- Is user + sys time equal to real/wall clock time?
- 4 Answers 4
- Related
- Hot Network Questions
- Subscribe to RSS
- Should I use «real» or «user+sys» on the time function?
- 1 Answer 1
- Linked
- Related
- Hot Network Questions
- Subscribe to RSS
- Introduction
- I have this code:
- That reports this:
- Why is sys time reporting zero?
- 1 Answer 1
- Basics First
- Understanding what is sys time reporting and what does 0 value mean
- How to use time command in Linux
- What is the use of time command in Linux
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Hammad Zahid
Is user + sys time equal to real/wall clock time?
Is this true? I read some other questions where people did things like saving the current time away in a variable and collecting it later, but why wouldn’t this work?
4 Answers 4
No, it is not. User and system time account only for used CPU time. While the program is asleep, real time still passes, but the user and system time stand still. Also, on multi-CPU systems, it may well happen that user+system is greater than real time.
C:\Temp> cat tt.pl sleep 5; my ($user, $system) = times; print "u = $user s = $system\n"; C:\Temp> tt u = 0.015 s = 0.015 Good point. it doesn’t count sleep(). I believe I knew that, but for some reason couldn’t think of that. Thanks.
No. User time and system time is something else.
my $start = time; sleep 5; my ($usr,$sys,$cusr,$csys) = times; my $stop = time; printf "Real time (approx): %gs User+sys: %gs\n", $stop-$start,$usr+$sys; Real time (approx): 5s User+sys: 0.077s Although a few people have showed you examples with sleep, also consider the real-life cases where your process is waiting for responses from remote machines, other processes, and so on. While you are waiting for your database query, wallclock time is marching on even as you aren’t using the processor.
Related
Hot Network Questions
Subscribe to RSS
To subscribe to this RSS feed, copy and paste this URL into your RSS reader.
Site design / logo © 2023 Stack Exchange Inc; user contributions licensed under CC BY-SA . rev 2023.7.14.43533
By clicking “Accept all cookies”, you agree Stack Exchange can store cookies on your device and disclose information in accordance with our Cookie Policy.
Should I use «real» or «user+sys» on the time function?
I understand the difference between «real»,»user» and «sys» when you use the time command on Linux, as explained on this other thread: What do ‘real’, ‘user’ and ‘sys’ mean in the output of time(1)? Now I am working on a small comparison between the performance of Python, Java and C, and I am wondering which report I should use. «User+sys» seems to be the more realistic one, but wouldn’t this cause problems when comparing C to Java, for instance, cause the JVM knows how to optimize the code for multi-processors/threads while GCC doesn’t? Also, wouldn’t «real» be realistic enough if I make sure no other heavy process is running on the background?
You seem to want to measure the cycles and not the time, maybe you should use another tool, no clue which one tho.
I know cycles would be better, but wouldn’t time be accurate enough to give a good idea of the performance of each language?
Don’t forget page faults. They are never accounted for in neither user nor sys. The clock keeps ticking on cache misses, but during page faults accounting is in essence stopped for your prococess. And page faults are expensive.
1 Answer 1
The answer will depend on what you mean by «the performance of (Python|Java|C)». In many cases what a user really cares about is the elapsed wall time, corresponding to real . Suppose you write some piece of code in a reasonable way in several languages and one of the languages can automatically parallelize it to use your 4 cores. If this makes the user wait less time for a reply, then I say this is a fair comparison. Of course it is valid for that particular machine, the results on a single core machine could be different. If an app causes page faults, then it makes the user wait. For the user it’s no help if you say the app took fewer cycles if they have to wait longer.
Any way you measure, be sure to repeat the tests multiple times, as there can be lots of variation between runs. Languages like Java also need a program to run for some time before it reaches top speed, due to JIT compilation (but again: if your program is very short by definition and doesn’t allow the Java Virtual Machine to warp up, then well it’s too bad for Java). Testing performance is very tricky and even experienced developers are prone to misinterpreting results or measuring not what they really intended.
Linked
Related
Hot Network Questions
Subscribe to RSS
To subscribe to this RSS feed, copy and paste this URL into your RSS reader.
