- Переименование файла или папки
- Чтобы переименовать файл или папку:
- Символы, допустимые в именах файлов
- Типичные проблемы
- Дополнительная информация
- How Do I Rename a File in the Ubuntu Terminal?
- Renaming Files in Ubuntu 20.04 LTS System Using Terminal
- Rename File in Ubuntu Using the mv Command
- Example
- How to Use the mv Command to Rename Multiple Files?
- How to Use the Rename Command to Rename Files in Ubuntu?
- Syntax of Rename Command
- Example
- Example
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Samreena Aslam
- Rename a File in Linux – Bash Terminal Command
- How to Use the Linux mv Command
- How to Name Files in Bulk Using mv
- Conclusion
Переименование файла или папки
Как и другие менеджеры файлов, приложение Файлы позволяет переименовать файл или папку.
Чтобы переименовать файл или папку:
- Нажмите на объект правой кнопкой и выберите Переименовать или выберите файл и нажмите клавишу F2 .
- Наберите новое имя и нажмите Enter или кнопку Переименовать .
Можно также переименовать файл из окна его свойств .
При переименовании файла выделяется только начало его имени, без расширения (части после . ). Расширение показывает тип файла (например, file.pdf — это документ PDF), и менять его обычно нет необходимости. Если нужно изменить и расширение, выделите имя файла целиком и измените его.
Если вы переименовали не тот файл, или дали ему неправильное имя, можно отменить переименование. Для этого немедленно нажмите кнопку меню в панели инструментов и выберите Переименовать или нажмите Ctrl + Z , чтобы вернуть прежнее имя файла.
Символы, допустимые в именах файлов
В именах файлов можно использовать любые символы, кроме / (слеш). Однако на некоторых устройствах используется файловая система с дополнительными ограничениями на имена файлов. Поэтому рекомендуется избегать использования следующих символов в именах файлов: | , \ , ? , * , < , " , : , >, / .
Если имя файла начинается с символа . , то этот файл будет скрытым в менеджере файлов.
Типичные проблемы
Нельзя поместить два файла с одинаковым именем в одну и ту же папку. Менеджер файлов не позволит переименовать файл, если такое имя уже существует в этой папке.
Имена файлов и папок чувствительны к регистру символов, поэтому File.txt и FILE.txt — это два разных имени. Использовать имена файлов, различающиеся только регистром символов разрешается, но не рекомендуется.
Слишком длинное имя файла
В некоторых файловых системах имена файлов не могут содержать более 255 символов. Это ограничение в 255 символов включает в себя как собственно имя файла, так и путь к файлу (например, /home/wanda/Documents/work/business-proposals/… ), поэтому по возможности следует избегать длинных имён файлов и папок.
Команда переименования неактивна
Если команда Переименовать недоступна, значит у вас нет прав на переименование файла. Следует соблюдать осторожность при переименовании подобных файлов, так как переименование некоторых защищённых файлов может привести к нестабильности системы. Подробнее смотрите Настройка прав доступа к файлам .
Дополнительная информация
You can choose the displayed language by adding a language suffix to the web address so it ends with e.g. .html.en or .html.de.
If the web address has no language suffix, the preferred language specified in your web browser’s settings is used. For your convenience:
[ Change to English Language | Change to Browser’s Preferred Language ]
The material in this document is available under a free license, see Legal for details.
For information on contributing see the Ubuntu Documentation Team wiki page. To report errors in this documentation, file a bug.
How Do I Rename a File in the Ubuntu Terminal?
Renaming an existing file is a basic operation that usually does not require a specialized tool in any operating system. Renaming a single file in Linux is quite a simple task but renaming more than one or multiple files via terminal is a more challenging job for new Linux users. In all Linux distributions, the terminal is an essential command-line application for administering the Linux systems.
However, to use effectively this CLI application, you should have strong knowledge about basic Linux commands and fundamentals such as create, delete and renaming an existing file. Different commands are available in the Ubuntu Linux system to rename a file that we will explore in this article.
We will provide comprehensive details in this tutorial on how you can rename a file in Ubuntu using the command-line application Terminal. All commands have implemented for the demonstration on the Ubuntu 20.04 Linux system.
Renaming Files in Ubuntu 20.04 LTS System Using Terminal
The two different commands ‘mv’ and ‘rename’ are available in the Ubuntu Linux system to rename a file via terminal or command-line approach. Let us discuss each command in detail.
Rename File in Ubuntu Using the mv Command
Before using the ‘mv’ command, you should know how it works on your system. The basic syntax of the ‘mv’ command is given below:
The most popular ‘mv’ command options are provided below:
-f – Displays no message or alerts before overwriting a file name.
