- How to Use the id Command in Linux: 5 Useful Examples
- id command in Linux
- Examples of id command
- Real vs Effective user and group ID?
- 1. Print the UID and GID of a certain user
- 2. Print only the UID of a user
- 3. Print only the GID of a user
- 4. Print the IDs of all other groups the user belongs to
- 5. Print names instead of the numeric IDs
- Bonus Tip: Print the real IDs
- Как узнать id пользователя Linux
- Как узнать id пользователя в Linux
- Выводы
- 5 Ways to find a Linux User ID (UID) in Ubuntu 20.04
- 5 Ways of Finding the UID in Ubuntu Linux
- Method # 1: Using the “id” Command
- Method # 2: Using the “id” Command with Username
- Method # 3: Using the “getent” Command
- Method # 4: Using the “lslogins” Utility
- Method # 5: Using the “grep” Command
- Conclusion
- Search
- About This Site
- Latest Tutorials
How to Use the id Command in Linux: 5 Useful Examples
Every user in Linux has a unique, numeric user ID and a default group with a unique numeric group ID. The id command prints this information.
The id command in Linux is used for displaying the real and effective user ID and group ID of a user.
In this tutorial, I’ll show you how to use id command in Linux with some of the most common and useful examples.
id command in Linux
This is the syntax for the id command:
If you don’t provide a username, the command displays the details about the currently logged-in user.
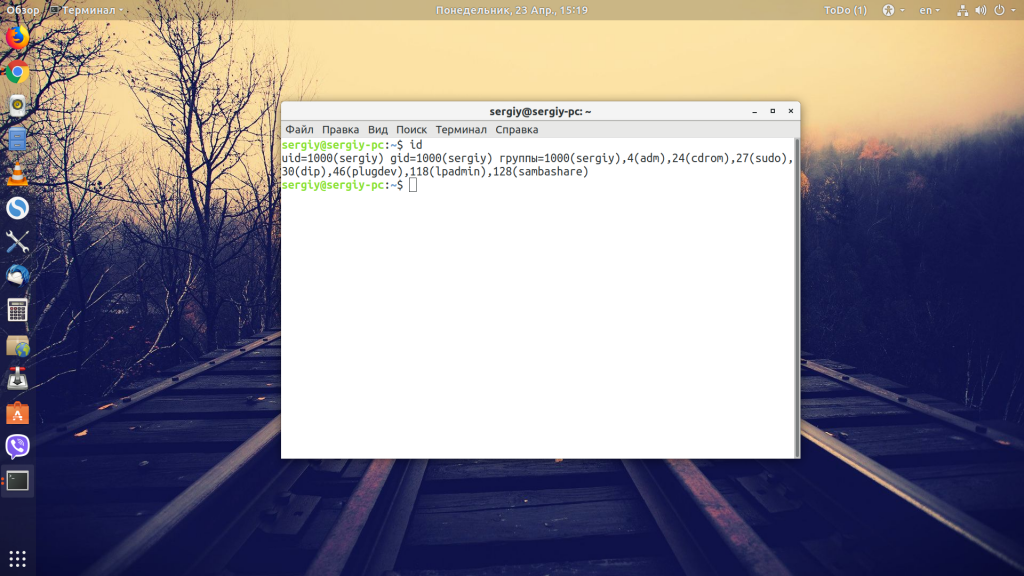
Here’s the output it displayed for me in Ubuntu Linux.
[email protected]:~$ id uid=1000(abhishek) gid=1000(abhishek) groups=1000(abhishek),4(adm),24(cdrom),27(sudo),30(dip),46(plugdev),119(lpadmin),130(lxd),131(sambashare)In the above output, user abhishek has uid 1000 and gid 1000. That’s the primary group the user abhishek belongs to by default.
Apart from that, the user abhishek is also member of certain other groups and those groups have also been displayed in the output.
Examples of id command
Here are the most common options for the id command:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| -u | Print the effective user id |
| -g | Print the effective group id |
| -G | Print the IDs of all groups user belongs to |
| -n | Print names instead of IDs (must be combined with -u, -g or -G) |
| -r | Print real ID instead of effective IDs (must be combined with -u, -g or -G) |
Real vs Effective user and group ID?
This could be confusing for you. When a user is created, it is given a username, a user ID (uid), a default group and the id of that default group is the gid for that user. This is the ‘real’ user and group ID.
