How to delete a non-empty directory in Terminal?
I’m unable to remove a directory like «New Folder» using all the above detailed commands. It’s double worded. But I want to remove that directory. Any suggestions will be welcomed. T.Divakara, Bengaluru, India
Its the blank space in the file name, try using ‘quotes’ > rmdir ‘New Folder’ < then the folder disapers, or use escape characters for non-vissible characters.
4 Answers 4
Use the below command :
It deletes all files and folders contained in the lampp directory.
In case user doesn’t have the permission to delete the folder:
Add sudo at the beginning of the command :
Otherwise, without sudo you will be returned permission denied. And it’s a good practice to try not to use -f while deleting a directory:
Note: this is assuming you are already on the same level of the folder you want to delete in terminal, if not:
sudo rm -r /path/to/folderName FYI: you can use letters -f , -r , -v :
- -f = to ignore non-existent files, never prompt
- -r = to remove directories and their contents recursively
- -v = to explain what is being done
In my humble opinion, it’s a good practice never to add the «f» on first attempt. Its purpose is to ignore certain warning prompts that may be important, especially if you’ve accidentally done it on/from the wrong directory. In my opinion it’s good to try without the «f» first, then only if you are encountering a lot of warning prompts and you’re sure it’s OK to ignore them all, Ctrl+C out of it and repeat the command with the «f».
@thomasrutter . Agree. A file «xxx» owner: root and group: root can BE deleted with the -f switch; and without sudo. This is the message without -f: «rm: remove write-protected regular file ‘/home/william/.cache/netbeans/v08.01/tmp/xxx’? _». _Tread gently.
However, you need to be careful with a recursive command like this, as it’s easy to accidentally delete a lot more than you intended.
It is a good idea to always double-check which directory you’re in, and whether you typed the command correctly, before pressing Enter.
Safer version
Adding -i makes it a little safer, because it will prompt you on every deletion. However, if you are deleting many files this is not going to be very practical. Still, you can try this first.
Many people suggest using -f (combining it into -Rf or -rf ), claiming that it gets rid of annoying prompts. However, in normal cases you don’t need it, and using it suppresses some problems that you probably do want to know about. When you use it, you won’t be warned if your arguments supply a non-existing directory or file(s): rm will just silently fail to delete anything. As a general rule, try first without the -f : if there are problems with your arguments, then you’ll notice. If you start getting too many prompts about files without write access, then you can try it with -f . Alternatively, run the command from a user (or the superuser using sudo) that has full permissions to the files and directories you’re deleting to prevent these prompts in the first place.
Linux ubuntu удалить папку
NAME
rm - remove files or directories
SYNOPSIS
DESCRIPTION
This manual page documents the GNU version of rm. rm removes each specified file. By default, it does not remove directories. If the -I or --interactive=once option is given, and there are more than three files or the -r, -R, or --recursive are given, then rm prompts the user for whether to proceed with the entire operation. If the response is not affirmative, the entire command is aborted. Otherwise, if a file is unwritable, standard input is a terminal, and the -f or --force option is not given, or the -i or --interactive=always option is given, rm prompts the user for whether to remove the file. If the response is not affirmative, the file is skipped.
OPTIONS
Remove (unlink) the FILE(s). -f, --force ignore nonexistent files and arguments, never prompt -i prompt before every removal -I prompt once before removing more than three files, or when removing recursively. Less intrusive than -i, while still giving protection against most mistakes --interactive[=WHEN] prompt according to WHEN: never, once (-I), or always (-i). Without WHEN, prompt always --one-file-system when removing a hierarchy recursively, skip any directory that is on a file system different from that of the corresponding command line argument --no-preserve-root do not treat '/' specially --preserve-root do not remove '/' (default) -r, -R, --recursive remove directories and their contents recursively -d, --dir remove empty directories -v, --verbose explain what is being done --help display this help and exit --version output version information and exit By default, rm does not remove directories. Use the --recursive (-r or -R) option to remove each listed directory, too, along with all of its contents. To remove a file whose name starts with a '-', for example '-foo', use one of these commands: rm -- -foo rm ./-foo Note that if you use rm to remove a file, it might be possible to recover some of its contents, given sufficient expertise and/or time. For greater assurance that the contents are truly unrecoverable, consider using shred.
AUTHOR
Written by Paul Rubin, David MacKenzie, Richard M. Stallman, and Jim Meyering.
REPORTING BUGS
Report rm bugs to bug-coreutils@gnu.org GNU coreutils home page: http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/> General help using GNU software: http://www.gnu.org/gethelp/> Report rm translation bugs to http://translationproject.org/team/>
COPYRIGHT
Copyright © 2013 Free Software Foundation, Inc. License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later http://gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html>. This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it. There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.
SEE ALSO
unlink(1), unlink(2), chattr(1), shred(1) The full documentation for rm is maintained as a Texinfo manual. If the info and rm programs are properly installed at your site, the command info coreutils 'rm invocation' should give you access to the complete manual.
© 2019 Canonical Ltd. Ubuntu and Canonical are registered trademarks of Canonical Ltd.
Как удалить каталог Linux
В операционной системе Linux можно выполнить большинство действий через терминал. Удаление каталога Linux — это достаточно простое действие, которое можно выполнить просто открыв файловый менеджер.
Однако в терминале это делается немного быстрее и вы получаете полный контроль над ситуацией. Например, можете выбрать только пустые папки или удалить несколько папок с одним названием. В этой статье мы рассмотрим как удалить каталог Linux через терминал.
Как удалить каталог Linux
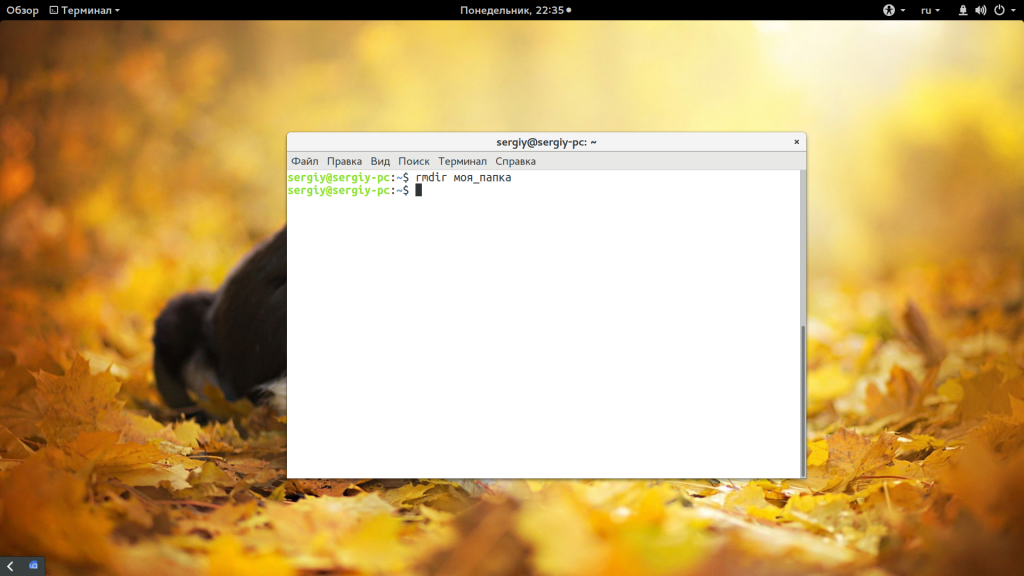
Существует несколько команд, которые вы можете использовать для удаления каталога Linux. Рассмотрим их все более подробно. Самый очевидный вариант — это утилита rmdir. Но с помощью нее можно удалять только пустые папки:
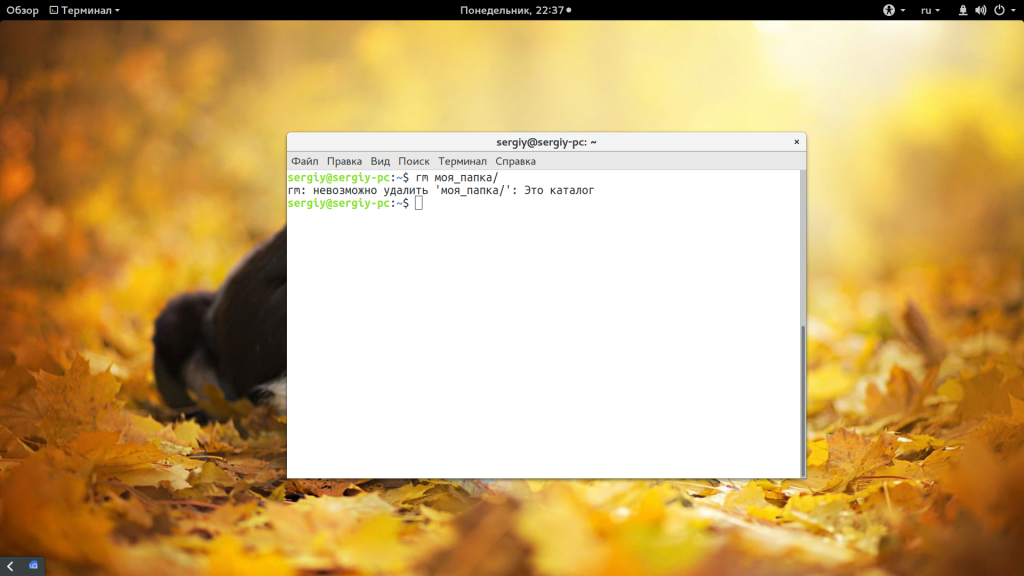
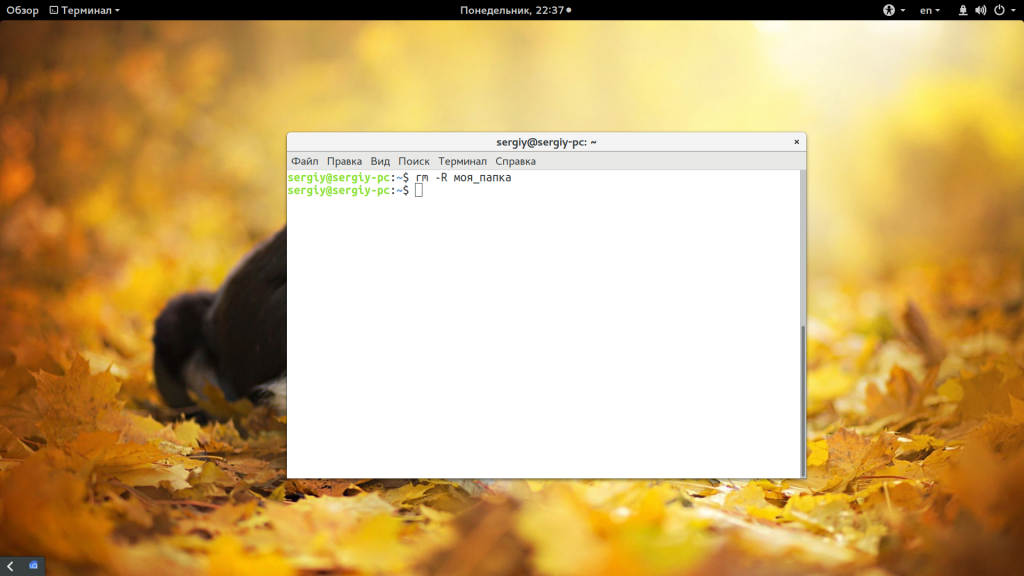
Другая команда, которую можно применить — это rm. Она предназначена для удаления файлов Linux, но может использоваться и для папок если ей передать опцию рекурсивного удаления -r:
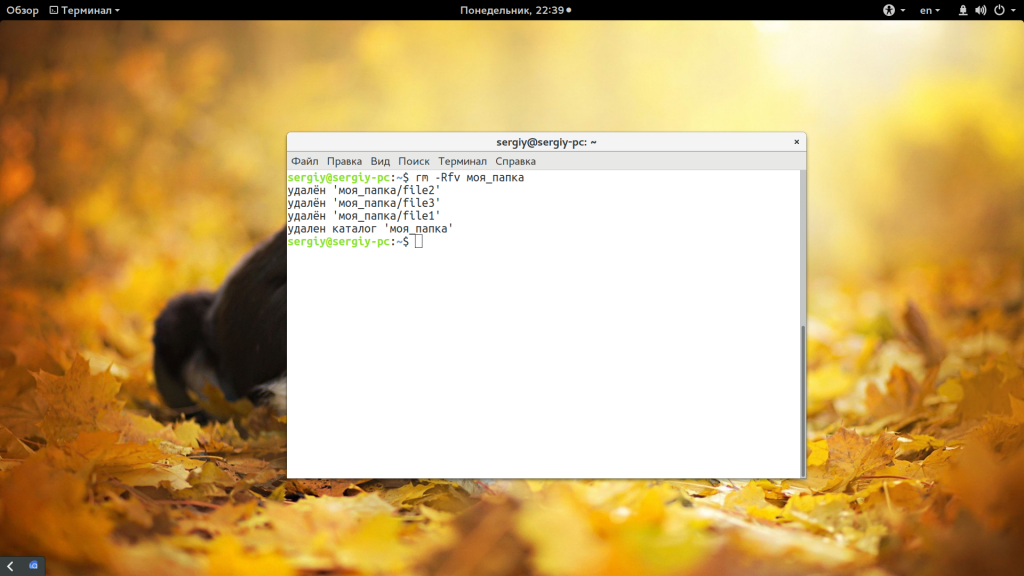
Такая команда уже позволяет удалить непустой каталог Linux. Но, можно по-другому, например, если вы хотите вывести информацию о файлах, которые удаляются:
Команда -R включает рекурсивное удаление всех подпапок и файлов в них, -f — разрешает удалять файлы без запроса, а -v показывает имена удаляемых файлов. В этих примерах я предполагаю что папка которую нужно удалить находится в текущей рабочей папке, например, домашней. Но это необязательно, вы можете указать полный путь к ней начиная от корня файловой системы:
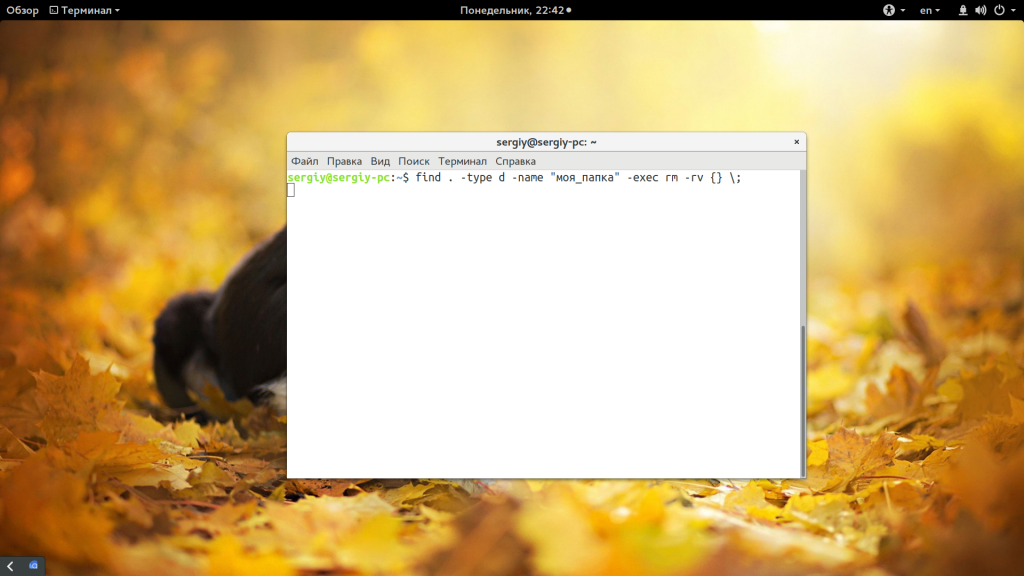
Читайте подробнее про пути в файловой системе в статье путь к файлу Linux. Теперь вы знаете как удалить непустой каталог в консоли linux, далее усложним задачу, будем удалять папки, которые содержат определенные слова в своем имени:
find . -type d -name «моя_папка» -exec rm -rf <> \;
Подробнее про команду find смотрите в отдельной статье. Если кратко, то -type d указывает, что мы ищем только папки, а параметром -name задаем имя нужных папок. Затем с помощью параметра -exec мы выполняем команду удаления. Таким же образом можно удалить только пустые папки, например, в домашней папке:
find ~/ -empty -type d -delete
Как видите, в find необязательно выполнять отдельную команду, утилита тоже умеет удалять. Вместо домашней папки, можно указать любой нужный вам путь:
find /var/www/public_html/ -empty -type d -delete
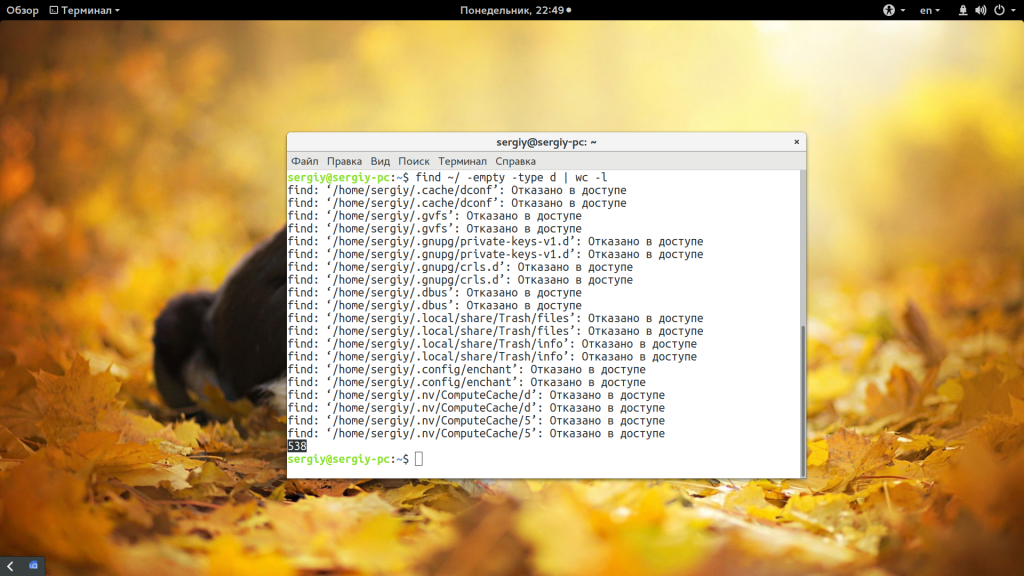
Перед удалением вы можете подсчитать количество пустых папок:
find /var/www/public_html/ -empty -type d | wc -l
Другой способ удалить папку linux с помощью find — использовать в дополнение утилиту xargs. Она позволяет подставить аргументы в нужное место. Например:
find ~/ -type f -empty -print0 | xargs -0 -I <> /bin/rm «<>«
Опция -print0 выводит полный путь к найденному файлу в стандартный вывод, а затем мы передаем его команде xargs. Опция -0 указывает, что нужно считать символом завершения строки \0, а -I — что нужно использовать команду из стандартного ввода.
Если вы хотите полностью удалить папку Linux, так, чтобы ее невозможно было восстановить, то можно использовать утилиту wipe. Она не поставляется по умолчанию, но вы можете ее достаточно просто установить:
Теперь для удаления каталога Linux используйте такую команду:
Опция -r указывает, что нужно удалять рекурсивно все под папки, -f — включает автоматическое удаление, без запроса пользователя, а -i показывает прогресс удаления. Так вы можете удалить все файлы в папке linux без возможности их восстановления поскольку все место на диске где они были будет несколько раз затерто.
Выводы
В этой статье мы рассмотрели как удалить каталог linux, а также как удалить все файлы в папке linux без возможности их будущего восстановления. Как видите, это очень просто, достаточно набрать несколько команд в терминале. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.