- Linux Zip Commands to Archive or Unarchive files
- 1. Install ZIP on Linux
- 2. Zip Linux Command Syntax
- 3. Create and update zip archive
- 4. Removes/Delete folders and/or files from an archive:
- 5. Display the contents of a zip archive
- 6. Password-protected Linux ZIP file
- 7. Unpack the zip archive
- How to Zip a File in Linux
- Check if zip Is Installed
- Zip Files in Linux With the zip Command
- zip Command Options
- Create a ZIP Archive
- List ZIP File Contents
- Add Specific File Types to ZIP Archive
- Add a Directory to ZIP Archive
- Delete Files From ZIP Archive
- Create and Encrypt ZIP File
- Control ZIP Compression Level
- Create a ZIP Archive Using The GUI
Linux Zip Commands to Archive or Unarchive files
Extracting zip files on Linux using the command line a piece of cake. It is super easy and the tool we require to do that mostly comes pre-installed. However, if not then here we let you know not only how to install and use ZIP commands on Linux such as Ubuntu, AlmaLinux, Rocky Linux, CentOS, Linux Mint, etc.
Archives files are very useful to compress and store multiple files into a single file. For example, if want to upload a folder containing multiple files online, then rather than doing this for every single one, we bundled them in an archive. So that other users can easily download them. Furthermore, various compression algorithms are there to keep the data size as small as possible, which also favors the transfer.
In most Linux distributions, standard tools are already installed that allow to extract ZIP files graphically and unpack an archive. For that usually, you have to just right-click on the archive file and select the unzip option. However, if you are looking for a command-line way then here it is.
1. Install ZIP on Linux
In order to be able to create or unpack Zip archives under Linux, you must first ensure that the required tools are available on the system. Although, generally ZIP tool comes pre-installed however, if not then use the below given commands as per your distro:
If you are using a Linux distro with APT package management such as Ubuntu, Debian, Linux Mint, Kali, Mx Linux, POP! OS etc then use:
sudo apt install zip unzip
Whereas the RPM baes Linux such as RHEL, CentOS, Fedora, AlmaLinux, Rocky Linux and others can use:
sudo dnf install zip unzip
2. Zip Linux Command Syntax
zip [-options] [-b path] [-t mmddyyyy] [-n suffixes] [zipfile list] [-xi list] The default action is to add or replace zipfile entries from list, which can include the special name - to compress standard input.
If zipfile and list are omitted, zip compresses stdin to stdout. # Here are the options that we can use with the ZIP commands- -f freshen: only changed files -u update: only changed or new files -d delete entries in zipfile -m move into zipfile (delete OS files) -r recurse into directories -j junk (don't record) directory names -0 store only -l convert LF to CR LF (-ll CR LF to LF) -1 compress faster -9 compress better -q quiet operation -v verbose operation/print version info -c add one-line comments -z add zipfile comment -@ read names from stdin -o make zipfile as old as latest entry -x exclude the following names -i include only the following names -F fix zipfile (-FF try harder) -D do not add directory entries -A adjust self-extracting exe -J junk zipfile prefix (unzipsfx) -T test zipfile integrity -X eXclude eXtra file attributes -y store symbolic links as the link instead of the referenced file -e encrypt -n don't compress these suffixes -h2 show more help
Let’s see some common commands that will help us to use this tool for extracting archive files and repacking the ones we want.
3. Create and update zip archive
The syntax of the individual commands is always the same:
zip options archive.zip files and folders list
If the archive already exists, the files and folders are added to the archive or updated. The archive is not going to be replaced.
Add individual files to an archive:
zip archive-filename.zip file1 file2 (. )
With this command, an archive “archive-filename.zip” with the files “file1” and “file2” is created or updated in the current directory.
To add a folder to an archive:
zip -r archive-filename.zip folder1 folder2 (. )
This command creates an archive “archive-filename.zip” with the folders “folder1” and “folder2” including all subfolders and files in the current directory.
Create Zip archive and delete the original files
With creating of Archive file you want to remove the original files or folders that have been used to create the ZIP archive file of yours, then use -m option. It is meant to move files permanently rather than copying them to the archive.
zip -m archive-filename.zip file1 file2
4. Removes/Delete folders and/or files from an archive:
zip -d archive.zip file1 file2 folder / * (. )
The command removes the files “file1” and “file2” as well as the folder “folder” & its contents from the archive “archive.zip”
Show more options:
Displays complete help with all available options.
