- Create a bootable USB stick on Ubuntu
- 2. Requirements
- 3. Launch Startup Disk Creator
- 4. ISO and USB selection
- 5. Confirm USB device
- 6. Installation complete
- Finding help
- Установка полноценной Ubuntu на USB-накопитель
- Подготовка к установке
- Запись образа
- Загрузка
- Подготовка USB-накопителя
- Установка
- Introduction
- Prerequisites
- Dummy headlines
Create a bootable USB stick on Ubuntu
Creating a bootable Ubuntu USB stick is very simple, especially from Ubuntu itself, and we’re going to cover the process in the next few steps.
Alternatively, we also have tutorials to help you create a bootable USB stick from both Microsoft Windows and Apple macOS.
2. Requirements
- A 4GB or larger USB stick/flash drive
- Ubuntu Desktop 14.04 or later installed
- An Ubuntu ISO file. See Get Ubuntu for download links
3. Launch Startup Disk Creator
We’re going to use an application called ‘Startup Disk Creator’ to write the ISO image to your USB stick. This is installed by default on Ubuntu, and can be launched as follows:
- Insert your USB stick (select ‘Do nothing’ if prompted by Ubuntu)
- On Ubuntu 18.04 and later, use the bottom left icon to open ‘Show Applications’
- In older versions of Ubuntu, use the top left icon to open the dash
- Use the search field to look for Startup Disk Creator
- Select Startup Disk Creator from the results to launch the application
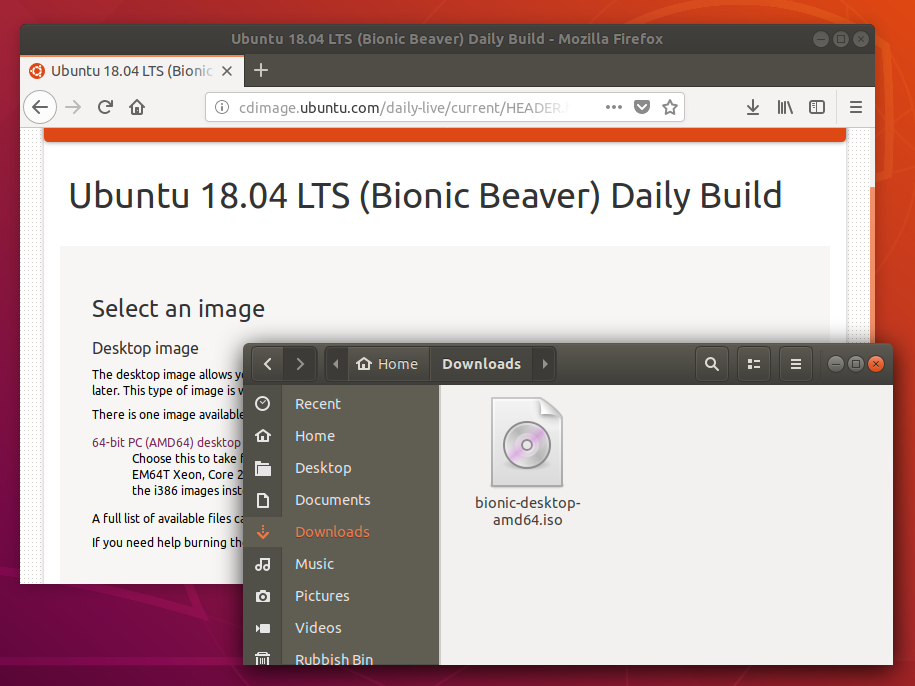
4. ISO and USB selection
When launched, Startup Disk Creator will look for the ISO files in your Downloads folder, as well as any attached USB storage it can write to.
It’s likely that both your Ubuntu ISO and the correct USB device will have been detected and set as ‘Source disc image’ and ‘Disk to use’ in the application window. If not, use the ‘Other’ button to locate your ISO file and select the exact USB device you want to use from the list of devices.
Click Make Startup Disk to start the process.
