- Как запускать команды Linux в фоновом режиме
- 1. Добавьте амперсанд после вашей команды
- 2. Используйте bg для отправки запущенных команд в фоновом режиме
- 3. Отправляйте команды в фоновом режиме с помощью nohup
- 4. Запускайте фоновые команды, используя системные перенаправления
- 5. Настройте выполнение команд Linux в фоновом режиме с помощью disown
- 6. Запускайте команды Linux в фоновом режиме с помощью tmux
- Оставьте свои команды Linux в фоновом режиме
- Как использовать рабочие пространства и активные углы в Linux Mint для повышения производительности
- Изменения Linux за эти годы
- 12 самых безопасных сайтов для загрузки свободного программного обеспечения Linux
- Send a Process to Background Linux
- What is a Process?
- How to Run a Process in the Background
- 1: Using an Ampersand (&)
- 2: Using CTRL + Z, bg command.
- How to Show Background Processes
- How to Make a Process Persistent After Shell Dies
- Conclusion
- About the author
- John Otieno
- Running Linux Commands in Background and Foreground
- Start a Linux process in the background directly
- Send a running Linux process to the background
- See all processes running in the background
- Bring a Process to Foreground in Linux
Как запускать команды Linux в фоновом режиме
Выполнение команды Linux занимает слишком много времени? Используйте любой из этих шести методов, чтобы отправить его в фоновый режим.
Команды Linux — отличный способ взаимодействия с системой с помощью терминала. Однако иногда для завершения текущей задачи может потребоваться некоторое время. Это заставляет пользователей либо ждать завершения процесса в течение значительного времени, либо вообще создавать новую оболочку.
К счастью, вы можете запускать команды Linux в фоновом режиме, следуя нескольким простым методам.
1. Добавьте амперсанд после вашей команды
Самый простой способ запустить фоновую команду Linux — добавить символ амперсанда ( & ) после команды. Например, если вы запустите текстовый редактор gedit со своего терминала, вы не сможете использовать оболочку, пока не закроете редактор. Однако, когда вы добавите дополнительный & к своей команде, вы сможете сразу же использовать оболочку.
2. Используйте bg для отправки запущенных команд в фоновом режиме
Иногда вы запускаете команду только для того, чтобы узнать, что для ее завершения требуется гораздо больше времени. Вы можете легко отправлять такие команды в фоновом режиме, нажимая клавиши Ctrl + Z , а затем используя команду bg . Нажатие Ctrl + Z останавливает запущенный процесс, и bg переводит его в фоновый режим.
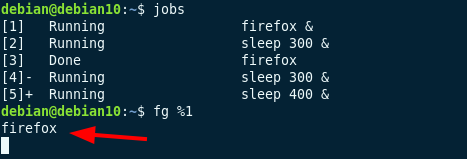
Вы можете просмотреть список всех фоновых задач, введя jobs в терминале. Используйте команду fg , чтобы вернуться к текущей задаче.
3. Отправляйте команды в фоновом режиме с помощью nohup
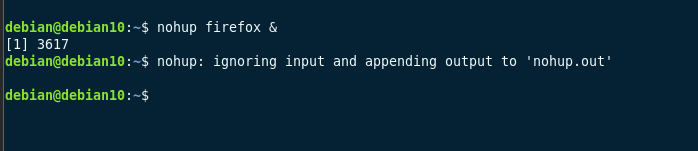
Команда nohup в Linux позволяет администраторам запускать команды терминала, невосприимчивые к сигналам HUP или Hang Up . Вы можете легко запускать команды в фоновом режиме в Linux с помощью nohup.
В приведенном ниже примере выполняется простое сканирование портов Nmap в фоновом режиме.
Одним из ключевых преимуществ nohup является то, что ваши команды будут выполняться, даже если вы выйдете из командной оболочки. Кроме того, он генерирует файлы журналов выполнения. Найдите nohup.out в текущем каталоге или внутри $HOME .
4. Запускайте фоновые команды, используя системные перенаправления
Вы также можете запускать фоновые команды в Linux, используя системные перенаправления. Например, если вы запустите приведенную ниже команду ping , ваша оболочка выполнит ее в фоновом режиме и немедленно вернет вам управление терминалом.
