- Debian / Ubuntu. Обновление, проблемы и тонкости
- Проблемы которые могут возникнуть
- Принудительный поиск обновлений
- Список команд
- How to Update the List of Linux Repositories
- What are Linux repositories?
- Different types of repositories in Ubuntu
- How to add new repositories to the software list
- Example to add Google Chrome repository from Terminal
- How to update the list of Linux repositories
Debian / Ubuntu. Обновление, проблемы и тонкости
По умолчанию используется репозиторий archive.ubuntu.com, но при желании можно выбрать другое зеркало, это можно сделать как редактированием файла из внешней оболочки, так и через консоль. Но будьте осторожны, иногда возникают проблемы с установкой пакетов или обновлением самого ядра, большинство из которых возникают из-за ошибочных данных в этом файле.
Команда для редактирования через консоль:
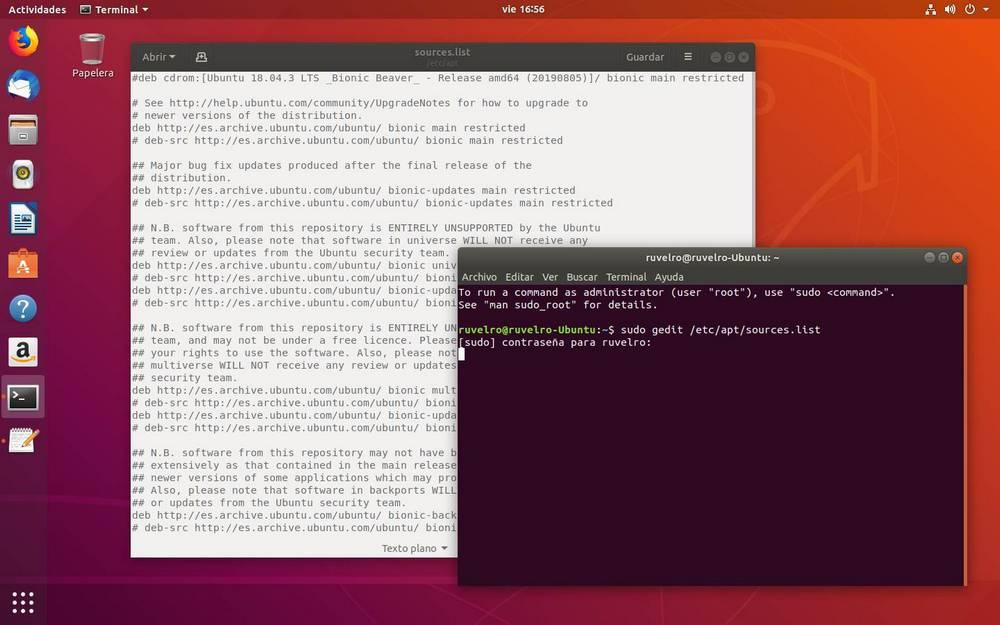
sudo gedit /etc/apt/sources.list или software-properties-gtkПуть для редактирования через веб интерфейс
Система → Администрирование → Источники приложений → Загрузить с → Другой → Выбрать лучший сервер
Либо просто пройти по адресу /etc/apt/sources.list и сделать даблклик по файлу.
Если вдруг использовавшийся репозиторий упал, для поиска подходящих в данный момент зеркал можно использовать специальную кнопку: в списке «Загрузить с» выбрать «Другой», там «Выбрать лучший сервер».
Структура записи репозиториев
deb http://old-releases.ubuntu.com/ubuntu natty main universedeb — тип репозитория. Может быть deb (двоичный) и deb-src (исходный).
natty — версия дистрибутива, в данном случае 11.04. Узнать название версии ubuntu
main, universe — Уровни поддержки. Может указываться как один, так и несколько, в строчку. Также бывают уровни multiverse и restricted.
Проблемы которые могут возникнуть
W: Duplicate sources.list entry http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ precise-updates/main i386 Packages (/var/lib/apt/lists/archive.ubuntu.com_ubuntu_dists_precise-updates_main_binary-i386_Packages) W: You may want to run apt-get update to correct these problemsW: Duplicate sources.list entry http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ precise-updates/main i386 Packages (/var/lib/apt/lists/archive.ubuntu.com_ubuntu_dists_precise-updates_main_binary-i386_Packages) W: You may want to run apt-get update to correct these problemsПодобная ошибка говорит о том, что дублируются записи репозиториев. Не адреса, а строка полностью, вместе с типом, версией и уровнем поддержки.
Когда при попытке обновить систему или при поиске подходящего репозитория возникает надпись «Ошибка при загрузке информации об источниках приложений. Проверьте интернет-соединение», это последствия ошибки 404, из примера ниже.
Ошибки вида 404 Not Found. Пример
Err http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ utopic/universe libfftw3-3 amd64 3.3.4-1ubuntu1 404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.88.152 80]Есть несколько причин возникновения подобных ошибок
- Репозитория больше не существует
- В адресе к репозиторию есть ошибка
- Установлена старая версия, которая больше не доступна на репозитории
- Выбрать другой репозиторий
- Исправить ошибку в написании
- В файле в качестве адреса сайта указать old-releases.ubuntu.com. Это сайт с архивами старых версий ubuntu. Указать этот адрес можно командой
sudo sed -i -re 's/([a-z]{2}\.)?archive.ubuntu.com|security.ubuntu.com/old-releases.ubuntu.com/g' /etc/apt/sources.listsudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get dist-upgradeПринудительный поиск обновлений
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install update-manager-core sudo do-release-upgradeupdate-manager-core — пакет содержащий базовые программы для менеджера обновлений
Список команд
sudo apt-get update — обновление установленных файлов
sudo apt-get upgrade — обновление всех пакетов
sudo apt-get dist-upgrade — обновление всех пакетов с принудительным механизмом разрешения конфликтов
do-release-upgrade — команда для обновления версии системы. В отличии от dist-upgrade позволяет отслеживать изменения в конфигурациях систем при переходе от выпуска к выпуску.
