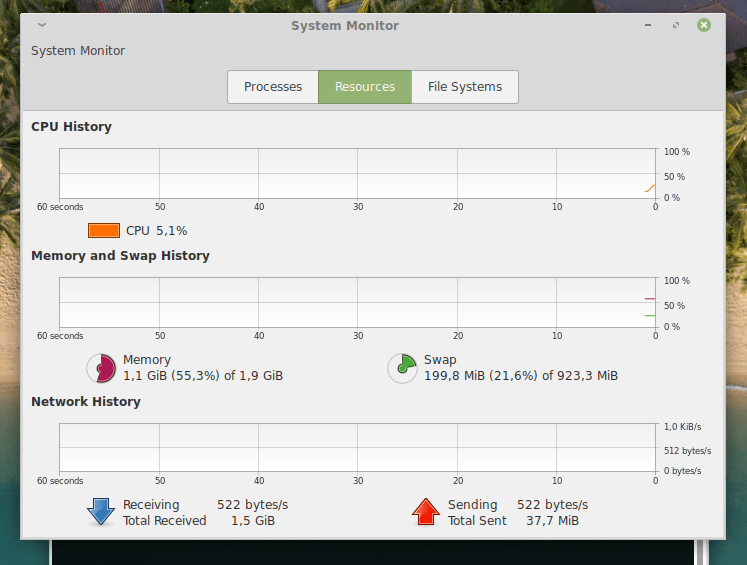
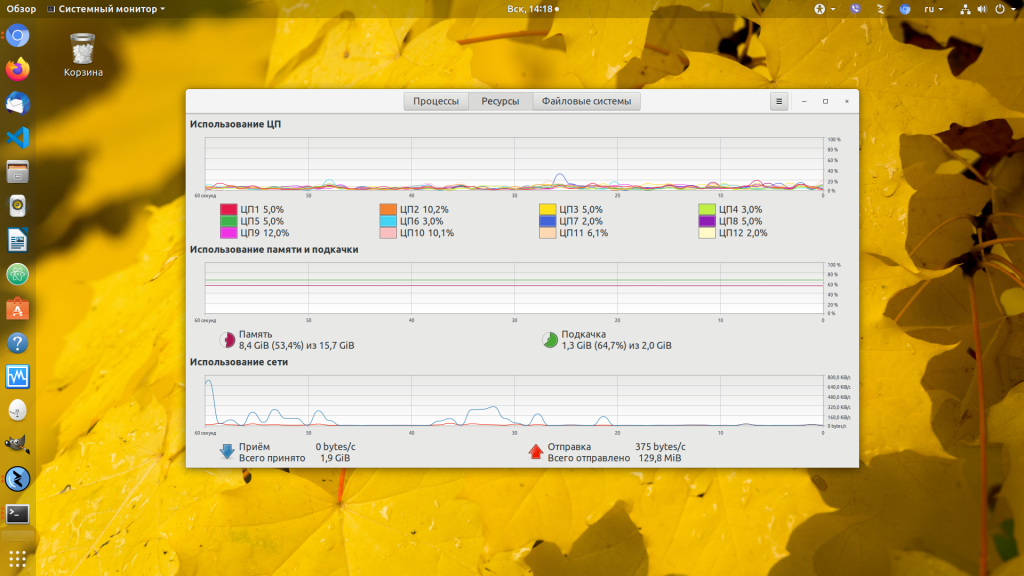
Вторая вкладка полностью посвящена отслеживанию потребляемых ресурсов. История нагрузки на процессор. История заполнения оперативной и физической памяти. А также история потребления трафика (загрузки и выгрузки).
