- Guide for changing your dev environment from Mac to Windows
- Keyboard shortcuts
- Trackpad shortcuts
- Command-line shells and terminals
- Windows shells
- Linux shells
- Windows Terminals
- Apps and utilities
- Feedback
- Изменение MAC-адреса в Linux
- Этап 2: Изменение MAC-адреса
- Вариант 1: ip link
- Вариант 2: ifconfig
- Вариант 3: macchanger
Guide for changing your dev environment from Mac to Windows
The following tips and control equivalents should help you in your transition between a Mac and Windows (or WSL/Linux) development environment.
For app development, the nearest equivalent to Xcode would be Visual Studio. There is also a version of Visual Studio for Mac, if you ever feel the need to go back. For cross-platform source code editing (and a huge number of plug-ins) Visual Studio Code is the most popular choice.
Keyboard shortcuts
You can use PowerToys Keyboard Manager to map Windows shortcuts to the shortcuts you use on a Mac.
| Operation | Mac | Windows |
|---|---|---|
| Copy | Command+C | Ctrl+C |
| Cut | Command+X | Ctrl+X |
| Paste | Command+V | Ctrl+V |
| Undo | Command+Z | Ctrl+Z |
| Save | Command+S | Ctrl+S |
| Open | Command+O | Ctrl+O |
| Lock computer | Command+Control+Q | WindowsKey+L |
| Show desktop | Command+F3 | WindowsKey+D |
| Open file browser | Command+N | WindowsKey+E |
| Minimize windows | Command+M | WindowsKey+M |
| Search | Command+Space | WindowsKey |
| Close active window | Command+W | Control+W |
| Switch current task | Command+Tab | Alt+Tab |
| Maximize a window to full screen | Control+Command+F | WindowsKey+Up |
| Save screen (Screenshot) | Command+Shift+3 | WindowsKey+Shift+S |
| Save window | Command+Shift+4 | WindowsKey+Shift+S |
| View item information or properties | Command+I | Alt+Enter |
| Select all items | Command+A | Ctrl+A |
| Select more than one item in a list (noncontiguous) | Command, then click each item | Control, then click each item |
| Type special characters | Option+ character key | Alt+ character key |
Trackpad shortcuts
Some of these shortcuts require a «Precision Trackpad», such as the trackpad on Surface devices and some other third-party laptops.
Trackpad options are configurable on both platforms.
| Operation | Mac | Windows |
|---|---|---|
| Scroll | Two finger vertical swipe | Two finger vertical swipe |
| Zoom | Two finger pinch in and out | Two finger pinch in and out |
| Swipe back and forward between views | Two finger sideways swipe | Two finger sideways swipe |
| Switch virtual workspaces | Four fingers sideways swipe | Four fingers sideways swipe |
| Display currently open apps | Four fingers upward swipe | Three fingers upward swipe |
| Switch between apps | N/A | Slow three finger sideways swipe |
| Go to desktop | Spread out four fingers | Three finger swipe downwards |
| Open Cortana / Action center | Two finger slide from right | Three finger tap |
| Open extra information | Three finger tap | N/A |
| Show launchpad / start an app | Pinch with four fingers | Tap with four fingers |
Command-line shells and terminals
Windows supports several command-line shells and terminals which sometimes work a little differently to the Mac’s BASH shell and terminal emulator apps like Terminal and iTerm.
Windows shells
Windows has two primary command-line shells:
- PowerShell — PowerShell is a cross-platform task automation and configuration management framework, consisting of a command-line shell and scripting language built on .NET. Using PowerShell, administrators, developers, and power-users can rapidly control and automate tasks that manage complex processes and various aspects of the environment and operating system upon which it is run. PowerShell is fully open-source, and because it is cross-platform, also available for Mac and Linux. Mac and Linux BASH shell users: PowerShell also supports many command-aliases that you are already familiar with. For example:
- List the contents of the current directory, using: ls
- Move files with: mv
- Move to a new directory with: cd
Some commands and arguments are different in PowerShell vs. BASH. Learn more by entering: get-help in PowerShell or checkout the compatibility aliases in the docs.
