- 6 Best To-Do List Managers for Linux Command Line
- 1. t Command-Line To-Do List Manager
- 2. Yokadi To-Do List Manager
- 3. Taskwarrior To-Do List Manager
- 4. DevTodo To-Do List Manager
- 5. Ultralist Task Management System
- 6. topydo To-Do List Manager
- Get Your Work Done Faster With These To-Do List Apps on Linux Desktop
- 1. Planner
- 2. WeekToDo Planner
- 3. Super Productivity
- 4. Go For It!
- 5. Endeavour (Previously GNOME To Do)
- 6. Todour
- 7. Task Coach
- Bonus: Terminal-based Taskwarrior to-do list app
- Wrapping Up
6 Best To-Do List Managers for Linux Command Line
As you grow your Linux operating system experience and become imprinted on its command-line environment, you start having more and more exciting tasks to do. With time, it might become impossible to keep track of what computing task or project milestone you have successfully accomplished.
Such a scenario might reduce your Linux OS productivity. However, with every problem associated with a Linux operating system, there is always a Linux-oriented solution. The best way of keeping track of your Linux OS activities/objectives is via a to-do list manager.
In this article guide, we will walk you through the analysis and installation of some recommended to-do list managers for your Linux command-line environment.
1. t Command-Line To-Do List Manager
t is a command-line to-do list manager that prioritizes the need to create a solution for users to finish tasks rather than organize them. Other list managers are attributed as feature-packed because their associated tasks can be prioritized, split, and tagged.
They also give users the opportunity to color-code tasks and order them if needed. As for t to-do list manager, it is simple and almost featureless. Its almost featureless attribute makes it faster to use than its mentioned nemesis such that you won’t spend too much time tagging tasks instead of finishing them. It is flexible and version-control-friendly.
To install t to-do list manager, you must have the latest Python3 (which comes preinstalled on most Linux distributions) and Git installed on your Linux system.
First, clone the repository and then create a directory for storing your to-do list:
$ git clone https://github.com/sjl/t.git $ cd t $ ls $ mkdir ~/tasks
Next, add an alias to t in the ~/.bashrc file.
alias t='python3 /path/to/t.py --task-dir ~/tasks --list tasks'
Reload the ~/.bashrc file.
To add, list, finish or edit a task, implement:
$ t [task description] #add a task $ t #list tasks $ t -f [task_ID] #finish a task $ t -e ID [edit description] #edit a task
More usage of t is on its manual page:
2. Yokadi To-Do List Manager
Yokadi is a command-line TO-DO list solution that is SQLITE-powered with the primary objective of aiding Linux users in organizing their workflow and ensuring they work on unfinished tasks.
Its functionality is characterized as efficient, intuitive, and simple. The tasks associated with this TO-DO list solution can have keywords, urgency, due date, and description.
To install Yokadi on Debian-based distributions using the apt package manager:
On other Linux distributions, we can make use of the pip – Python package manager.
$ sudo nano $HOME/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sqlalchemy/sql/base.py
Replace all instances of collections.MutableMapping with collections.abc.MutableMapping to avoid running into the error message:
AttributeError: module 'collections' has no attribute 'MutableMapping'
To launch and know the usage of yokadi, use:
$ yokadi > t_add virtualbox download and install virtualbox #create a task
As you can see, the first portion of the command has been taken as the project name (virtualbox) and the remaining portion as a task (download and install virtualbox).
We can add more tasks in the following manner:
> t_add _ install Ubuntu 20.04 on virtualbox
The underscore links the task to the last used project:
> t_add _ install RHEL8 on virtualbox > t_add _ install Arch Linux on virtualbox
To list the tasks associated with our project (virtualbox), we’ll run:
To mark a task as done, we will use its task ID e.g mark “install arch Linux on virtualbox” as done.
> t_mark_done 4 > t_list virtualbox
To list tasks accomplished today (present date):
> t_list virtualbox --done today
To associate a task with a due date, we will use the task ID:
> t_due 1 +2d > t_due 3 21/08 11:00
Refer to the Yokadi manual page for more command usage and references.
3. Taskwarrior To-Do List Manager
Taskwarrior is a command line task list management tool that comes with a multitude of features. To install Taskwarrior, use:
$ git clone --recursive -b stable https://github.com/GothenburgBitFactory/taskwarrior.git $ cd taskwarrior $ cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=release . $ make $ sudo make install
To create a task or to-do list associated with a due date:
$ task add Pay Internet due:eom
To create a task without a due date and add a due date later:
$ task add Pay Water Bill $ task 2 modify due:eom
To remove the due date from the specific task:
If your task has multiple line description, you can create it in the following manner:
$ task add "Ten things to learn from LinuxShellTips before 2022 ends!"