Следим за используемыми ресурсами
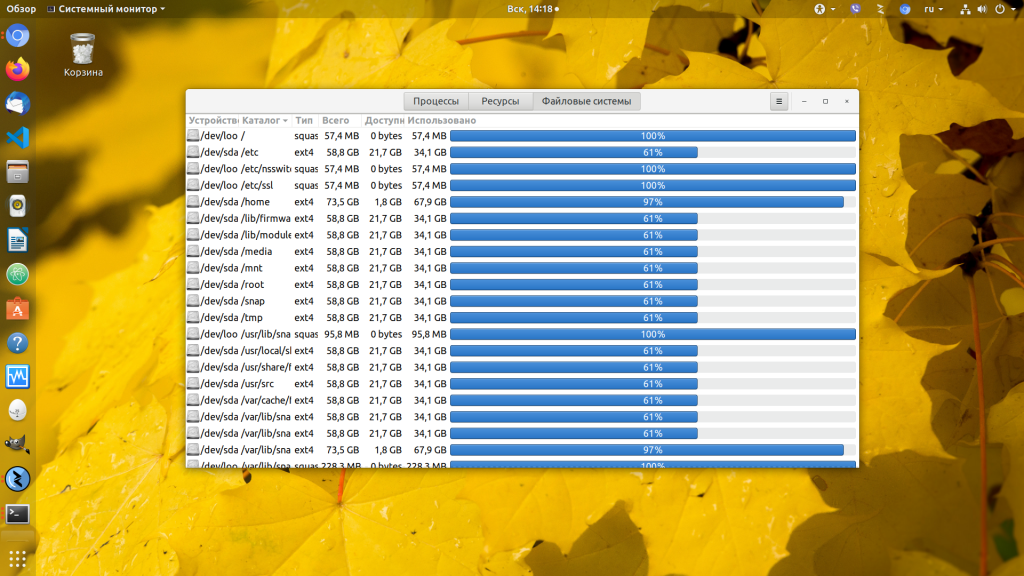
В третьей вкладке отображаются все подключенные физические диски (включая внешние диски и флешки). Можно посмотреть сколько места занято и свободно.
linux task manager console
How to open Task Manager in Ubuntu Linux Terminal. Use Ctrl+Alt+Del for Task Manager in Ubuntu Linux to kill unwanted tasks and programs. Just like Windows have Task Manager, Ubuntu has a built-in utility called System Monitor which can be used to monitor or kill unwanted system programs or running processes.
What is the standard console Task Manager in Linux?
1. Top. “top” is one of the most common task managers used by Linux users. Unlike other tools, the top task-manager comes preinstalled on all Linux distributions.
How do I open Task Manager in Ubuntu?
You may want an Ubuntu equivalent of the Windows Task Manager and open it via Ctrl+Alt+Del key combination. Ubuntu has the built-in utility to monitor or kill system running processes which acts like the “Task Manager”, it’s called System Monitor.
What is the Linux equivalent of Ctrl Alt Del?
In the Linux console, by default in most distributions, Ctrl + Alt + Del behaves as in the MS-DOS — it restarts the system. In the GUI, Ctrl + Alt + Backspace will kill the current X server and start a new one, thus behaving like the SAK sequence in Windows ( Ctrl + Alt + Del ). REISUB would be the closest equivalent.
Does Linux have a task manager?
In Windows you can easily kill any task by pressing Ctrl+Alt+Del and bringing up the task manager. Linux running the GNOME desktop environment (i.e. Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint, etc.) has a similar tool that can be enabled to run exactly the same way.
How do you kill a task in Linux?
- What Processes Can You Kill in Linux?
- Step 1: View Running Linux Processes.
- Step 2: Locate the Process to Kill. Locate a Process with ps Command. Finding the PID with pgrep or pidof.
- Step 3: Use Kill Command Options to Terminate a Process. killall Command. pkill Command. .
- Key Takeaways on Terminating a Linux Process.
How do I open Task Manager?
Hit Ctrl + Alt + Del and say that you want to run Task Manager. Task Manager will run, but it’s covered by the always-on-top fullscreen window. Whenever you need to see Task Manager, use Alt + Tab to select Task Manager and hold the Alt for a few seconds.
How do I see CPU usage on Linux?
- 1) Top. The top command displays real-time view of performance-related data of all running processes in a system. .
- 2) Iostat. .
- 3) Vmstat. .
