- How to list all enabled services from systemctl?
- 9 Answers 9
- How to List All Running Services Under Systemd in Linux
- Listing Running Services Under SystemD in Linux
- Listing Linux Services With Systemctl
- List Services Using Systemctl in Linux
- List All Services
- List Loaded Services
- Running Services
- Enabled Services
- Disabled Services
- Check Service Status
- Where are systemctl service files
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Syeda Wardah Batool
How to list all enabled services from systemctl?
How can I list all enabled services from systemctl ? I know running systemctl command by itself lists all services, but I would like to only get the enabled ones.
Fascinating. The lowest rated answer is the most «correct» answer, even though it is clearly not the best answer. This excellent question (and its answers) is an interesting example of how systemd violates the long-standing (and brilliant) design principles of Unix & Co. @FelipeAlvarez complains that the most-accepted answer assumes systemd follows the unix design philosopy, but systemd/systemctl can do exactly what he wants (most experienced users will just consider that complete bloat). I begin to see more clearly why Linus Torvalds is so vehemently critical of systemd.
If you want to list «templated» services (blabla@instance.service), do not forget to add «—all» — thanks to @rafdouglas below.
9 Answers 9
systemctl list-unit-files | grep enabled will list all enabled ones.
If you want which ones are currently running, you need systemctl | grep running .
Use the one you’re looking for. Enabled, doesn’t mean it’s running. And running doesn’t mean it’s enabled. They are two different things.
Enabled means the system will run the service on the next boot. So if you enable a service, you still need to manually start it, or reboot and it will start.
Running means it’s actually running right now, but if it’s not enabled, it won’t restart when you reboot.
annoying to have to use an external tool (grep) to show this vital information. But thank you for showing us the way 🙂
@FelipeAlvarez Correct. But that’s how Linux works. Many small binaries that work well with each other. systemctl does what is asked, it lists services. There is no filtering command built-in to systemctl because grep already exists and can do that well with any program’s output. It’s how it’s always been 🙂
I agree and so it should be. But, systemd already tries to do SO much that I wonder why it can’t list enabled services?
systemctl | grep running do not list anything to me! Even if something is running is only listed as for his status like: enabled, disabled, masked, static
—state=
The argument should be a comma-separated list of unit LOAD , SUB , or ACTIVE states. When listing units, show only those in the specified states. Use —state=failed to show only failed units.
LOAD : Reflects whether the unit definition was properly loaded.
ACTIVE : The high-level unit activation state, i.e. generalization of SUB .
SUB : The low-level unit activation state, values depend on unit type.
Though you can also use this to only show enabled units with:
systemctl list-unit-files --state=enabled If a unit is enabled that means that the system will start it on startup. Though setting something to enabled doesn’t actually also start it so you will need to do that manually, or reboot the system after setting it to enabled .
How to List All Running Services Under Systemd in Linux
Linux systems provide a variety of system services (such as process management, login, syslog, cron, etc.) and network services (such as remote login, e-mail, printers, web hosting, data storage, file transfer, domain name resolution (using DNS), dynamic IP address assignment (using DHCP), and much more).
Technically, a service is a process or group of processes (commonly known as daemons) running continuously in the background, waiting for requests to come in (especially from clients).
Linux supports different ways to manage (start, stop, restart, enable auto-start at system boot, etc.) services, typically through a process or service manager. Most if not all modern Linux distributions now use the same process manager: systemd.
Systemd is a system and service manager for Linux; a drop-in replacement for the init process, which is compatible with SysV and LSB init scripts, and the systemctl command is the primary tool to manage systemd.
In this guide, we will demonstrate how to list all running services under systemd in Linux.
Listing Running Services Under SystemD in Linux
When you run the systemctl command without any arguments, it will display a list of all loaded systemd units (read the systemd documentation for more information about systemd units) including services, showing their status (whether active or not).