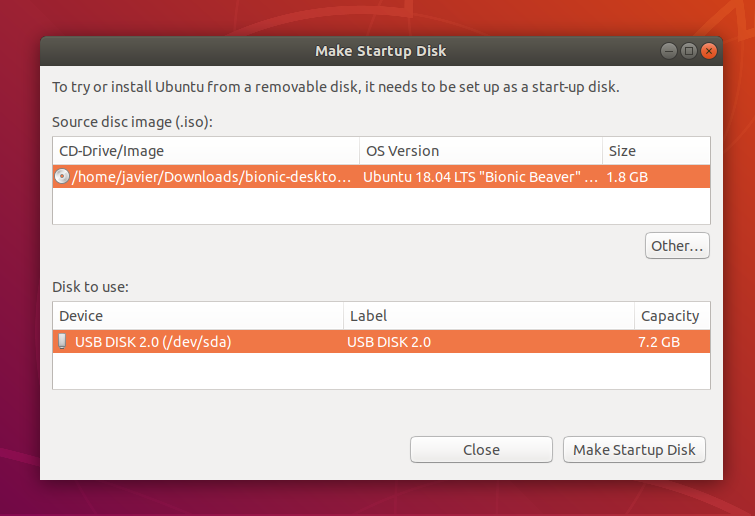
5. Confirm USB device
Before making any permanent changes, you will be asked to confirm the USB device you’ve chosen is correct. This is important because any data currently stored on this device will be destroyed.
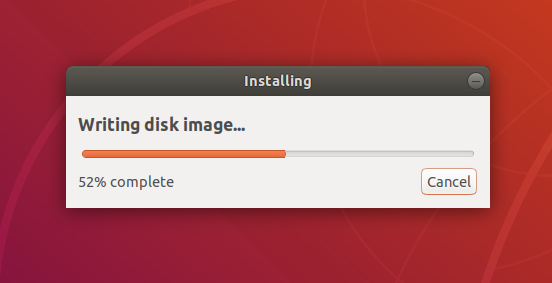
After confirming, the write process will start and a progress bar appears.
6. Installation complete
That’s it! You now have Ubuntu on a USB stick, bootable and ready to go.
If you want to install Ubuntu, take a look at our install Ubuntu desktop tutorial.
Finding help
If you get stuck, help is always at hand:
Установка полноценной Ubuntu на USB-накопитель
Очень часто у людей возникает желание или необходимость поставить Ubuntu на USB-накопитель и получить возможность пользоваться своей ОС на любом компьютере (лишь бы была возможность загрузится с USB).
В этой статье описывается процесс установки Ubuntu на USB-накопители.
Не стоит путать установку с простой записью образа. Подробнее о записи образов на на USB-накопители смотрите в Usb-creator-gtk.
Некоторые важные замечания и полезная информация собраны в статье Установка и использование Ubuntu на USB флешке. Стоит ознакомиться с ней перед началом установки Ubuntu на USB-накопитель.
Подготовка к установке
Скачайте образ системы отсюда. Если не планируете запускать систему на машинах с более 4 Гб оперативной памяти предпочтительней выбирать 32-х разрядную.
Запись образа
После того, как образ загрузился, его надо записать на CD или USB-накопитель.
На USB носитель образ проще всего записать при помощи UNetbootin. Эта программа существует под большинство популярных ОС (Windows, Linux, Mac) и достаточно проста в обращении. Все что потребуется – указать путь к скачанному образу и выбрать диск, на который будет записан образ.
Можно обойтись без записи образа на какие-либо носители воспользовавшись виртуальной машиной, например VirtualBox или QEMU. Достаточно лишь пробросить в виртуальную машину USB-накопитель. Дальнейшие инструкции для этого метода не поменяются.
Загрузка
Перед тем как загрузится, убедитесь, что в BIOS первым загрузочным устройством выбран USB или CD-ROM, в зависимости от того, с чего вы производите загрузку. В BIOS можно попасть нажав клавишу Del для стационарных компьютеров и F2 или F12 для ноутбуков. О том, как выбрать устройство для загрузки смотрите в интернете или читайте инструкцию к вашему компьютеру.
