- Linux: how to get all login logs from my system [closed]
- 2 Answers 2
- How to check user login history in Linux?
- How Linux store log files?
- How to check the login history?
- How to check the login history of a specific user?
- How to check the specific number of logins?
- How to check bad login attempts:
- Conclusion:
- About the author
- Sam U
- Просмотр истории входа в Linux. Кто и когда входил в систему
- Где хранятся логи входа в систему
- Просмотр истории входа в систему
- Просмотр истории входа для определенного пользователя
- Ограничить количество строк
- Просмотр неудачных попыток входа в систему
- Заключение
Linux: how to get all login logs from my system [closed]
I want to know all the times a user logs since last year into my system?
I used last command but it is not useful.
welcome to Stack Exchange! please remember that we’re all volunteers here. as such, we expect that you’ve done some basic research. it looks like you have a start — since you mention trying the last command — but you should be doing more research than that, and in any case, you haven’t actually specified why the last command isn’t useful. also, define «logged in». do you want to track console logins? SSH logins? Emacs forbid, telnet logins? or just anything authenticating with PAM? be specific.
2 Answers 2
The login logs on redhat-style linux are called wtmp ( man wtmp ), stored in /var/log/ by default, and you can retrieve them using utmpdump (on RHEL6).
[root@server ~]# utmpdump /var/log/wtmp* | awk '$4~"root" ' Utmp dump of /var/log/wtmp [7] [01320] [ts/0] [root ] [pts/0 ] [192.168.1.101 ] [192.168.1.101 ] [Tue Sep 24 00:31:47 2013 UTC] [7] [01817] [ts/3] [root ] [pts/3 ] [192.168.1.101 ] [192.168.1.101 ] [Tue Sep 24 00:38:22 2013 UTC] [7] [01690] [ts/0] [root ] [pts/0 ] [192.168.1.101 ] [192.168.1.101 ] [Tue Sep 24 00:59:04 2013 UTC] [7] [23641] [ts/0] [root ] [pts/0 ] [192.168.1.101 ] [192.168.1.101 ] [Wed Sep 25 19:12:44 2013 UTC] [7] [03020] [ts/0] [root ] [pts/0 ] [192.168.1.100 ] [192.168.1.100 ] [Fri Sep 27 21:33:40 2013 UTC] . It seems last can be used to achieve what you are trying to do. You need to append the date to the last command to extract the information.
last | while read line; do date=`date -d "$(echo $line | awk '< print $5" "$6" "$7 >')" +%s`; [[ $date -ge `date -d "Aug 25 00:00" +%s` && $date -le `date -d "Aug 28 00:00" +%s` ]] && echo $line; done However, if you are concerned with finding information about a particular user, you can modify the last command as last username and then pipe the while loop to it. It would give you the information of a particular user’s login information for the last one year.
I tested the above command and it works perfectly fine in my system. I took the above command from here.
You can change the date in the command to suit your requirements.
How to check user login history in Linux?
Linux is one of the most accepted operating systems for multi-user setup. A multi-user operating system means a system that more than one user can access. These systems are mostly used in servers of large organizations, businesses, government, and educational sectors.
Different users access the multi-user operating system, and to monitor users’ activity, it is important to keep an eye on login history. Login history gives useful information about different users who have accessed the machine, such as username, terminal name, IP address, date, and time of logging in. Moreover, login history also helps to identify different issues, especially for troubleshooting.
This write-up is focusing on an approach to check the user login history. Before getting into that, let’s understand how Linux arrange and manage login data:
How Linux store log files?
Linux (Ubuntu) stores login data into three locations:
- var/log/utmp – It contains information about users who are currently logged in
- var/log/utmw – It contains the history of all logged-in users
- var/log/btmp – It keeps all bad login attempts
All of these files stores login information and login attempts as well.
How to check the login history?
