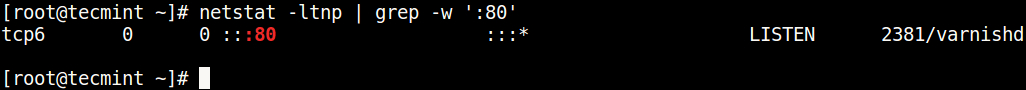- Determine the process pid listening on a certain port
- 8 Answers 8
- Проверка занятости порта сервисом в Linux
- Oct 4, 2018 06:09 · 637 words · 3 minute read lsof netstat fuser tips
- 3 Ways to Find Out Which Process Listening on a Particular Port
- 1. Using netstat Command
- 2. Using lsof Command
- 3. Using fuser Command
Determine the process pid listening on a certain port
As the title says, I’m running multiple game servers, and every of them has the same name but different PID and the port number. I would like to match the PID of the server which is listening on certain port, and then I would like to kill this process. I need that in order to complete my bash script. Is that even possible? Because it didn’t find yet any solutions on the web.
8 Answers 8
Short version which you can pass to kill command:
This also includes processes that are connected on that port. lsof -i4TCP:80 -sTCP:LISTEN -t is probably what you want, instead.
Exactly what I was looking for. I wanted to kill a process by searching for the port it is running at.
@Nevir what do you mean by » also includes processes that are connected on that port»? Can you please explain?
The -p flag of netstat gives you PID of the process:
*use sudo if showing — instead of PID
Edit: The command that is needed to get PIDs of socket users in FreeBSD is sockstat . As we worked out during the discussion with @Cyclone, the line that does the job is:
sockstat -4 -l | grep :80 | awk '' | head -1 netstat: 80: unknown or uninstrumented protocol used the 80 (nginx) port for testing purpoes. Not worked.
netstat -p -l | grep $PORT and lsof -i :$PORT solutions are good but I prefer fuser $PORT/tcp extension syntax to POSIX (which work for coreutils ) as with pipe:
it prints pure pid so you can drop sed magic out.
One thing that makes fuser my lover tools is ability to send signal to that process directly (this syntax is also extension to POSIX):
$ fuser -k $port/tcp # with SIGKILL $ fuser -k -15 $port/tcp # with SIGTERM $ fuser -k -TERM $port/tcp # with SIGTERM Проверка занятости порта сервисом в Linux
Oct 4, 2018 06:09 · 637 words · 3 minute read lsof netstat fuser tips
Однажды вам обязательно понадобится проверить используемый порт определенного сервиса (или наоборот, найти сервисы, слушающие конкретный порт) — в Linux существует несколько утилит командной строки, которые могут с этим помочь. Давайте разберемся!
Первым делом на ум приходит утилита netstat , с помощью которой можно проверить сетевые соединения, статистику сетевых интерфейсов, таблицу маршрутизации и т. д.
Устанавливается данная утилита в разных дистрибутивах по-разному, например, для RedHat и CentOS:
sudo yum install net-tools sudo apt-get install net-tools Для вывода детальной информации о всех TCP и UDP ендпоинтах можно воспользоваться следующей командой:
Вывод будет примерно следующим:
Active Internet connections (only servers) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name tcp 0 0 127.0.0.53:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1323/systemd-resolv tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1661/sshd tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:17123 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1753/python tcp6 0 0 . 31341 . * LISTEN 30068/java tcp6 0 0 . 22222 . * LISTEN 30068/java tcp6 0 0 . 80 . * LISTEN 30068/java tcp6 0 0 . 10769 . * LISTEN 126755/docker-proxy tcp6 0 0 . 10770 . * LISTEN 129459/docker-proxy tcp6 0 0 . 10771 . * LISTEN 129540/docker-proxy tcp6 0 0 . 10772 . * LISTEN 130172/docker-proxy tcp6 0 0 . 10773 . * LISTEN 130187/docker-proxy tcp6 0 0 . 10774 . * LISTEN 130545/docker-proxy tcp6 0 0 . 22 . * LISTEN 1661/sshd tcp6 0 0 . 10775 . * LISTEN 7406/docker-proxy - -p — вывод ID процесса и его имени;
- -n — вывод адресов;
- -l — вывод сокетов;
- -t — вывод TCP соединений;
- -u — вывод UDP соединений.