-i – Displays prompt confirmation or warning messages before renaming a file.
-u – It moves a file if the file does not exist on the specified destination or in case of a new file.
The file source can be the destination of one or more files. The destination only represents a single file.
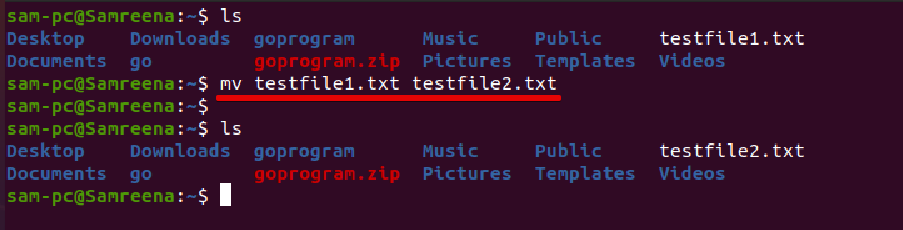
Example
For example, to rename the file ‘testfile1.txt’ to ‘testfile2.txt, you need to run the following command:
How to Use the mv Command to Rename Multiple Files?
Usually, you can only rename a single file using the move command. To rename multiple files using the mv command, you can use the mv command to combine with different commands. Let us say, mv command can be used along with for loop, while loop, and find command.
Let us explain with the help of an example. Here, we want to rename all .txt extension files of the current directory replaced with another .html extension. In this case, the following code will help us:
The above code will iterate using for loop through the files list having the .txt extension. After that, in the second line, it will replace each file extension .txt with .html. In the end, ‘done’ indicated the end of the for loop segment.
How to Use the Rename Command to Rename Files in Ubuntu?
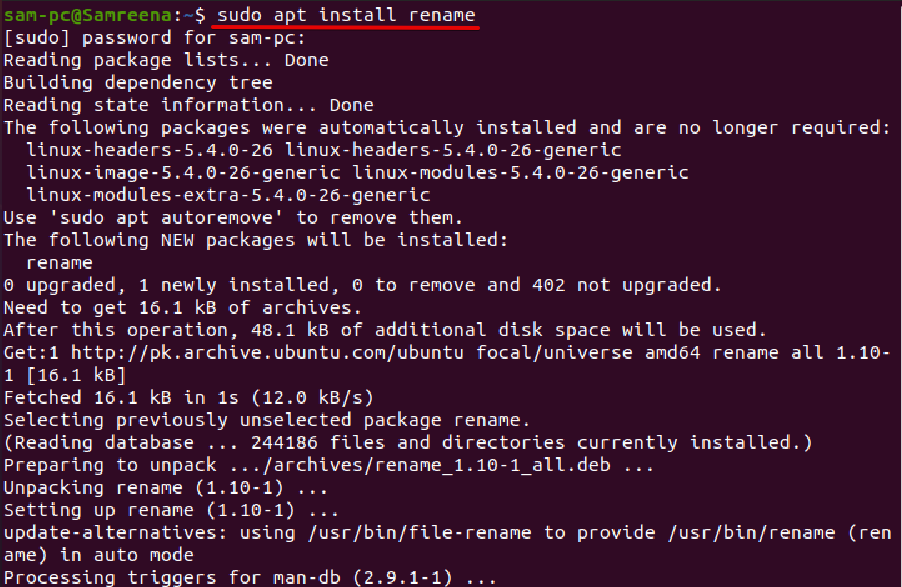
Using the rename command, you can rename multiple files of a current directly at once. This command contains more advance features as compared to the ‘mv’ command. For renaming files using the rename command, you should have basic knowledge about regular expressions usage.
In most Linux distributions, the ‘rename’ command is installed by default. However, if you have not installed the rename command on your Ubuntu system then, it can be easily installed on Ubuntu and its derivatives by running the following command:
Syntax of Rename Command
Using the following syntax, you can use the rename command:
The rename command will rename files according to the specific regular Perl expressions.
