- How to view all installed packages in terminal (Ubuntu)
- How to Check if a Package is Available In Yum
- Yum List Available Packages
- Yum Check Installed Packages
- Yum Search Specific Package
- Show Available Packages From A Specific Repo
- Conclusion
- About the author
- John Otieno
- How To List All Packages In A Repository On Ubuntu, Debian Or Linux Mint [APT]
- List all packages in a Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint repository using a GUI
- List all packages in a repository in Ubuntu, Debian or Linux Mint from the command line
How to view all installed packages in terminal (Ubuntu)
dpkg-query actions See dpkg-query(1) for more information about the following actions.
-l, --list package-name-pattern. List packages matching given pattern. -s, --status package-name. Report status of specified package. -L, --listfiles package-name. List files installed to your system from package-name. -S, --search filename-search-pattern. Search for a filename from installed packages. -p, --print-avail package-name. Display details about package-name, as found in /var/lib/dpkg/available. Users of APT-based frontends should use apt-cache show package-name instead. To list packages installed only by you:
gunzip -c /var/log/apt/history.log.*.gz | grep 'apt-get install' | cut -f4- -d" " | tr ' ' $'\n' | sort -u Solution: In order to view all installed packages in linux Ubuntu, run on terminal apt —installed list ,
Use apt flags and would be able to see available upgrades to some packages ( —upgradeable ) / current installed packages ( —installed ) / all available versions ( —all-versions ).
From Documentation:
DESCRIPTION apt provides a high-level commandline interface for the package management system. It is intended as an end user interface and enables some options better suited for interactive usage by default compared to more specialized APT tools like apt-get(8) and apt-cache(8). Much like apt itself, its manpage is intended as an end user interface and as such only mentions the most used commands and options partly to not duplicate information in multiple places and partly to avoid overwhelming readers with a cornucopia of options and details. the list flag offers 3 options:
list (work-in-progress) list is somewhat similar to dpkg-query --list in that it can display a list of packages satisfying certain criteria. It supports glob(7) patterns for matching package names as well as options to list installed (--installed), upgradeable (--upgradeable) or all available (--all-versions) versions. How to Check if a Package is Available In Yum
Yellowdog Updater Modified or Yum for short is a package management tool for RPM packages. It is popular in the REHL family of Linux distributions, including CentOS and Fedora. Thus, you can think of yum as a bootstrap for RPM package manager.
Like popular package managers, Yum works via repositories that contain collections of tools in rpm format.
For this quick one, we will discuss the basics of yum and show available packages on a system using yum as a package manager.
Yum List Available Packages
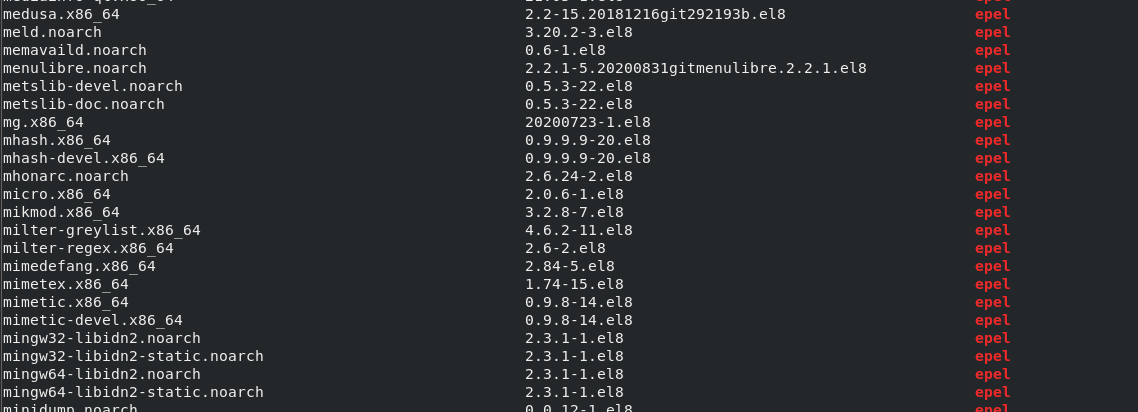
To show available packages, we can use the yum list command as shown:
This command will display the name of all the available packages, the latest version, and the repositories to which they belong
Yum Check Installed Packages
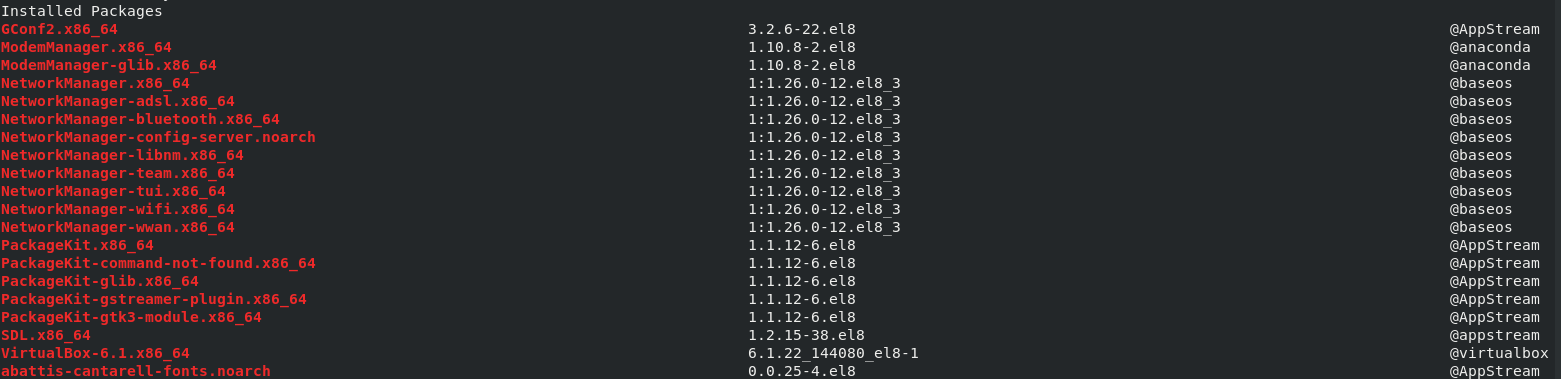
Yum is incredibly easy to use; like most package managers, it allows you to pass intuitive options. For example, to show the list of installed packages, we can use the command:
Similar to show available packages, the command above will show the name of the packages installed, the version, and the source repository of the packages
You can pass the output from the command above to tools such as grep, less, etc.
Yum Search Specific Package
An example use case of the yum list command is checking if you have a specific package installed. For example, let us see if awk is installed.
The above command passes the output of the yum list to grep, which then searches for the specific string, in this case, ‘awk.’ Take a look at the example output below:
As you can see, we have awk installed (as part of gawk) and the python-Hawkey package.
Show Available Packages From A Specific Repo
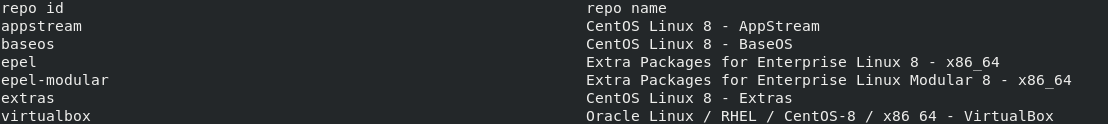
You can also filter for the available package in a specific repository. We can start by listing all enabled repositories with the command:
This will list all the available repositories in the system.
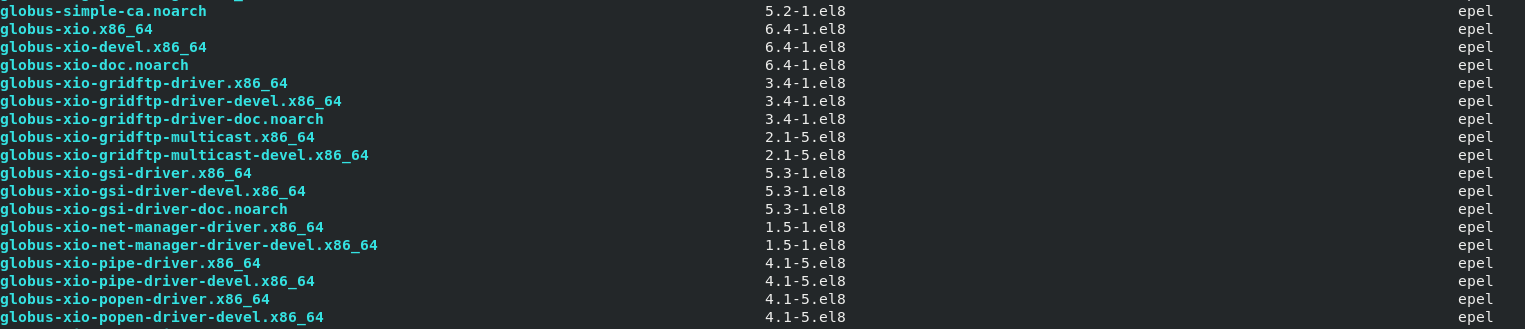
To search for packages available only in a specific repo. An example, in the epel repository, we use the command:
Example output is as shown:
Conclusion
In this quick tutorial, we covered yum and showed the available and installed packages in the system.
About the author
John Otieno
My name is John and am a fellow geek like you. I am passionate about all things computers from Hardware, Operating systems to Programming. My dream is to share my knowledge with the world and help out fellow geeks. Follow my content by subscribing to LinuxHint mailing list
How To List All Packages In A Repository On Ubuntu, Debian Or Linux Mint [APT]
This article explains how to list all the packages available in an Ubuntu, Linux Mint or Debian repository (installed and available for install), be it an official repository or a third-party source like a PPA, and so on.
Below you’ll find 2 ways of listing packages from a repository: using a GUI or from the command line.
List all packages in a Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint repository using a GUI
If you want to list all the packages in a repository on your desktop, you can use Synaptic Package Manager.
Synaptic is a graphical package management application for APT (APT being the main command line package manager for Debian and its derivatives).
If you don’t have Synaptic installed, you can install it on Debian, Ubuntu, and any Debian or Ubuntu based Linux distribution, including elementary OS, Linux Mint and so on, by using this command:
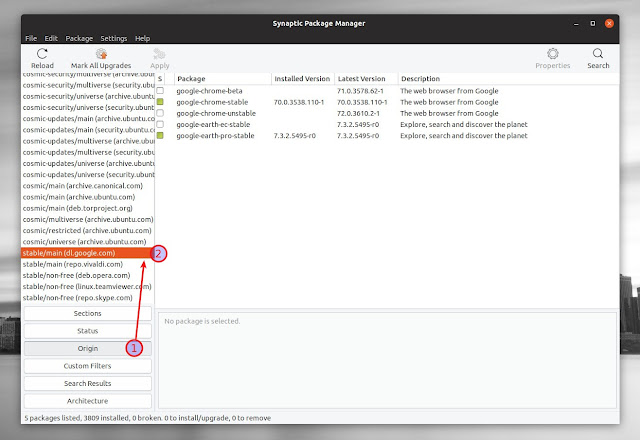
sudo apt install synapticTo list all the packages in a particular software repository using Synaptic, launch the application and click on Origin in the bottom left-hand side of its window. Next, select the repository for which you want to list all available packages (both installed and available for installation) from the list that’s displayed in the left-hand side of Synaptic Package Manager.
For example, here’s Synaptic showing all the packages available in the Google repository, listing Google Chrome stable, beta and unstable, as well as Google Earth Pro and EC:
As you can see, all the software sources are listed here, including the official repositories.
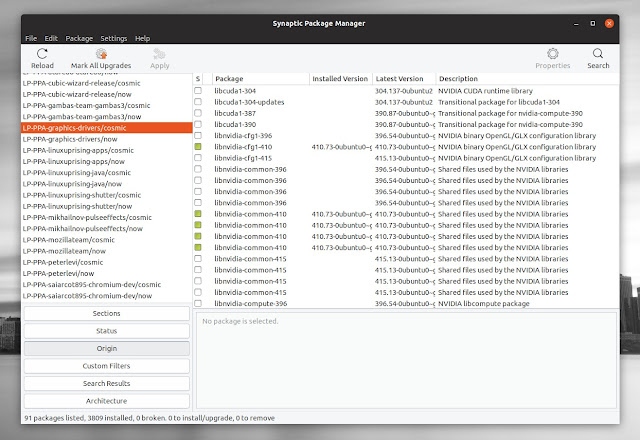
Launchpad PPA repositories are supported as well. Their name begins with LP-PPA, followed by the actual PPA name. Synaptic lists 2 entries for each PPA — make sure you select the PPA entry ending with /ubuntu-codename , for example /bionic , /cosmic , etc. The entry ending in /now doesn’t list all the available packages in the PPA.
This is a screenshot showing all the packages available in the Ubuntu Graphics Drivers PPA (for Ubuntu 18.10 Cosmic Cuttlefish, since that’s what I’m using), including showing which are installed on my system:
I’m not sure why, but some packages are listed multiple times for PPA sources (and only for PPA repositories). That only a display thing, and it doesn’t break any functionality.
List all packages in a repository in Ubuntu, Debian or Linux Mint from the command line
Listing all packages in a repository from the command line in Ubuntu, Debian or Linux Mint is a bit tricky, but still quite easy to do.
There are multiple ways of doing this from the command, but I’ll only list one. The command to list all packages available in repository-name is the one that follows:
grep ^Package /var/lib/apt/lists/repository-name*_Packages | awk '' | sort -uI’ll explain later on how to find out the repository name from /var/list/apt/lists and how to use it. Before that I’ll explain what this command does:
- grep ^Package . searches for lines beginning with ^Package in the /var/lib/apt/lists/*_Packages file
- awk » prints the second column for each line (so it filters out everything but the package name)
- sort -u sorts the lines and outputs only unique lines (removes duplicates)
ls /var/lib/apt/lists/*_PackagesSince the results may be very long, you can run the command output through more for easier reading:
ls /var/lib/apt/lists/*_Packages | moreIf you know part of the repository name (I’m using KEYWORD in the command below as the name), you can filter the ls results using grep , like this:
ls /var/lib/apt/lists/*_Packages | grep KEYWORDFor example, let’s say you want to list all the packages in the official Tor repository, and you know the repository name must contain tor . In this case, you’d use this command to find out the _Packages filename from /var/lib/apt/lists/
ls /var/lib/apt/lists/*_Packages | grep torFor short queries, some unrelated repositories might be displayed, but it’s still easier to see what you’re looking for using grep than listing all the repositories _Packages files.
Now that you know the _Packages filename, you can list all the packages available in that repository by issuing this command:
grep ^Package /var/lib/apt/lists/some-repository-amd64_Packages | awk '' | sort -uUse the file containing the architecture for which you want to list all available packages in that repository. The example above is for 64bit ( amd64 ), but you could use i386 for 32bit, etc.
You don’t need the complete repository _Packages filename. Back to my Tor repository example, the _Packages filename for Tor is deb.torproject.org_torproject.org_dists_cosmic_main_binary-amd64_Packages . In this case, you could use deb.torproject followed by *_Packages to simplify things, like this:
grep ^Package /var/lib/apt/lists/deb.torproject*_Packages | awk '' | sort -uWhich outputs the following:
deb.torproject.org-keyring tor tor-geoipdbAnother example. Let’s say you want to see all packages available in the Linux Uprising Oracle Java 11 PPA ( ppa:linuxuprising/java ). You can list them by using:
grep ^Package /var/lib/apt/lists/ppa.launchpad.net_linuxuprising_java*_Packages | awk '' | sort -uoracle-java11-installer oracle-java11-set-defaultTo use this with other PPA repositories, replace linuxuprising with the first part of the PPA name, and java with the second part of the PPA name, and the command will list all the packages from that PPA (both installed and not installed).
You can also list all the packages available in all the PPA repositories you have added on your system, by using:
grep ^Package /var/lib/apt/lists/ppa.launchpad.net*_Packages | awk '' | sort -uFor easy access, you could bookmark this command using Marker commands bookmark manager (while used primarily for searching, HSTR can bookmark commands as well).