- Fedora Server remote interactive installation guide
- 1. How it works
- 2. Prerequisites
- Установка и конфигурация VNC-сервера в Fedora
- Установка VNC-сервера Tiger VNC
- Конфигурация VNC-сервера
- Добавляем в файрволл
- Настройка пользователя
- How to Configure VNC Server in Fedora Linux?
- What we will cover
- Prerequisites
- Terms to Know
- Installing TigerVNC on Fedora 32 XFCE
- Starting VNC Server
- Stopping a VNC Session
- Conclusion:
- About the author
- Ali Imran Nagori
Fedora Server remote interactive installation guide
With this method, the server is usually residing in a remote location, such as a data center. It boots from a prepared installation media into the Anaconda installation program configured to start and use a «virtual network console» (VNC) server instead of a local physical console. The system administrator connects using a VNC viewer on a local desktop to the server and runs through the Anaconda graphical installer. This method is best suited for servers without any or just cumbersome available direct console access.
1. How it works
Anaconda provides 2 ways to connect Fedora Sever and a remote desktop.
In this mode, Anaconda starts the installation and waits for an incoming connection from a VNC viewer before proceeding. While waiting for an incoming connection, the console displays the system’s IP address and the port on which the installer expects the connection, if available; this implies that you need at least a serial console to connect using this mode, but you can work around this limitation if you know the default VNC port and the system’s IP address.
In this mode, the sysadmin first starts a VNC viewer on a desktop system in listening mode. The VNC viewer waits for an incoming connection on a specified port. After that, Anaconda starts and initiates a connection to the VNC Viewer. Again, a boot option or a kickstart command configures host name/IP address and port number. When the installation begins, the installation program establishes a connection with the listening VNC viewer using the specified host name/IP address and port number. Connect mode is always required if the server’s network does not allow any incoming connection. But it also may require additional preparation, because the viewer system must be able to accept incoming connections on the specified port, which usually requires changing firewall settings.
After a successful connection, both methods work the same.
2. Prerequisites
You need one of the installation media variants ready to use as described in Server Installation
Accessible Firewall Configuration
Depending on which of the previous mentioned VNC variants you are to use, Firewalls on the desktop and any firewall along the connection path (the server to be installed doesn’t have an active firewall) must allow either a connection originating on the desktop (which should at least in case of public accessible servers work anyway) or a connection originating on the server (what is usually blocked and requires additional configuration and may induce security related issues).
Performing a VNC installation requires a VNC viewer running on your workstation or another terminal computer. VNC viewers are available in the repositories of most Linux distributions; free VNC viewers are also available for other operating systems, such as Windows. On Linux systems, use your package manager to search for a viewer for your distribution.
The following VNC viewers are available in Fedora:
- TigerVNC — A basic viewer independent of your desktop environment. Installed as the tigervnc package.
- Vinagre — A viewer for the GNOME desktop environment. Installed as the vinagre package.
- KRDC — A viewer integrated with the KDE desktop environment. Installed as the kdenetwork-krdc package.
Установка и конфигурация VNC-сервера в Fedora
Установка и настройка VNC-сервера для удаленного подключения и управления.
Установка VNC-сервера Tiger VNC
yum -y install tigervnc-server
Это установит VNC-сервер, теперь приступим к его конфигурации.
Конфигурация VNC-сервера
Теперь нам необходимо скопировать файл конфигурации VNC-сервера, если нам нужно настроить смещение порта. По умолчанию VNC-сервер использует порт 5900, но мы можем использовать смещения порта, для того чтобы настроить сервер на суб-порте. Например при использовании 5 порта, сервер будет доступен по порту 5905.
Когда настроено порт-смещение, подключение осуществляется по связке адрес порт — IP:PORT Eg: 10.0.0.1:5905
cp /lib/systemd/system/[email protected] /etc/systemd/system/vncserver@:5.service
vi /etc/systemd/system/vncserver@\:5.service
[Unit]
Description=Remote desktop service (VNC)
After=syslog.target network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
# Clean any existing files in /tmp/.X11-unix environment
ExecStartPre=/bin/sh -c ‘/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :’
ExecStart=/sbin/runuser -l -c «/usr/bin/vncserver %i»
PIDFile=/home//.vnc/%H%i.pid
ExecStop=/bin/sh -c ‘/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :’
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Изменяем на пользователя, которого будем использовать
[Unit]
Description=Remote desktop service (VNC)
After=syslog.target network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
# Clean any existing files in /tmp/.X11-unix environment
ExecStartPre=/bin/sh -c ‘/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :’
ExecStart=/sbin/runuser -l testuser -c «/usr/bin/vncserver %i»
PIDFile=/home/testuser/.vnc/%H%i.pid
ExecStop=/bin/sh -c ‘/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :’
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Добавляем в файрволл
firewall-cmd —permanent —zone=public —add-service vnc-server
Настройка пользователя
Входим под пользователем, которого будем использовать для VNC и меняем пароль для VNC доступа.