Здесь вывод команды ping перенаправляется на output.log . Вы можете заменить его на /dev/null , если хотите отменить результат. 2> & 1 сообщает Bash перенаправлять любые ошибки в тот же файл. Последний & сигнализирует о запуске этой команды в фоновом режиме.
5. Настройте выполнение команд Linux в фоновом режиме с помощью disown
Команда disown упрощает запуск процессов в фоновом режиме. Во-первых, вам нужно отправить задачу в фоновый режим с помощью оператора & . Затем введите disown , чтобы отсоединить его от вашей оболочки.
Одним из основных преимуществ disown является то, что, как и nohup, система продолжит выполнение вашей задачи, когда вы закроете свою оболочку или выйдете из системы.
6. Запускайте команды Linux в фоновом режиме с помощью tmux
tmux — это мощный мультиплексор, который позволяет запускать несколько сеансов терминала в одном окне. Изучение того, как использовать и настраивать tmux в Linux, является отличным выбором для людей, которые не знакомы с ним. tmux упрощает выполнение фоновых команд в Linux.
Когда вы запустите приведенную выше команду tmux , она выполнит команду ping в отдельной оболочке и продолжит ее выполнение в фоновом режиме. Вы можете запустить любой процесс или команду Linux в фоновом режиме, используя этот метод.
Оставьте свои команды Linux в фоновом режиме
Возможность запускать команды в фоновом режиме делает управление системой более продуктивным для администраторов. Вы можете отправлять свои задачи в фоновый режим несколькими способами. Функции Bash, такие как символ & и Ctrl + Z , удобны, но система завершит фоновое задание при закрытии оболочки.
С другой стороны, такие инструменты, как nohup и disown , поддерживают выполнение вашей команды, даже когда вы выходите из системы или завершаете работу оболочки.
Если вы оставите свои программы в фоновом режиме на долгое время, они могут превратиться в процессы-зомби, если не будут правильно настроены. Эти процессы могут значительно замедлить работу системы. Поэтому обязательно время от времени выявляйте и уничтожайте процессы-зомби.
Смотрите другие статьи на нашем канале .
Как использовать рабочие пространства и активные углы в Linux Mint для повышения производительности
Изменения Linux за эти годы
12 самых безопасных сайтов для загрузки свободного программного обеспечения Linux
Вы также можете оставить свое мнение об этом посте в разделе комментариев.
Send a Process to Background Linux
When working with graphical desktop environments, we rarely worry about background processes. If we have a process running in the foreground, we can quickly spawn another terminal window and continue with our work.
However, if you are in a raw terminal shell such as SSH, you will often feel concerned about processes that occupy and block the shell until they are completed, especially on long-running jobs. That is where the concept of background and foreground processes comes into play.
This tutorial will discuss what background and foreground processes are, including creating and managing them in Linux.
What is a Process?
Allow me to start at the basic level: what is a process?
In Linux, a process is an instance of a program. Typically, this means any command or executable in a shell is a process.
There are mainly two types of processes:
Foreground processes are mainly typical applications that we launch and interact with them. An example would be the nautilus file manager in Gnome. In most cases, we can start foreground processes from the shell or the desktop environment.
On the other hand, background processes run in the background and require no input or interaction from the user. An example would be any typical Linux daemon.
How to Run a Process in the Background
Suppose we have a process that, while running, occupies the shell session and hinders us from executing commands until it exits.
For example, if we run the Firefox browser in the shell, it will occupy the session until process termination.
As you can see, as long as Firefox is running, the shell prompt is unavailable, and we cannot execute any more commands.