To run PowerShell as an Administrator, enter «PowerShell» in your Windows start menu, then select «Run as Administrator.»
Linux shells
Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) can now be installed to support running a Linux shell within Windows. This means that you can run bash, with whichever specific Linux distribution you choose, integrated right inside Windows. Using WSL will provide the kind of environment most familiar to Mac users. For example, you will ls to list the files in a current directory, not dir as you would with the traditional Windows Cmd Shell. To learn about installing and using WSL, see the Windows Subsystem for Linux Installation Guide. Linux distributions that can be installed on Windows with WSL include:
Just to name a few. Find more in the WSL install docs and install them directly from the Microsoft Store.
Windows Terminals
In addition to many 3rd party offerings, Microsoft provides two «terminals» – GUI applications that provide access to command-line shells and applications.
- Windows Terminal: Windows Terminal is a new, modern, highly configurable command-line terminal application that provides very high performance, low-latency command-line user experience, multiple tabs, split window panes, custom themes and styles, multiple «profiles» for different shells or command-line apps, and considerable opportunities for you to configure and personalize many aspects of your command-line user experience. You can use Windows Terminal to open tabs connected to PowerShell, WSL shells (like Ubuntu or Debian), the traditional Windows Command Prompt, or any other command-line app (e.g. SSH, Azure CLI, Git Bash).
- Console: On Mac and Linux, users usually start their preferred terminal application which then creates and connects to the user’s default shell (e.g. BASH). However, due to a quirk of history, Windows users traditionally start their shell, and Windows automatically starts and connects a GUI Console app. While one can still launch shells directly and use the legacy Windows Console, it’s highly recommended that users instead install and use Windows Terminal to experience the best, fastest, most productive command-line experience.
Apps and utilities
| App | Mac | Windows |
|---|---|---|
| Settings and Preferences | System Preferences | Settings |
| Task manager | Activity Monitor | Task Manager |
| Disk formatting | Disk Utility | Disk Management |
| Text editing | TextEdit | Notepad |
| Event viewing | Console | Event Viewer |
| Find files/apps | Command+Space | Windows key |
Feedback
Submit and view feedback for
Изменение MAC-адреса в Linux
Прежде чем изменить существующий МАК, следует узнать его текущее значение. Как и большинство других системных операций, рассматриваемая выполняется посредством терминала.
- Запустить требуемое приложение можно несколькими способами. Первый – откройте перечень установленного софта нажатием на соответствующую кнопку в левом нижнем углу, затем выберите пункт «Утилиты» – «Терминал».
Второй и более предпочтительный – воспользоваться сочетанием клавиш, по умолчанию это Alt+Ctrl+T.
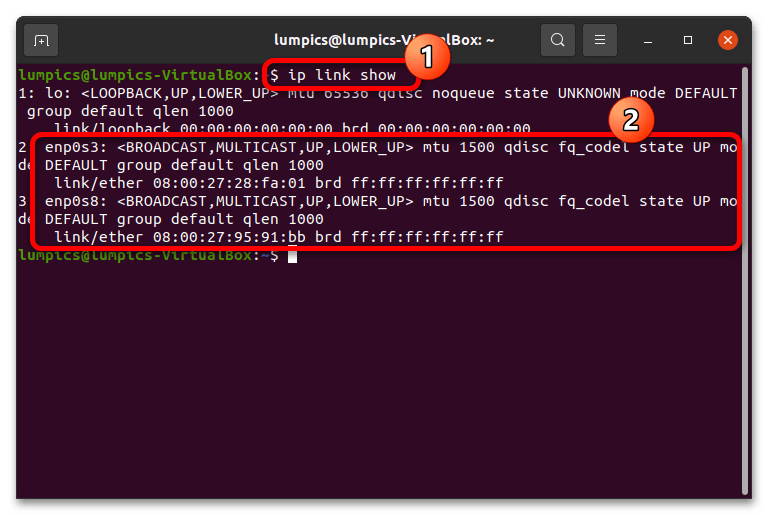
- После вызова терминала введите в нём следующую команду: ip link show Это отобразит адреса всех сетевых адаптеров, распознанных операционной системой. Нужные значения представляют собой последовательность после строки link/show, а в начале находится конкретный идентификатор того или иного адаптера.