После этого будет создана новая директория .vnc в папке пользователя, а также файл с паролем.
Перезапускаем демон и стартуем VNC-сервер
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl enable vncserver@:5.service
systemctl start vncserver@:5.service
Теперь подключаемся к нашему VNC-серверу.
Для подключения с Windows систем используйте TightVNC клиент.
How to Configure VNC Server in Fedora Linux?
The VNC or Virtual Network Computing protocol is a popular protocol for remotely viewing and accessing servers and interacting with their desktop environments or user interfaces. It is based on a client-server model. It basically has two types of components: a server that creates a display and a viewer that renders that display from the server on the client-side. The client and server may reside on the same machine or different machine with either the same or different system architecture.
VNC is based on the principle of a remote framebuffer (RFB). Since it operates at the framebuffer level, it could be used by any operating system, windowing system, or application.
VNC is an actual “thin-client” protocol, as it was developed with the idea of very few requirements for the viewer on the client-side. Thus, on the clients’ end, the software can run on a broad range of hardware, and setting up a client is very simple. E.g., we can simply design a VNC Viewer with reliable transport (like TCP/IP) and a method for displaying pixels.
What we will cover
In this guide, we will learn how to install and configure the tigervnc server on Fedora 32 xfce OS. We will also see how we can retrieve the server’s display on the client-side using a vnc viewer. Let us get started with the installation process of TigerVNC.
Prerequisites
- Fedora 32 xfce OS installed on server.
- Logged in as root user or an account with “sudo” privileges.
