- Expanded Security Maintenance (ESM)
- Extra security patching for Ubuntu LTS, now included in Ubuntu Pro
- 10 year security coverage
- What’s the difference?
- Case studies
- Interana uses ESM while planning public cloud upgrades to 18.04
- TIM maintains system security and client confidence with ESM
- What’s covered?
- ESM on public clouds with Ubuntu Pro
- Ubuntu 16.04 LTS out of standard security maintenance
- Secure your Ubuntu estate. Get in touch to discuss ESM
- Как установить обновления безопасности в Ubuntu
- Установка обновлений безопасности в Ubuntu
- Обновление одного пакета в Ubuntu
- Обновление системы Ubuntu
- Автоматическая установка последних обновлений безопасности в Ubuntu
- Ubuntu Wiki
- Desktop
- Server
- How to Install Security Updates in Ubuntu
- Intalling Security Updates on Ubuntu
- Updating a Single Package on Ubuntu
- Upgrading a Ubuntu System
- Installing Latest Security Updates Automatically on Ubuntu
Expanded Security Maintenance (ESM)
Extra security patching for Ubuntu LTS, now included in Ubuntu Pro
10 year security coverage
Security maintenance for the entire collection of software packages shipped with Ubuntu.
ESM enables continuous vulnerability management for critical, high and medium CVEs.
What’s the difference?
| Security patching (Coverage for critical, high and selected medium CVEs) | Ubuntu LTS | Ubuntu Pro (Infra-only) (Previously known as ”Ubuntu Advantage for Infrastructure”) | Ubuntu Pro |
|---|---|---|---|
| Over 2,300 packages in Ubuntu Main repository | 5 years | 10 years | 10 years |
| Over 23,000 packages in Ubuntu Universe repository | Best effort | Best effort | 10 years |
2,300 Ubuntu Main packages +
23,000 Ubuntu Universe packages
2,300 Ubuntu Main packages
Case studies
Interana uses ESM while planning public cloud upgrades to 18.04
Due to the large amounts of customer data that Interana handles, ensuring that security was tight was a priority. Rather than rush the upgrade from Ubuntu 14.04LTS, which would have been a major inconvenience for its customers, Interana turned to Canonical and ESM.
TIM maintains system security and client confidence with ESM
To ensure the ongoing security of Ubuntu 14.04 LTS machines, ESM provided TIM, the world’s largest trade recommendations network, the freedom to upgrade within their own timeframe.
This approach saved time and money for this finserv organisation.
What’s covered?
ESM continues security updates and kernel livepatching for high and critical CVEs (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures).
| Release | Ubuntu Base OS security coverage | Security updates for applications and toolchains in the Universe repository | Kernel Livepatch | Architectures supported with ESM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ubuntu 14.04 LTS (Trusty Tahr) | Until 2024 | n/a | yes | amd64 |
| Ubuntu 16.04 LTS (Xenial Xerus) | Until 2026 | Until 2026 | yes | amd64, s390X |
| Ubuntu 18.04 LTS (Bionic Beaver) | Until 2028 | Until 2028 | yes | amd64, arm64, s390X, PowerPC |
| Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (Focal Fossa) | Until 2030 | Until 2030 | yes | amd64, arm64, s390X, PowerPC |
| Ubuntu 22.04 LTS (Jammy Jellyfish) | Until 2032 | Until 2032 | yes | amd64, arm64, s390X, PowerPC |
ESM on public clouds
with Ubuntu Pro
If you are running Ubuntu 16.04 LTS images on the public cloud and are looking for continued security coverage with ESM, it is recommended to launch new, Ubuntu Pro images for Azure, AWS and Google Cloud. Ubuntu Pro images are paid, premium images that are optimised and priced for the cloud, with security and compliance features built-in.
Learn more about Ubuntu 16.04 LTS on Azure | AWS | Google Cloud
Ubuntu 16.04 LTS out of standard security maintenance
Ubuntu 16.04 LTS Xenial Xerus moves out from the standard LTS security updates transitions to the expanded security maintenance (ESM) period in April 2021. Learn about the ESM period and six key considerations when assessing and planning your migration path.
Secure your Ubuntu estate.
Get in touch to discuss ESM
© 2023 Canonical Ltd. Ubuntu and Canonical are registered trademarks of Canonical Ltd.
Как установить обновления безопасности в Ubuntu
Один из самых простых способов защитить ваши системы Ubuntu — поддерживать на них новейшее программное обеспечение. Поэтому частое применение обновлений является важной частью поддержания безопасности систем. В этой статье мы покажем, как установить обновления безопасности в системах Ubuntu и Linux Mint.
Установка обновлений безопасности в Ubuntu
Если в вашей системе установлен пакет update-notifier-common, Ubuntu будет предупреждать вас об ожидающих обновлениях через сообщение дня (motd) при консольном или удалённом входе в систему.
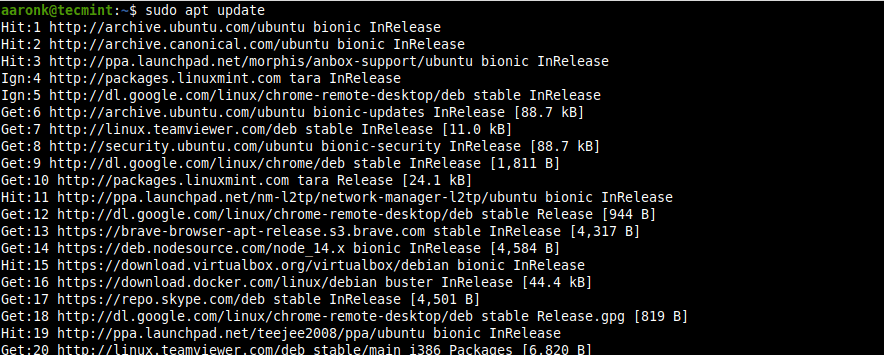
После входа в систему Ubuntu вы можете проверить наличие новых обновлений, используя следующую команду apt.
Обновление одного пакета в Ubuntu
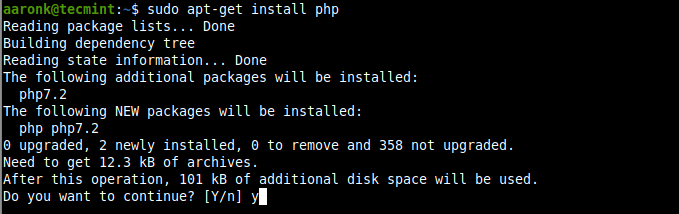
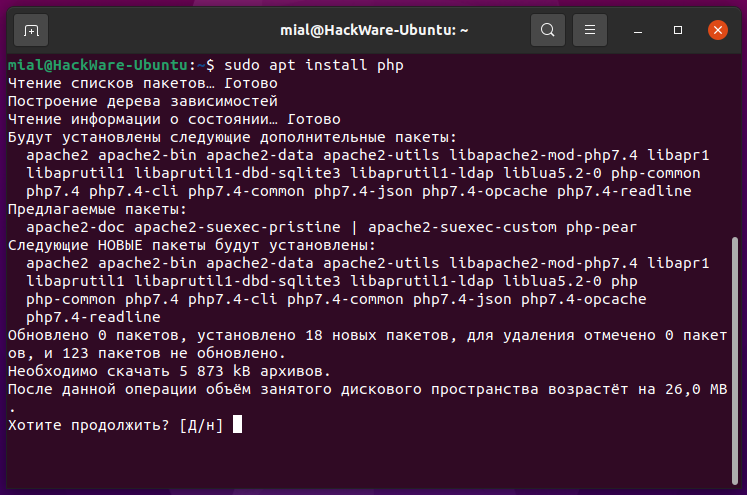
Чтобы, после обновления кеша пакетов вашей системы, проверить и обновить один пакет, например, пакет с именем php, сделайте это следующим образом. Если пакет php уже установлен, эта команда попытается обновить его до последней доступной версии:
Обновление системы Ubuntu
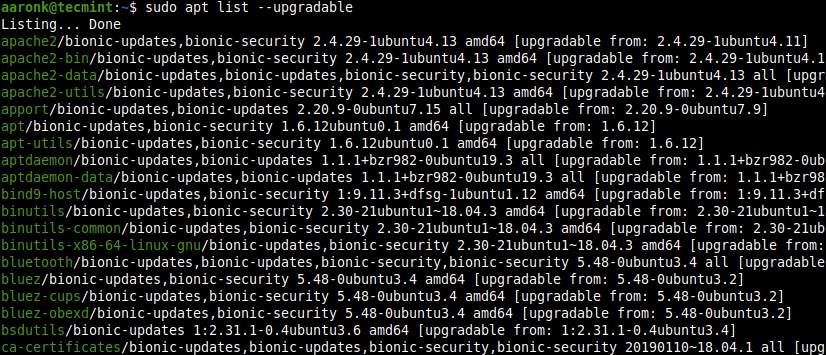
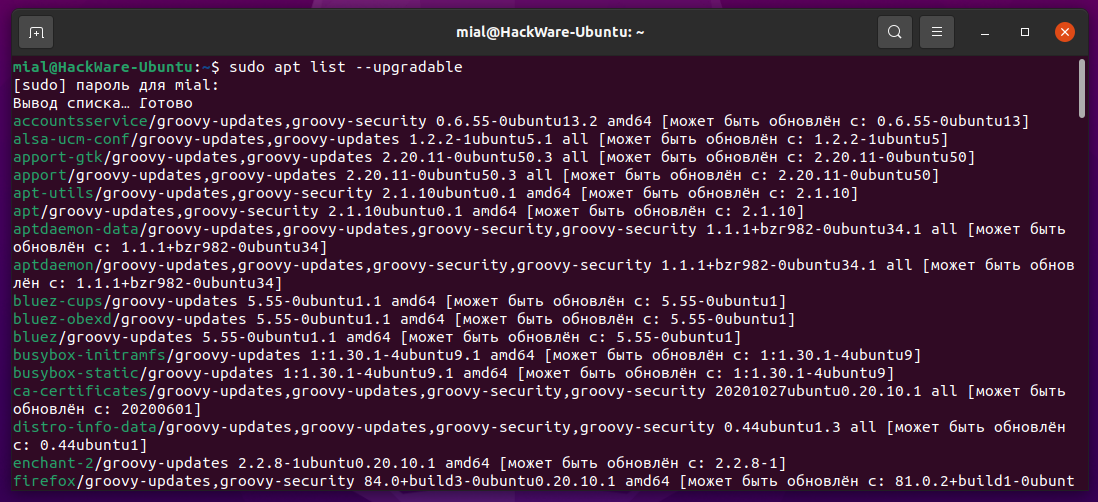
Чтобы вывести список всех свежих доступных обновлений для вашей системы Ubuntu, выполните:
Чтобы установить все обновления, запустите:
Автоматическая установка последних обновлений безопасности в Ubuntu
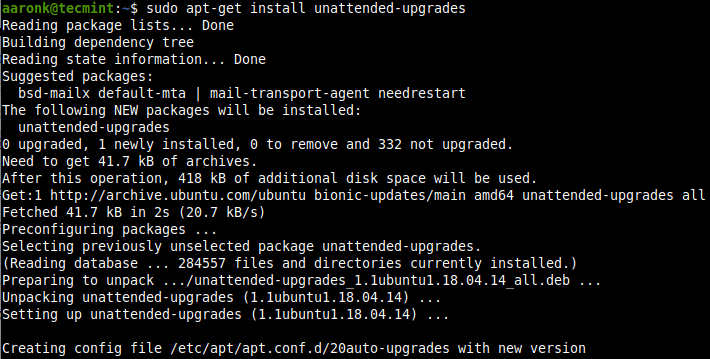
Вы можете использовать пакет unattended-updates, чтобы в системе Ubuntu автоматически устанавливались последние (и другие) обновления безопасности. Чтобы установить пакет unattended-updates, если он ещё не установлен, выполните следующую команду:
sudo apt install unattended-upgrades
Чтобы включить автоматические обновления, запустите:
sudo dpkg-reconfigure unattended-upgrades
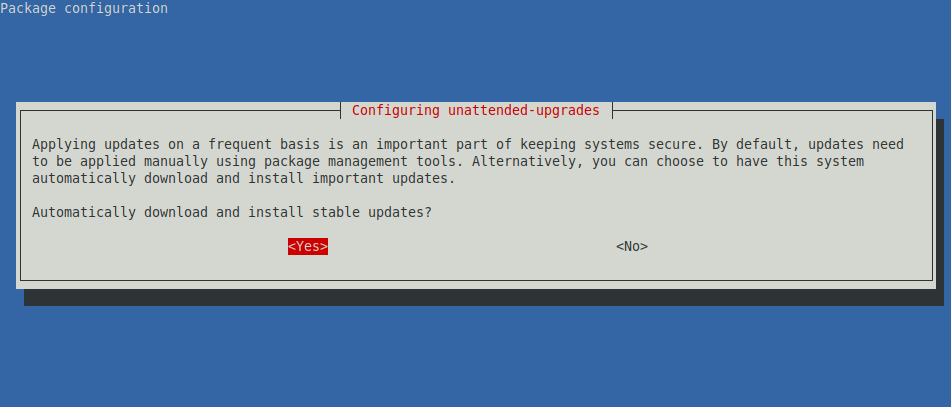
Затем настройте пакет для установки автоматических обновлений, выбрав «Да» в приведённом ниже интерфейсе.