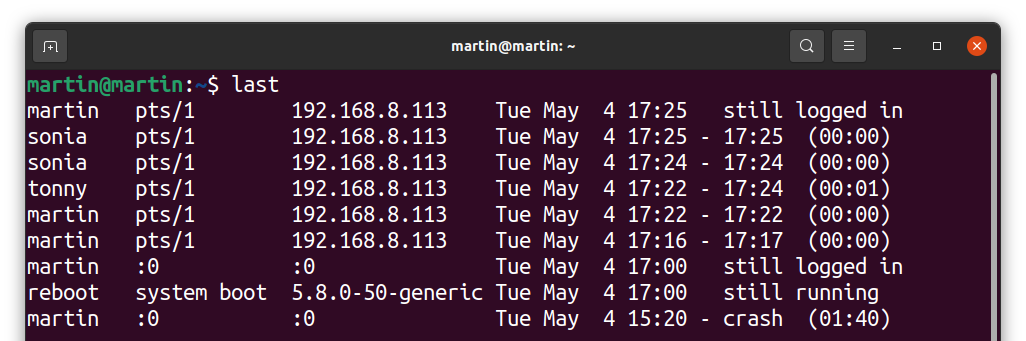
To check the login history, use the following command:
It gives information about all the users who logged in successfully. It searches through the “var/log/utmw” file and displays the history of all users who have logged in since creating the file.
The above output shows that the different users connected to the server from a machine with IP “192.168.8.113”, “pts/1” indicate that the server was accessed via SSH.
How to check the login history of a specific user?
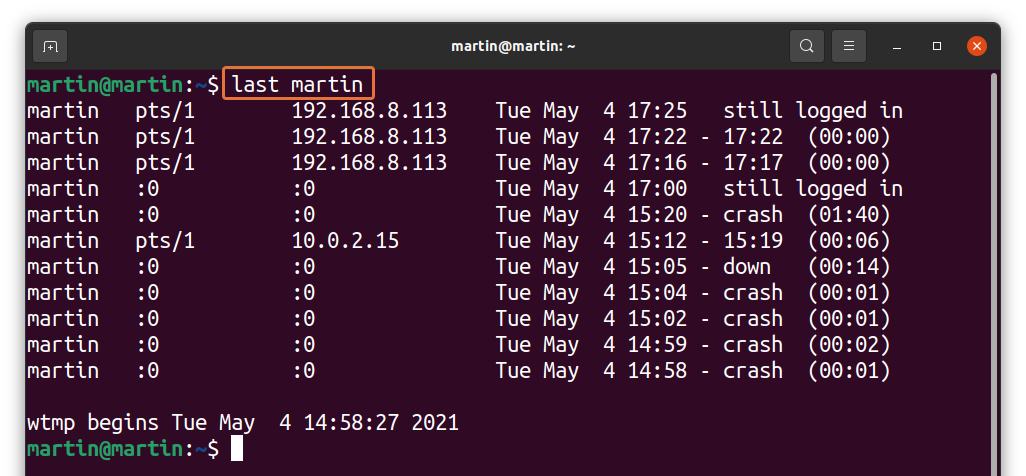
To check the login history of a specific user, uses the “last” command with the username of that particular user:
I am checking for “martin”; the command would be:
How to check the specific number of logins?
