- Установка графической оболочки в Debian
- Возникшие проблемы:
- Подключение репозиториев Debian
- Установка графической подсистемы (ставим иксы в Linux)
- Установка графической оболочки GNOME
- Linux установка графической оболочки debian
- 13.3.1. GNOME
- 13.3.2. KDE and Plasma
- 13.3.3. Xfce и другие
- How to Change Debian Desktop Environment
- Desktop environment on Debian
- Installing desktop environment on Debian
- Listing all available desktop environments
- Installing GNOME
- Installing Xfce
- Installing KDE Plasma
- Installing LXDE
- Installing MATE desktop
- Installing Cinnamon desktop
- Installing desktop environments using tasksel
- Switching to a different desktop environment
- Final thoughts
- About the author
- Sidratul Muntaha
Установка графической оболочки в Debian
Итак, базовая система — установлена, оживим ее графическим интерфейсом!
Подключим основной официальный репозиторий Debian. Для этого добавим в файл /etc/apt/sources.list следующие строки:
Затем обновляем список доступных пакетов (aptitude предварительно надо установить или использовать вместо него apt-get):
Информацию об имеющихся в репозиториях пакетах можно узнать с помощью команды:
Далее устанавливаем графическую подсистему (ставим иксы в Linux)
И наконец, производим установку графической оболочки GNOME:
Возникшие проблемы:
Для того чтобы установить графическую оболочку в базовой системе Debian, придется проделать следующие действия: во-первых, подключить репозитории Debian в систему и добавить их для установки программ, во-вторых, установить графическую подсистему (иксы) и только после этого станет возможным поставить выбранную графическую оболочку.
Подключение репозиториев Debian
Репозиторий — специальной структуры файловое хранилище, в котором данные хранятся в удобном виде. Репозиторий может быть доступен по сети, в качестве репозитория может использоваться диск, флэшка, простая папка с необходимой структурой и другие варианты.
Репозитории Debian хранят в себе не только исходники программного обеспечения, но и готовые скомпилированные пакеты, которые можно с помощью менеджера пакетов dpkg, apt-get, aptitude установить.
Информация о подключенных репозиториях хранится в файле /etc/apt/sources.list. Для того, чтобы подключить репозиторий надо добавить информацию о нем в данный файл. После изменения списка необходимо обновить информацию о доступных пакетах в репозиториях с помощью менеджера пакетов apt-get или aptitude. Существует множество репозиториев Debian ( список официальных репозиториев debian, полезные репозитории для Debian), но я добавлю лишь основной репозиторий,
Так выглядит файл /etc/apt/sources.list сразу после установки базовой системы:
Добавим в него основной официальный репозиторий.
Сохраняем изменения в файле и закрываем его.
# aptitude update ($ sudo aptitude update)
# apt-get update ($ sudo apt-get update)
Установка графической подсистемы (ставим иксы в Linux)
# aptitude install xorg ($ aptitude install xorg)
Это приведёт к тому, что установится базовая графическая система. В процессе установки система запросит разрешение поставить необходимые пакеты, на что соглашаемся. Это может занять много времени, ждём пока пакетная система всё настроит и вернёт нам управление.
Чтобы запустить иксы, в консоли даём команду:
Экран может помигать, почернеть и вылезет серая сеточка с крестиком. Подёргайте мышку, крестик должен последовать за мышью. Если это произошло — графическая система завелась. Нажмите левой кнопкой мыши и держите — увидите унылого болотно-зелёного цвета менюшку. Знакомьтесь: это twm, Tab Window Manager, графический интерфейс иксов по умолчанию. Теперь можно устанавливать желаемую графическую оболочку. Но перед этим гасим иксы, нажимая одновременно Ctrl+Alt+Backspace.
Установка графической оболочки GNOME
Вот и настал долгожданный момент, когда наконец-то можно непостредственно приступить к установке выбранной графической оболочки, справедливости ради отметим, что выбрать — есть из чего, но об этом — попозже. Установим графическую среду GNOME, остальные среды, надо думать, устанавливаются аналогично.
После перезагрузки попадаем в GNOME
Linux установка графической оболочки debian
The free graphical desktop field is dominated by two large software collections: GNOME and Plasma by KDE. Both of them are very popular.
This diversity is rooted in history. Plasma (initially only KDE, which is now the name of the community) was the first graphical desktop project, but it chose the Qt graphical toolkit and that choice wasn’t acceptable for a large number of developers. Qt was not free software at the time, and GNOME was started based on the GTK+ toolkit. Qt has since become free software, but the projects still evolved in parallel.
The GNOME and KDE communities still work together: under the FreeDesktop.org umbrella, the projects collaborated in defining standards for interoperability across applications.
Выбор «лучшего» графического рабочего стола является деликатной темой, от которой мы предпочитаем держаться подальше. Мы просто опишем их возможности и дадим несколько советов для дальнейших размышлений. Лучшим выбором будет тот, который вы сделаете после некоторых экспериментов.