Site design / logo © 2023 Stack Exchange Inc; user contributions licensed under CC BY-SA . rev 2023.7.14.43533
By clicking “Accept all cookies”, you agree Stack Exchange can store cookies on your device and disclose information in accordance with our Cookie Policy.
Introduction
I’ve been fine-tuning code to reduce processing from 30 seconds to under a second in various parts of my bash program. I’m having trouble wrapping my mind about how the time command works when it reports real , user and sys variables.
I have this code:
echo " " echo "Time to build DirsNdxArr from DirsArr $DirsArrCnt elements:" DirsArrCnt=$ time for (( i=1; i"]=$i AllItemSizes=$(( $AllItemSizes + $ )) done echo " " echo "Time to build FilesNdxArr from FilesArr $FilesArrCnt elements:" FilesArrCnt=$ time for (( i=0; i"]=$i AllTagSizes=$(( $AllTagSizes + $ )) done That reports this:
Time to build DirsNdxArr from DirsArr 56700 elements: real 0m0.149s user 0m0.149s sys 0m0.000s Time to build FilesNdxArr from FilesArr 390 elements: real 0m0.002s user 0m0.002s sys 0m0.000s Why is sys time reporting zero?
Interpreting the output of time builtin command one would assume the system is doing nothing but surely this isn’t what is happening? ps I know \n can be used as a new-line to echo with -e parameter. My habit is to sacrifice one liner-cuteness and fringe arguments in favor of readability.
@muru I did check for duplicates in Ask Ubuntu but I must admit I did not search Stack Overflow.
1 Answer 1
Long story short, it simply means that your program didn’t request to perform any privileged tasks, hence CPU has spend no time in the privileged (kernel) mode.
Basics First
First of all, there’s several things you need to understand in order to interpret the output of time properly:
- which time command you’re running (because there’s multiple)
- the meaning of each field and what each one of them means (extra reading here)
- the difference between kernel and user mode
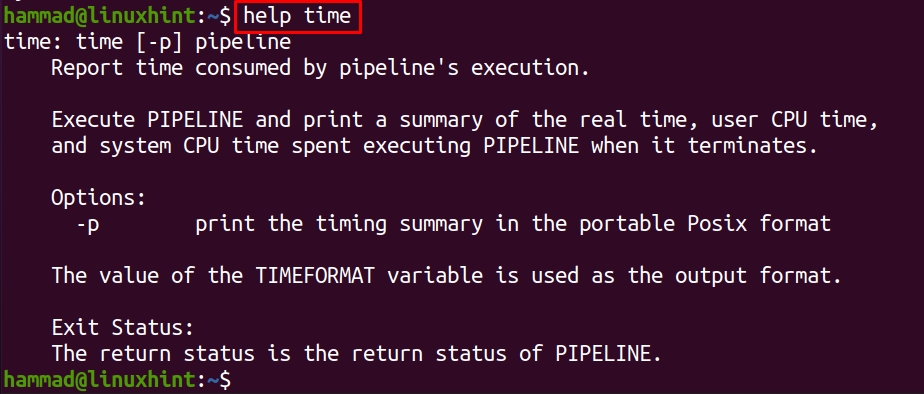
There’s two types time command. There’s shell built-in and there’s /usr/bin/time . The shell built in is the one that you’re using and it defaults to showing 3 lines, real , user ,and sys . The manual for time also mentions this same form of output:
-p, --portability Use the following format string, for conformance with POSIX standard 1003.2: real %e user %U sys %S And if you check the «FORMATTING THE OUTPUT» section we have:
E Elapsed real (wall clock) time used by the process, in [hours:]minutes:seconds. U Total number of CPU-seconds that the process used directly (in user mode), in seconds. S Total number of CPU-seconds used by the system on behalf of the process (in kernel mode), in seconds. From all this info we can gather that there’s two modes in which CPU can run — user mode and kernel mode, and the time command displays how long CPU remains in a given mode to do whatever your program/app has asked CPU to do.