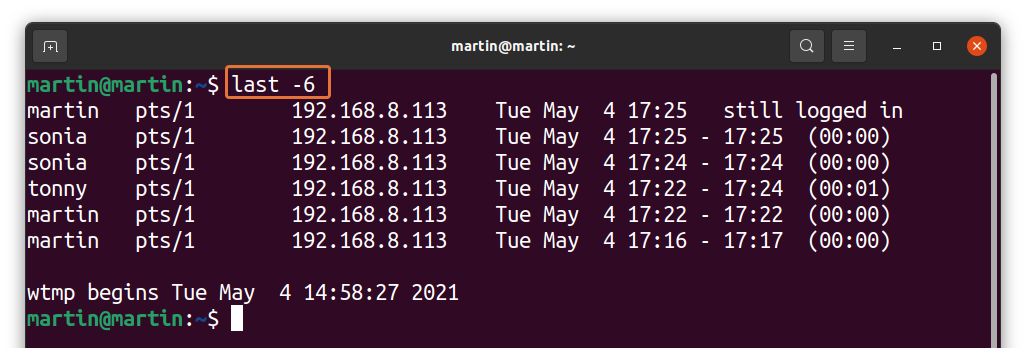
If numerous people are accessing the server, then the login history would be huge. To trim the number of logins, follow the below-mentioned syntax:
Replace “X” with the number of logins you want to display as standard output:
You can also use it with a specific username:
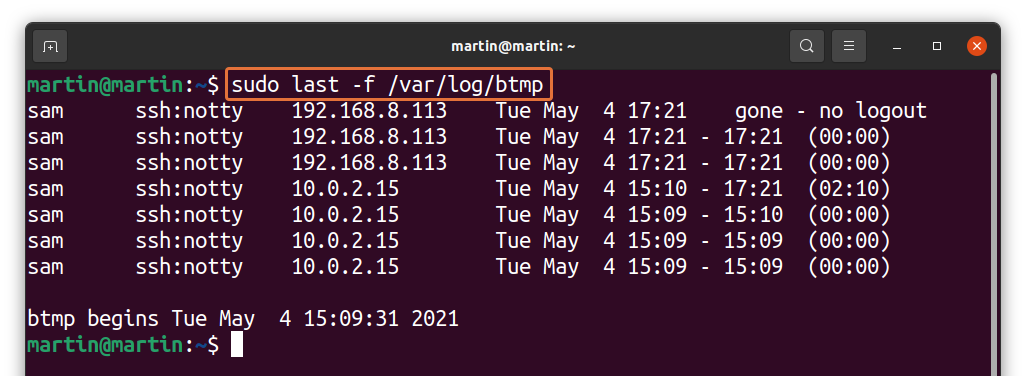
How to check bad login attempts:
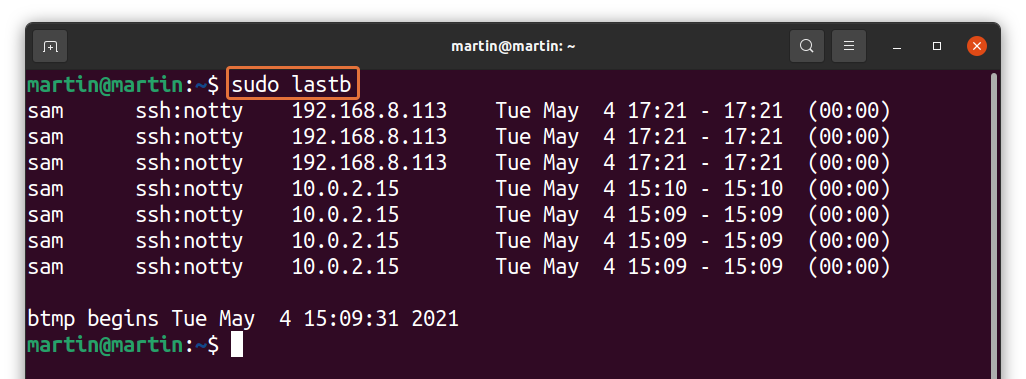
As discussed above that Linux also keeps the information of bad login attempts. To display it, use the command given below:
Observing bad login attempts is very critical for security reasons of the server. You can easily identify an unknown IP address that is probably trying to access the server.
Conclusion:
Linux is the most preferred operating system for servers in many businesses because it is a secure multi-user platform. Many users access a server, and to keep a check on user activity, we need user login information. In this guide, we learned how to examine user login history in Linux. Moreover, we also analyzed how bad attempts can be tackled to secure the server. We used the “last” command, but another tool called “aureport” tracks successful and failed logins.
About the author
Sam U
I am a professional graphics designer with over 6 years of experience. Currently doing research in virtual reality, augmented reality and mixed reality.
I hardly watch movies but love to read tech related books and articles.
Просмотр истории входа в Linux. Кто и когда входил в систему
Данная информация обычно нужна системным администраторам для просмотра истории входа в систему на многопользовательском сервере.
