- How Do I Get Runlevel In Linux
- How do I find runlevel in Linux?
- What is the default runlevel in Linux?
- How do I find my default runlevel Ubuntu?
- What is run level 4 in Linux?
- How do I find the Linux version?
- How do I get to runlevel 3 in Linux?
- What are the two most commonly used runlevels?
- How do I check my current runlevel details?
- What does init do in Linux?
- How do I find my default run level?
- How do I change the run level in Ubuntu?
- How do I permanently change my runlevel in Linux?
- What are the 6 runlevels in Linux?
- What is Linux single user mode?
- Which is not a Linux Flavour?
- How many Linux versions are there?
- How do I find the Redhat version in Linux?
- How do I find system information in Linux?
- What is Telinit in Linux?
- Where are the startup scripts in Linux?
- What is a target in Linux?
- Recent Posts
- How can I see or change default run level?
- 4 Answers 4
How Do I Get Runlevel In Linux
Use the runlevel command /sbin/runlevel to find the current and previous runlevel of an operating system. Runlevels zero through six are generally delegated to single-user mode, multi-user mode with and without network services started, system shutdown and system reboot.
How do I find runlevel in Linux?
Linux Changing Run Levels Linux Find Out Current Run Level Command. Type the following command: $ who -r. Linux Change Run Level Command. Use the init command to change rune levels: # init 1. Runlevel And Its Usage. The Init is the parent of all processes with PID # 1.
What is the default runlevel in Linux?
By default most of the LINUX based system boots to runlevel 3 or runlevel 5. In addition to the standard runlevels, users can modify the preset runlevels or even create new ones according to the requirement.
How do I find my default runlevel Ubuntu?
To change the default runlevel, use your favorite text editor on /etc/init/rc-sysinit. conf Change this line to whichever runlevel you want Then, at each boot, upstart will use that runlevel.
What is run level 4 in Linux?
A runlevel is a mode of operation in the computer operating systems that implements Unix System V-style initialization. For example, runlevel 4 might be a multi-user GUI no-server configuration on one distribution, and nothing on another.
How do I find the Linux version?
Check os version in Linux Open the terminal application (bash shell) For remote server login using the ssh: ssh user@server-name. Type any one of the following command to find os name and version in Linux: cat /etc/os-release. lsb_release -a. hostnamectl. Type the following command to find Linux kernel version: uname -r.

How do I get to runlevel 3 in Linux?
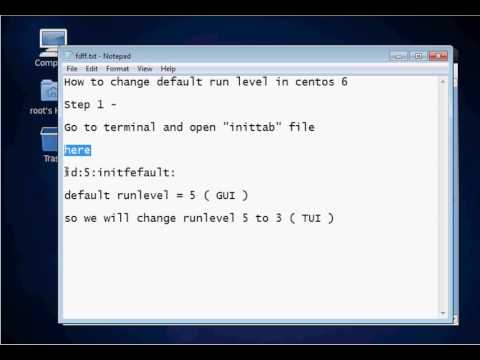
Changing and Viewing the default runlevel You can view it as follows. # grep ^id /etc/inittab id:5:initdefault: As you can see from the above output, the default runlevel is 5. If you want to change this to 3, edit the /etc/inittab file with the following.
What are the two most commonly used runlevels?
Fedora can be booted into different runlevels, each of which starts a specific collection of software for a particular purpose. The most commonly used are runlevel 3, which starts the system with a character-based user interface, and runlevel 5, which starts the system with a graphical user interface.
How do I check my current runlevel details?
How to check a current runlevel of your Linux system Checking the current runlevel on a Linux system. Checking the current runlevel on a Linux system. You can see here how systemd targets are mapped to Sys-V style runlevels. Determining the default systemd target. Checking the dependencies of the graphical.target in systemd.

What does init do in Linux?
In simple words the role of init is to create processes from script stored in the file /etc/inittab which is a configuration file which is to be used by initialization system. It is the last step of the kernel boot sequence. /etc/inittab Specifies the init command control file.
How do I find my default run level?
The default runlevel is specified in /etc/inittab file in most Linux operating systems. Using runlevel, we can easily find out whether X is running, or network is operational, and so on.
How do I change the run level in Ubuntu?
Either change this or use manually generated /etc/inittab . Ubuntu uses the upstart init daemon which by default boots to (an equivalent of?) runlevel 2. If you want to change the default runlevel then create an /etc/inittab with an initdefault entry for the runlevel you want.
How do I permanently change my runlevel in Linux?
To make a permanent change, you can edit /etc/inittab and change the default level that you just saw above. If you only need to bring the system up in a different runlevel for one boot, you can do this.
What are the 6 runlevels in Linux?
A runlevel is an operating state on a Unix and Unix-based operating system that is preset on the Linux-based system. Runlevels are numbered from zero to six.runlevel. Runlevel 0 shuts down the system Runlevel 5 multi-user mode with networking Runlevel 6 reboots the system to restart it.
What is Linux single user mode?
Single User Mode (sometimes known as Maintenance Mode) is a mode in Unix-like operating systems such as Linux operate, where a handful of services are started at system boot for basic functionality to enable a single superuser perform certain critical tasks. It is runlevel 1 under system SysV init, and runlevel1.
Which is not a Linux Flavour?
Choosing a Linux Distro Distribution Why To Use Red hat enterprise To be used commercially. CentOS If you want to use red hat but without its trademark. OpenSUSE It works same as Fedora but slightly older and more stable. Arch Linux It is not for the beginners because every package has to be installed by yourself.
How many Linux versions are there?
There are over 600 Linux distros and about 500 in active development. However, we felt the need to focus on some of the widely used distros some of which have inspired other Linux flavors.
How do I find the Redhat version in Linux?
How do I determine RHEL version? To determine RHEL version, type: cat /etc/redhat-release. Execute command to find RHEL version: more /etc/issue. Show RHEL version using command line, run: Another option to get Red Hat Enterprise Linux version: RHEL 7.x or above user can use the hostnamectl command to get RHEL version.

How do I find system information in Linux?
How to View Linux System Information. To know only the system name, you can use the uname command without any switch that will print system information or the uname -s command will print the kernel name of your system. To view your network hostname, use the ‘-n’ switch with the uname command as shown.
What is Telinit in Linux?
A runlevel is a software configuration of the system that allows only a selected group of processes to exist. Init can be in one of eight runlevels: 0 through 6, and S or s. The runlevel is changed by having a privileged user run telinit, which sends appropriate signals to init, telling it which runlevel to change to.
Where are the startup scripts in Linux?
local script using your text editor. On Fedora systems, this script is located in /etc/rc. d/rc. local, and in Ubuntu, it is located in /etc/rc.

What is a target in Linux?
target” encodes information about a target unit of systemd, which is used for grouping units and as well-known synchronization points during start-up. This unit type has no specific options. target exist which are used by the SysV runlevel compatibility code in systemd. See systemd.
Related Posts
- Quick Answer: How To Check Runlevel In Linux
- Question: What Is My Current Runlevel Linux
- Quick Answer: In Which Runlevel Linux System Reboots
- What Is Default Runlevel In Linux
- Quick Answer: What Is X11 Runlevel In Linux
- How Do I Find Runlevel In Linux
- Question: Why Runlevel 4 Is Unused In Linux
- Quick Answer: How Do I Start Linux In Runlevel 3
- Question: How Do I Change Runlevel On Boot Linux
- Quick Answer: Quick Answer How Do I Change Runlevel In Linux
- Quick Answer: How Do I Set The Default Runlevel In Linux
- Question: How Do I Find My Default Runlevel In Linux
Recent Posts
- Question: Is Hyperterminal Available In Windows 10
- How Do I Reset My Sound On Windows 8
- Question: How Do I Reinstall Operating System After Replacing Hard Drive
- Quick Answer: Question Can I Use My Android Phone As A Universal Remote
- Quick Answer: Best Answer Can Windows 10 Run On Intel Pentium
- How Do I Find Out My Motherboard Ubuntu
- You Asked What Happens If I Reset Bios To Factory Settings
- Quick Answer: You Asked How Long Does It Take To Install Ubuntu On Windows 10
- How Do You Repair Windows 7 That Will Not Boot
- How Do I Download Vlc On Linux
- How Do I Change The Font On My Computer Windows 7
- Question Is Windows 8 1 Update Still Available
- Quick Answer: Will Windows 10 Erase My Files
- How Do I Turn My Android Into A Monitor
- Frequent Question Is Debian Better Than Ubuntu
- Question: Question What Operating System Does This Computer Have
- Question How Can I Permanently Activate My Windows For Free
- What Is The Least Android Version
- Question: How Do I Test My Microphone On My Headphones Windows 7
- Question: How Can I Record My Android Gameplay
How can I see or change default run level?
In the Linux / Unix administration handbook it mentions that you can edit the /etc/inittab file to change the run level. I don’t have that file on 10.04. I Googled this and found a tip saying that file had been replaced with /etc/event.d/rc-default — however I don’t have that file on my system either. Have these been deleted or does 10.04 deal with run levels differently?
4 Answers 4
Yes, it deals with them differently.
To see the current (and previous) runlevel:
The init you are reading about was replaced by upstart starting with Edgy Eft 6.10; and, one of the programs provided by upstart is its own implementation of init. Here are the docs for 10.04.
To change the default runlevel, use your favorite text editor on /etc/init/rc-sysinit.conf.
sudo vim /etc/init/rc-sysinit.conf Change this line to whichever runlevel you want.
Then, at each boot, upstart will use that runlevel.
To See the Current Run Level Command:
$ who -r or $ runlevel
If you want chance the runlevel Command
$ sudo init 1 ( it will take to u single user mode)
This are differnt runlevel you can perform :
0 — System halt; no activity, the system can be safely powered down.
1 — Single user; rarely used.
2 — Multiple users, no NFS (network filesystem); also used rarely.
3 — Multiple users, command line (i.e., all-text mode) interface; the standard runlevel for most Linux-based server hardware.
5 — Multiple users, GUI (graphical user interface); the standard runlevel for most Linux-based desktop systems.
6 — Reboot; used when restarting the system.
This is an old thread, but no matter. @Premkumar, yr answer applies more to Unix type specifications such as the Lx Standard Base (LSB) than to Debian GNU Lx or Ubuntu for that matter. Check the run level of yr Ubuntu type distro and you will see that it is probably 2 or perhaps 1, in rare cases where a single user mode runlevel is preferred. See this Wiki for a detailed description. In Ubuntu, Runlevel 2 is for «Graphical multi-user with networking». The Wiki holds descriptions for many distros.
Normally this is done by explicitly adding a number to the kernel options in the GRUB entry.
Let’s say, you want to change default grub entry from default run level (5) to 3:
Find a place of default boot entry, and have a look at linux line. Might look something like this:
linux /boot/vmlinuz-3.0.0-13-generic root=UUID=d07e0c99-65ba-4eda-98d8-79693dc79554 ro quiet splash vt.handoff=7 Add 3 at the end of that line:
linux /boot/vmlinuz-3.0.0-13-generic root=UUID=d07e0c99-65ba-4eda-98d8-79693dc79554 ro quiet splash vt.handoff=7 3 You could also make use of the corresponding target of your desired runlevel. You can check which of the available target your system is running as default using:
Supposing the graphical.target is the default, you can further check its definition and detailed information using: systemctl cat graphical.target . There are some target units tailored after the corresponding runlevels. You can find which of them are available on your system by listing them: systemctl list-unit-files -t target Suppose you want to set runlevel 2 as default, you can do this by running:
sudo systemctl set-default runlevel2.target You should use this with caution and make sure you are not causing any issues running on the inappropriate target.