5. Display the contents of a zip archive
This command shows the complete content of the archive “archive.zip”
6. Password-protected Linux ZIP file
Many times, we need protection for sensitive files or data while archiving them. Thus, if you want to create a Linux zip with a password then simply use -e option. With this, we can significantly improve the security of our zipped files.
zip -e archive.zip file1 file2
As you use -e parameter, the system will ask you to create a password for the files by entering it two times.
7. Unpack the zip archive
Unpack the complete archive:
Unpacks the complete archive into the current directory.
Extract the archive to a specific location:
unzip archiv.zip -d /tmp/target
Extract the complete archive to “/tmp/target”
Extract only certain files or folders:
unzip archive.zip file1 folder1 file2 -d /tmp/target
-d stands for the directory.
Show more options:
Displays complete help with all available options.
unzipsfx options: -c, -p - Output to pipe. (See above for unzip.) -f, -u - Freshen and Update, as for unzip. -t - Test embedded archive. (Can be used to list contents.) -z - Print archive comment. (See unzip above.) unzipsfx modifiers: Most unzip modifiers are supported. These include -a - Convert text files. -n - Never overwrite. -o - Overwrite without prompting. -q - Quiet operation. -C - Match names case-insensitively. -j - Junk paths. -V - Keep version numbers. -s - Convert spaces to underscores. -$ - Restore volume label.
Ending note:
These were a few common ZIP commands that we can use on Linux operating system for packaging or unpacking archive files using the terminal.
Other tutorials:
How to Zip a File in Linux
ZIP is the most popular archive file format for compressing files and directories. Compressing files into an archived format helps conserve space and network bandwidth. Even though the tape archive (tar) format is more common on Linux systems, ZIP is also used often due to its popularity.
Linux offers the zip command for compressing files into ZIP format. Alternatively, creating ZIP files is possible through the GUI, too.
This guide shows how to zip files and directories through the command line and GUI in Linux.
Check if zip Is Installed
Not all Linux systems have the zip program installed by default. See whether the utility is available by checking the version:
If the output prints the program version, continue to the following section. However, if the output shows the command is not found, install the zip and unzip utility with the following command:
sudo apt install zip unzipNote: Installing unzip is not mandatory, but the command goes hand-in-hand with zip .
If you’re looking to unzip files, check out our guide on how to unzip a ZIP file.
Enter the sudo password and wait for the installation to complete.
Zip Files in Linux With the zip Command
The zip command helps create ZIP archive files. The general syntax for the zip command is:
Without any options, the command creates a new ZIP file. The additional options and syntax change the behavior and provide different functionalities.
zip Command Options
The zip command offers various work modes and options to help create ZIP files. The table below shows a short overview of the available options.
| Tag | Option or Mode | Description |
|---|---|---|
| -u —update | Mode | Updates and adds new files. Creates a new archive if not found. |
| -f —freshen | Mode | Updates files without adding new ones. Creates a new archive if not found. |
| -d —delete | Mode | Chooses entries in an existing archive and removes them. |
| -U —copy-entries | Mode | Chooses entries from an existing archive and copies them into a new archive. |
| -e —encrypt | Option | Encrypts ZIP archive contents with a password. Starts a password entry prompt. |
| -i —include | Option | Includes only specified files. |
| -R —recurse-patterns | Option | Archives files recursively. |
| -sf —show-files | Option | Lists files the command would operate on, then exits. |
| -x —exclude | Option | Excludes specified files. |
| — | Option | Regulates compression speed (0-9). Lower numbers are faster. |
The zip command offers many other options you can view using the man command.
Create a ZIP Archive
The zip command, without any options, creates a new file. To test the command, do the following:
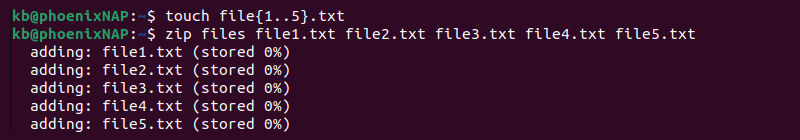
1. Create files for archiving:
The command creates five empty text files.
2. Use the zip command to archive the files:
zip files file1.txt file2.txt file3.txt file4.txt file5.txtThe command outputs the actions taken and creates a files.zip archive.
List ZIP File Contents
The -sf option lists the contents of a ZIP file. Provide only the ZIP file name, for example:
The command lists the archive’s contents and exists.
Add Specific File Types to ZIP Archive
To add only specific file types to a ZIP file, use a wildcard and provide the filetype extension. For example:
The command adds all files with the .txt extension to the archive.
Add a Directory to ZIP Archive
Use the -r (recursive) option to add a directory to a ZIP file. For instance:
The zip command adds the empty directory first, then populates it with the files.
Delete Files From ZIP Archive
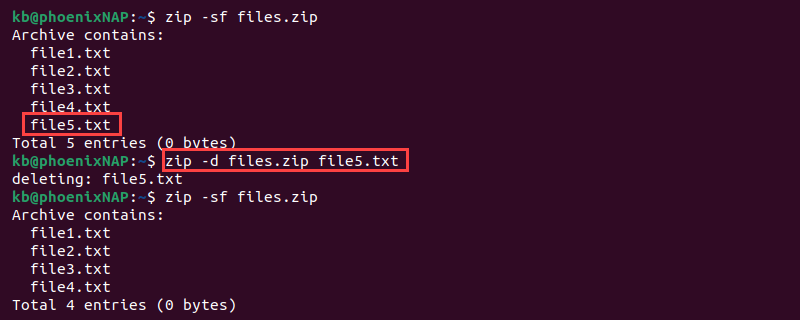
1. To delete files from a ZIP archive, list the files from the archive using the -sf option first. For example:
2. Locate the file for deletion and run zip with the -d tag:
The command removes the specified files from the ZIP archive.
Create and Encrypt ZIP File
A password protects the ZIP archive from extraction. To add password encryption to a ZIP file, use the -e option:
The command starts a password entry prompt. After confirming, the files are added to the ZIP archive.
Control ZIP Compression Level
The zip command allows controlling the compression level. The ZIP file compression level and speed are reversely proportional. As the level increases, the compression takes longer.
To control the ZIP file compression level, use the following syntax:
For the fastest compression, use -1 . For the highest level of compression, use -9 . Values between 1 and 9 provide in-between results (fast vs. level of compression).
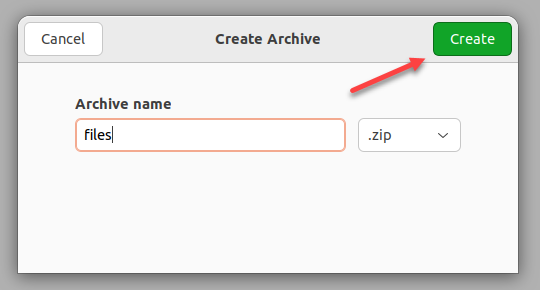
Create a ZIP Archive Using The GUI
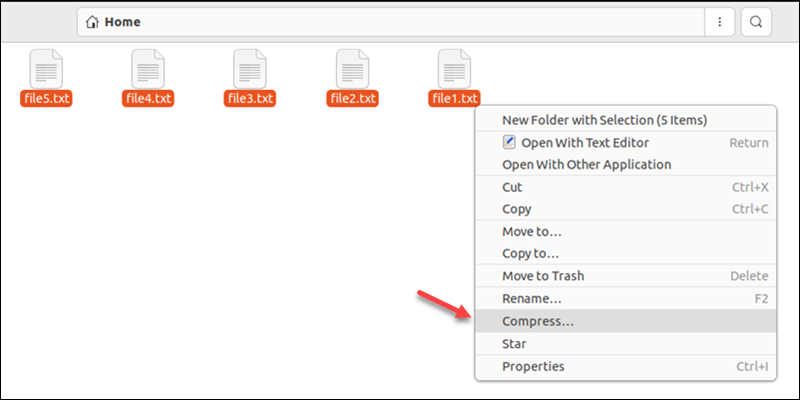
To create a ZIP file in Linux through the GUI, do the following:
1. Open Files and navigate to the appropriate directory.
2. Select the files for archiving, right-click the files, and choose Compress.
3. Enter the archive name and choose the .zip format from the dropdown menu.
4. Click Create to create the ZIP file.
The process creates a ZIP archive in the current location.
After reading this guide, you should know how to create a ZIP file in Linux with the zip command and GUI. For other file compression and archiving commands, check out the tar command.