Помимо этого, бывает полезно узнать о неудачных попытках входа. Это могут быть боты, но могут быть и попытки взлома вашего сервера.
Где хранятся логи входа в систему
Информация о том, кто входил (залогинивался) или пытался войти в систему, хранится в лог файлах. Для этого используется три лог-файла:
/var/log/btmp — неудачные попытки входа.
/var/run/utmp — кто в данный момент залогинен (текущие сессии).
/var/log/wtmp — список всех сессий входа в систему.
Эти файлы, в отличии от большинства других лог-файлов Linux, имеют бинарный формат. Если вы попробуете просмотреть их командой cat , то на экран будет выведена «каша». Для их просмотра используется команда last .
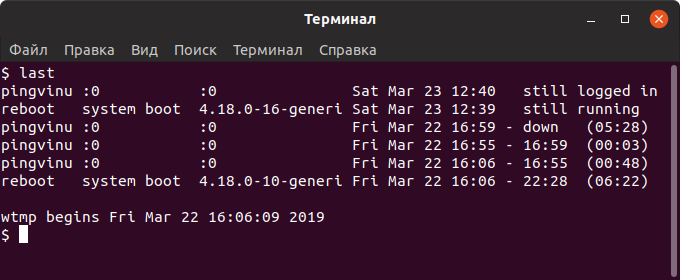
Просмотр истории входа в систему
Для просмотра логов входа в систему используется команда last . По умолчанию команда last выводит информацию из файла /var/log/wtmp , в котором хранятся записи обо всех сессиях входа.
yuriy pts/0 181.23.456.189 Sat Mar 23 12:27 still logged in nifnif pts/11 181.45.678.912 Wed Mar 20 05:30 - 05:49 (00:19) nafnaf pts/22 181.45.678.312 Fri Mar 15 00:01 - 02:27 (02:26) nufnuf pts/33 181.45.678.411 Wed Mar 13 11:02 - 11:28 (00:26) . Как вы можете видеть, выводится таблица с информацией. В ней содержатся имена пользователей, IP-адрес, с которого осуществлялся вход, дата и время входа и продолжительность сессии. Запись вида pts/0 означает, что для входа использовалось SSH соединение (или другое удаленное соединение, например, telnet).
Также выводится информация о включении/выключении системы.
Последняя строка в файле /var/log/wtmp показывает, когда был создан файл.
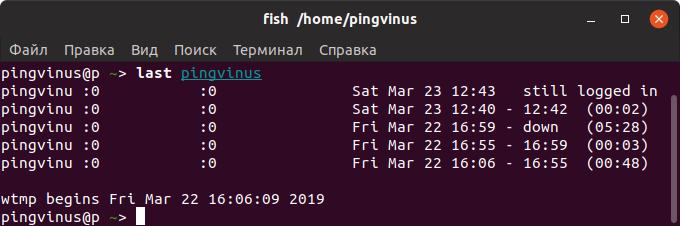
Просмотр истории входа для определенного пользователя
Чтобы показать информацию о сессиях определенного пользователя, то для команды last необходимо указать имя этого пользователя:
Ограничить количество строк
Иногда лог, который выводит команда last , может быть очень большой. Чтобы ограничить количество выводимых строк, используется опция -n ЧислоСтрок или просто -ЧислоСтрок .
Выведем только десять свежих записей:
Просмотр неудачных попыток входа в систему
Как было сказано выше, записи о неудачных попытках входа в систему хранятся в лог-файле /var/log/btmp .
Команда last по умолчанию выводит информацию из файла /var/log/wtmp . Чтобы вывести информацию из другого файла, используется опция -f ИмяФайла
Выведем записи о неудачных попытках входа (из файла /var/log/btmp ):
Или же можно воспользоваться командой lastb . Команда lastb работает точно также, как и команда last , но выводит информацию из файла /var/log/btmp
Заключение
Мы рассмотрели использование команды last для просмотра информации об истории входа в систему.
Дополнительную информацию по использованию команды last можно получить, выполнив в терминале: