This post and this website contains affiliate links. See my disclosure about affiliate links.
how to list all running services in linux from command line
In operating system talk, a service is an application that can be run in the background, usually in perpetuity in order to perform some task or waiting for service requests from other applications to perform tasks. All operating systems, including Linux has some kind of support for these type of applications. Services are also sometimes referred to as daemons.
There are different services that are required for the functioning of an operating system, while others are used by the user. Some common examples of user services are web servers such as Apache or Nginx and database servers such as Oracle or MySql. Some examples of OS specific services are dbus, xdm, network etc.
Most Linux systems have a similar implementation when it comes to running services, but there are still some differences between distros. Many distros also comes with some easy to use GUI applications that allow you to view and manage system services, but not all. We will look at how this can be done from the command prompt.
I should confess that I have exclusively used and worked on Gentoo and have not been keeping up much with the other distros. So, it is quite possible that this post will skew more towards Gentoo but i will try to keep it as generic as possible.
This post solely deals with how to list all services that you are installed or are running on your system. It does not deal with how add, delete or manage the services. I will probably write another post to deal with those functions. I will however describe how to find the status of the service as well, as that somehow corresponds to the reason you might be listing them in the first place.
Systemd or SysV Init/OpenRC
Despite some difference with the commands used to manage the service, most Linux systems have one thing in common. It stores the service related files in the /etc/ folder. The startup scripts for the services are usually in the /etc/init.d/ folder. You might also want to check the /etc/rc.d folder if you do not find the init.d/ folder.
As your system starts up, there needs to be a program or application that finds and launches appropriate drivers and start services. The old and tried system has been SysV init which mainly loaded and ran the startup scripts from /etc/init.d folder. Systemd is a modern day replacement for init and is being adopted by many distros.
It is important that you be aware of what boot system you have, which will help you with finding the startup scripts. A detailed discussion on that topic is probably not for this post.
How to List all Services
As mentioned earlier, most systems keep the startup scripts for the services in the /etc/init.d/ folder. So, a simple listing of the directory contents should show you the list of services that are installed and available to you.
How to List All Running Services Under Systemd in Linux
Linux systems provide a variety of system services (such as process management, login, syslog, cron, etc.) and network services (such as remote login, e-mail, printers, web hosting, data storage, file transfer, domain name resolution (using DNS), dynamic IP address assignment (using DHCP), and much more).
Technically, a service is a process or group of processes (commonly known as daemons) running continuously in the background, waiting for requests to come in (especially from clients).
Linux supports different ways to manage (start, stop, restart, enable auto-start at system boot, etc.) services, typically through a process or service manager. Most if not all modern Linux distributions now use the same process manager: systemd.
Systemd is a system and service manager for Linux; a drop-in replacement for the init process, which is compatible with SysV and LSB init scripts, and the systemctl command is the primary tool to manage systemd.
In this guide, we will demonstrate how to list all running services under systemd in Linux.
Listing Running Services Under SystemD in Linux
When you run the systemctl command without any arguments, it will display a list of all loaded systemd units (read the systemd documentation for more information about systemd units) including services, showing their status (whether active or not).
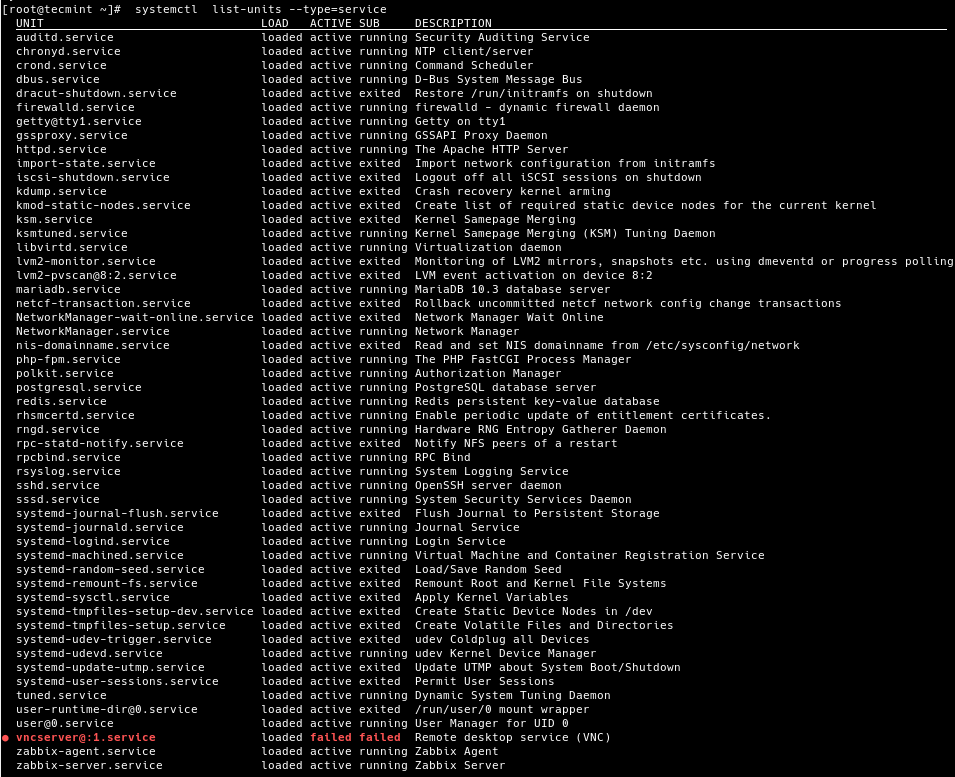
To list all loaded services on your system (whether active; running, exited, or failed, use the list-units subcommand and —type switch with a value of service.
# systemctl list-units --type=service OR # systemctl --type=service
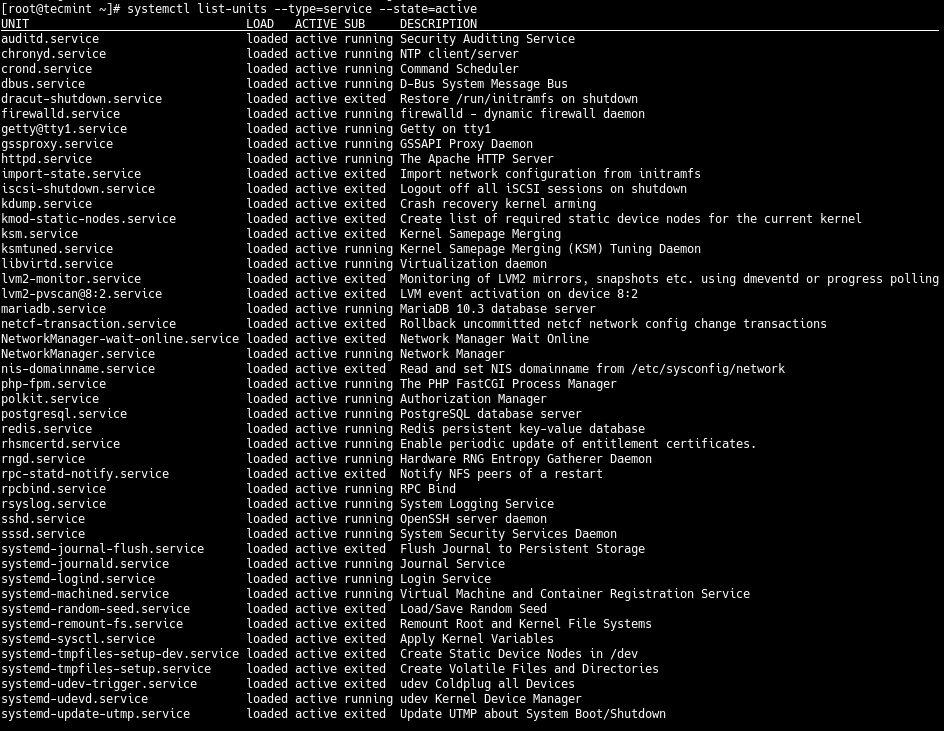
And to list all loaded but active services, both running and those that have exited, you can add the —state option with a value of active, as follows.
# systemctl list-units --type=service --state=active OR # systemctl --type=service --state=active
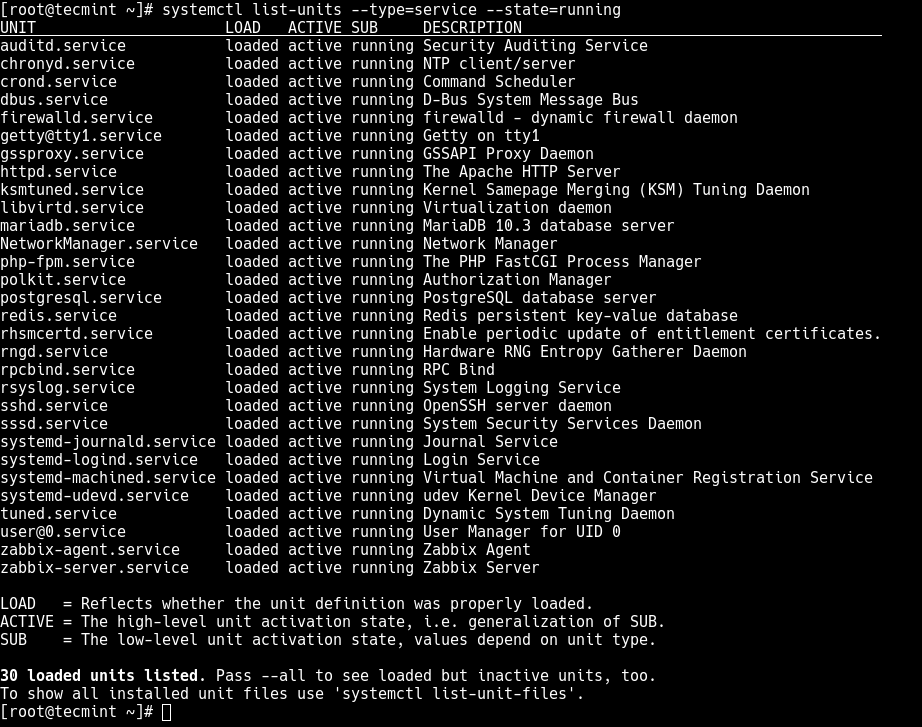
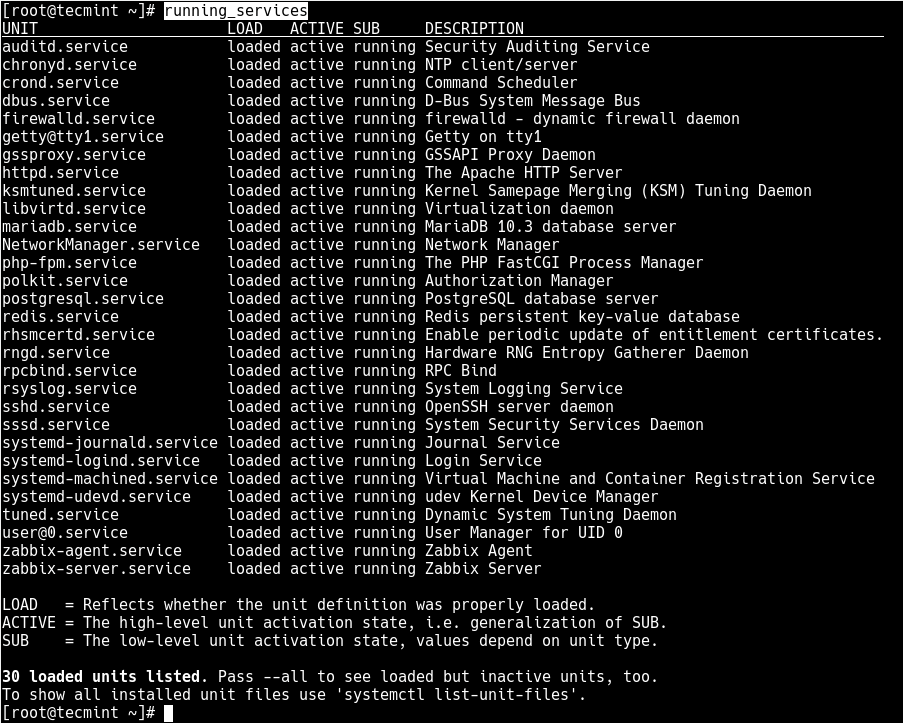
But to get a quick glance at all running services (i.e. all loaded and actively running services), run the following command.
# systemctl list-units --type=service --state=running OR # systemctl --type=service --state=running
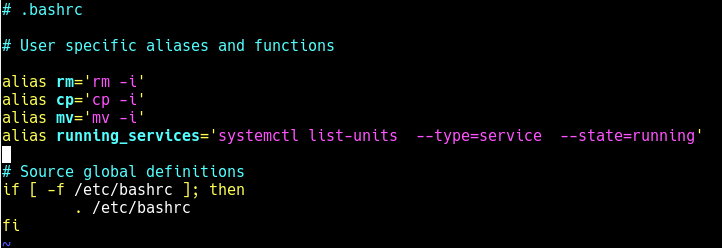
If you frequently use the previous command, you can create an alias command in your ~/.bashrc file as shown, to easily invoke it.
Then add the following line under the list of aliases as shown in the screenshot.
alias running_services='systemctl list-units --type=service --state=running'
Save the changes in the file and close it. And from now onwards, use the “running_services” command to view a list of all loaded, actively running services on your server.
# running_services #use the Tab completion
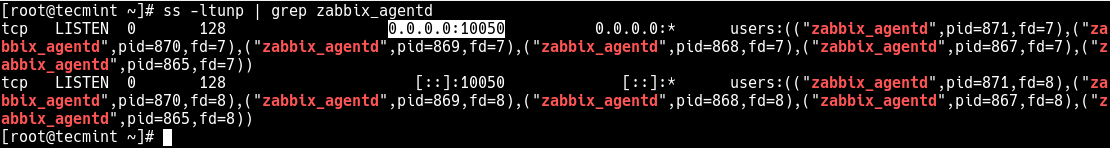
Besides, an important aspect of services is the port they use. To determine the port a daemon process is listening on, you can use the netstat or ss command as shown.
Where the flag -l means print all listening sockets, -t displays all TCP connections, -u shows all UDP connections, -n means print numeric port numbers (instead of application names) and -p means show the application name.
# netstat -ltup | grep zabbix_agentd OR # ss -ltup | grep zabbix_agentd
The fifth column shows the socket: Local Address:Port. In this case, the process zabbix_agentd is listening on port 10050.
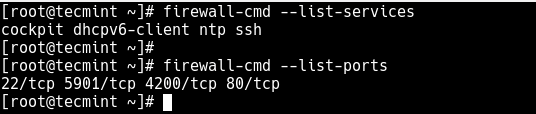
Also, if your server has a firewall service running, which controls how to block or allow traffic to or from selected services or ports, you can list services or ports that have been opened in the firewall, using the firewall-cmd or ufw command (depending on the Linux distributions you are using) as shown.
# firewall-cmd --list-services [FirewallD] # firewall-cmd --list-ports $ sudo ufw status [UFW Firewall]
That’s all for now! In this guide, we demonstrated how to view running services under systemd in Linux. We also covered how to check the port service is listening on and how to view services or ports opened in the system firewall.
Do you have any additions to make or questions? If yes, reach us using the comment form below.
List Running Services on Linux:(Ubuntu,Debian,CentOS)
As a Linux user, you will need to list running services on Linux at some point. However, you cannot go for the Windows approach and press Ctrl + Alt + Delete! So, what can you do?
Linux is a powerful open-source software system that was first released in 1991. It is based on the Unix operating system and has been used on a wide range of devices, from smartphones to supercomputers. Linux is known for its reliability, flexibility, and security features. It can be used as a standalone operating system or as part of a larger networked system.
People use Linux as a service and list running services Linux because it has several advantages. First, it can be managed remotely, making it ideal for use in distributed systems. Second, it can be used for applications that must run continuously or at high loads. Third, running Linux as a service takes advantage of virtualization technologies to create isolated environments for servers. Finally, it can be cost-effective because you do not need to purchase or maintain hardware separately.
Linux offers users many great features, including the ability to list running services. This feature allows users to see what services are currently active on their system and can help identify any potential issues. When you list running services Linux, you can troubleshoot and fix any problems that may be occurring and keep your systems running smoothly and without any hassle.
There are many different Linux distributions that can be used to run services. Each distribution has its own advantages and disadvantages. Some of the most popular distributions are Debian, Ubuntu, CentOS, and Fedora.
When choosing a distribution, it is important to consider the needs of the application. For example, if the application requires a specific version of Python or Ruby, then the distribution must support that version. Otherwise, the application may not work properly.
Running services on Linux can be a hard and daunting task. Whether you’re looking to list all running services Linux or just get an idea of what’s going on, there are a few ways to do it.
This guide will show you the best way to list running services Linux on each distribution and desktop environment.