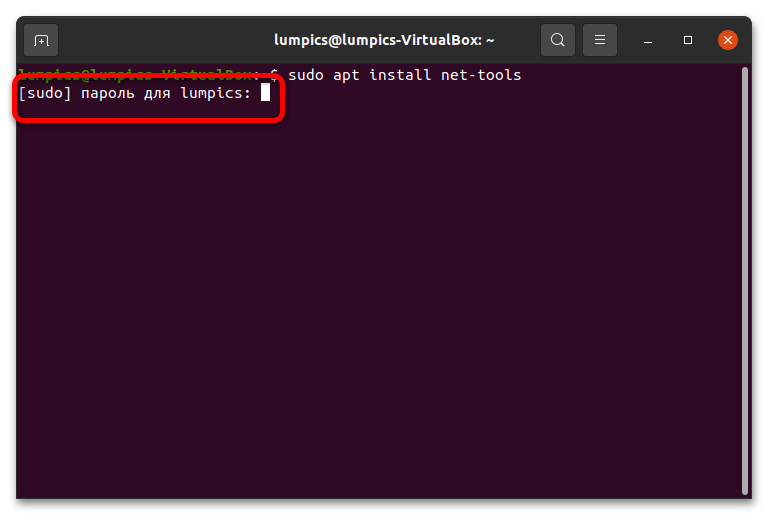
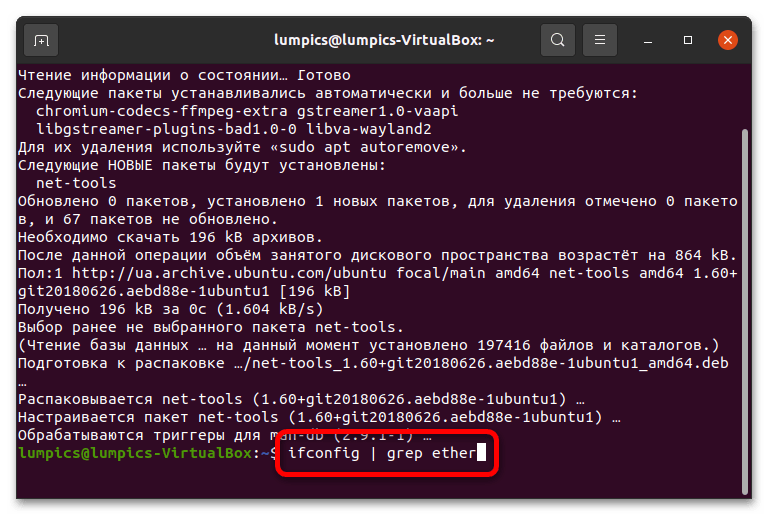
Альтернативный метод просмотра MAC-адреса – использование пакета сетевых инструментов. Последние сперва потребуется установить путем ввода в терминале следующей команды: sudo apt install net-tools
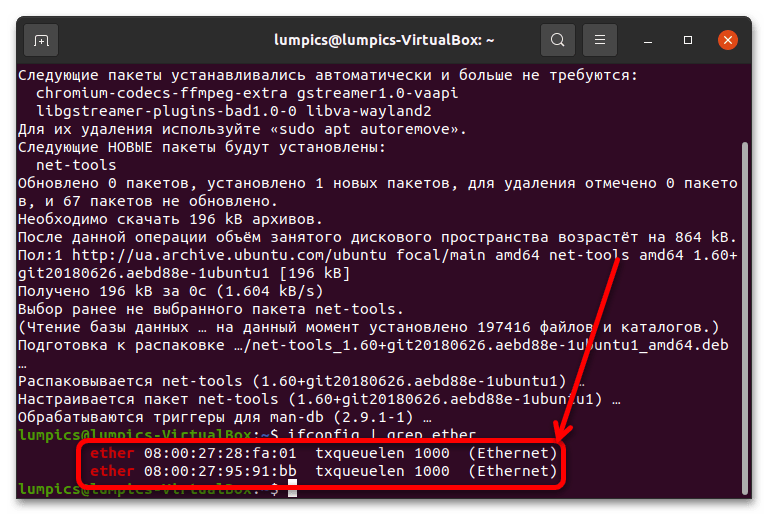
При первом применении с аргументом sudo нужно ввести пароль от учётной записи. Далее, когда нужные пакеты будут загружены и установлены, введите следующее: ifconfig | grep ether
Этап 2: Изменение MAC-адреса
Дальше у нас есть несколько вариантов решения рассматриваемой задачи: использовать ip link, уже инсталлированные на предыдущем этапе net-tools или воспользоваться загружаемой утилитой macchanger.
