- How to extract a zip file to a specific folder?
- 2 Answers 2
- How To Unzip A File In Linux | Unzip Syntax | 8 Unzip Commands
- Unzip syntax
- Extract the zip file with Linux
- Unzip arguments in Linux
- Unzip commands/Options in Linux
- Summary
- How to Create and Extract Zip Files to Specific Directory in Linux
- Create Zip Archive File in Linux
- Extract Zip File to Specific or Different Directory
- How to Unzip into a Specific folder in Linux
- Method 1: Using the unzip command
- Method 2: Using the tar command
- Method 3: Using GUI tools
- Conclusion
How to extract a zip file to a specific folder?
I have a zip file that I need to extract into another folder. When I set up extraction to said folder it says «permission denied». I’ve read here how to log into a terminal as root and superuser but can’t find anything to help me. I need to extract a file from my Downloads directory to /var/lib/plexmediaserver/Library/Application Support/Plex Media Server/Plug-ins . Please explain how to extract a zip file to the correct folder.
yes the extension is .zip im trying to extract the zip file to plex media server plug ins . its in my downloads folder but when i try and extract to new directory it says i dont have permission
var/lib/plexmediaserver/Library/Application Support/Plex Media Server/Plug-ins to be exact is where i want it to go
2 Answers 2
We’ll extract to a different folder to be sure that permissions aren’t in our way:
- Open a terminal ( Ctrl + Alt + T should work).
- Now create a temporary folder to extract the file:
mkdir temp_for_zip_extract unzip /path/to/file.zip -d temp_for_zip_extract You should now have the contents of your zip file temp_for_zip_extract and can copy them into the desired folder.
If you can’t copy the files to your folder, then check the permissions on your target folder.
The path to the downloads folder depends on what you used to download it to, try ~/Downloads . If you can’t find it, then try this in a terminal:
cd ~; find -name 'filename.zip' You can also use a file manager, of course. There is Nautilus, Nemo, Thunar and many more, depending on your environment. Start the file manager and double click on your zip file, just like you would do in Windows.
How To Unzip A File In Linux | Unzip Syntax | 8 Unzip Commands
If you have a compressed zip file, you can unzip it using the Linux command line. Linux’s unzip command is highly flexible just like zip commands and can be used for much more than simply extracting zip files. Files from a ZIP archive, which are often seen on MS-DOS computers, can be listed, tested, or extracted using Unzip. If no settings are provided, the default behavior i.e. with no options will extract all files from the supplied ZIP archive into the current file and all subdirectories beneath it.
Unzip syntax
First of all, you need to install the unzip package. To do so, type in a terminal command:
sudo apt-get install unzip
Once all the packets have been installed, to unzip the archive files type in a terminal command:
A more useful tool is 7z, which zips and unzips a range of compression formats, notably lzma, usually the protocol offering the highest compression rates.
sudo apt-get install p7zip-full
Extract the zip file with Linux
- Open the Files app and navigate to the directory where the zip file is located.
- Locate the file which you want to unzip.
- Right-click on the file and the context menu will appear with the list of options.
- Select the “Extract Here” option to unzip files into the present working directory or choose “Extract to. ” for a different directory.
Unzip arguments in Linux
Some of the most commonly used arguments by unzip are listed below:
It tells the path of the zip archive(s). When a wildcard is used in the file specification, the operating system chooses the order in which each matching file is processed (or file system). The path itself cannot be a wildcard; only the filename can.
A list of archive members to process that can be optional, delimited by spaces. (VMS versions that have VMSCLI specified during compilation had to delimit files using commas. (For further information, see -v in the section below that lists your options.) You can match several members using regular expressions (wildcards).
An optional list of archive members to be excluded from processing. This option can be used to exclude any files that are in subdirectories because wildcard characters often match (‘/’) directory separators (for exceptions see the option -W).
If specified, files will be extracted to the target directory exdir. By default, all files and subdirectories are recreated in the current directory; the -d option allows extraction in an arbitrary directory (always assuming one has permission to write to the current working directory). This option need not appear at the end of the command line; it is also accepted before the zip file specification (with the normal options), immediately after the zip file path, or between the file(s) and the -x option.
Unzip commands/Options in Linux
To unzip a file, you do not need to add any options like the zip command. With unzip, the default behavior is to always seek permission before overwriting current files. Using unzip, you can extract every letter from the archive. Create any necessary subdirectories, then unzip into the current directory and any subdirectories below it options and commands that unzip accepts and uses are:
1. Unzip a file to a different directory
To unzip a ZIP file to a different directory than the current folder, we use the -D (Directory) Option. Go to the file manager and click on the zip file you want to unzip. Now open the terminal window and run the following command:
Command: $ unzip filename.zip -d /path/to/directory
2. Unzip tar/tar.gz/tgz files to a specific directory
Most files in Linux are compressed using the tar format. A .tar file is a collection of uncompressed files, sometimes known as a tarball. Since .tar doesn’t compress anything, it requires a separate compression utility for compression. The tar command allows you to create tar archive files as well as decompress them. This technique can be used on other file types/ file formats also. Using tar UtilityA tar.gz file is a combination of a .tar file and a .gz file. By default, the tar command will extract files to your current directory. Go to the terminal window and run the following command:
Command: $ tar -xf file-name.tar -C /path/to/directory
The -x option tells tar to extract the files. You can also use xargs with tar to create a tar.gz archive and populate it with files from the find command. Note: Some graphical interfaces include a tool for managing tar.gz files without the command line. Working with the graphical interface is a little difficult task.