- Basic understanding of the concept of VNC protocol.
- VNC viewer installed on the client computer.
Terms to Know
- vncserver: It is a utility by which users can run different sessions simultaneously on a machine. These sessions can be accessed from any location and any number of clients.
- vncviewer: It is a software that displays the graphical user interfaces of vncserver and controls it.
Installing TigerVNC on Fedora 32 XFCE
Before you start installing TigerVNC server, check if your server is installed with GUI. If you are on a minimal install of Fedora, you will probably only have a command line interface. If this is the case, you will need to install the XFCE environment, which we will use in this guide. For installing the XFCE desktop, use the command:
Step 1. TigerVNC or Tiger Virtual Network Computing is a platform-independent implementation of VNC protocol. It is available for different platforms like Linux(32/64 bit), Mac(binary format) and Windows(32/64 bit).
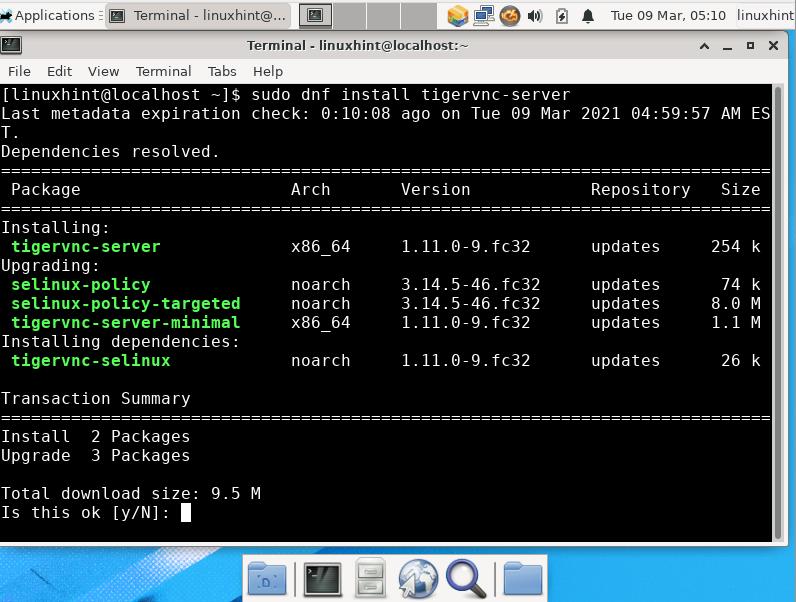
We can install TigerVNC from the official Fedora repository with the command:
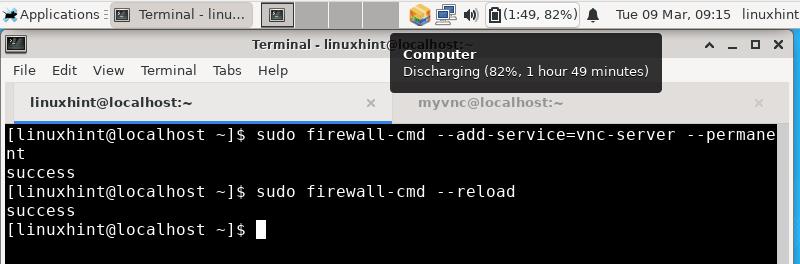
Step 2. Configure firewall to allow the VNC service to run:
sudo firewall-cmd —add-service =vnc-server —permanent
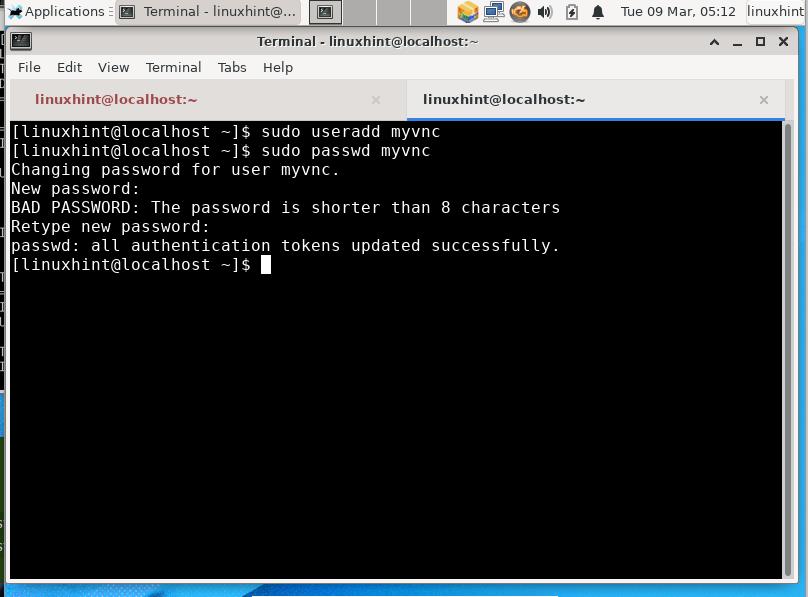
Step 3. Add a new user whose session will be shared with remote clients.
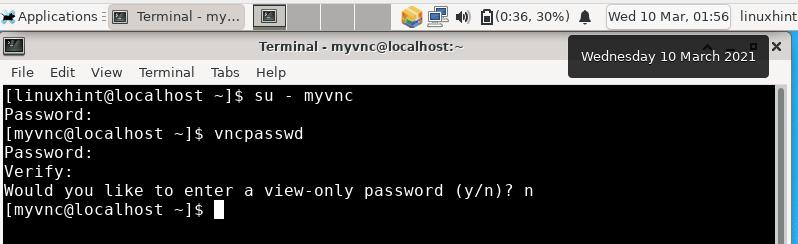
Step 4. Next, log in to the above created user and create a password for vnc session. This password will be used to authenticate any user trying to connect with your VNC server. To do this, follow the below steps:
Password: [Enter your password here]
Verify: [Retype the password to confirm]
Would you like to enter a view-only password (y/n)? n [ Enter ‘n’ here]
NOTE: The vnc password of a user is not encrypted, it is a plain-text password.
Starting VNC Server
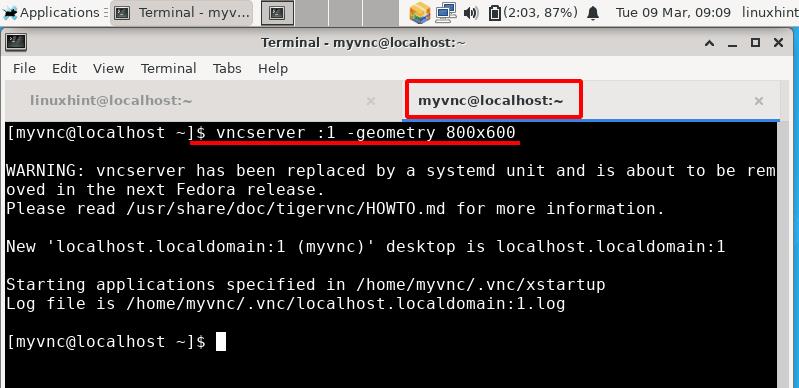
Step 1. We are all set to start the VNC server. Switch to the VNC user, myvnc in our case, and run the following command:
The geometry parameter describes the size of the remote desktop on the client side. The default value of VNC desktop size is 1024×768.
The above command will start the VNC server with a display number ‘1’. You can change this number by entering another valid number after the colon in the above command.
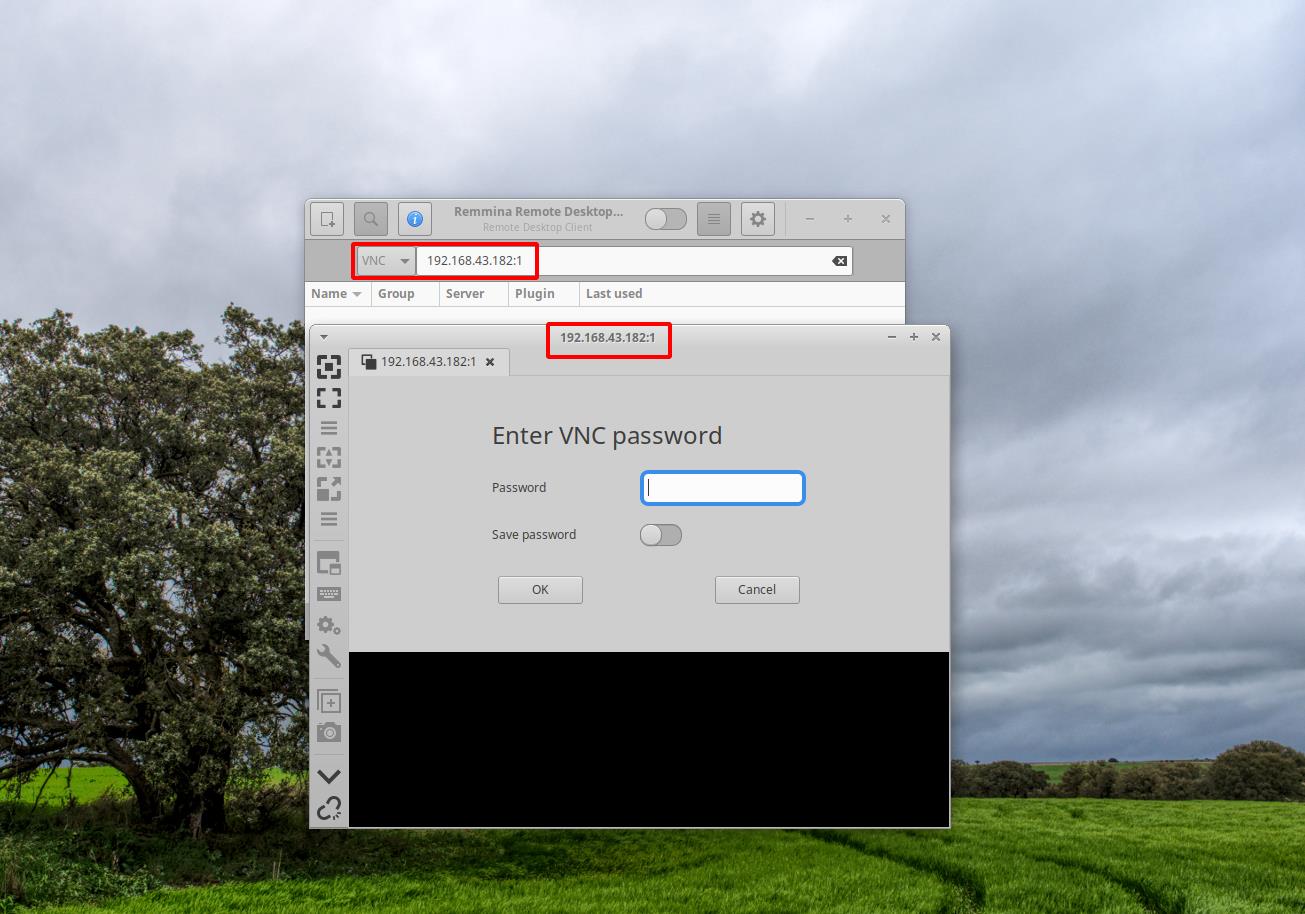
Step 2. To remotely view the desktop of our Fedora 32 OS, we need to install a VNC client. We are using the Remmina client from Xubuntu machine. Remmina can be installed from the software center on Xubuntu. Start Remmina from Application menu and enter the Fedora OS’s IP address and display number in the address bar..
Enter the IP and display number in the format: IP:x
Be sure to select the VNC protocol in the left drop down list.
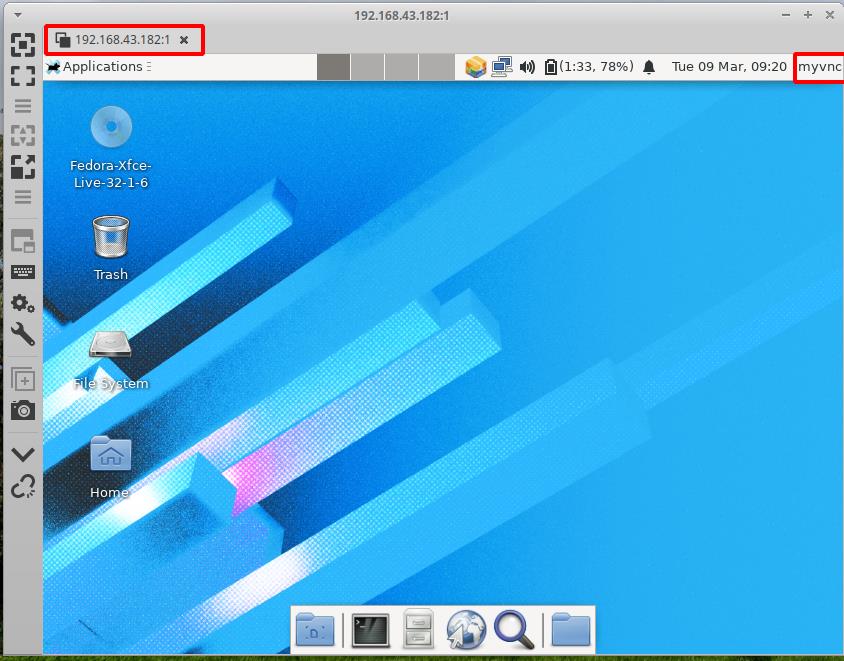
As you can see in the above picture, a new window will open-up after entering the IP address and the display number. Enter the VNC password you have set earlier using vncpasswd. If everything goes right, you will see the desktop of the “myvnc” user, as shown in the below picture:
Note: You may get an error like: “xfce policykit agent …….. user of caller and user of subject differs”. We have just ignored it and found no issue in using the remote desktop.
Stopping a VNC Session
A vnc session can be easily stopped. Just run the below command from the VNC user (myvnc in our case):
Replace the x with the actual display number we used in the step 2 of section ‘Starting VNC Server’.
Conclusion:
Congratulations, we have successfully installed the TigerVNC server on Fedora 32 xfce system. Fedora’s official website has a guide regarding installing TigerVNC but it was outdated as they were written for an older Fedora version. We have tried those guides on the latest Fedora releases, but they do not seem to work anymore. Also, there was no more revision available for that guide. We have got many errors like 1) vnc service created from the systemd utility could not start the vncserver. 2) gnome desktop session was not properly working.
VNC protocol uses plain text and has no encryption. After configuring TigerVNC on Fedora, you can make it secure by encrypting the client-server communication. Try adding a SSH tunnel between the server and client to implement encryption.
This guide is applicable to other Red Hat based distributions like Centos and RHEL.
About the author
Ali Imran Nagori
Ali imran is a technical writer and Linux enthusiast who loves to write about Linux system administration and related technologies. You can connect with him on LinkedIn
.