13.3.1. GNOME
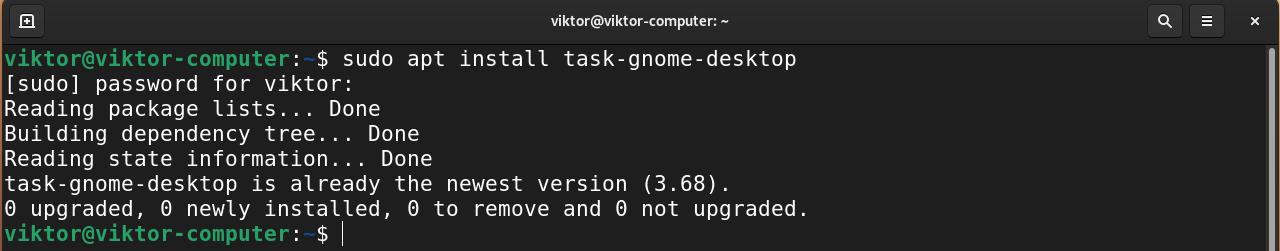
Debian Bullseye includes GNOME version 3.38, which can be installed by a simple apt install gnome (it can also be installed by selecting the “Debian desktop environment” task — task-desktop and task-gnome-desktop ).
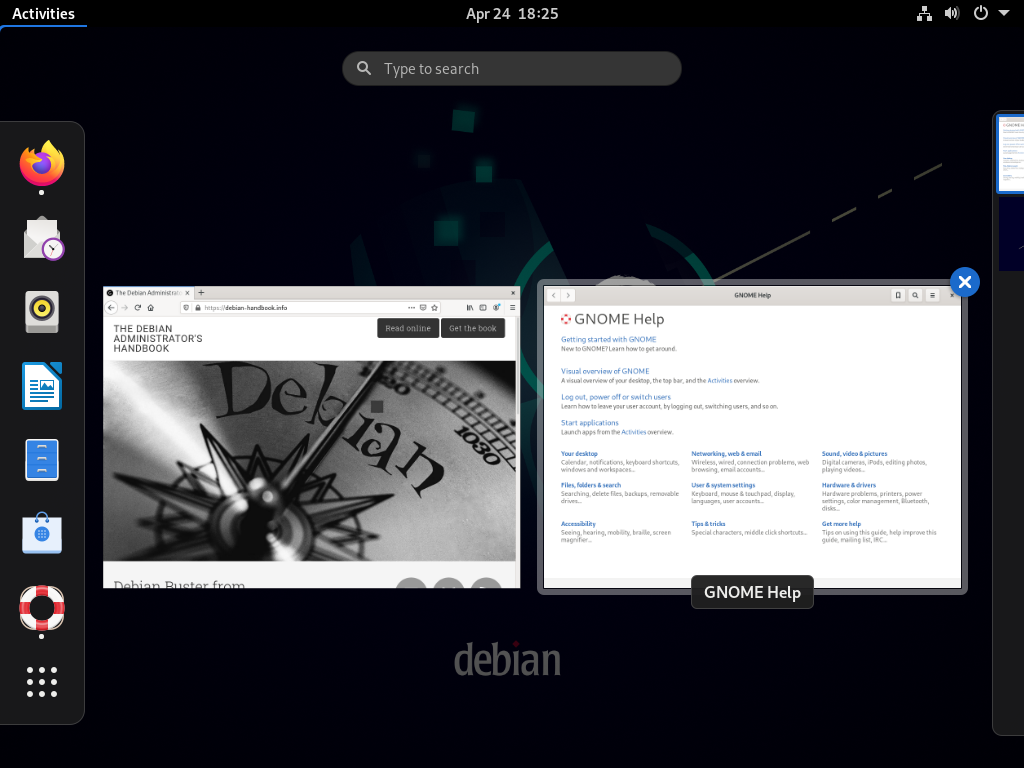
GNOME is noteworthy for its efforts in usability and accessibility. Design professionals have been involved in writing its standards and recommendations, which has helped developers to create satisfying graphical user interfaces. The project also gets encouragement from the big players of computing, such as Intel, IBM, Oracle, Novell, and of course, various Linux distributions. Finally, many programming languages can be used in developing applications interfacing to GNOME.
Рисунок 13.1. Рабочий стол GNOME
For administrators, GNOME seems to be better prepared for massive deployments. Application configuration is handled through the GSettings interface and stores its data in the DConf database. The configuration settings can thus be queried and edited with the gsettings , and dconf command-line tools, or by the dconf-editor graphical user interfaces. The administrator can therefore change users’ configuration with a simple script. The GNOME website provides information to guide administrators who manage GNOME workstations:
13.3.2. KDE and Plasma
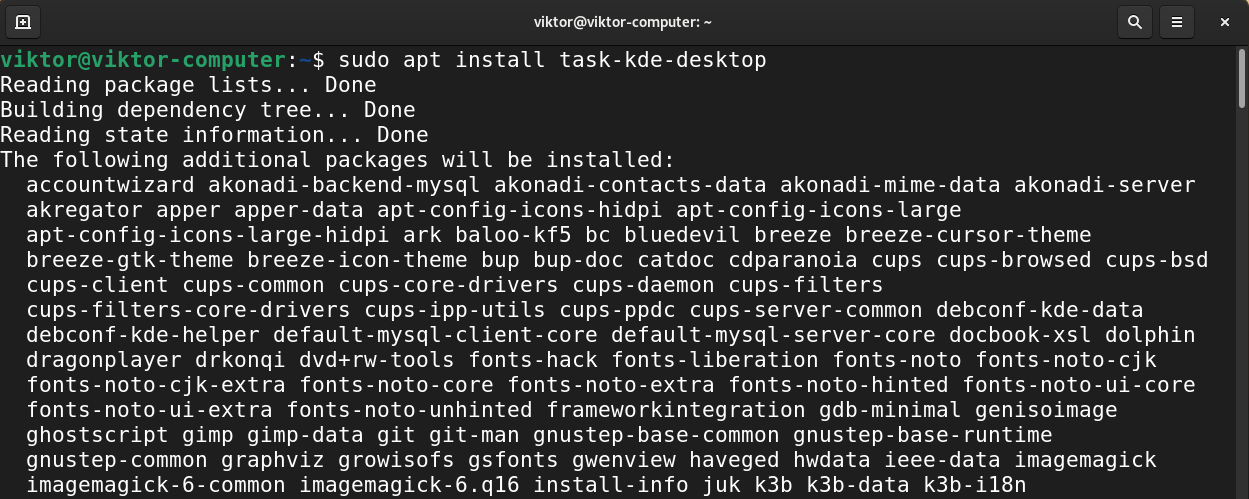
Debian Bullseye includes version 5.20 of KDE Plasma, which can be installed with apt install kde-standard ( task-kde-desktop ).
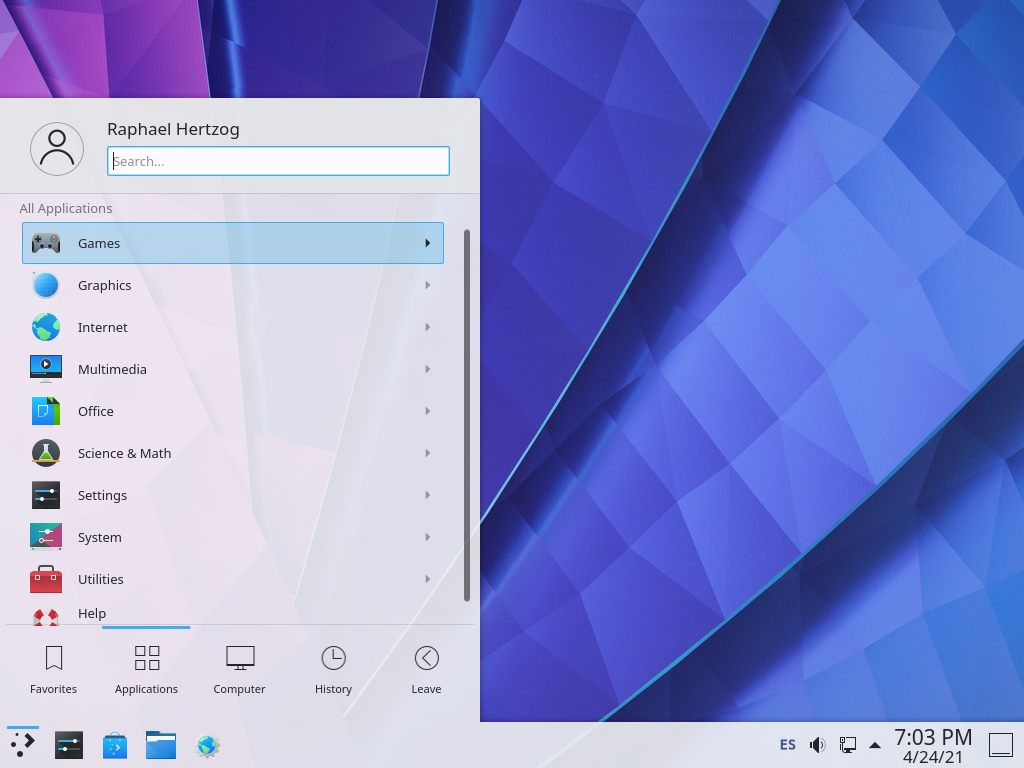
Plasma has had a rapid evolution based on a very hands-on approach. Its authors quickly got very good results, which allowed them to grow a large user-base. These factors contributed to the overall project quality. Plasma is a mature desktop environment with a wide range of applications.
Рисунок 13.2. The Plasma desktop
Since the Qt 4.0 release, the last remaining license problem with KDE software has been solved. This version was released under the GPL both for Linux and Windows (the Windows version was previously released under a non-free license). KDE applications are primarily developed using the C++ language.
13.3.3. Xfce и другие
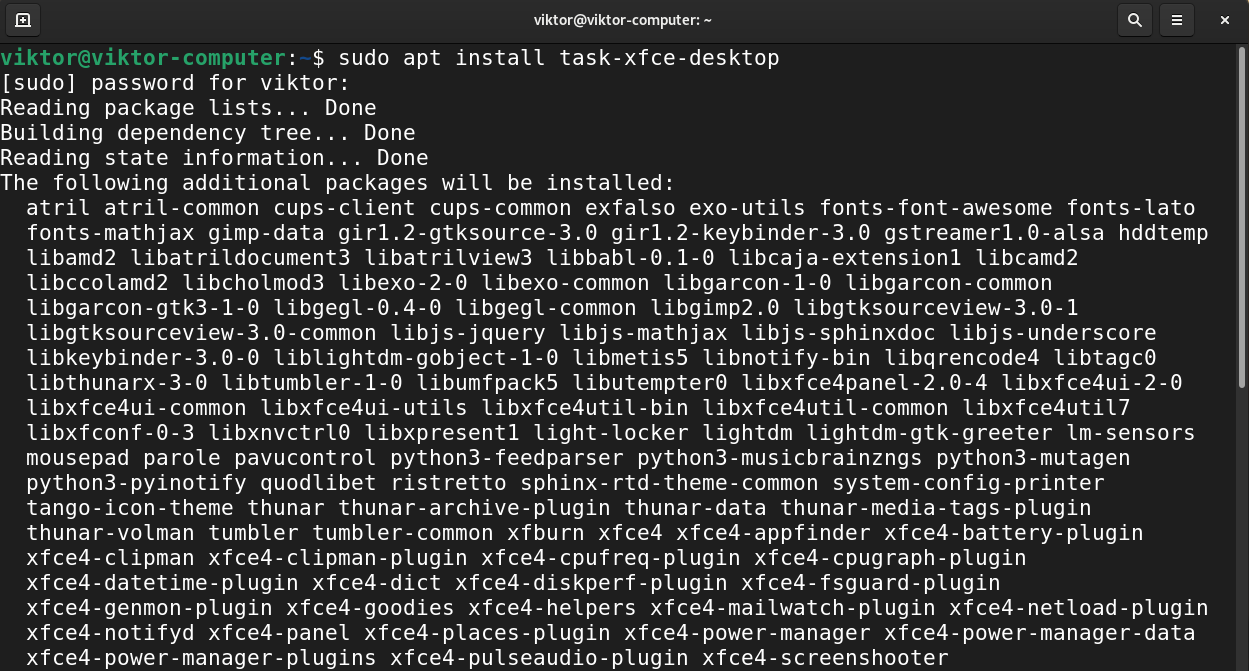
Xfce is a simple and lightweight graphical desktop, which is a perfect match for computers with limited resources. It can be installed with apt install xfce4 ( task-xfce-desktop ). Like GNOME, Xfce is based on the GTK+ toolkit, and several components are common across both desktops.
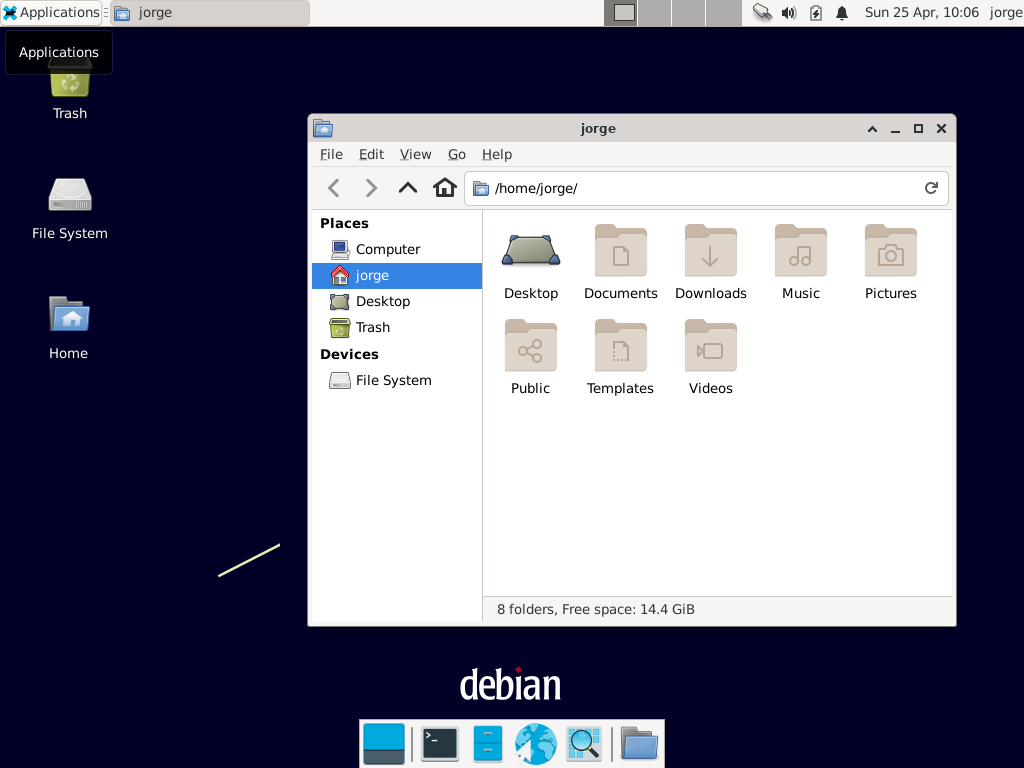
Unlike GNOME and Plasma, Xfce does not aim to become a vast project. Beyond the basic components of a modern desktop (file manager, window manager, session manager, a panel for application launchers and so on), it only provides a few specific applications: a terminal, a calendar ( orage ), an image viewer, a CD/DVD burning tool, a media player ( parole ), sound volume control and a text editor ( mousepad ).