3. Unzip a password-protected zip file
To unzip a file that is password-protected, invoke the unzip command with the -P option i.e -P (Password) Option followed by the password:
Command: $ unzip -P PasswOrd filename.zip
4. Exclude Files when Unzipping a ZIP File
To exclude specific files or directories from being extracted, use the -X (Exclude) option in the terminal :
Command: $ unzip filename.zip -x file1-to-exclude file2-to-exclude
5. Suppress the Output of the unzip Command
By default, unzip prints the names of all the files it’s extracting and a summary when the extraction is completed. Use the -q switch to suppress the printing of these messages.
Command: $ unzip -q filename.zip
6. Overwrite existing files
If you want to overwrite existing files without prompting, it can be done using the -o option. To run the -o (overwrite) option open the terminal window and run the following command:
Command: $ unzip -o filename.zip
7. Unzip a zip file without overwriting existing files
This command can be performed using the -n option which forces unzip to skip the extraction of a file that already exists:
Command: $ unzip -n filename.zip
8. List the Contents of a zip file
To list the contents of a given zip file we use the -l (list archive) option. To execute the -l option to the current file, open the windows terminal and type the following command:
Command: $ unzip -l filename.zip
Summary
The unzip utility is an extremely effective and straightforward tool for transferring compressed files over a network or even between operating systems. From the above tutorial, you can easily unzip files in Linux systems through the command line using the unzip command.
Suggested reads:
I am a storyteller by nature. At Unstop, I tell stories ripe with promise and inspiration, and in life, I voice out the stories of our four-legged furry friends. Providing a prospect of a good life filled with equal opportunities to students and our pawsome buddies helps me sleep better at night. And for those rainy evenings, I turn to my colors.
How to Create and Extract Zip Files to Specific Directory in Linux
In one of our several articles about the tar command, we showed you how to extract tar files to a specific or different directory in Linux. This short guide explains to you how to extract/unzip .zip archive files to a specific or different directory in Linux.
Zip is a simple, cross-platform file packaging and compression utility for Unix-like systems including Linux and Windows OS; plus many other operating systems. The “zip” format is a common archiving file format used on Windows PC’s and most importantly, it enables you to specify the compression level between 1 and 9 as an option.
Create Zip Archive File in Linux
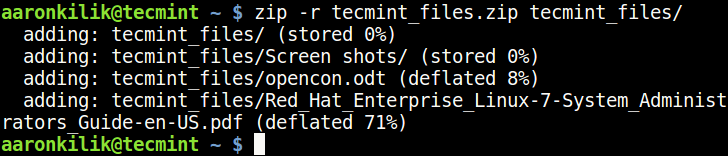
To create a .zip (packaged and compressed) file from the command line, you can run a similar command like the one below, The -r flag enables recursive reading of files directory structure.
$ zip -r tecmint_files.zip tecmint_files
To unzip the tecmint_files.zip archive file you have just created above, you can run the unzip command as follows.
The above command will extract the files into the current working directory. What if you want to send the unzipped files into a specific or different directory – you can learn this in the next section.
Extract Zip File to Specific or Different Directory
To extract/unzip .zip archive files to specific or different directory from the command line, include the -d unzip command flag as shown below. We will use the same example above to demonstrate this.
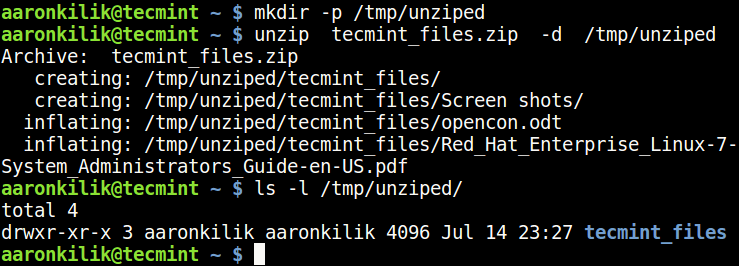
This will extract the .zip file content into the /tmp directory:
$ mkdir -p /tmp/unziped $ unzip tecmint_files.zip -d /tmp/unziped $ ls -l /tmp/unziped/
For more usage information, read zip and unzip command man pages.
You may also like to read the following related articles.
In this short article, we have explained how to extract/unzip .zip archive files to a specific or different directory in Linux. You can add your thoughts to this article via the feedback form below.
How to Unzip into a Specific folder in Linux
Unzipping files is a common task in Linux. However, it can become a bit tricky when you need to unzip files into a specific folder. In this article, we will explore different methods to unzip files into a specific folder in Linux.
Method 1: Using the unzip command
The unzip command is a built-in utility in Linux that can be used to extract files from zip archives. To unzip a file into a specific folder, you can use the -d flag followed by the path to the target folder.
For example, if you want to unzip a file called sample.zip into a folder called “unzipped” in your home directory, you can use the following command:
unzip ~/sample.zip -d ~/unzipped Method 2: Using the tar command
The tar command is another built-in utility in Linux that can be used to create and extract tar archives. To extract a tar archive into a specific folder, you can use the -C flag followed by the path to the target folder.
For example, if you want to extract a file called sample.tar into a folder called “unzipped” in your home directory, you can use the following command:
tar -xvf ~/sample.tar -C ~/unzipped Method 3: Using GUI tools
If you prefer to use a graphical user interface (GUI), there are many file archiving and extraction tools available in Linux. One popular tool is the file roller, which is the default archive manager for many Linux distributions.
To extract a file using the file roller, you can simply right-click on the zip or tar archive and select “Extract Here” or “Extract to” to specify the target folder.
Conclusion
Unzipping files into a specific folder in Linux is a simple task once you know the right command syntax or have a GUI tool that supports this functionality. The methods discussed in this article should be enough to get you started. However, there are many other options and flags available for the unzip and tar commands that you can explore by reading their respective manuals.