Вариант 1: ip link
Для смены MAC с помощью этих средств потребуется выполнить следующие действия:
- Для начала понадобится отмонтировать рассматриваемое устройство следующей командой (вместо *интерфейс* впишите название нужного сетевого адаптера, полученного на предыдущем этапе): sudo ip link set dev *интерфейс* down
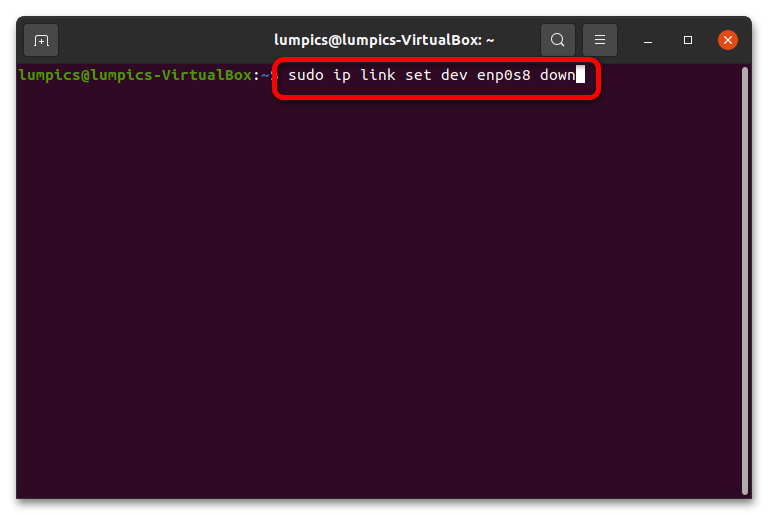
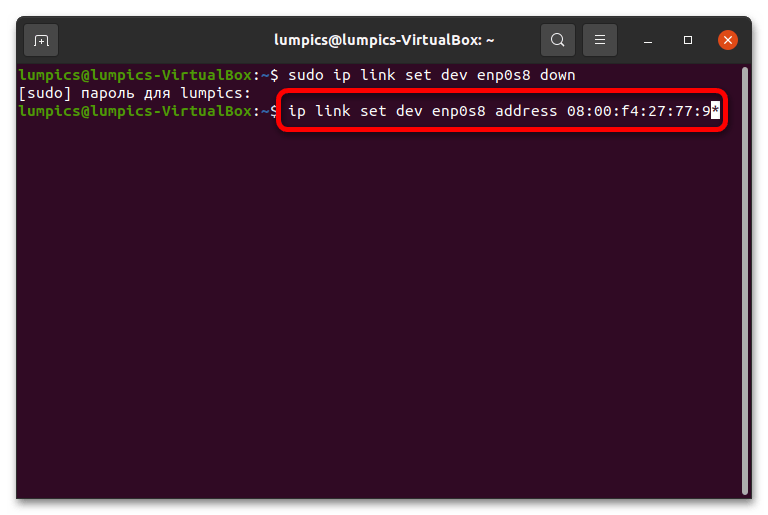
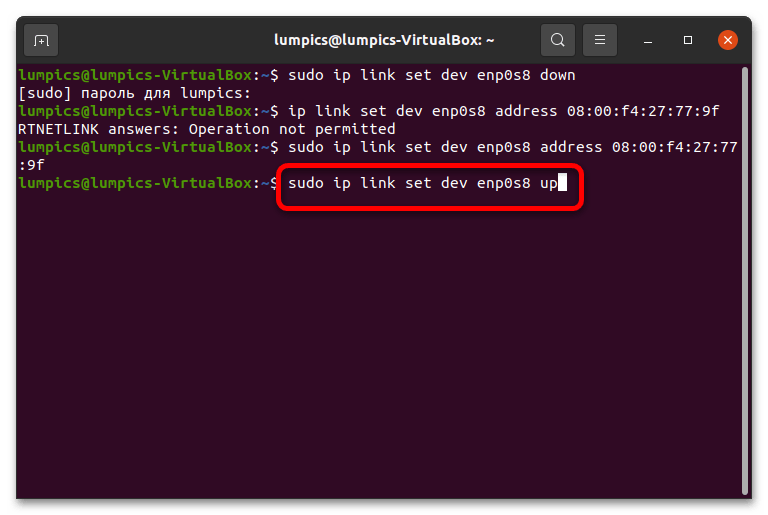
Вариант 2: ifconfig