To solve this, we can do it two ways:
1: Using an Ampersand (&)
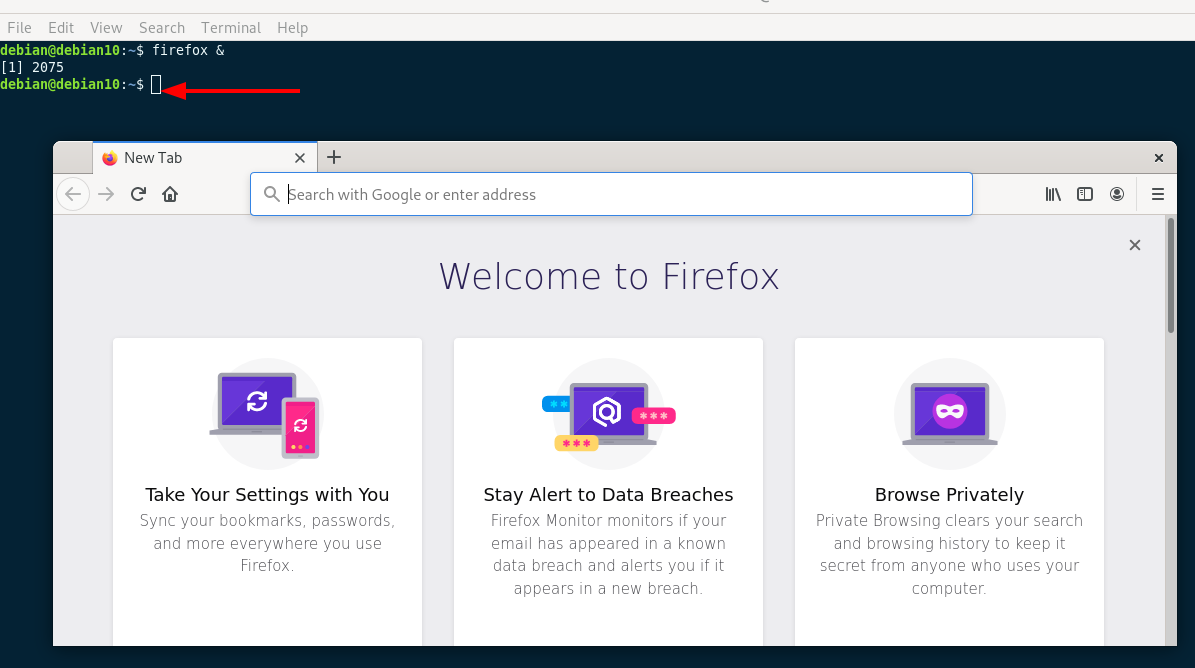
The first method is using the ampersand & sign. This tells the shell to run whatever command precedes the ampersand in the background.
In such a scenario, the process executes in the background and spawns as a new shell prompt allowing us to continue executing commands.
It also gives two numerical identifiers. The first one enclosed in square brackets is the Job ID, while the next one is the process ID.
2: Using CTRL + Z, bg command.
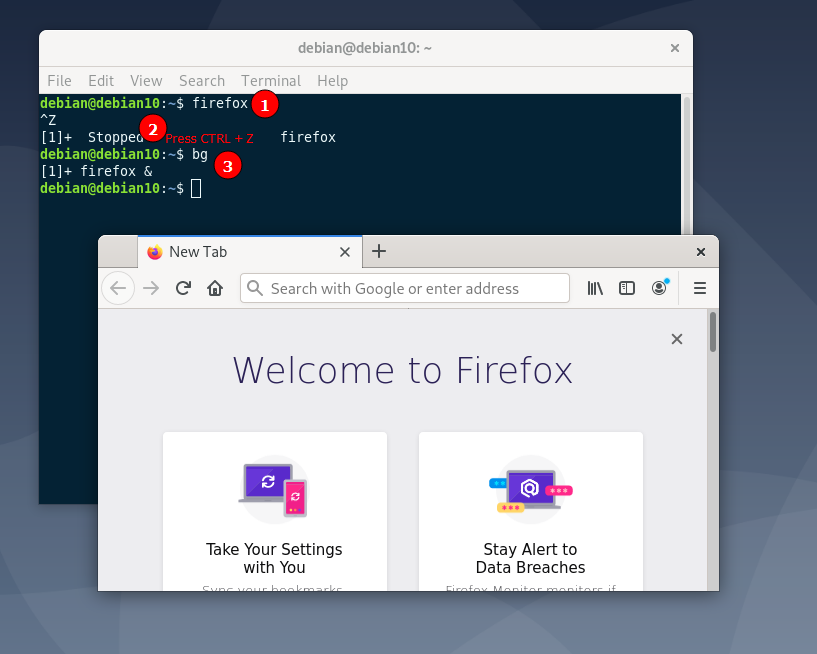
The next method you can use to put a process in the background is to use the shortcut CTRL + Z. This stops the process from blocking the shell. You can then use the bg command to push it to the background.
For example, start by launching Firefox as:
While the process is running, press CTRL + Z. This returns your shell prompt. Finally, enter the bg command to push the process in the background.