Since in Linux, processes can be run as other user and group, there is also a second set of IDs called effective IDs.
Most of the time the real and effective UIDs and GIDs are the same. But there are situations when a regular user has to modify a privileged file. This is where the effective ID concept is used. Most common example is the using passwd command to change the password which modifies the /etc/passwd file owned by root.
I cannot go in detail here but I recommend reading about it here. You should also read about SUID, GUID and sticky bit permissions in Linux.
1. Print the UID and GID of a certain user
To print the uid and gid and all the other group IDs of a user, you just have to specify the username:
You can list all the users in your Linux system to get the desired user name.
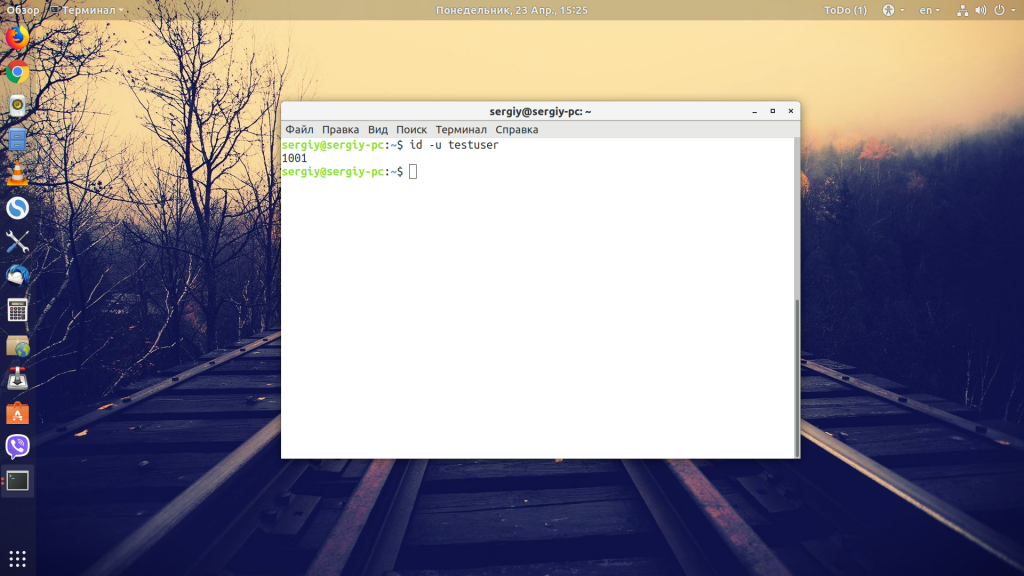
2. Print only the UID of a user
You can use the -u option to print the UID in Linux. As mentioned previously, if you omit the username, it displays the information about the logged-in user.
Keep in mind that it displays only the UID, the numeric value, not the name.
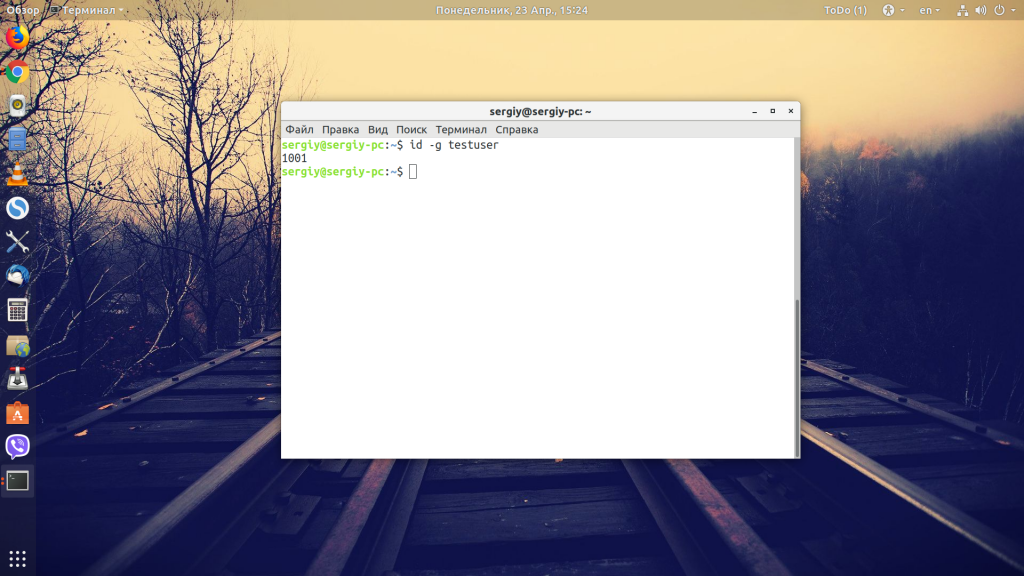
3. Print only the GID of a user
Similarly, you can use the option -g to print the GID of a user. When I say GID, it’s the numeric ID of the default group the user belongs to.