- 4) Mpstat. .
- 5) Sar. .
- 6) CoreFreq. .
- 7) Htop. .
- 8) Nmon.
How do I see running processes in Linux?
- Open the terminal window on Linux.
- For remote Linux server use the ssh command for log in purpose.
- Type the ps aux command to see all running process in Linux.
- Alternatively, you can issue the top command or htop command to view running process in Linux.
How do I kill a process in Ubuntu?
- Step 1: Find the process ID (PID) of the program. There are several ways you can use for finding the PID of a process. .
- Step 2: Kill the process using the PID. Once you have the PID of the desired application, use the following command to kill the process: sudo kill -9 process_id.
Is there a Ctrl Alt Delete for Ubuntu?
You can now use Ctrl + Alt + Del to launch the task manager on your Ubuntu system. That can be very useful in situations where your system has frozen, and you need to kill some applications forcefully.
How do I unfreeze Ubuntu?
When everything stops working, first try Ctrl + Alt + F1 to go to a terminal, where you can likely kill X or other problem processes. If even that doesn’t work, try using holding down Alt + SysReq while pressing (slowly, with a few seconds between each) R E I S U B .
Firefox
How to Install Firefox 83 on Fedora 33/32 & CentOS 8/7Step 1 – Remove Existing Version. Some of the Linux distributions have pre installed firefox.
Wine
How To Install Wine 5.0 on Debian 10 (Buster)Step 1 – Prerequsiteis. In order to run Winehq, You need to enable i386 architecture on your Debian syste.
Zoom
Debian, Ubuntu, or Linux MintOpen the terminal, type in the following command and press Enter to install GDebi. . Enter your admin password and cont.
Latest news, practical advice, detailed reviews and guides. We have everything about the Linux operating system
How to open task manager in Linux?
Most Linux beginners tend to look for similarities between Linux and Windows, especially if they’re coming over from the latter. While there are some stark resemblances between the two, there are quite a few differences as well.
In this article, we’re going over how to open a task manager in Linux.
Linux task manager
There isn’t a task manager in Linux per se; it’s called the system monitor instead. The Linux terminal is the primary way of doing just about anything on a Linux system, but there are GUI alternatives.
How to open the GUI task manager in Linux?
To open the GUI system monitor in GNOME-based Linux machines, hit the windows key and search for System Monitor. You’ll see a utility quite similar to the Windows Task Manager.
Here you can monitor and close processes as well as keep an eye on your System resources.
How to access the command-line task manager on Linux?
Another way to accessing the Linux system monitor is using the htop command. It launches a command-line utility that can be used to monitor processes and system resources.
If you get an error while trying to run the htop command, you can install the tool using this command.
apt install htopHow to use the Ctrl+Alt+Del shortcut to launch task manager?
In GNOME-based systems, the Ctrl + Alt + Del shortcut launches the system shutdown prompt by default. However, you can change this shortcut to launch the System Monitor instead. Here’s how.
Step 1: Press the Windows key and search for Keyboard shortcuts. Click on the corresponding result.
Step 2: Scroll down and click on the + icon.
Step 3: Now type the name, command and keyboard shortcut. The command is going to be a gnome-system-monitor, and the shortcut can be anything you want. In this case, we’re going to enter Ctrl + Alt + Del.
Click Add when you’re done.
Now you can access the System Monitor using the keyboard shortcut you just set.
Yadullah Abidi
Yadullah is a Computer Science graduate who writes/edits/shoots/codes all things cybersecurity, gaming, and tech hardware. When he’s not, he streams himself racing virtual cars. He’s been writing and reporting on tech and cybersecurity with websites like Candid.Technology and MakeUseOf since 2018. You can contact him here: [email protected]
Диспетчер задач в Ubuntu
Многих новых пользователей Linux, только-только перешедших с Windows, интересует, где же диспетчер задач в Ubuntu. Да и вообще, что делать, если какая-либо программа не отвечает. Но такая вот штука — нет в Ubuntu диспетчера задач, зато есть системный монитор и пара очень полезных консольных команд.