Данное средство является частью пакета net-tools и уже достаточно давно не используется в дистрибутивах Linux как инструмент управления сетями, однако с его помощью также можно решить рассматриваемую задачу.
- По умолчанию ifconfig отсутствует в стандартном пакете программ, поэтому его потребуется доустановить, если этого не было сделано на шаге 4 предыдущего этапа.
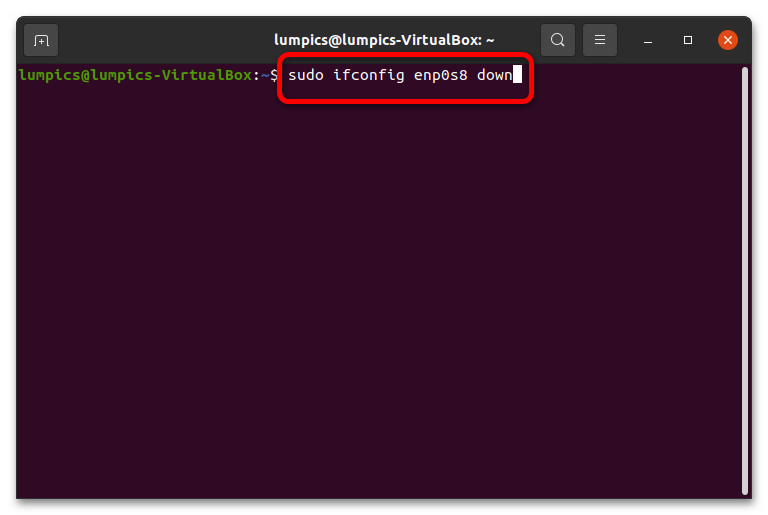
- Как и в случае с утилитой ip link, сперва потребуется отключить используемое устройство командой: sudo ifconfig *интерфейс* down Замените *интерфейс* именем требуемого сетевого устройства.