To display a list of your created tasks, run:
A complete user manual of this utility can be found by running the command:
4. DevTodo To-Do List Manager
DevTodo utility is hierarchically organized such that it can track the creation and completion time of tasks. To install it, you need Homebrew installed on your machine.
$ todo -a Pay Monthly Internet
We can also add a sub-task to the above task by specifying its index:
$ todo -ag 1 Vilcom Subscription
To add another sub-task, we will reference the sub-task index 1.1 above:
A complete user manual of this utility can be found by running the command:
5. Ultralist Task Management System
Ultralist is easy to use, powerful, and open-source task management system for the Linux command line. We can install it via Homebrew in the following manner:
The first step is to initialize an ultralist repo:
The following screenshot reveals a summary of commands associated with using Ultralist as a to-do list manager.
For instance, to add, mark, or list tasks:
$ ultralist add task_name $ ultralist complete task_name $ ultralist list
6. topydo To-Do List Manager
Users can benefit from topydo utility’s due and start date features, and recurring to-do items. Its installation requires pip3 (Python3 package manager).
To see all available commands associated with topydo, run:
For example, to add or list items:
$ topydo add item_1 $ topydo ls
These solutions ensure that your TO-DO lists are purely command-line driven. Know of another TO-DO list manager for the Linux command line? Feel free to leave a comment or feedback.
Get Your Work Done Faster With These To-Do List Apps on Linux Desktop
A good to-do list app helps you organize your work and be more productive by focusing on meaningful work. Here are the best to-do list apps for Linux desktop.
Getting work done is super important. If you have a planned list of things to do, it makes your work easier. So, it’s no surprise why we’re talking about to-do list apps on Linux here. Sure, you can easily utilize some of the best note-taking apps on Linux for this purpose, but using a dedicated to-do app helps you stay focused on work. You might be aware of some online services for that— but how about some cool Linux apps that you can use to create a to-do list? In this article, I will highlight the best to-do list apps available for Linux. I have tested these apps on Pop!_OS. I have also mentioned the app installation steps, but you should check your distribution package manager for details.
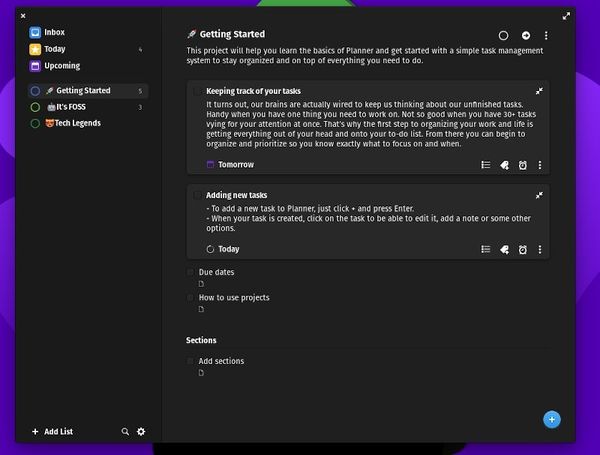
1. Planner
Planner is probably the best to-do list app I’ve come across for Linux distributions. The best thing is — it is a free and open-source project. It provides a beautiful user interface that aims to give you a meaningful user experience. In other words, it’s simple yet attractive. Not to forget, you get a gorgeous dark mode. As you can see in the screenshot above, you can also choose to add emojis to add some fun to your serious work tasks. Overall, it looks clean while offering features like the ability to add repeating tasks, create separate folders/projects, sync with todoist etc. How to install it? You can try install its Flatpak package from Flathub. Unless you have Flatpak integration in your software centre, you should follow our guide to use Flatpak on Linux to get it installed. In case you want to explore the source code, take a look at its GitHub page.