Если все правильно сделано, вы увидите перед собой загруженную с Live CD систему.

Подготовка USB-накопителя
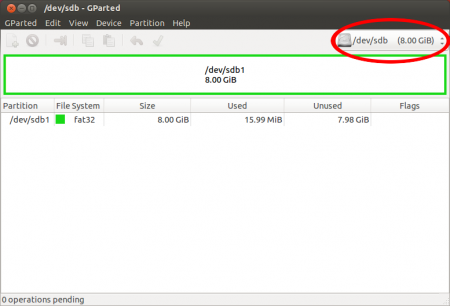
Запустите программу GParted.
Выберите устройство, на которое вы собираетесь установить Ubuntu.
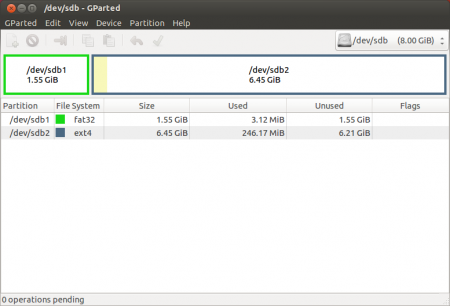
Отформатируйте его в файловую систему Ext2 или Ext4. Так-же можно разделить USB-диск на 2 раздела для того, чтоб его можно было использовать по прямому назначению (перенос файлов с одного компьютера на другой). Для этого первый раздел раздел отформатируйте в FAT32 (для того, чтобы раздел был виден в Windows), вторым разделом выберите файловую систему Ext2 или Ext4 под Ubuntu. На второй раздел желательно выделить минимум 6 Гб, чтобы можно было не переживать за нехватку места для установки дополнительных программ.
Установка
Дальнейшая установка Ubuntu ничем не отличается от установки на жесткий диск.
Выберите на рабочем столе Install Ubuntu и выполните установку по скриншотам:



Главное — не забудьте указать установщику что GRUB надо установить на флеш-накопитель (по умолчанию он ставится на первый жесткий диск в системе).
Introduction
Ubuntu can be installed from a USB flash drive. This may be necessary for most new portable computers without DVD drives and is handy for others because a USB flash drive is so convenient. Also, you can configure Ubuntu on the USB flash drive to save changes you make, unlike a read-only CD/DVD disk.
Booting from a USB flash drive created with usb-creator alias Startup Disk Creator and mkusb will behave just as if you had booted from the install CD. It will show the language selection and then the install menu, from which you can install Ubuntu onto the computer’s hard drive or launch the LiveCD environment. Other utilities, e.g. UNetbootin, may create slightly different boot drives or if on UEFI might not work at all with Debian iso files due to a bug
Note: This article uses the term «USB flash drive» alongside USB stick, USB drive, USB device, USB pendrive and thumb drive.
Prerequisites
- a 4 GB USB flash device/drive/stick. If the iso file is smaller than 2 GB, it is possible to use a 2 GB USB device, at least with some of the methods. Files on this USB device will be erased, so backup the files you want to keep before making the device bootable. Some of the tools require that this USB device is properly formatted and mounted while other tools will overwrite whatever is on the target device. Please follow the instructions for each tool.
- an Ubuntu flavour ISO file downloaded from an official web page, ubuntu.com/download or http://releases.ubuntu.com, stored in your running computer (for example in the directory Downloads in the internal drive, not in the USB flash drive that you want to make into a USB boot drive).
- Check with md5sum (or another checksum tool) that the download was good. In Linux there is the tool ‘md5sum’. In Windows you can do it with Rufus: click on the circle with a tick mark (more about Rufus here.)
Dummy headlines
After a major remake of this help page the following headlines are kept here because they may be linked to from other web sites. Several other headlines further down in the page are also kept for this reason.