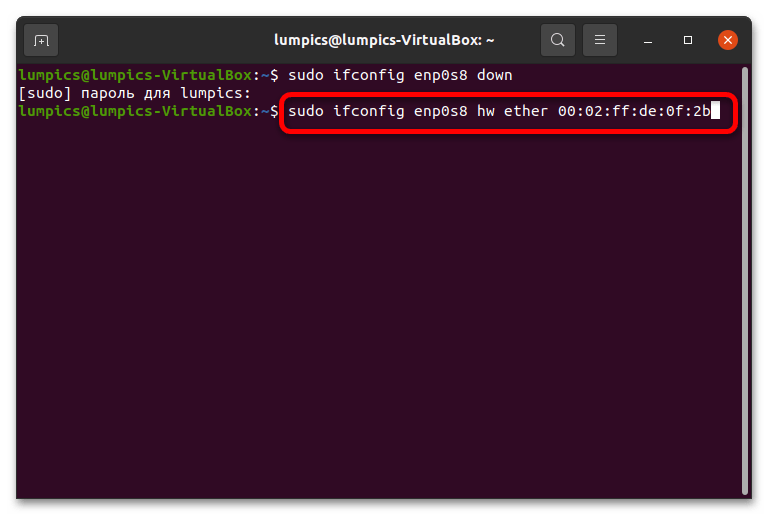
- Теперь предстоит ввод операторов замены адреса – сама последовательность выглядит так: sudo ifconfig *интерфейс* hw ether *XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX* Не забудьте заменить вставки на идентификатор адаптера и новый MAC соответственно.
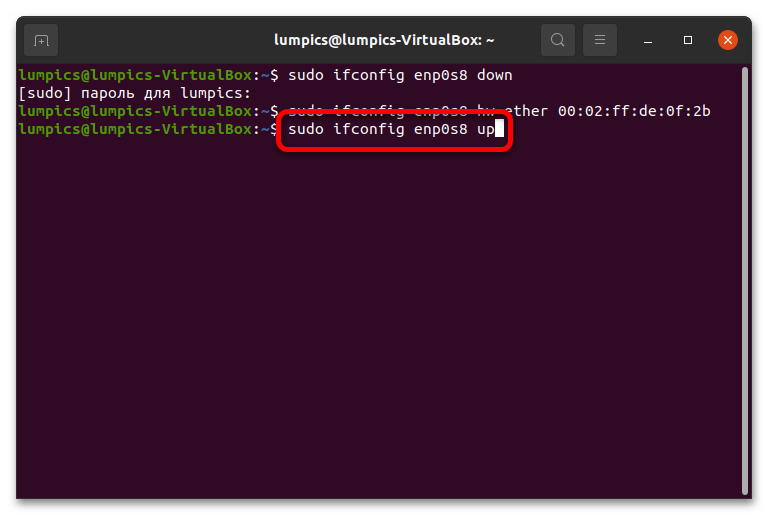
- После применения команды заново активируем отсоединённый сетевой интерфейс, прописав в консоли следующее: sudo ifconfig *интерфейс* up
Вариант 3: macchanger
Последним способом решения рассматриваемой задачи будет очередная консольная программа, именуемая macchanger.
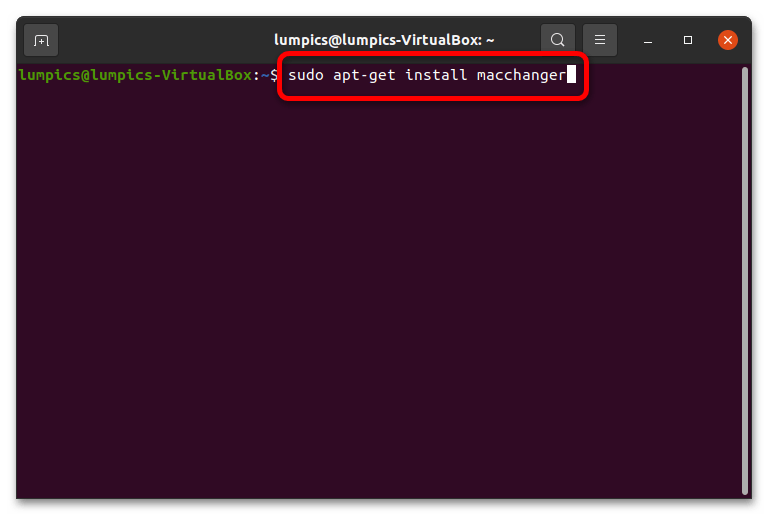
- Приложение не является частью ядра или оболочки, поэтому его нужно устанавливать отдельно. Вызовите терминал и введите в нём следующую команду: sudo apt-get install macchanger
Префикс sudo потребует ввода пароля учётной записи.