Again, it will only display the numeric ID of the group.
4. Print the IDs of all other groups the user belongs to
A user can belong to several groups. This is basic feature of the Linux filesystem. You can use the usermod command and add it to sudo group to give it root privileges.
You can use the -G option to display the IDs of all the groups the user belongs to.
This too displays the ID only.
[email protected]:~$ id -G abhishek 1000 4 24 27 30 46 119 130 1315. Print names instead of the numeric IDs
The numeric IDs only can be confusing. If you want the names, you can combine the -n option with -u , -g or -G to display the names.
For example, if you want to display all the groups a user belongs to, you can use it like this:
If I use the previous example with option -n here’s what it shows:
[email protected]:~$ id -nG abhishek abhishek adm cdrom sudo dip plugdev lpadmin lxd sambashareBonus Tip: Print the real IDs
All the above examples display the effective IDs. Almost all the time it will be the real ID.
However, if you want to make sure to get the real ID, you can combine option -r with -u , -g or -G .
Alright! I think you know enough about the id command now. If you have questions or suggestions, feel free to leave a comment.
Как узнать id пользователя Linux
Иногда возникает необходимость узнать id пользователя Linux. Это может понадобиться, если вы хотите вручную добавить группу для пользователя или вам нужно выполнить другие операции с файлами /etc/passwd или /etc/shadow.
В этой небольшой заметке мы поговорим о том, как посмотреть id пользователя с помощью различных команд в Linux.