Understanding what is sys time reporting and what does 0 value mean
OK, so we understand the difference is that there’s user mode and kernel mode in which code can run. We already can figure that this basically means the program didn’t use kernel mode for executing some tasks. What does that actually mean ?
In Kernel mode, the executing code has complete and unrestricted access to the underlying hardware. It can execute any CPU instruction and reference any memory address.
And from another answer on the same post:
The switch from user mode to kernel mode is not done automatically by CPU. CPU is interrupted by interrupts (timers, keyboard, I/O). When interrupt occurs, CPU stops executing the current running program, switch to kernel mode, executes interrupt handler. This handler saves the state of CPU, performs its operations, restore the state and returns to user mode.
So that’s what your output means — there was no switch to kernel mode and CPU did not receive any interrupts from the program to do so. This also means that your code doesn’t have anything that would require elevated privileges from CPU
Note: this probably should be rephrased as «there was no long/noticeable switch into kernel mode», since allocating memory with something like malloc() function in C would require switching into kernel mode, but these are microscopic switches, which we’d really have to investigate with a debugger or strace command.
How to use time command in Linux
Time is the essential parameter to evaluate the efficiency or performance of any task. Such a good processor is judged by good processing speed which is evaluated on the basis of time. Similarly, in Linux, the “time” command is used to evaluate the processing time taken by different commands in their execution. There are different ways to do the same task, for example, we can edit the text files using the vim editor as well as the nano editor, with the help of the time command we can evaluate which editor takes less execution time, then we can use that editor for text editing purposes for better performance.
What is the use of time command in Linux
In Linux, the time command is used to determine the execution time taken by the processor to execute the specified command.
The general syntax of using the time command:
The explanation to the above syntax is:
- Use the time clause to determine the time taken by the command
- Choose any options along with the time clause
- Type the command whose executed time you want to find out
For example, we execute a command which will take 4 seconds execution time and determine its time using the “time” command:
The output displayed that the command was executed in 4.002 seconds, there are three types of values in the output real, user, and sys, the explanation to them is as:
- Real: This is the actual time taken by the processor of the computer to execute the command from pressing the button to complete the command.
- User: CPU time that is taken by the user mode.
- SYS: This is the time taken by the system or the Kernel to execute the command.
We can also add an option by adding a flag of “-p”, that will display the time in portable POSIX format, to understand it, again run the above command using the “-p” flag:
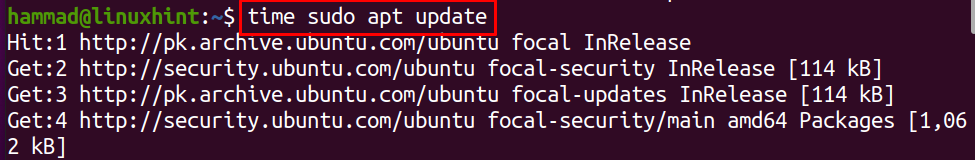
We will update the repository of the Linux and will monitor the time of update by using the time command:
It will take some time to update the repository:
It takes 36.289 seconds to update the packages repository. To understand more about the time command, we can run the help using the command:
If we want that the output of the time command is not displayed on the screen, instead of that it should be saved in the text file we can run the following command:
Note: We will use the “/usr/bin/time” instead of the “time” command because the shell built-in time command does not support the “-o” option.
To view the output of the file “output.txt”, use the command:
To have the detailed summary of the executed time, use the option “-v” with the “/usr/bin/time” command:
The above figure displays the detailed summary of the executed time for the command. In the last, Linux provides the manuals of all the built-in commands, to view the manual of the time command to seek some information, use:

Conclusion
The time command is used in Linux for testing purposes; it is used to test the performance of newly created applications. In this write-up, we have discussed the use of the time command in Linux that is used to monitor the execution time of the commands in Linux. We have discussed two syntaxes, the built-in “time” command and “/usr/bin/time” command with its different options.
About the author
Hammad Zahid
I’m an Engineering graduate and my passion for IT has brought me to Linux. Now here I’m learning and sharing my knowledge with the world.