How to Show Background Processes
To view and manage processes in the background, use the jobs command in the shell. That will show the background jobs in the current terminal session.
An example output of background jobs:
To bring a process running in the background to the foreground, use the fg command followed by the job id.
For example, to bring the firefox job in the foreground, we use the command:
To put in the background again, press CTRL + Z followed by the bg command.
How to Make a Process Persistent After Shell Dies
When you are running processes in the background, and your shell session dies, all the processes associated with it terminate, which can be problematic, especially if it is an SSH session.
However, this is not too big an issue if you use a terminal multiplexer such as tmux or screen because, in that case, you can simply reattach the session.
However, if you run a shell session without a multiplexer, you can use the nohup command.
The nohup command is immune to hang-ups and can ignore the SIGHUP signal sent to a process.
Hence, if you run a command with nohup, it continues to run even if the shell session accidentally dies.
For example, to run Firefox with nohup, use the command:
This will run the process in the background as persist a shell terminate.
You can run a new terminal session and view the background jobs. You will see the process still running in the background.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we discussed various ways to run and send processes to the background in Linux. We also covered how to bring a background process to the background and persist hang-up upon shell termination.
About the author
John Otieno
My name is John and am a fellow geek like you. I am passionate about all things computers from Hardware, Operating systems to Programming. My dream is to share my knowledge with the world and help out fellow geeks. Follow my content by subscribing to LinuxHint mailing list
Running Linux Commands in Background and Foreground
Learn how to run commands in background in Linux. You’ll also learn how to bring the background jobs back to foreground.
If you have a long-running task, it’s not always wise to wait for it to finish. I mean why keep the terminal occupied for a particular command? In Linux, you can send a command or process to the background so that the command would be running but the terminal will be free for you to run other commands.
In this tutorial, I’ll show you a couple of ways to send a process in the background. I’ll also show you how to bring the background processes back to the foreground.
Start a Linux process in the background directly
If you know that the command or process is going to take a long time, it would be a better idea to start the command in the background itself.
To run a Linux command in the background, all you have to do is to add an ampersand (&) at the end of the command, like this:
Let’s take a simple bash sleep command and send it to the background.
When the command finishes in the background, you should see information about that on the terminal.
Send a running Linux process to the background
If you already ran a program and then realized that you should have run it in the background, don’t worry. You can send a running process to the background as well.
What you have to do here is to use Ctrl+Z to suspend the running process and then use ‘bg‘ (short for background) to send the process in the background. The suspended process will now run in the background.
Let’s take the same example as before.
[email protected]:~$ sleep 60 ^Z [1]+ Stopped sleep 60 [email protected]:~$ bg [1]+ sleep 60 &See all processes running in the background
Now that you know how to send the processes in the background, you might be interested in knowing which commands are running in the background.
For this purpose, you can enter this command in the terminal:
Let’s put some commands in the background first.
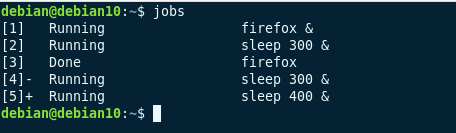
Now the jobs command will show you all the running jobs/processes/commands in the background like this:
jobs [1] Running firefox & [2]- Running gedit & [3]+ Stopped vimDo you notice the numbers [1], [2] and [3] etc? These are the job ids. You would also notice the – and + sign on two of the commands. The + sign indicates the last job you have run or foregrounded. The – sign indicates the second last job that you ran or foregrounded.
Bring a Process to Foreground in Linux
Alright! So you learned to run commands in the background in Linux. But what about bringing a process running in the background to the foreground again?
To send the command to the background, you used ‘bg’. To bring the background process back, use the command ‘fg’.
Now if you simply use fg, it will bring the last process in the background job queue to the foreground. In our previous example, running ‘fg’ will bring Vim editor back to the terminal.
If you want to bring a certain process to the foreground, you need to specify its job id. The job id is the number you see at the beginning of each line in the output of the ‘jobs’ command.
Where n is the job id as displayed in the output of the command jobs.
This was a quick one but enough for you to learn a few things about running commands in the background in Linux. I would advise learning nohup command as well. This command lets you run commands in the background even after you log out of the session.
If you have questions or suggestions, please leave a comment below.