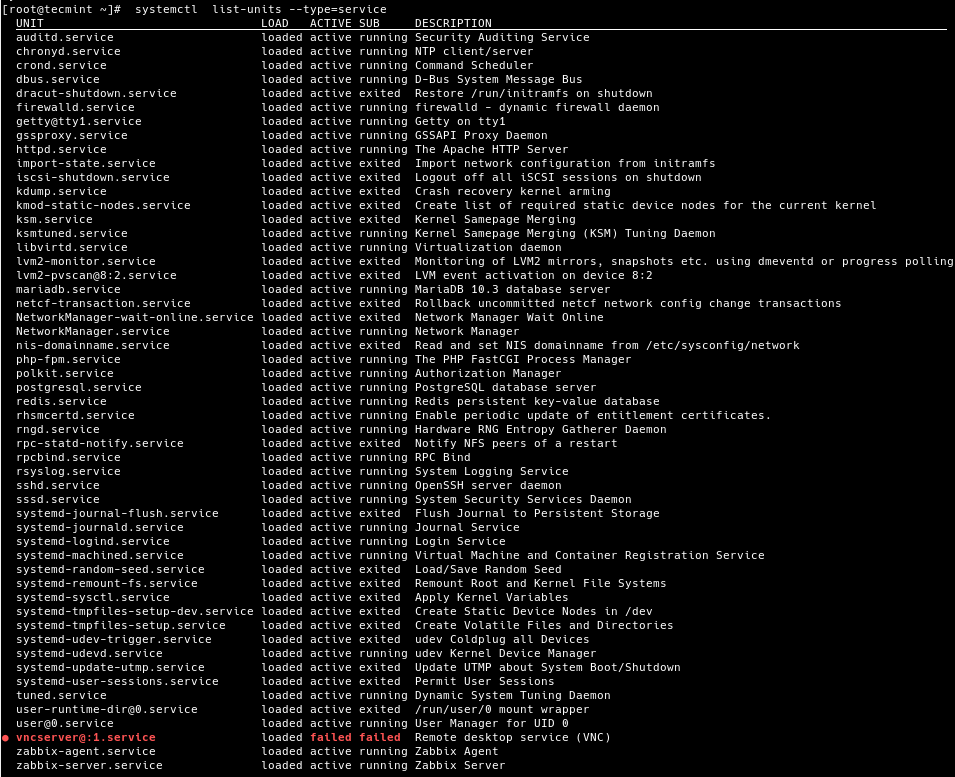
To list all loaded services on your system (whether active; running, exited, or failed, use the list-units subcommand and —type switch with a value of service.
# systemctl list-units --type=service OR # systemctl --type=service
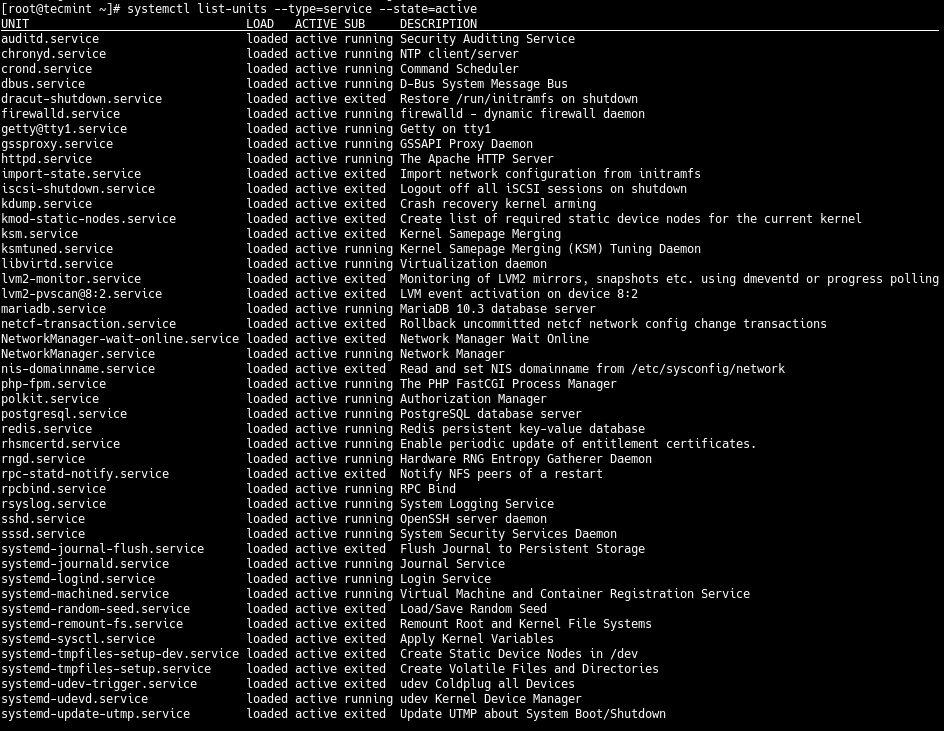
And to list all loaded but active services, both running and those that have exited, you can add the —state option with a value of active, as follows.
# systemctl list-units --type=service --state=active OR # systemctl --type=service --state=active
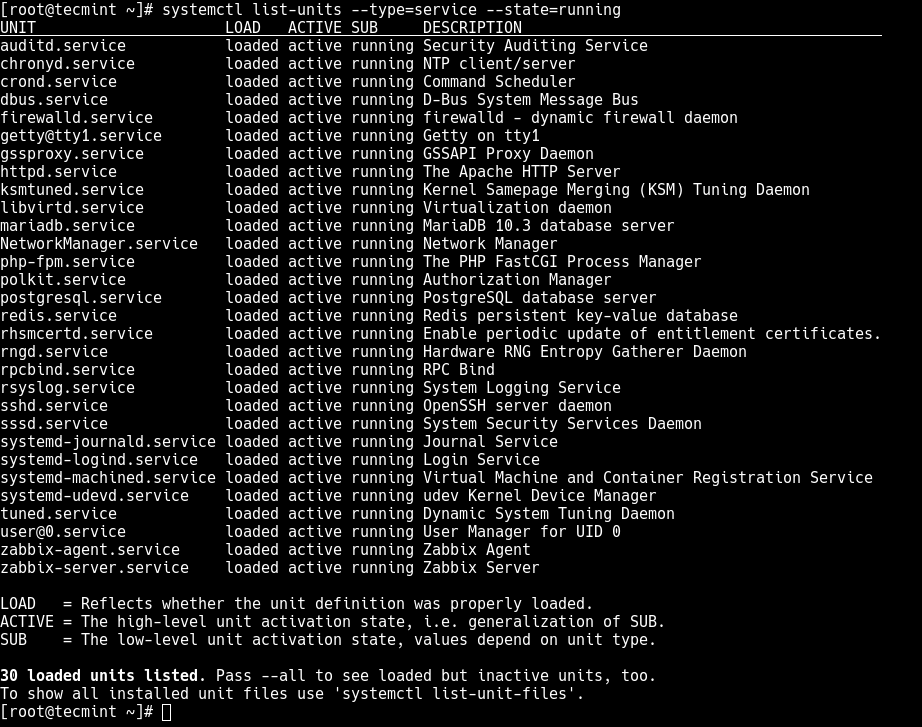
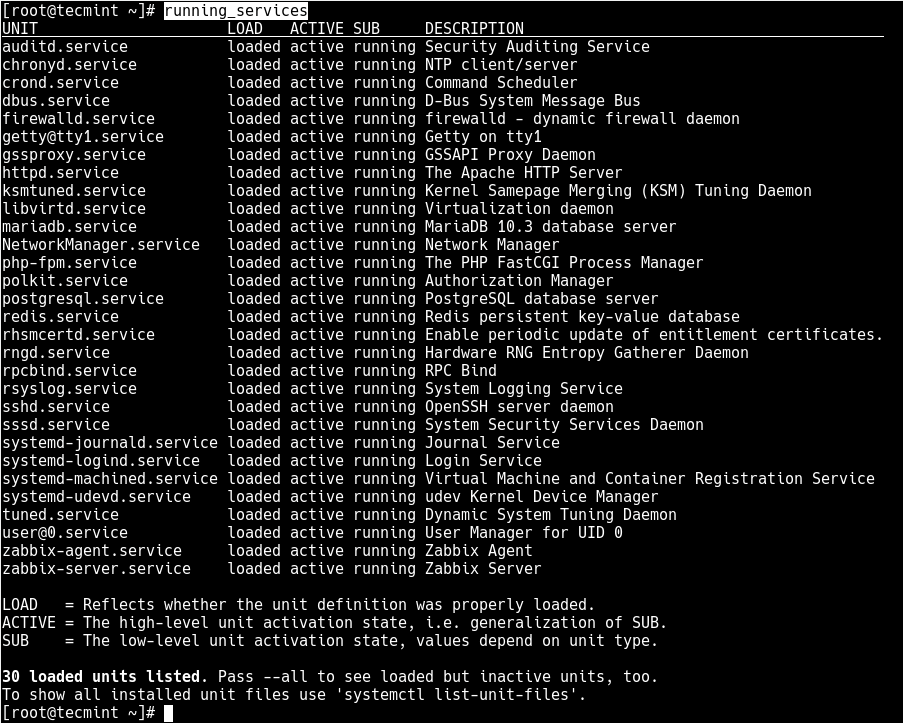
But to get a quick glance at all running services (i.e. all loaded and actively running services), run the following command.
# systemctl list-units --type=service --state=running OR # systemctl --type=service --state=running
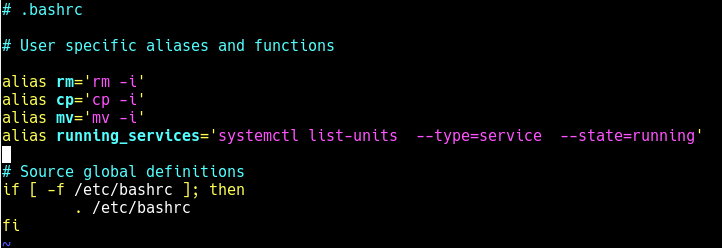
If you frequently use the previous command, you can create an alias command in your ~/.bashrc file as shown, to easily invoke it.
Then add the following line under the list of aliases as shown in the screenshot.
alias running_services='systemctl list-units --type=service --state=running'
Save the changes in the file and close it. And from now onwards, use the “running_services” command to view a list of all loaded, actively running services on your server.
# running_services #use the Tab completion
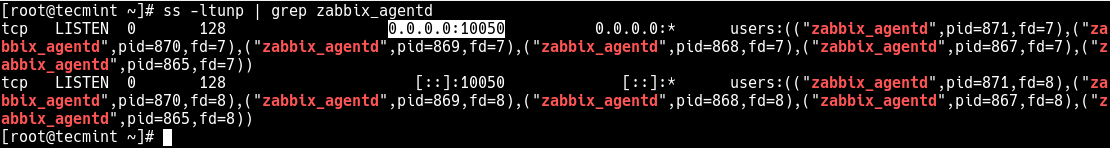
Besides, an important aspect of services is the port they use. To determine the port a daemon process is listening on, you can use the netstat or ss command as shown.
Where the flag -l means print all listening sockets, -t displays all TCP connections, -u shows all UDP connections, -n means print numeric port numbers (instead of application names) and -p means show the application name.
# netstat -ltup | grep zabbix_agentd OR # ss -ltup | grep zabbix_agentd
The fifth column shows the socket: Local Address:Port. In this case, the process zabbix_agentd is listening on port 10050.
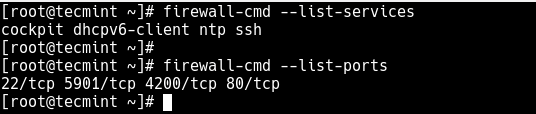
Also, if your server has a firewall service running, which controls how to block or allow traffic to or from selected services or ports, you can list services or ports that have been opened in the firewall, using the firewall-cmd or ufw command (depending on the Linux distributions you are using) as shown.
# firewall-cmd --list-services [FirewallD] # firewall-cmd --list-ports $ sudo ufw status [UFW Firewall]
That’s all for now! In this guide, we demonstrated how to view running services under systemd in Linux. We also covered how to check the port service is listening on and how to view services or ports opened in the system firewall.
Do you have any additions to make or questions? If yes, reach us using the comment form below.
Listing Linux Services With Systemctl
A variety of services run continuously on a Linux background, such as network and system services. Services running on Linux are also known as daemons, which refers to a group of processes working on the back-end.
Services can be managed and listed through different methods and tools. The Systemd is a software suite of tools with the ability to manage Linux systems adopted by Linux distribution as a drop-in replacement of the init process.
All system tasks can be controlled through Systemd. The process can be started or ended using this tool, and all enabled and disabled services information can also be listed with Systemd.
List Services Using Systemctl in Linux
Systemctl is a utility with the responsibility to manage and control the systemd system. The systemctl command can be used to list all services in Linux.
We will now show you how systemctl works.
List All Services
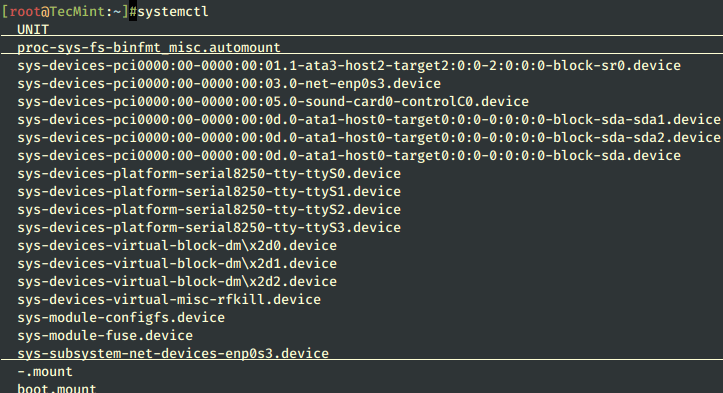
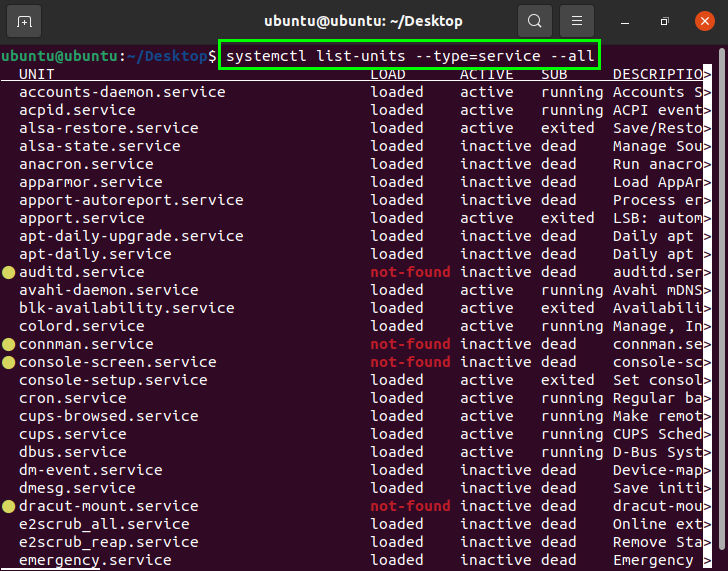
To get a list of all the services on the system, whether they are loaded or inactive, issue the following systemctl command in the terminal:
All services in your system will appear on the screen, as you can see in the output shown in the image above.
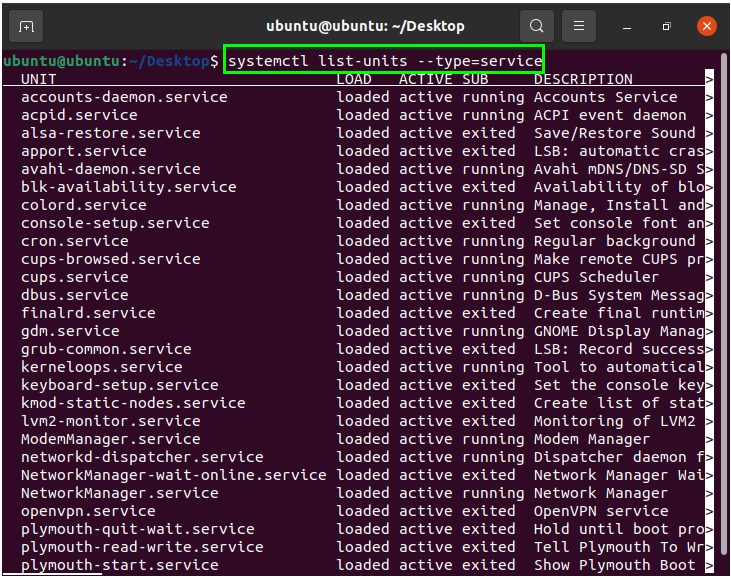
List Loaded Services
The following command will list every loaded service that is running, active, or failed:
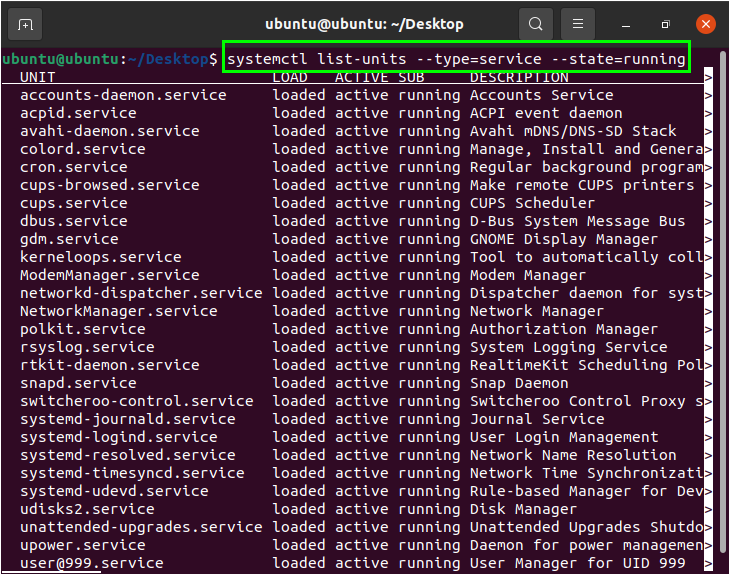
Running Services
In many cases, it can be difficult to distinguish the running services from all the other services. Run the following command to obtain a quick response that shows the loaded and running services in the system:
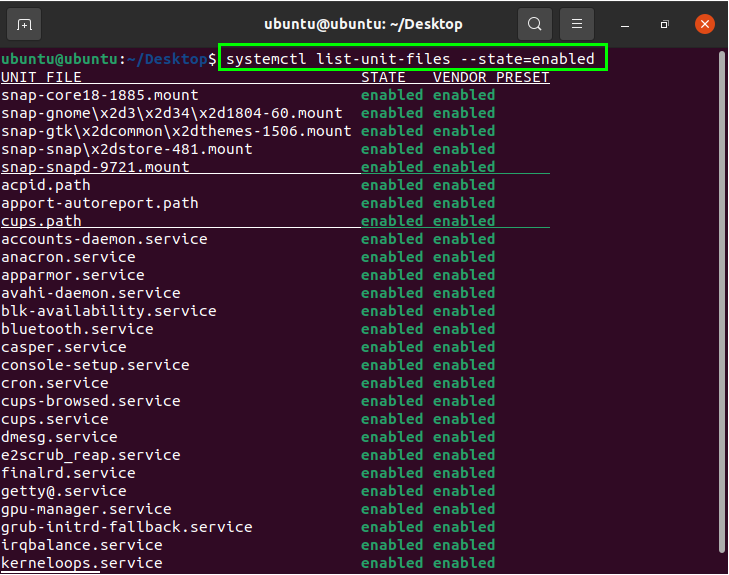
Enabled Services
Enter the following command to check the enabled services in the system:
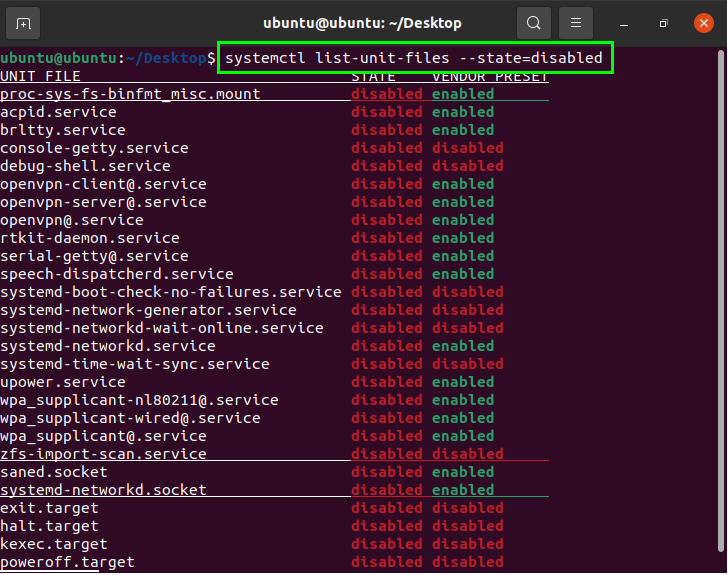
Disabled Services
Disabled services will not start up or activate automatically. To enable a desired/required service, select the service from the disabled category. The following command is used to obtain a list of the disabled services in the system:
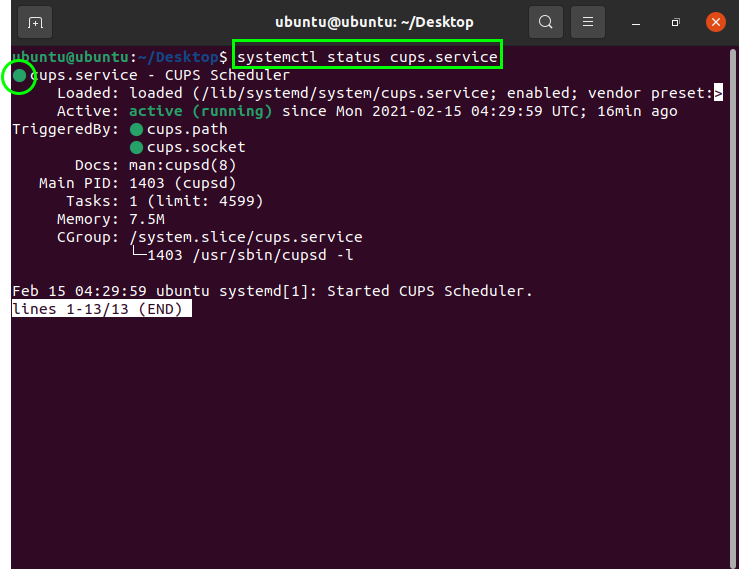
Check Service Status
The “cup” command is used to obtain more information about the status of a service. Cup is a modular printing system through which the computer acts as a print server and displays information. Use the cups command to obtain more information about the enabled/disabled services in the system:
Where are systemctl service files
Systemd configuration files are stored in specific directories. There are System unit directories and User unit directories.
You can find the location of the System Unit and User Unit directories using the pkg-config systemd command.
Run the following commands to find the directories on your system:
$ pkg-config systemd —variable =systemdsystemunitdir
$ pkg-config systemd —variable =systemduserunitdir
You can browse to these directories and see the systemd unit files.
Conclusion
This article showed you how to use systemctl commands to list services in Linux, including multiple options for viewing the services. With the correct knowledge, it is easy to pick the required command.
About the author
Syeda Wardah Batool
I am a Software Engineer Graduate and Self Motivated Linux writer. I also love to read latest Linux books. Moreover, in my free time, i love to read books on Personal development.