Да и сама система виснет очень редко, зависнуть может только окружение рабочего стола, да и то, если что-то намудрить с настройками. Подробнее о том, что делать в таких случаях, читайте в статье что делать если зависла Ubuntu, а пока поговорим про диспетчер задач.
Диспетчер задач Ubuntu
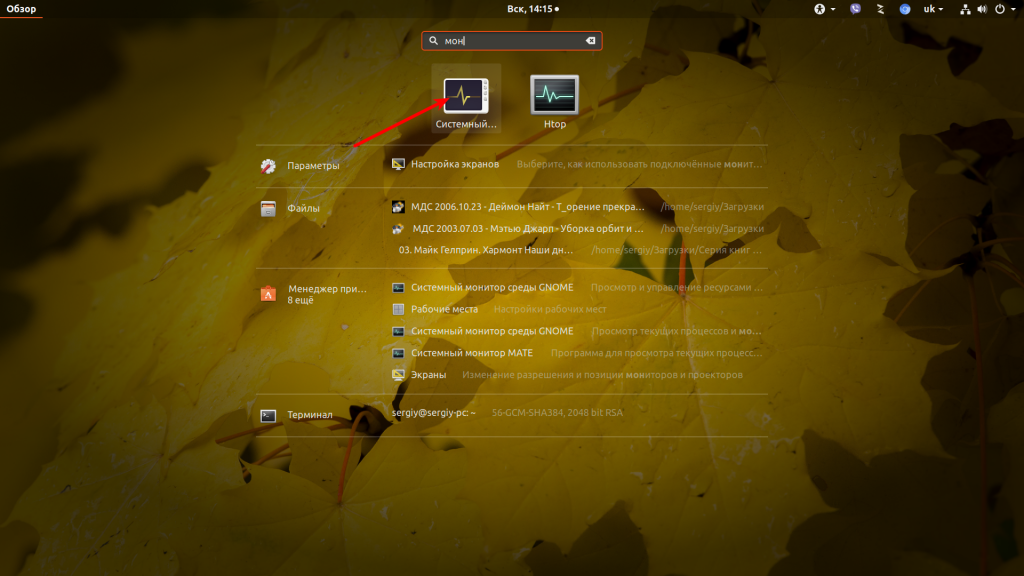
Чтобы запустить системный монитор, откройте главное меню системы и наберите в поиске monitor или монитор:
Здесь так же как и диспетчере задач вы можете просмотреть список запущенных процессов, завершать процессы, следить за использованием памяти, центрального процессора и файловых систем. Для этого у программы есть три вкладки:
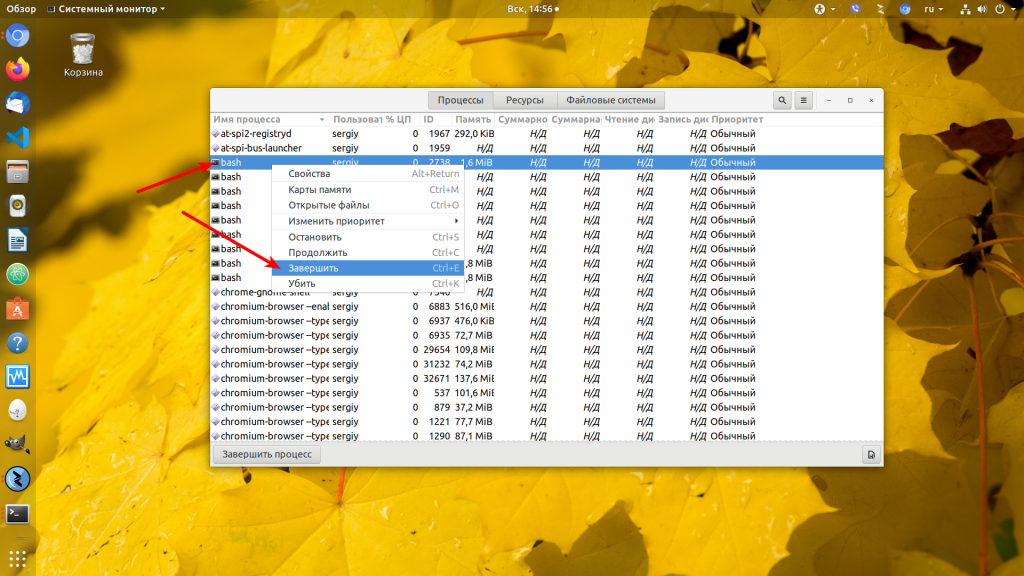
Чтобы завершить программу кликните, по ней в списке правой кнопкой мыши и выберите:
Если программа после этого не завершилась, можете выбрать в том же меню пункт Убить. Подробнее об этом читайте в статье как убить процесс Linux.
