- show gateway IP address when performing ifconfig command
- 3 Answers 3
- You must log in to answer this question.
- Related
- Hot Network Questions
- Subscribe to RSS
- 💆♀️ Четыре метода проверки IP-адреса шлюза или маршрутизатора по умолчанию в Linux
- 1) Как проверить IP-адрес шлюза или маршрутизатора по умолчанию в Linux с помощью команды route?
- 2) Как проверить IP-адрес шлюза или маршрутизатора по умолчанию в Linux с помощью команды ip?
- 3) Как проверить IP-адрес шлюза или маршрутизатора по умолчанию в Linux с помощью команды netstat?
- 4) Как проверить IP-адрес шлюза или маршрутизатора по умолчанию в Linux с помощью команды routel?
- How to Find Default Gateway IP in Linux
- Other methods to find gateway IP address in Linux
- Find gateway in Linux with route command
- Show gateway in Linux with netstat command
- How can I find the default gateway of a machine?
show gateway IP address when performing ifconfig command
Currently, when using the ifconfig command, the following IP addresses are shown: own IP, broadcast and mask. Is there a way to show the related gateway IP address as well (on the same screen with all the others, not by using ‘route’ command)?
The addresses shows are parameters of the IP configuration of the interface. The gateway is a system routing parameter, not an interface parameter. It wouldn’t make sense to show it in the interface configuration.
3 Answers 3
You can with the ip command, and given that ifconfig is in the process of being deprecated by most distributions it’s now the preferred tool. An example:
$ ip route show 212.13.197.0/28 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 212.13.197.13 default via 212.13.197.1 dev eth0 Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface default 10.0.2.2 0.0.0.0 UG 1024 0 0 eth0 10.0.2.0 * 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0 No, there isn’t. According to the man page you can’t modify the output of ifconfig (except showing disabled interfaces, too).
You must log in to answer this question.
Highly active question. Earn 10 reputation (not counting the association bonus) in order to answer this question. The reputation requirement helps protect this question from spam and non-answer activity.
Related
Hot Network Questions
Subscribe to RSS
To subscribe to this RSS feed, copy and paste this URL into your RSS reader.
Site design / logo © 2023 Stack Exchange Inc; user contributions licensed under CC BY-SA . rev 2023.7.14.43533
Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds. UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
This site is not affiliated with Linus Torvalds or The Open Group in any way.
By clicking “Accept all cookies”, you agree Stack Exchange can store cookies on your device and disclose information in accordance with our Cookie Policy.
💆♀️ Четыре метода проверки IP-адреса шлюза или маршрутизатора по умолчанию в Linux
Ваш шлюз по умолчанию – это IP-адрес вашего маршрутизатора, о котором вы должны знать.
Обычно он автоматически определяется операционной системой во время установки, в противном случае вам может потребоваться изменить его.
Если ваша система не может проверить связь с самим собой, то, вероятно, это может быть проблема шлюза, и вы должны это исправить.
Это может произойти, если у вас есть несколько сетевых адаптеров или маршрутизаторов в сети.
Шлюз – это маршрутизатор, который действует как точка доступа для передачи сетевых данных из одной сети в другую.
Это можно сделать с помощью следующих четырех команд.
- Команда route: команда route используется для отображения и управления таблицей IP-маршрутизации.
- Команда ip: команда IP аналогична команде ifconfig, которая очень хорошо знакома для назначения статического IP-адреса, маршрута и шлюза по умолчанию и т. д.
- Команда netstat: netstat («статистика сети») – это инструмент командной строки, который отображает информацию, связанную с сетевыми соединениями (как входящими, так и исходящими), такими как таблицы маршрутизации, маскарадные соединения, многоадресное членство и номера сетевых интерфейсов.
- Команда routel: команда routel используется для вывода списка маршрутов с хорошим выходным форматом.
1) Как проверить IP-адрес шлюза или маршрутизатора по умолчанию в Linux с помощью команды route?
Команда route используется для отображения и управления таблицей IP-маршрутизации.
Его основное назначение – установка статических маршрутов к конкретным хостам или сетям через интерфейс после настройки интерфейса.
Когда используются параметры добавления или удаления, маршрут изменяет таблицы маршрутизации.
Без этих параметров в маршруте отображается текущее содержимое таблиц маршрутизации.
# route или # route -n Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface default www.routerlogin 0.0.0.0 UG 600 0 0 wlp8s0 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 600 0 0 wlp8s0
2) Как проверить IP-адрес шлюза или маршрутизатора по умолчанию в Linux с помощью команды ip?
Команда IP аналогична ifconfig, которая очень хорошо знакома для назначения статического IP-адреса, маршрута и шлюза по умолчанию и т.д.
