Linux Kernel
Linux Kernel is the heart of Linux operating systems. It is an open-source (source code that can be used by anyone freely) software that is most popular and widely used in the industry as well as on a personal use basis. Who created Linux and why? Linux was created by Linus Torvalds in 1991 as a hobby project. Since then, many of the users have contributed to its growth and development of it. Before Jumping directly to the main topic “Linux Kernel” one must know a few concepts (prerequisites) to better understand the Linux Kernel.
What is Linux Operating System and Kernel?
An operating system (OS) is a software system that manages the computer that provides some services for computer programs and manages computer hardware and software. Basically, it is a communication or resource allocation between computer hardware and applications. It provides some services like managing input and output devices, managing file systems, providing UI (User Interface) and also managing computer memory. It also governs and executes all the programs.
Linux operating System also consists of various components for example system libraries, user-space utilities, Linux kernel, and applications. The kernel is the core component of an operating system. This provides a platform for programs and various services to run on top of it. The Linux kernel is modifiable according to the user’s needs. Overall, the Linux Operating System and Linux kernel together provide a strong and user-friendly platform.
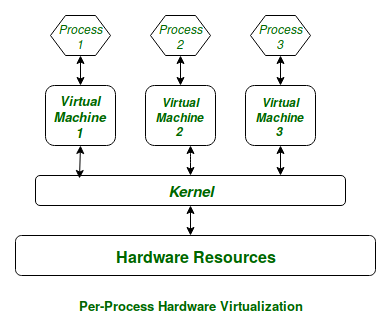
In a General-Purpose Computer running many processes simultaneously, we need a middle layer to manage the distribution of the computer’s hardware resources efficiently and fairly among all the various processes running on the computer. This middle layer is referred to as the kernel. The kernel virtualizes the computer’s common hardware resources to provide each process with its own virtual resources. This makes the process seem as if it is the sole process running on the machine. The kernel is also responsible for preventing and mitigating conflicts between different processes. This is schematically represented below:
Schematical representation of Kernel working
Figure: Virtual Resources for each Process
The Core Subsystems of the Linux Kernel are as follows:
- The Process Scheduler
- The Memory Management Unit (MMU)
- The Virtual File System (VFS)
- The Networking Unit
- Inter-Process Communication Unit
Core Subsystems of the Linux Kernel
Figure: The Linux Kernel for the purpose of this article we will only be focusing on the 1st three important subsystems of the Linux Kernel. The basic functioning of each of the 1st three subsystems is elaborated below:
- The Process Scheduler: This kernel subsystem is responsible for fairly distributing the CPU time among all the processes running on the system simultaneously.
- The Memory Management Unit: This kernel sub-unit is responsible for proper distribution of the memory resources among the various processes running on the system. The MMU does more than just simply provide separate virtual address spaces for each of the processes.
- The Virtual File System: This subsystem is responsible for providing a unified interface to access stored data across different filesystems and physical storage media.
Some Basic Commands:
Some Basic Commands we need to know while working on Linux Kernel.
- `ls` : Use to list all the files and directories in a particular location specified by us.
ls [OPTION] [FILE]
In this example we are going to list all the file and directories in our current location , we have one directory name `snap`.
Here in second time we use `a` option (to see all the hidden files).
In third time we specified a `snap` directory.
mkdir [OPTION] DIRECTORY
In this we will make a directory name `test` and to check it we can use command `ls`.
cat [OPTION] [FILE]
Printing a content inside a text file name `example`.
- `pwd` : In this we will get to know the name and path of the current working directory.
Conclusion:
The most powerful and versatile component of the Linux Operating System is known as the Linux kernel. The Kernel has provided a wide range of features, for example, memory management, filesystem management, process management, device drive management and networking support. After understanding all this one can conclude that customizability and extensibility have made it the most popular choice for a computer system.
What Is Linux Kernel?
So Linux is now 25 years old. Linus Torvalds, a 21-year-old computer science student at the University of Helsinki in Finland at the time, built the Linux kernel in 1991. On August 25, 1991, Torvalds wrote the following to comp.os.minix, a Usenet newsgroup.
I’m doing a (free) operating system (just a hobby, won’t be big and professional like gnu) for 386 (486) AT clones. This has been brewing since April, and is starting to get ready. I’d like any feedback on things people like/dislike in minix, as my OS resembles it somewhat (same physical layout of the file-system (due to practical reasons) among other things).
Linus Torvalds
Linus then released the kernel under the GPL licence, which meant that it was open source and available to the general public to examine the code, tweak it to suit their needs, and distribute it under the same GPL licence. The Linux kernel 1.0.0, containing 176,250 lines of code, was published on March 14, 1994. The Linux kernel version 3.10, released in June 2013, comprises 15,803,499 lines of code, whereas version 4.1, released in June 2015, has expanded to over 19.5 million lines of code provided by about 14,000 programmers.
So What Does Linux Kernel Do?
Every operating system, in some form or another, makes use of a kernel. A computer without a kernel is technically conceivable, but it is impractical. It is nearly difficult to have a functioning operating system without the kernel. In general, the kernel is a piece of software that acts as a barrier between the hardware and the main applications that run on a computer.
It is the first component to load when the operating system boots up. It is loaded into memory and remains there for the duration of the computer’s session. So let’s have a look at some of the Linux kernel’s features.
1. Communication and Resource Management
The Linux kernel enables communication between hardware and software via drivers included in the kernel or added via kernel modules. It is also in charge of managing the system’s resources, including as memory management, process and task management, and disc management. As a result, the kernel ensures that a programme has enough memory. It also ensures that the processor runs and completes duties efficiently.
2. The Linux Kernel Is Monolithic
The Linux kernel is monolithic, as opposed to a microkernel, which strives to have the smallest install and memory footprint feasible by handling only what it needs to, such as the CPU, memory, and IPC (Inter Process Communication). Device drivers, system server calls, and the file management system are also part of the Linux kernel. Because there is a direct route to any information required from memory or any running process, the Linux kernel is much better at accessing hardware and multitasking.
The kernel’s monolithic structure also means that it has a very big footprint, however one significant method the developers have avoided this issue is through the usage of kernel modules. Kernel modules can be loaded and unloaded at runtime, allowing features to be added and withdrawn at any moment.
3. Portability
The Linux kernel was not originally intended to be portable, although it has since been ported to a variety of systems. It is the operating system (kernel) of choice for nearly all of the top 500 fastest supercomputers. It is the brains behind Google Android, the most popular operating system ever. The Linux kernel also powers other mobile operating systems such as Firefox OS, HP webOS, and Samsung’s Tizen.
4. Patching
Live kernel patching was introduced with the release of the Linux kernel version 4.0 in April 2015. Updates to the kernel can be applied or even replaced without the need to restart your computer. This enables for system updates with no downtime, which is extremely useful in server systems.
Conclusion
The kernel and the BIOS should not be confused. The BIOS is a self-contained programme that is stored in a chip on a computer’s main circuit board. During the boot process, it performs activities such as initialising the hardware and loading the kernel into memory.
The kernel, unlike the BIOS, can be readily replaced or upgraded by replacing or upgrading the operating system or, in the case of Linux, by introducing a newer kernel or modifying an existing kernel. Windows and macOS, like Linux, have their own kernels that are all distinct. The Linux kernel is the main common component among the different Linux distributions available, whether broad or specialised.