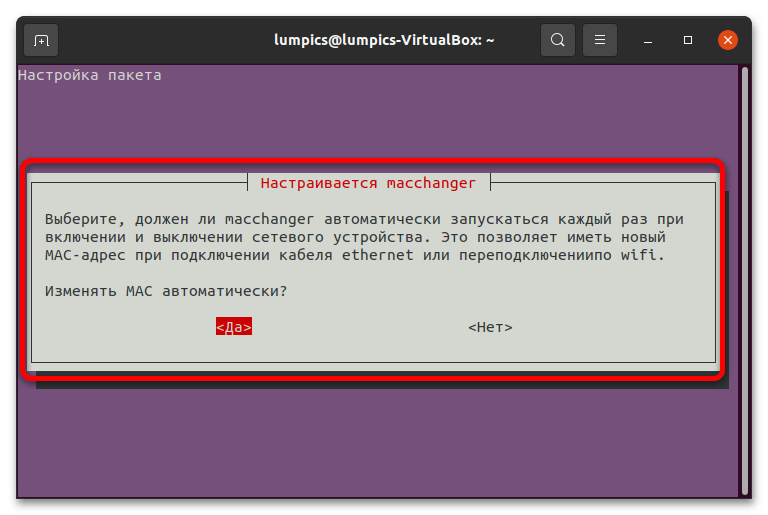
- В процессе инсталляции появится информационное сообщение с запросом на автоматическую смену MAC при каждом подключении сетевого кабеля или активации Wi-Fi. Выберите желаемый вариант с помощью стрелок и нажмите Enter.
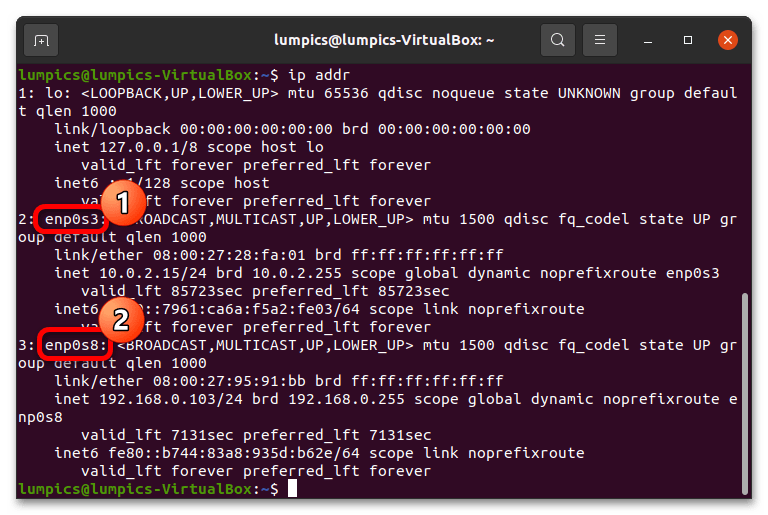
- Теперь нужно получить имя устройства, аппаратный идентификатор которого мы будем изменять, воспользовавшись для этого следующей командой: ip addr
Ознакомьтесь с перечнем – как правило, обычно имеются два устройства, одно из которых отвечает за соединение по кабелю, второе – за коннектор Wi-Fi. Ориентируйтесь на вид названия – имена беспроводных адаптеров начинаются с букв wl, кабельных – с e либо enp.