Рисунок 13.3. Рабочий стол Xfce
How to Change Debian Desktop Environment
In Linux, a desktop environment refers to the bundle of components that provide the common graphical user interface (GUI) components on the screen, such as icons, wallpapers, toolbars, widgets, etc. Thanks to the desktop environment, it’s possible to use Linux with your mouse and keyboard like any other graphical operating system.
There are numerous desktop environments available on Debian, each with its own perks and features. Interested in switching to a new desktop environment? In this guide, we’ll explore how to install and change the desktop environment on Debian.
Desktop environment on Debian
Debian supports a wide range of desktop environments, from full-fledged desktop environments to lighter/minimalist alternatives. By default, Debian comes with the GNOME desktop. Check out the official Debian documentation on supported desktop environments, window managers, and display managers.
We’ll be showcasing how to install additional desktop environments, for example, GNOME, Xfce, LXDE, KDE Plasma, and MATE. All of them are directly available from the official Debian package repos.
Installing desktop environment on Debian
It requires root permission to perform any system-level change on any Linux system. In Debian, the root permission is stricter by default. I’ll be assuming that you have access to either the root account or a non-root user with sudo permission. Here’s how to grant a non-root user permission to sudo.
Listing all available desktop environments
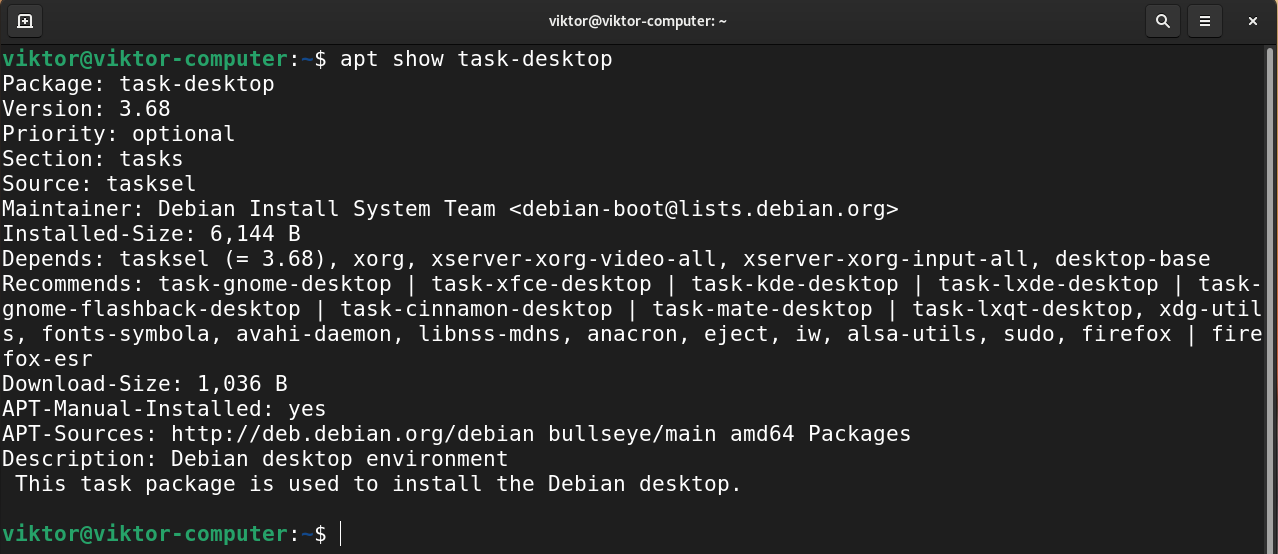
We need to check the list of all the available desktop environments. Run the following APT command.
Here, each desktop environment is denoted as a task—desktop format.
Installing GNOME
This is the default desktop environment of Debian. It’s one of the most widely used desktop environments. It also has its own suite of apps. GNOME is elegant and intuitive.
To install GNOME, run the following command.
Installing Xfce
Xfce is a lightweight desktop environment. It’s designed for productivity while having minimal impact on system resources.
From the list of the available desktops, we’ve determined that Xfce is available as the package task-xfce-desktop.
Run the following APT command to install the Xfce desktop.