How to Update the List of Linux Repositories
When installing applications and programs on Linux there are several ways to do it. More advanced users can choose to download the source code from the developer’s website and compile it directly on their computer. Something very slow and impractical really. The most inexperienced users usually choose the easy way: search and download the binary (for example, the deb) and install it, from the package manager, by double clicking. As in Windows. And, thirdly, we have intermediate users who seek comfort and ease and make use of Linux repositories to download, install and update their programs.
What are Linux repositories?
Repositories are one of the best features that Linux has. A repository is a list of programs, usually always updated, that allows us to easily search and download all kinds of programs and tools in our distribution.
Thanks to the repositories we will be able to have a safe and reliable place from which to download software and the latest updates of all our programs. These programs will be installed without any dependency problems, and we can also update our entire program repertoire with a simple command.
The developers of the distros usually include their own repositories with useful programs. In addition, many developers maintain their own independent repositories to distribute their programs. Even any user can create and maintain their own repository, very useful, for example, to distribute software lists.
Different types of repositories in Ubuntu
- Main: the repository installed by default. It consists of free FOSS software that can be distributed freely and without restrictions.
- Universe: includes free and open source software, but cannot guarantee regular security updates.
- Multiverse: includes software that is from the FOSS. It must be the user who analyzes the licenses and decides whether or not to use these programs legally.
- Restricted: within this channel we can find closed source software. It is used, for example, to distribute NVIDIA drivers, among many others.
- Partner: includes proprietary software that has been packaged by Canonical.
And in addition to these repositories, we can also add third-party repositories to our Linux distro to install other software safely.
The steps we are going to see next have been done on Ubuntu, but they should be the same for any Debian-based distro.
How to add new repositories to the software list
To see the list of repositories that we have in our Ubuntu distro, what we must do is open a Terminal (Control + Alt + T) and execute the following command in this:
sudo gedit /etc/apt/sources.list
In case it does not work, or we do not have gedit installed in our distro, we can do it with the following, by going to the “nano” editor.
sudo nano /etc/apt/sources.list
As we will see, we will open a list with all the repositories that we have in our distro. Repositories (for example, deb http://en.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ bionic-updates main restricted) that start without # are those that are being used. On the other hand, those that appear at the beginning with a # are those that we have installed, but they are disabled.
If we want to add a new repo, we just have to add it, as follows, to the end of the text file:
We save the changes and go. Of course, before updating the repositories and installing any program we must install the security keys of that repository. These are usually offered together with the PPA, and then we will see an example with the official Google Chrome repo.
Example to add Google Chrome repository from Terminal
To add a repository, or PPA, from Linux , we must do it as follows. The first thing will be to search the Internet for the repository we want to add. In the case of Google Chrome (this example), we can find it on the Google website .
In the terminal, we will execute the following command to add the keys of the official Google repositories to our Linux. Otherwise, the repositories software cannot be validated and will return an error:
wget -q -O – https://dl.google.com/linux/linux_signing_key.pub | sudo apt-key add –
Once the previous command has been executed, we can add the repository to the list of Ubuntu repositories. And we will do that with the following command:
sudo sh -c ‘echo “deb [arch = amd64] http://dl.google.com/linux/chrome/deb/ stable main” >> /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google.list’
Obviously, if we have added the repository from GEDIT as we explained in the previous step, this last command will not be necessary.
Now, first of all, we will have to update the list of Linux repositories to register in our system all the programs and to be able to download and install them with apt install.
How to update the list of Linux repositories
If we have already added the repositories we want to the list with the previous steps, or we simply want to update our software without adding new repositories, the process is much faster.
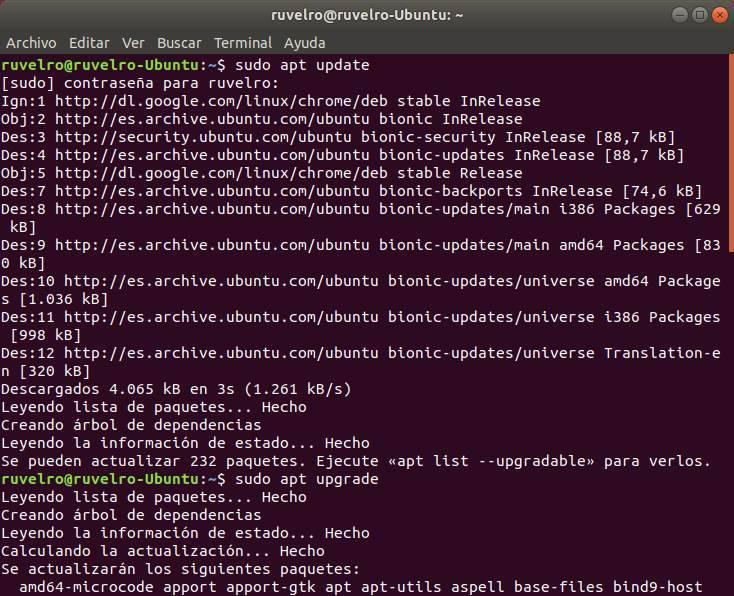
All we have left to do is open a Terminal (Control + Alt + T) in our Linux and execute the following two commands:
- sudo apt update (to update the software lists of the repositories).
- sudo apt upgrade (to download available packages).
When the process is finished, all the programs of our Linux, which have been installed through the repositories, will have been updated to their latest version.
We can now install the programs we want from the repositories of our Linux using apt install (for example: sudo apt install google-chrome).