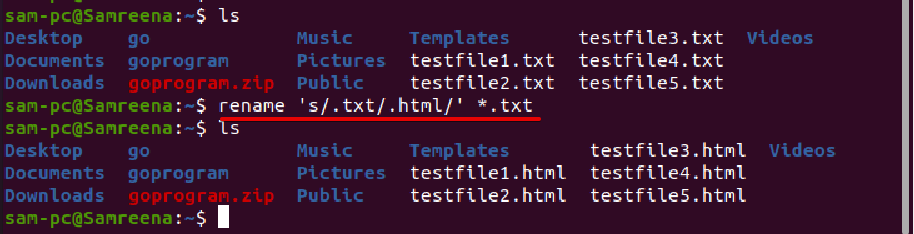
Example
In the following example, we want to change the extension of all text files. So, we will change or replace all files with extension .txt to .html by executing the following command:
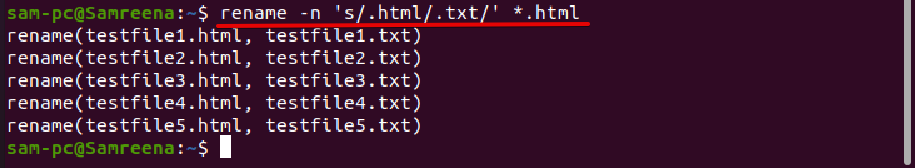
When you use the rename command followed by option ‘-n’, it also displays the file names to be renamed and renaming them as follows:
The above command displays the following result on the terminal window:
By default, the rename command does not overwrite an existing file. However, if you pass option -f along with the rename command then, it will help you to overwrite the existing files. Execute the following command to use the rename command followed by the -f option:
To change or rename the file name using rename command use the following command:
Example
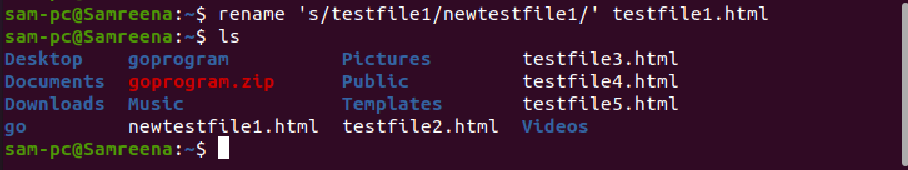
For example, we want to rename a single file with the name ‘testfile.txt’ to newtestfile.txt. In this case, the above command will be modified into the following form:
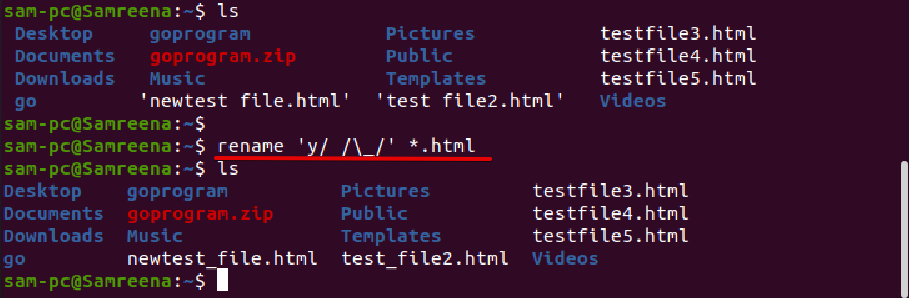
To see more usage of rename command, let us try the following examples:
For example, to rename all those files, which contain spaces in file name and you want to replace it with underscores. In this case, the rename command will help you in the following way:
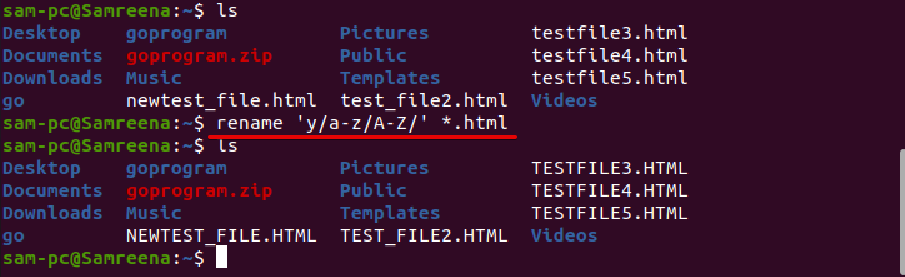
Using rename command, you can convert the file name in all lowercase letters as follows:
Similarly, to convert the file name to all uppercase letters, use the following command:
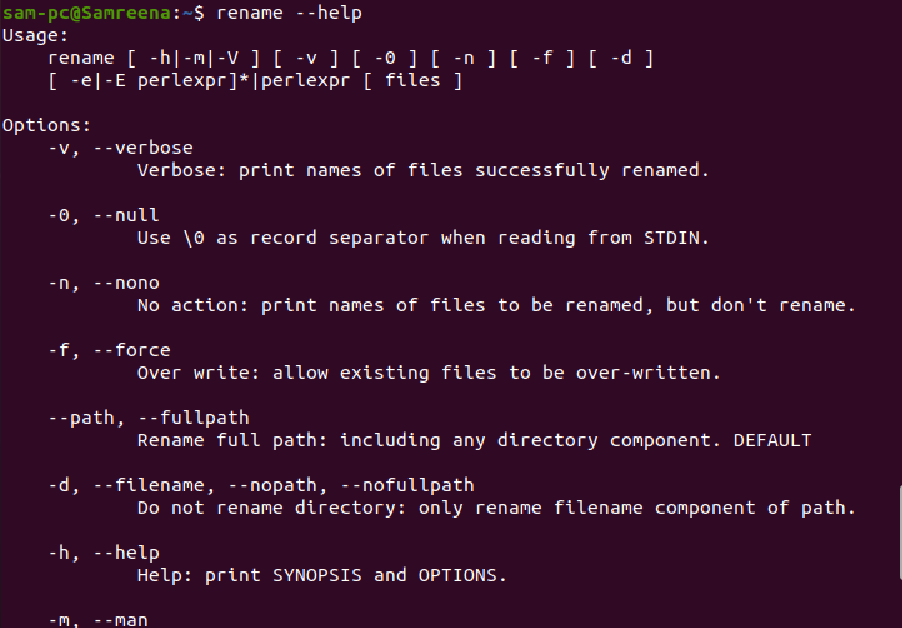
To explore more options and uses of rename command, type the following terminal command:
Conclusion
We discussed in this article how to rename files in Ubuntu 20.04 LTS distribution using the terminal application. Moreover, we explored the working and uses of the ‘mv’ and ‘rename’ commands for renaming a file. From the above discussion, we concluded mv command is useful for renaming a file but, rename command offers more advanced options for file renaming in the Ubuntu system.
About the author
Samreena Aslam
Samreena Aslam holds a master’s degree in Software Engineering. Currently, she’s working as a Freelancer & Technical writer. She’s a Linux enthusiast and has written various articles on Computer programming, different Linux flavors including Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, and Mint.
Rename a File in Linux – Bash Terminal Command
Zaira Hira
Renaming files is a very common operation whether you are using the command line or the GUI.
Compared to the GUI (or Graphical User Interface), the CLI is especially powerful. This is in part because you can rename files in bulk or even schedule the scripts to rename files at a certain point in time.
In this tutorial, you will see how you can rename files in the Linux command line using the built-in mv command.
How to Use the Linux mv Command
You can use the built-in Linux command mv to rename files.
The mv command follows this syntax:
mv [options] source_file destination_fileHere are some of the options that can come in handy with the mv command:
- -v , —verbose : Explains what is being done.
- -i , —interactive : Prompts before renaming the file.
Let’s say you want to rename index.html to web_page.html . You use the mv command as follows:
zaira@Zaira:~/rename-files$ mv index.html web_page.html Let’s list the files and see if the file has been renamed:
zaira@Zaira:~/rename-files$ ls web_page.htmlHow to Name Files in Bulk Using mv
Let’s discuss a script where you can rename files in a bulk using a loop and the mv command.
Here we have a list of files with the extension .js .
zaira@Zaira:~/rename-files$ ls -lrt total 0 -rw-r--r-- 1 zaira zaira 0 Sep 30 00:24 index.js -rw-r--r-- 1 zaira zaira 0 Sep 30 00:24 config.js -rw-r--r-- 1 zaira zaira 0 Sep 30 00:24 blog.jsNext, you want to convert them to .html .
You can use the command below to rename all the files in the folder:
for f in *.js; do mv -- "$f" "$.html"; doneLet’s break down this long string to see what’s happening under the hood:
- The first part [ for f in *.js ] tells the for loop to process each “.js” file in the directory.
- The next part [ do mv — «$f» «$.html ] specifies what the processing will do. It is using mv to rename each file. The new file is going to be named with the original file’s name excluding the .js part. A new extension of .html will be appended instead.
- The last part [ done ] simply ends the loop once all the files have been processed.
zaira@Zaira:~/rename-files$ ls -lrt total 0 -rw-r--r-- 1 zaira zaira 0 Sep 30 00:24 index.html -rw-r--r-- 1 zaira zaira 0 Sep 30 00:24 config.html -rw-r--r-- 1 zaira zaira 0 Sep 30 00:24 blog.htmlConclusion
As you can see, renaming files is quite easy using the CLI. It can be really powerful when deployed in a script.
What’s your favorite thing you learned here? Let me know on Twitter!
You can read my other posts here.