Команда ifconfig устарела из-за отсутствия обслуживания в течение многих лет, хотя она по-прежнему доступна в большинстве дистрибутивов Linux.
Команда ifconfig была заменена командой IP, которая является очень мощной и выполняет несколько задач сетевого администрирования одной командой.
Командная утилита IP идет в комплекте с пакетом iproute2.
По умолчанию утилита iproute2 предустановила все основные дистрибутивы Linux.
Если нет, вы можете установить его, указав iproute2 на своем терминале с помощью менеджера пакетов.
# ip r или # ip route или # ip route show default via 192.168.1.1 dev wlp8s0 proto dhcp metric 600 192.168.1.0/24 dev wlp8s0 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.1.6 metric 600
3) Как проверить IP-адрес шлюза или маршрутизатора по умолчанию в Linux с помощью команды netstat?
netstat расшифровывается как Network Statistics.
Это инструмент командной строки, который отображает информацию о сетевых подключениях (как входящих, так и исходящих), таких как таблицы маршрутизации, маскарадные соединения, многоадресное членство и имена сетевых интерфейсов.
В нем перечислены все соединения сокетов tcp, udp и сокетов unix.
Он используется для диагностики сетевых проблем в сети и определения объема трафика в сети в качестве измерения производительности.
# netstat -r Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags MSS Window irtt Iface default www.routerlogin 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 wlp8s0 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 wlp8s0
4) Как проверить IP-адрес шлюза или маршрутизатора по умолчанию в Linux с помощью команды routel?
Он используется для вывода списка маршрутов с красивым форматом вывода.
Эта программа представляет собой набор вспомогательных скриптов, которые вы можете использовать вместо необработанных команд iproute2.
Скрипт Routel выведет список маршрутов в формате, который некоторые могут посчитать более понятным, чем эквивалент списка маршрутов ip.
Скрипт routef не принимает никаких аргументов и просто сбрасывает таблицу маршрутизации. Осторожно! Это означает удаление всех маршрутов, которые сделают вашу сеть непригодной для использования!
# routel target gateway source proto scope dev tbl default 192.168.1.1 dhcp wlp8s0 192.168.1.0/ 24 192.168.1.6 kernel link wlp8s0 127.0.0.0 broadcast 127.0.0.1 kernel link lo local 127.0.0.0/ 8 local 127.0.0.1 kernel host lo local 127.0.0.1 local 127.0.0.1 kernel host lo local 127.255.255.255 broadcast 127.0.0.1 kernel link lo local 192.168.1.0 broadcast 192.168.1.6 kernel link wlp8s0 local 192.168.1.6 local 192.168.1.6 kernel host wlp8s0 local 192.168.1.255 broadcast 192.168.1.6 kernel link wlp8s0 local ::1 kernel lo fe80::/ 64 kernel wlp8s0 ::1 local kernel lo local fe80::ad00:2f7e:d882:5add local kernel wlp8s0 local ff00::/ 8 wlp8s0 local
Если вы хотите вывести только шлюз по умолчанию, используйте следующий формат.
# routel | grep default default 192.168.1.1 dhcp wlp8s0
How to Find Default Gateway IP in Linux
This quick Linux tip shows various methods to find gateway IP address of your router in Linux command line.
In an earlier article, I told you about finding IP address in Linux command line. In this quick tip, I’ll show you how to find the default gateway IP in Linux command line.
A gateway is works as the entrance or a door between two networks. A router is an example of the gateway. All your traffic goes to the router and then to the rest of the internet.
Sometimes, you’ll need to know the IP address of your router. The gateway IP is your router’s IP address in the normal setup.
I am going to use the IP command to show the gateway IP in Linux.
Open a terminal and use the following command:
You should see an output like this:
default via 192.168.0.1 dev wlp58s0 proto dhcp metric 600 169.254.0.0/16 dev wlp58s0 scope link metric 1000 192.168.0.0/24 dev wlp58s0 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.0.106 metric 600Focus on the line that starts with default. This will give the default gateway IP.
Alternatively and conveniently, you can use the above command in combination with the grep command:
This will just give the default gateway IP in the output:
default via 192.168.0.1 dev wlp1s0 proto dhcp metric 600And as you can see, 192.168.0.1 is the default gateway IP in my case.
Other methods to find gateway IP address in Linux
The IP command in Linux provides most of your basic networking needs. But as you have already noticed by now, there are multiple ways to do a certain things in Linux.
To know the gateway IP, you can use other networking command line tools as well. Let me show them to you.
Find gateway in Linux with route command
You can use the -n option with the route command to display the routing table with the IP addresses.
The sample output should be like this:
Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface 0.0.0.0 192.168.0.1 0.0.0.0 UG 600 0 0 wlp58s0 169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 1000 0 0 wlp58s0 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 600 0 0 wlp58s0Notice the U and G flags? U means the route is ‘up’ and the G indicates that it is gateway.