Installing KDE Plasma
Plasma by KDE is a powerful desktop environment. It features ease of use, robust functionalities, and gorgeous graphics. It also comes with its own suite of applications.
To install KDE Plasma, tell APT to install the package task-kde-desktop.
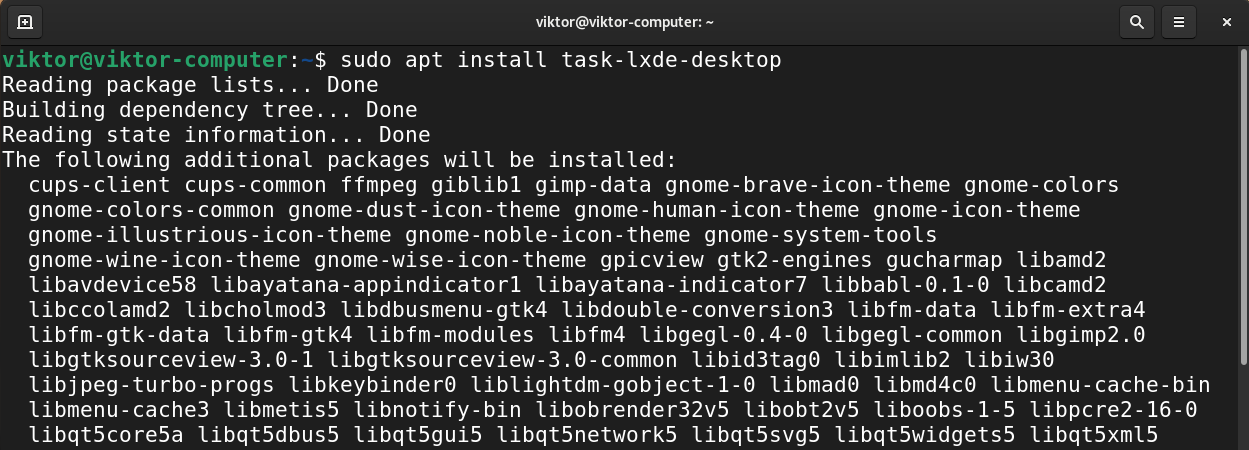
Installing LXDE
The goal of LXDE is to work on low-end machines with fewer hardware resources, for example, the older resource-constrained machines. Because of its nature, LXDE is also highly suitable for netbooks and other small computers.
To install LXDE, install the package task-lxde-desktop.
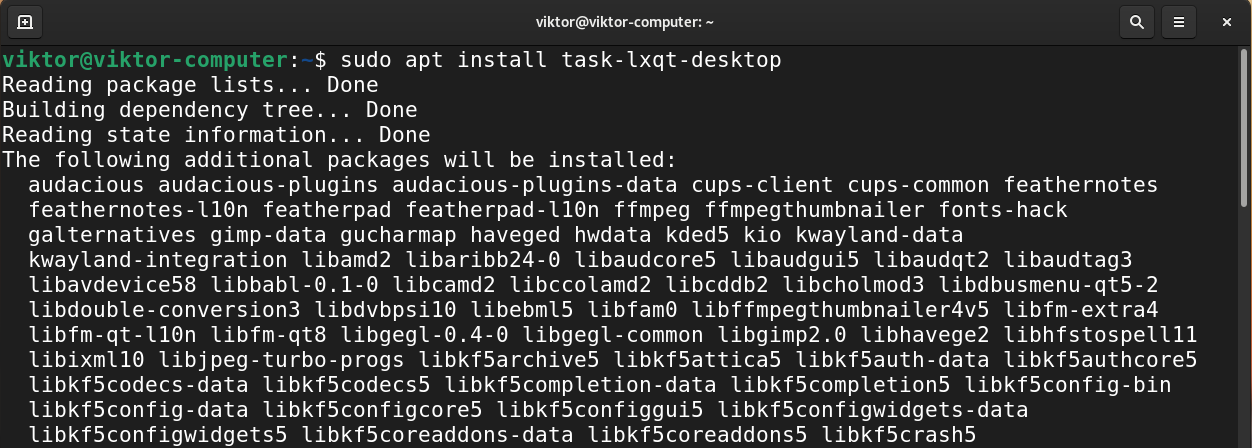
To install the LXQt desktop instead, install the package task-lxqt-desktop.
Installing MATE desktop
The MATE desktop is the continuation of GNOME 2. It offers an intuitive and attractive desktop environment incorporating the traditional metaphors for Linux/UNIX-like operating systems.