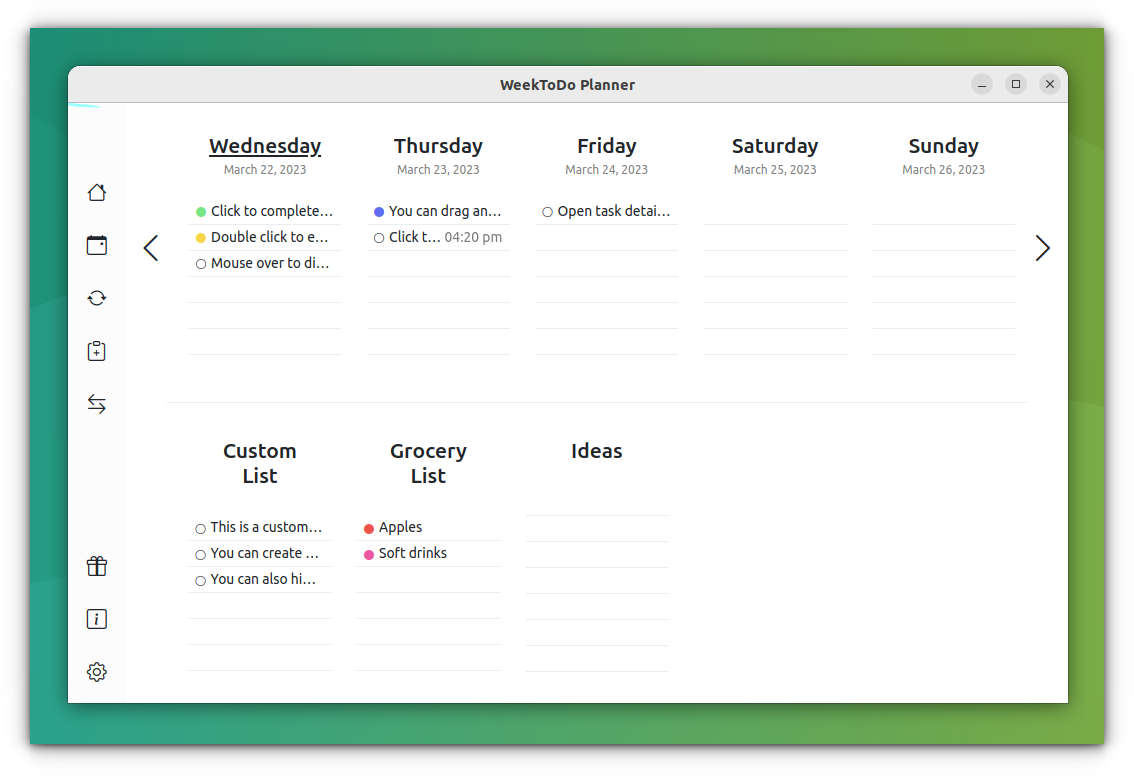
2. WeekToDo Planner
WeekToDo Planner is a free and open-source weekly planner app. It provides a minimalistic and simple user interface to plan your week. Apart from weekly planning, it offers features like custom lists, calendar support, recurring tasks, etc. You can also set alarms, subtasks, notes to tasks, etc. It also features beautiful dark theme support. It is privacy-friendly because all your data is stored on your device. How to Install it? Getting Weektodo planner working is really simple because it provides an installation file for almost all systems. You can download deb/rpm or go for the AppImage file from their official downloads page. Visit their GitHub repo for more information about the project.
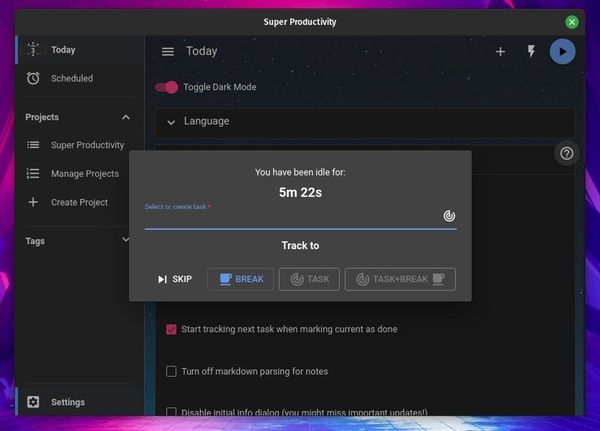
3. Super Productivity
It is a mind-blowing to-do app with a lot of essential features. You can even integrate GitHub issues and assign yourself tasks if you want. How to install Super Productivity? You can find the AppImage file, and the DEB/RPM package in its GitHub releases section. In addition to that, you can also find a snap for it available.
4. Go For It!
Yet another impressive open-source to-do app for Linux which is based on todotxt. In addition to the ability to add tasks, you can also specify the duration/interval of your break. So, with this to-do app, you will not just end up completing the tasks but also being productive without stressing out. The user interface is plain and simple with no fancy features. We also have a separate article on Go For It — if you’d like to know more about it. How to install it? In case you want to install it on any Linux distro, you can try the Flatpak package on Flathub. If you don’t know about Flatpak — take a look at our complete guide on using Flatpak. To explore more about it, you can also head to their GitHub page.
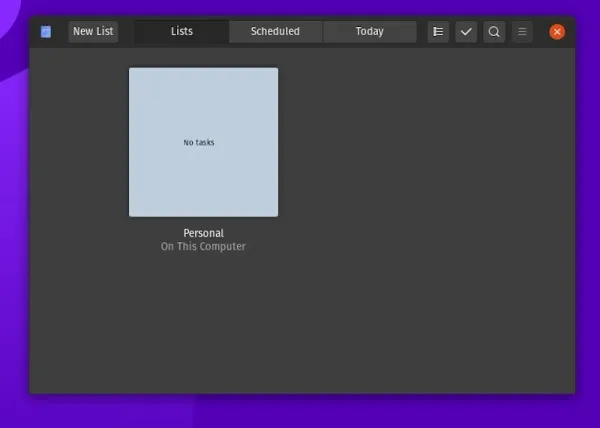
5. Endeavour (Previously GNOME To Do)
If you’re using Ubuntu, you should already have it installed until Ubuntu 22.04 LTS. Just search for “To Do” and you should find it. It’s a simple to-do app that presents the list in the form of cards and you can have a separate set of tasks for every card. You can add a schedule to the tasks as well. It supports extensions with which you can enable the support for todo.txt files and also integration with todoist.