Как узнать id пользователя в Linux
Самый простой способ посмотреть идентификатор текущего пользователя — использовать команду id, она выводит не только сам UID, но и идентификатор группы пользователя, а также основные группы этого пользователя:
Первым выводится именно id пользовтеля. Если вам нужно узнать информацию о другом пользователе, вы можете передать его имя в параметры утилиты:
Когда необходимо вывести только id пользователя:
Если вам надо узнать только id группы определенного пользователя, то используйте опцию -g:
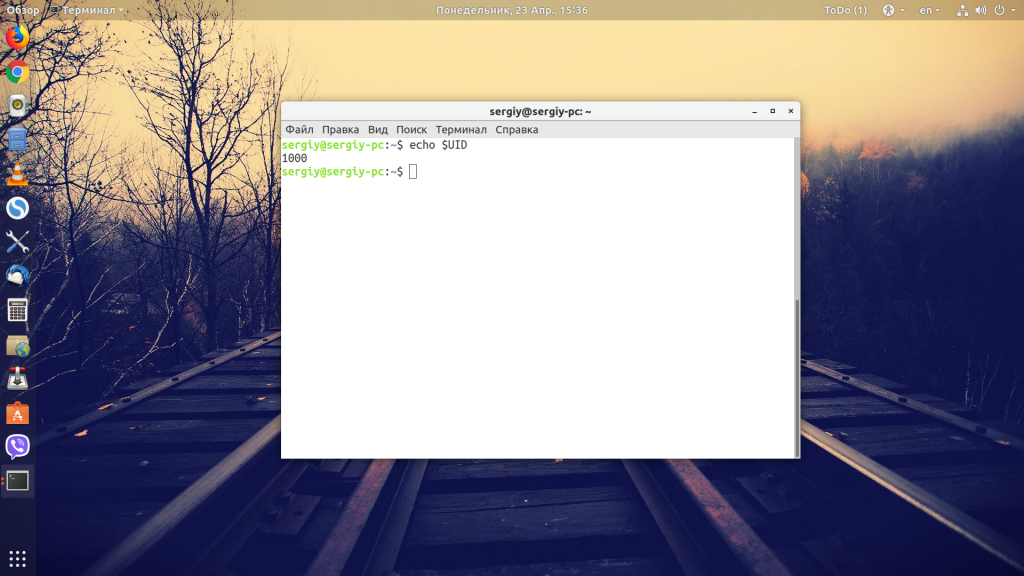
Есть ещё несколько способов посмотреть id. Например, для текущего пользователя его можно найти в переменной окружения UID:
Ещё один вариант — утилита getent:
getent passwd имя_пользователя
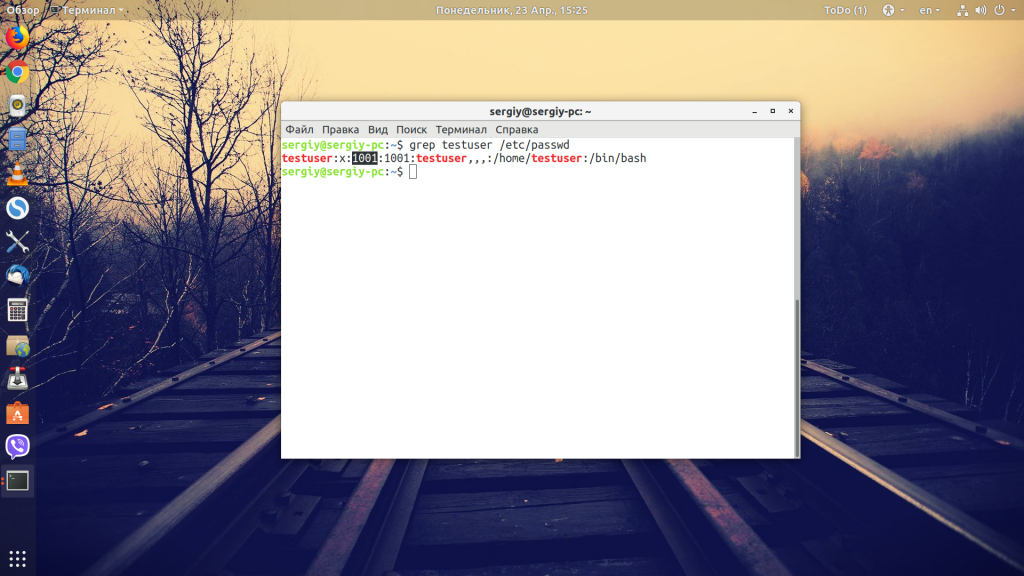
Или смотрим содержимое файла /etc/passwd с помощью команды grep:
grep имя_пользователя /etc/passwd
Здесь первый цифровой параметр — это сам id, а второй, который расположен за двоеточием, — это GID.
Выводы
В этой небольшой статье мы рассмотрели, как узнать id пользователя Linux. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!

Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
5 Ways to find a Linux User ID (UID) in Ubuntu 20.04
The User ID or UID in Linux is a unique entity through which a user is identified on a system. Every user on a Linux system has a dedicated UID. There are several ways of finding the UID of a Linux user and we are going to share with you all those ways for an Ubuntu or Linux Mint system.