Show gateway in Linux with netstat command
To display the gateway information, you can use the netstat command and display the routing table that consists the gateway as well.
Output should be identical to what you saw with the route command:
Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags MSS Window irtt Iface 0.0.0.0 192.168.0.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 wlp58s0 169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 0 0 0 wlp58s0 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 wlp58s0You can identify the gateway with the G flag.
I hope this quick Linux tip helped you in finding the default gateway IP in Linux command line. Add this website to your feed reader for such regular Linux tips and tutorials.
How can I find the default gateway of a machine?
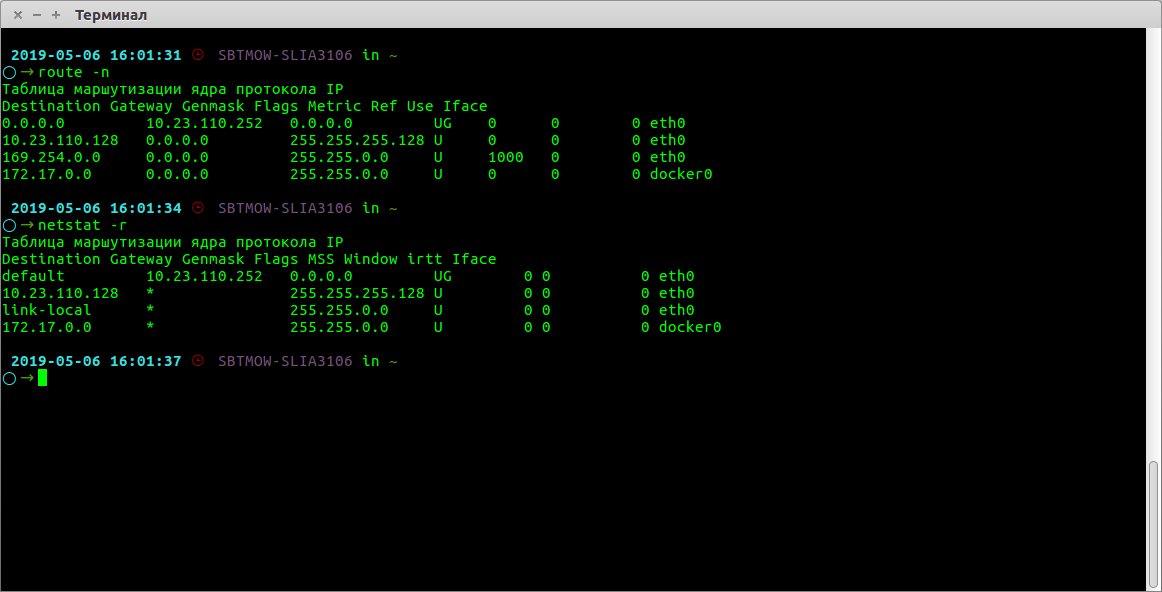
I’m trying to find the default Gateway of a machine, but I see multiple interfaces. Also, when I find my IP address from the below website, it gives me a different IP address. I thought the default Gateway and external IP would be the same? Correct me if I’m wrong.
https://www.privateinternetaccess.com/pages/whats-my-ip/ Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface 0.0.0.0 10.0.2.2 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0 10.0.2.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0 10.2.0.0 192.168.255.9 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 tun0 192.168.33.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth1 192.168.255.1 192.168.255.9 255.255.255.255 UGH 0 0 0 tun0 192.168.255.5 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 UH 0 0 0 tun4 192.168.255.5 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 UH 0 0 0 tun6 192.168.255.5 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 UH 0 0 0 tun5 192.168.255.5 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 UH 0 0 0 tun2 192.168.255.9 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 UH 0 0 0 tun0 192.168.255.13 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 UH 0 0 0 tun3 192.168.255.13 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 UH 0 0 0 tun1 $ netstat -r Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags MSS Window irtt Iface default 10.0.2.2 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0 10.0.2.0 * 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0 10.2.0.0 192.168.255.5 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 tun6 192.168.33.0 * 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth1 192.168.255.1 192.168.255.5 255.255.255.255 UGH 0 0 0 tun6 192.168.255.5 * 255.255.255.255 UH 0 0 0 tun6 192.168.255.5 * 255.255.255.255 UH 0 0 0 tun3 192.168.255.5 * 255.255.255.255 UH 0 0 0 tun2 192.168.255.5 * 255.255.255.255 UH 0 0 0 tun4 192.168.255.9 * 255.255.255.255 UH 0 0 0 tun5 192.168.255.13 * 255.255.255.255 UH 0 0 0 tun0 192.168.255.13 * 255.255.255.255 UH 0 0 0 tun1