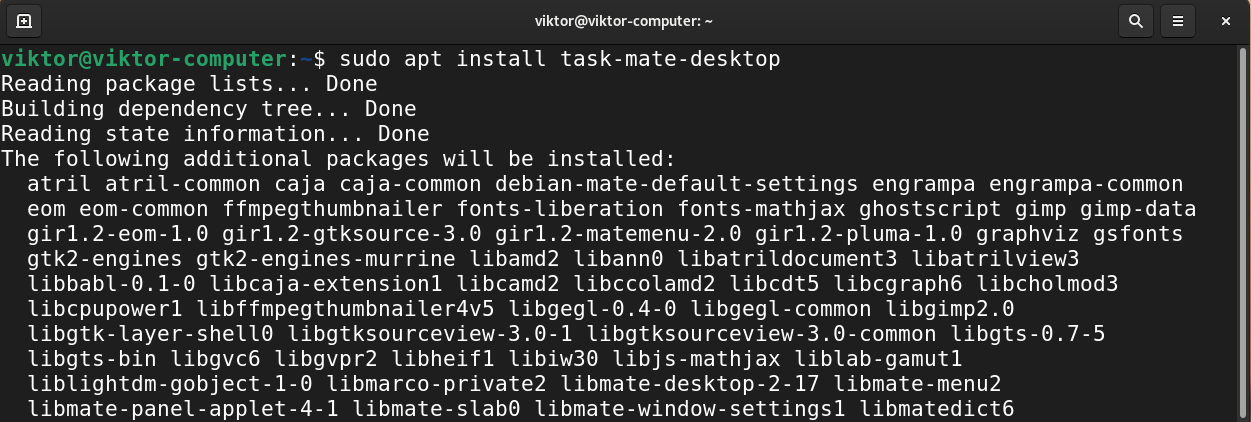
Installing the package task-mate-desktop will install the MATE desktop.
Installing Cinnamon desktop
The Cinnamon desktop is a derivative of GNOME 3. However, it keeps the traditional desktop metaphor conventions. It’s primarily developed as a part of Linux Mint. However, it’s available on many other Linux distros (including Debian).
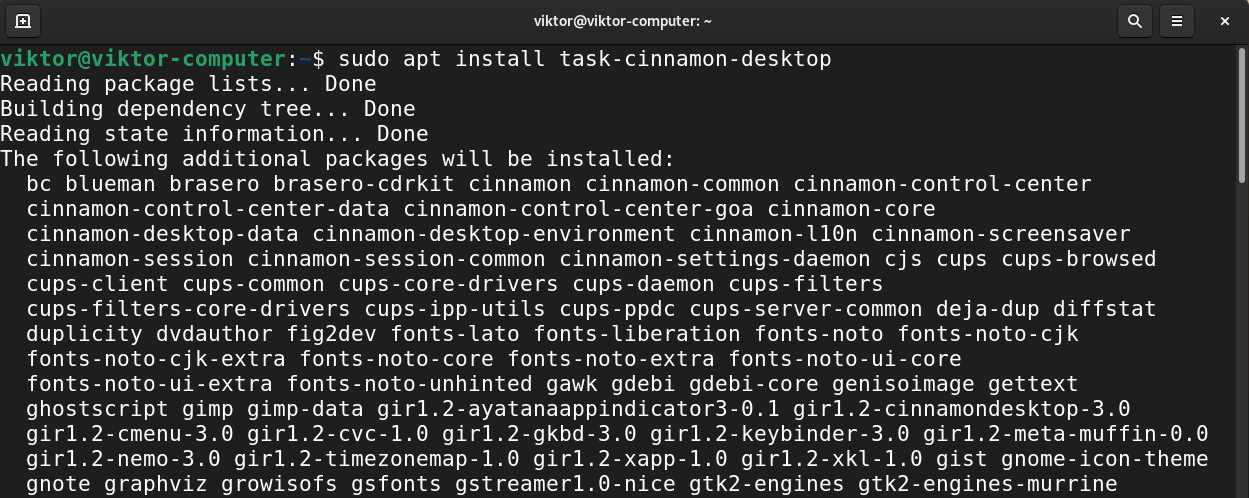
To install Cinnamon desktop, run the following command.