5 Ways of Finding the UID in Ubuntu Linux
There are five main methods for finding the UID in Linux Mint 20 which are as follows:
Method # 1: Using the “id” Command
For using the “id” command to find the UID of the currently logged in user in Ubuntu, you have to execute it in the following manner:
The UID of our currently logged in user is highlighted in the image shown below:
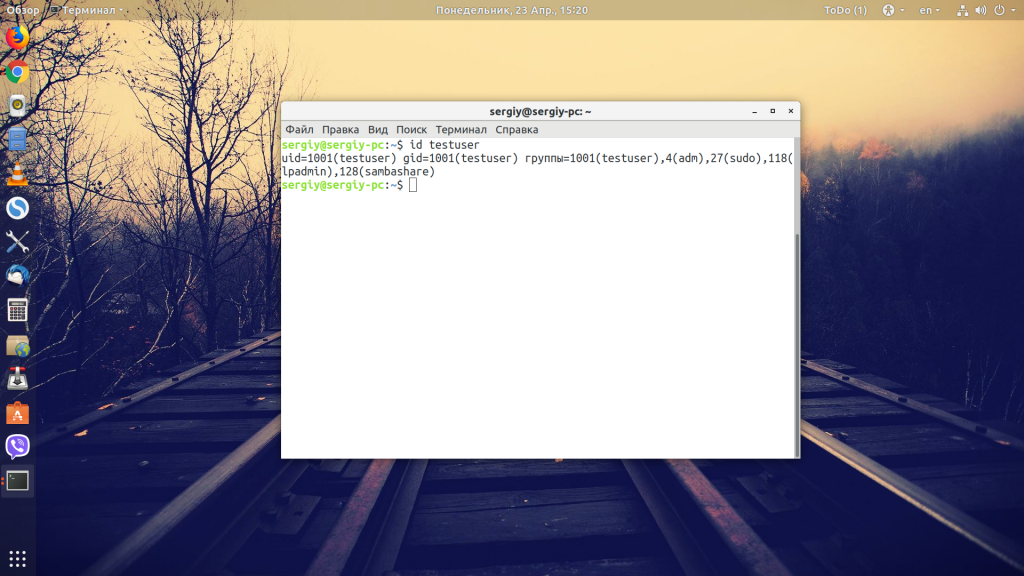
Method # 2: Using the “id” Command with Username
The “id” command can also be paired up with the username of your desired user to get that user’s UID in the following manner:
Replace username with the name of the user whose UID you want to find out.
The UID of our specified user is shown in the image below:
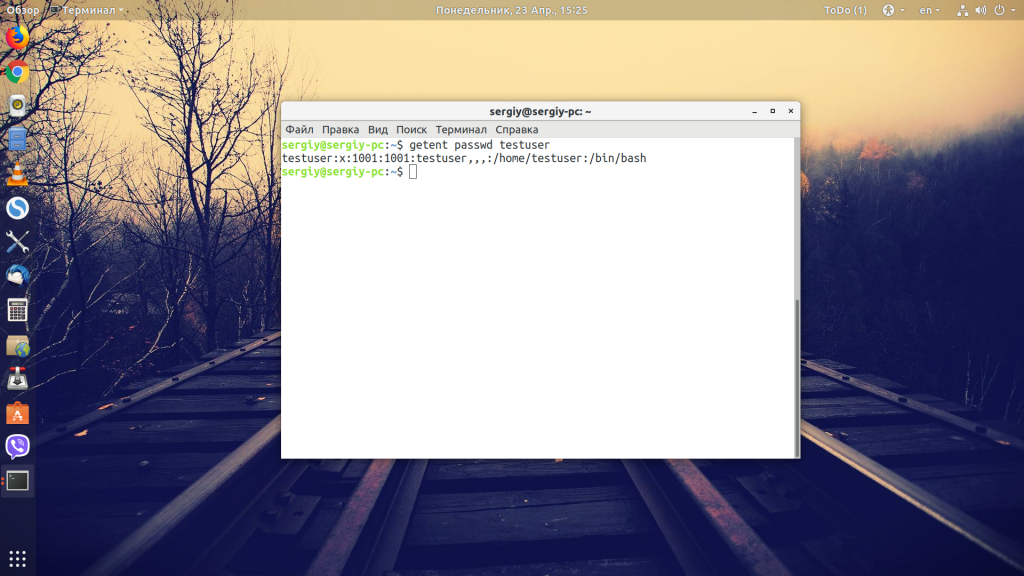
Method # 3: Using the “getent” Command
To use the “getent” command for finding the UID in Linux Mint 20, you will have to execute it in the following manner:
Replace username with the name of the user whose UID you want to find out.
The UID of our specified user is shown in the image below:
Method # 4: Using the “lslogins” Utility
For using the “lslogins” utility to find the UID in Linux Mint 20, you will have to execute the following command:
This utility will present you with a list of all of your system users along with their respective UIDs as shown in the image below:
Method # 5: Using the “grep” Command
The “grep” command can also be used for finding the UID of the specified user in Ubuntu in the following manner:
Replace username with the name of the user whose UID you want to find out.
The UID of our specified user is shown in the image below:
Conclusion
By picking out any method of your choice from this tutorial, you will be able to find the UID of any user you want while using Ubuntu 20.04. All the commands and utilities that we have used for this tutorial are built-in. Therefore, you will not have to waste your precious time in installing anything while following this tutorial.
Search
About This Site
Vitux.com aims to become a Linux compendium with lots of unique and up to date tutorials.