Найти сервис, запущенный на определенном порту можно так:
Аналогично можно найти на каком порту запущен определенный сервис:
netstat -pnltu | grep -i "sshd" Также для наших целей подойдет утилита командной строки fuser . По умолчанию она не установлена в большинстве операционных систем, чтобы установить ее в Centos/RedHat делаем так:
Например, чтобы найти идентификаторы процессов (PIDs), запущенных на 80-м порту, выполняем команду:
Результат выполнения будет примерно следующим:
Далее можем найти имя процесса по его идентификатору (PID):
Еще один способ — использование утилиты lsof . Установка ее в RedHat/CentOS выглядит так:
Вывод всех активных TCP и UPD соединений:
Результатом будет примерно следующее:
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME systemd-r 1323 systemd-resolve 12u IPv4 20197 0t0 UDP 127.0.0.53:domain systemd-r 1323 systemd-resolve 13u IPv4 20198 0t0 TCP 127.0.0.53:domain (LISTEN) sshd 1661 root 3u IPv4 29741 0t0 TCP *:ssh (LISTEN) sshd 1661 root 4u IPv6 29743 0t0 TCP *:ssh (LISTEN) python 1754 dd-agent 4u IPv6 39499 0t0 UDP localhost.localdomain:8125 docker-pr 7406 root 4u IPv6 287933991 0t0 TCP *:10775 (LISTEN) docker-pr 7459 root 4u IPv6 287906596 0t0 TCP *:10776 (LISTEN) docker-pr 7792 root 4u IPv6 287937795 0t0 TCP *:10777 (LISTEN) docker-pr 8435 root 4u IPv6 287955267 0t0 TCP *:10778 (LISTEN) docker-pr 8447 root 4u IPv6 287915222 0t0 TCP *:10779 (LISTEN) docker-pr 9060 root 4u IPv6 287891442 0t0 TCP *:10780 (LISTEN) docker-pr 9429 root 4u IPv6 287957044 0t0 TCP *:10781 (LISTEN) docker-pr 9463 root 4u IPv6 287921075 0t0 TCP *:10782 (LISTEN) ntpd 10594 ntp 16u IPv6 35365570 0t0 UDP *:ntp Проверить использование конкретного порта можно так:
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME sshd 1661 root 3u IPv4 29741 0t0 TCP *:ssh (LISTEN) sshd 1661 root 4u IPv6 29743 0t0 TCP *:ssh (LISTEN) Напоследок можно также воспользоваться утилитой whatportis . Ее установка в RedHat/Centos требует чуть больше действий:
yum install python34-setuptools В Debian/Ubuntu все гораздо проще:
В общем виде использование утилиты выглядит так:
whatportis [номер_порта | имя_сервиса] Если вам неизвестно точное имя сервиса, можно воспользоваться опцией —like , например:
Также доступен вывод информации в json-формате:
3 Ways to Find Out Which Process Listening on a Particular Port
A port is a logical entity that represents an endpoint of communication and is associated with a given process or service in an operating system. In previous articles, we explained how to find out the list of all open ports in Linux and how to check if remote ports are reachable using the Netcat command.
In this short guide, we will show different ways of finding the process/service listening on a particular port in Linux.
1. Using netstat Command
netstat (network statistics) command is used to display information concerning network connections, routing tables, interface stats, and beyond. It is available on all Unix-like operating systems including Linux and also on Windows OS.
In case you do not have it installed by default, use the following command to install it.
$ sudo apt-get install net-tools [On Debian/Ubuntu & Mint] $ sudo dnf install net-tools [On CentOS/RHEL/Fedora and Rocky Linux/AlmaLinux] $ pacman -S netstat-nat [On Arch Linux] $ emerge sys-apps/net-tools [On Gentoo] $ sudo dnf install net-tools [On Fedora] $ sudo zypper install net-tools [On openSUSE]
Once installed, you can use it with the grep command to find the process or service listening on a particular port in Linux as follows (specify the port).
In the above command, the flags.
- l – tells netstat to only show listening sockets.
- t – tells it to display tcp connections.
- n – instructs it to show numerical addresses.
- p – enables showing of the process ID and the process name.
- grep -w – shows matching of exact string (:80).
Note: The netstat command is deprecated and replaced by the modern ss command in Linux.
2. Using lsof Command
lsof command (List Open Files) is used to list all open files on a Linux system.
To install it on your system, type the command below.
$ sudo apt-get install lsof [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] $ sudo yum install lsof [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky Linux/AlmaLinux] $ sudo emerge -a sys-apps/lsof [On Gentoo Linux] $ sudo pacman -S lsof [On Arch Linux] $ sudo zypper install lsof [On OpenSUSE]
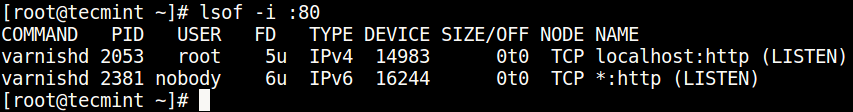
To find the process/service listening on a particular port, type (specify the port).
3. Using fuser Command
fuser command shows the PIDs of processes using the specified files or file systems in Linux.
You can install it as follows:
$ sudo apt-get install psmisc [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] $ sudo yum install psmisc [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky Linux/AlmaLinux] $ sudo emerge -a sys-apps/psmisc [On Gentoo Linux] $ sudo pacman -S psmisc [On Arch Linux] $ sudo zypper install psmisc [On OpenSUSE]
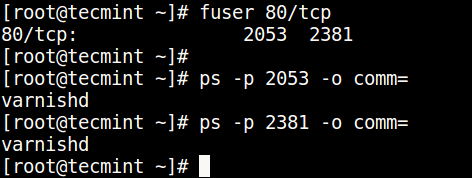
You can find the process/service listening on a particular port by running the command below (specify the port).
Then find the process name using PID number with the ps command like so.
$ ps -p 2053 -o comm= $ ps -p 2381 -o comm=
You can also check out these useful guides about processes in Linux.
You might also like:
That’s all! Do you know of any other ways of finding the process/service listening on a particular port in Linux, let us know via the comment form below.