Но если зависло окружение рабочего стола то системный монитор уже не поможет, в этом случае можно воспользоваться всей мощностью терминала Linux. По умолчанию в системе открывается 7 независимых терминалов, в одном из которых запускается окружение рабочего стола. Обычно это седьмой терминал. Переключаться между ними можно с помощью сочетания клавиш Ctrl+ Alt + номер терминала, чтобы открыть первый терминал, нужно нажать Ctrl+Alt+1 и т д:
Здесь нужно авторизоваться, указав сначала логин, затем пароль. После авторизации можно делать всё что угодно, например, перезапустить графическое окружение командой:
sudo systemctl restart display-manager
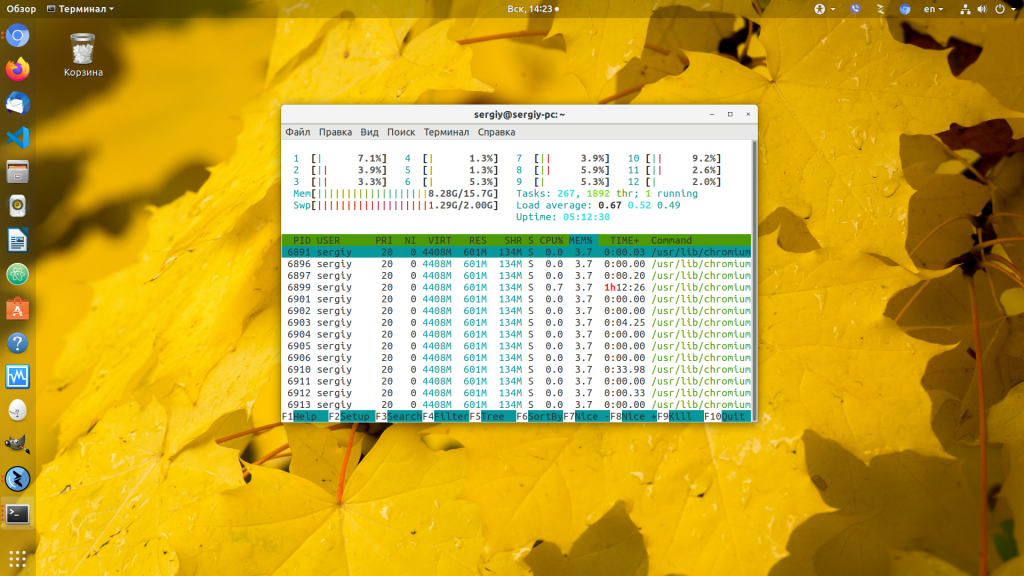
Если вам нужен аналог диспетчера задач в терминале, можете воспользоваться утилитой htop. Для её установки выполните:
Затем её можно запустить одноимённой командой:
Если вам нужно завершить конкретное приложение, его легче найти командой:
ps aux | grep имя_приложения
Затем завершить его командой:
sudo kill -TERM pid_приложения
Где pid_приложения — уникальный идентификатор приложения в системе, который вы узнали в предыдущей команде, во второй колонке:
На этом всё. Желаю вам, чтобы ваша система никогда не зависала.
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.