Installing desktop environments using tasksel
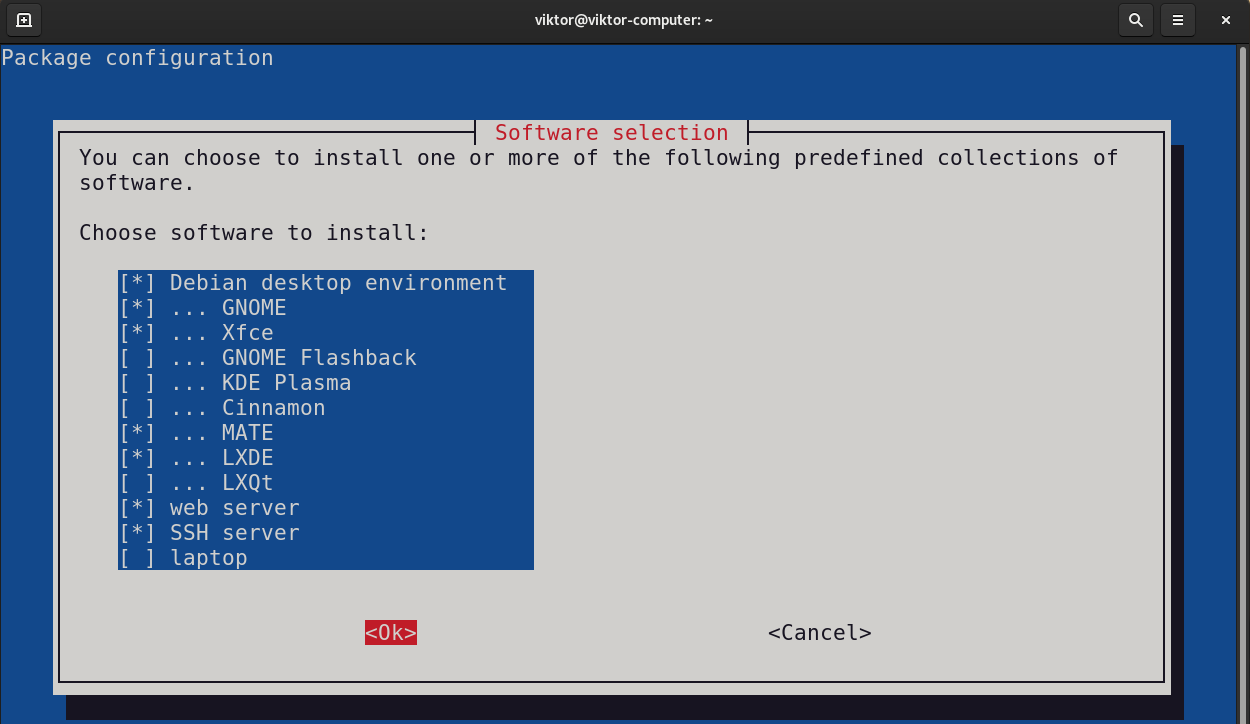
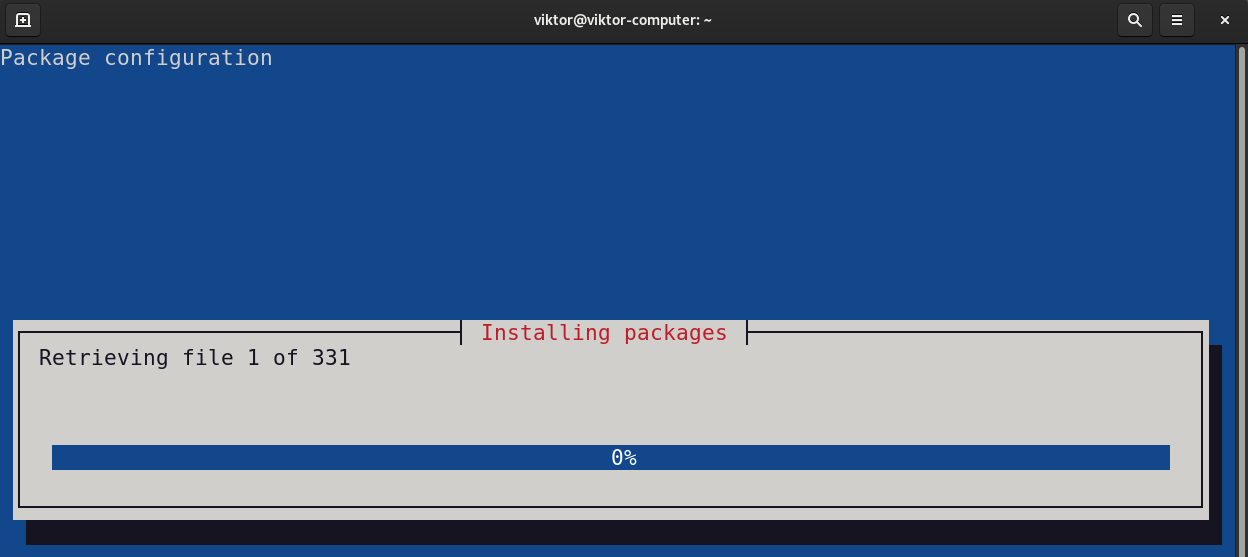
Instead of installing the desktop environments manually, we can use tasksel. It’s a UI tool for easier management of tasks (including various desktop environments).
Besides desktop environments, tasksel can also manage other component groups like SSH server, web server, etc. To select/deselect a component, press the spacebar. Select the desired desktop environment(s) you want to install, then select “Ok”.
The tool will download and install the necessary packages.
The man page of tasksel has an in-depth explanation of its functionalities.
Switching to a different desktop environment
We now have all the desired desktop environments installed. Time to switch to the new desktop environment.
Log out of the current session or restart the system. From the login screen, click the gear icon.
Select the desired desktop environment. Log in to your user account as usual.
Voila! The new desktop environment is in action! If not changed, it will be the default desktop environment for the rest of the time.
Final thoughts
Desktop environments offer an elegant way of interacting with the system. It also serves as visual customization.
We can further customize the look using themes. GTK-based desktop environments (GNOME, MATE, Xfce, etc.) can use numerous GTK themes to spice things up. Check out some of the best GTK3 themes for Linux.
About the author
Sidratul Muntaha
Student of CSE. I love Linux and playing with tech and gadgets. I use both Ubuntu and Linux Mint.