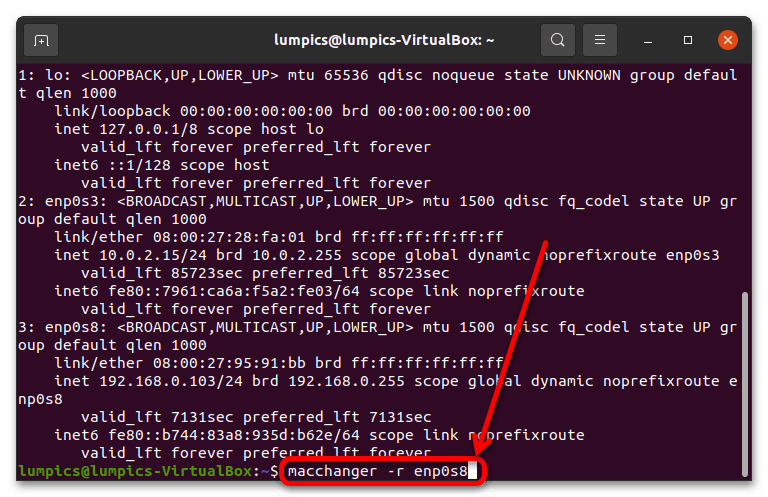
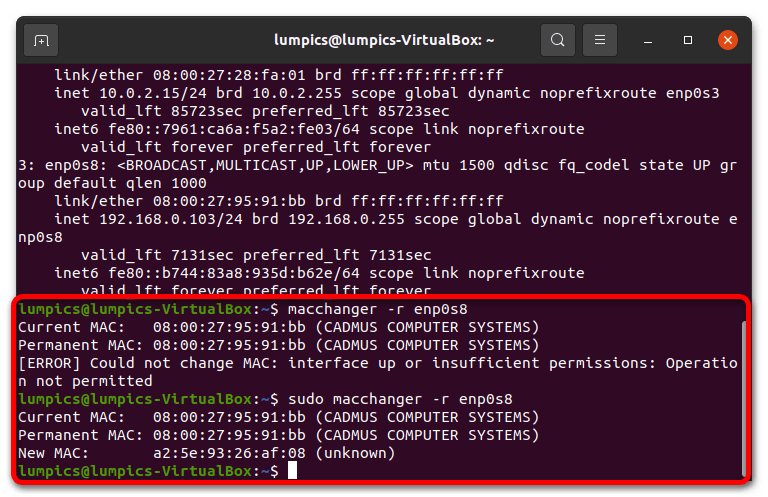
- Для присвоения случайного MAC в терминале следует ввести следующее: macchanger -r *интерфейс* Вместо *интерфейс* напечатайте значение, полученное на шаге 2.
Если вы получили ошибку, это значит, что команду нужно вводить с префиксом sudo .
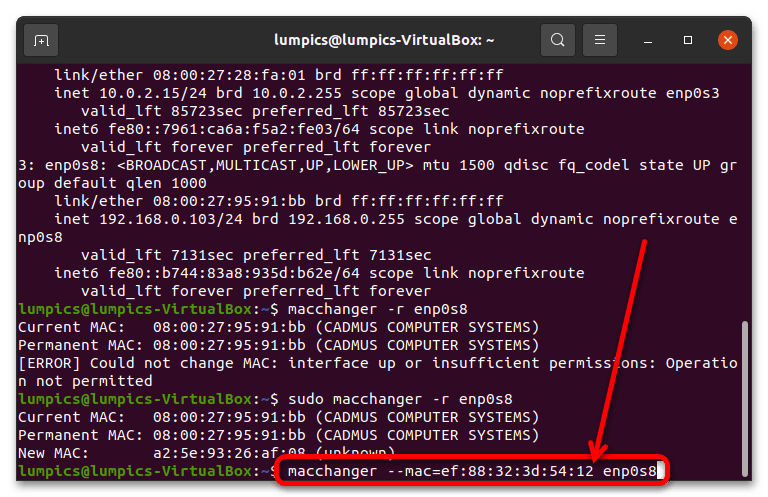
- Установка определённой последовательности выглядит похожим образом: macchanger —mac=*XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX* *интерфейс* Как и в предыдущем случае, вместо вставок со звёздочками впишите идентификатор сетевого адаптера и желаемое значение МАК. Замечание о необходимости sudo для этой команды также справедливо.
- С помощью macchanger можно восстановить и заводской идентификатор – просто напишите такую команду: macchanger -p enp0s8