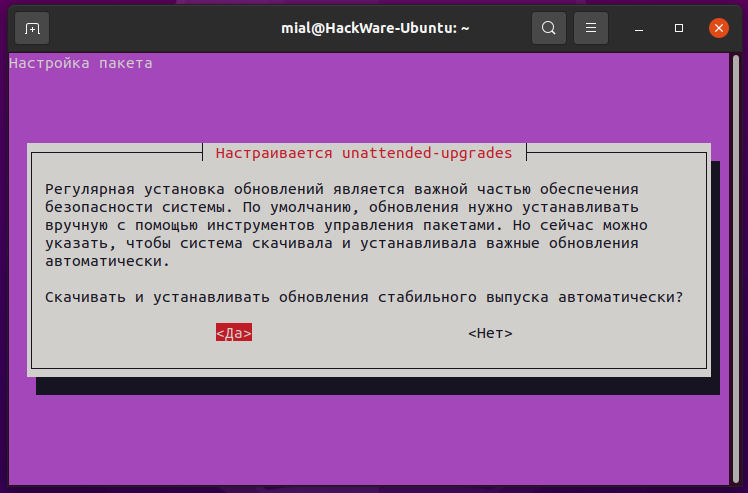
Примечание: обратите внимание, что обновления могут перезапускать службы на вашем сервере, поэтому автоматическое применение обновлений может подходить не для всех сред, особенно для серверов.
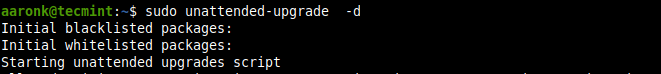
Вы также можете запускать автоматические обновления вручную:
Или добавьте флаг -d, чтобы включить режим отладки:
На этом пока все. По любым вопросам или комментариям, которыми вы хотели бы поделиться с нами, используйте форму комментариев ниже.
Если вы хотите в одну команду обновить систему целиком (установить обновления безопасности и все другие обновления), то запустите:
sudo apt update && sudo apt full-upgrade
Ubuntu Wiki
Keeping your computer’s software up to date is the single most important task for protecting your system. Ubuntu can alert you to pending updates, and also be configured to apply updates automatically. Security updates for Ubuntu are announced via Ubuntu Security Notices (USNs).
Desktop
By default, users are notified daily for security updates and weekly for non-security updates. How Ubuntu alerts you as well as configuring your system to install updates automatically can be setup within Update Manager. You can access Update Manager anytime by pressing ‘Alt+F2’, entering 'update-manager' and pressing Enter. Its settings can be adjusted by pressing the ‘Settings’ button.
Once Update Manager is open, you can review and select pending updates as well as check for new updates. Simply press the ‘Install Updates’ button to upgrade the selected packages to the updated version.
Server
If the update-notifier-common package is installed, Ubuntu will alert you about pending updates via the message of the day (motd) upon console or remote login.
After logging in, you can check for and apply new updates with:
$ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
When performing an update, first review what apt is going to do, then confirm that you want to apply the updates (this is particularly true when running the development release).
If you would prefer to have updates applied automatically, make sure the unattended-upgrades package is installed, then run 'sudo dpkg-reconfigure unattended-upgrades' . Please note that updates may restart services on your server, so this may not be appropriate for all environments.
Security/Upgrades (последним исправлял пользователь jdstrand 2011-10-12 21:02:00)
How to Install Security Updates in Ubuntu
One of the easiest ways to protect your Ubuntu systems is by keeping up to date software on them. Therefore applying updates frequently is an important part of maintaining secure systems. In this article, we will show how to install security updates in Ubuntu and Linux Mint systems.
Intalling Security Updates on Ubuntu
If your system has the update-notifier-common package installed, Ubuntu will alert you about pending updates via the message of the day (motd) upon console or remote login.
Once you have logged into your Ubuntu system, you can check for new updates using the following apt command.
Updating a Single Package on Ubuntu
To check and update a single package, for example, a package called php , after updating your system’s package cache, then update the required package as follows. If the php package already installed it will try to update to the latest version available:
Upgrading a Ubuntu System
To list all the newly available updates for your Ubuntu system, run:
To install all updates, run:
Installing Latest Security Updates Automatically on Ubuntu
You can use the unattended-upgrades package to keep the Ubuntu system with the latest security (and other) updates automatically. To install the unattended-upgrades package if it isn’t already installed, run the following command:
$ sudo apt-get install unattended-upgrades
To enable automatic updates, run:
$ sudo dpkg-reconfigure unattended-upgrades
Then configure the package to install automatic updates by selecting yes from the interface below.
Attention: Please note that updates may restart services on your server, so applying updates automatically may not be appropriate for all environments particularly servers.
You can run unattended-upgrades manually also:
Or add the -d flag to enable debugging mode:
That’s all for now. For any queries or comments, you would like to share with us, use the comment section below.