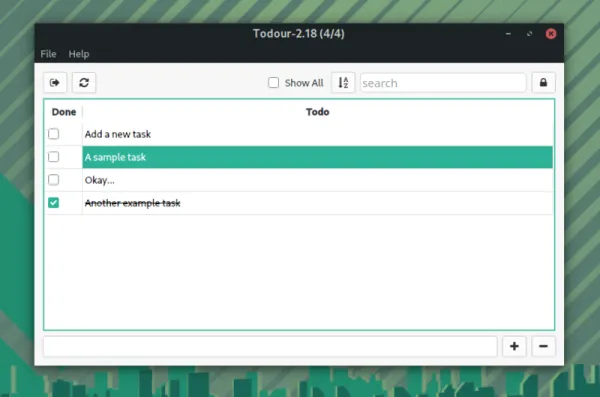
6. Todour
A very simple open-source to-do list app that lets you utilize the todo.txt file as well. You may not get a lot of options to choose from — but you get a couple of useful settings to tweak. It may not be the most actively developed to-do list app — but it does the work as expected. How to install Todour? If you’re using Manjaro Linux, you can utilize pamac to install Todour from AUR. It provides a .deb package for Ubuntu, which was built using 22.04 and works smoothly on the latest version also. Explore more about it on its GitHub page.
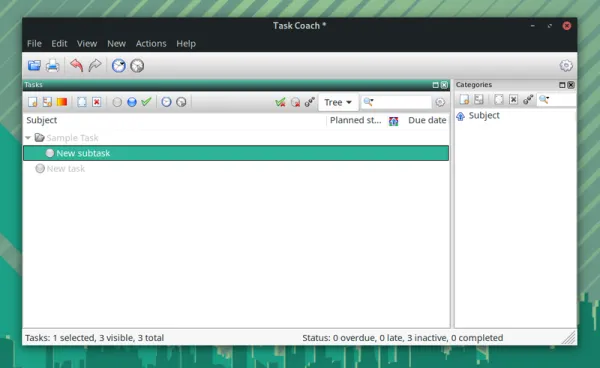
7. Task Coach
Task Coach is yet another open-source to-do list app that offers quite a lot of essential features. You can add sub-tasks and descriptions to your task, add dates, notes, and a lot more things. It also supports a tree view for the task lists you add and manage. It’s a good thing to see that it offers cross-platform support (Windows, macOS, and Android). Overall, it’s easy to use with tons of options and works well. How to install it? It offers AppImage files for Linux distributions. You can find all the necessary files and instructions from its official download page. It is available for Arch users in AUR.
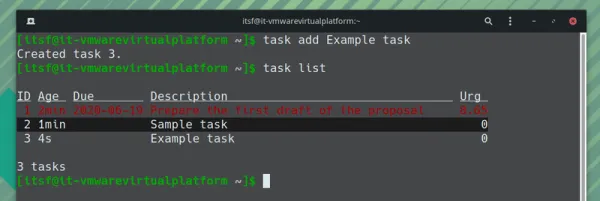
Bonus: Terminal-based Taskwarrior to-do list app
A command-line based open-source to-do list program “Taskwarrior” is an impressive tool if you don’t need a Graphical User Interface (GUI). It also provides cross-platform support (Windows and macOS). It’s quite easy to add and list tasks along with a due date as shown in the screenshot above. To make the most out of it, I would suggest you follow the official documentation to know how to use it and the options/features that it offers. How to install it? You can find it in your respective package managers on any Linux distribution. To get it installed in Ubuntu, you will have to type the following in the terminal:
sudo apt install taskwarriorFor Manjaro Linux, you can simply get it installed through the pamac, which you usually use to install any software in Manjaro Linux. In case of any other Linux distributions, you should head to its official download page and follow the instructions.
Wrapping Up
As an interesting mention, I’d like you to take a look at TodoList, which is an applet for KDE-powered distributions. Among mainstream to-do list applications, Remember The Milk is the rare one that provides a Linux client. It is not open source, though. I hope this list of to-do list apps helped you get things done on Linux. Did I miss any of your favorite to-do list apps on Linux? Feel free to let me know what you think! Suggested Read 📖 For those who are interested in kanban board style for task management: