- List files over a specific size in current directory and all subdirectories
- 5 Answers 5
- How to List or Sort All Files by Size in Linux
- List or Sort All Files by Size in Linux
- List All Files Ordered by Size
- List or Sort Files by Size According to a Specific File Type
- Exclude Directories When Listing or Sorting Files by Size
- List or Sort All Files Using a Common Unit Size
- How to List All Files Ordered by Size in Linux
- The Linux LS Command – How to List Files in a Directory + Option Flags
- Prerequisites
- The Linux ls Command
- How to list Files in a Directory with Options
- List files in the current working directory
- List files in another directory
- List files in the root directory
- List files in the parent directory
- List files in the user’s home directory (/home/user)
- List only directories
- List files with subdirectories
- List files recursively
- List files with their sizes
- List files in long format
- List files in long format with readable file sizes
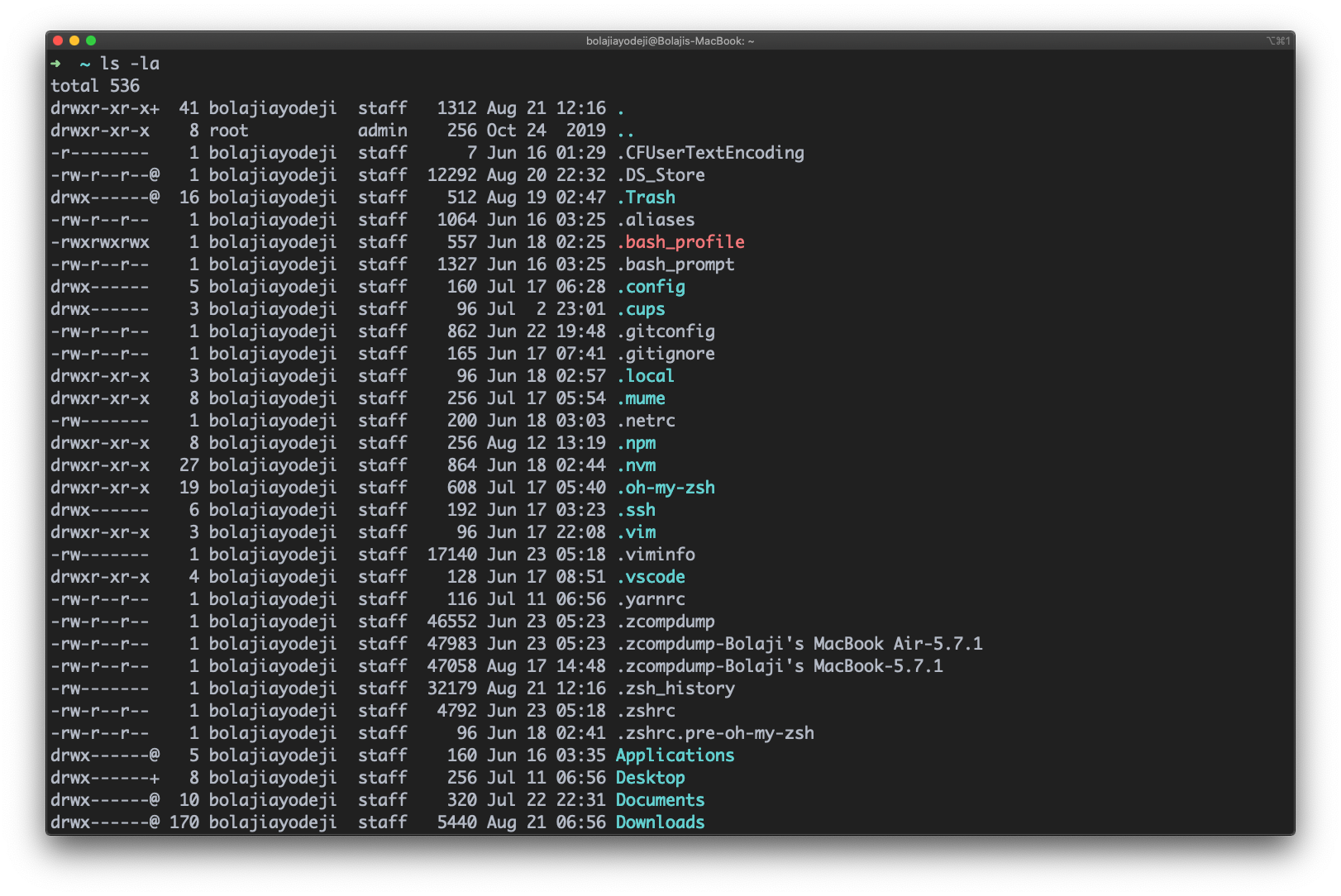
- List files including hidden files
- List files in long format including hidden files
- List files and sort by date and time
- List files and sort by file size
- List files and output the result to a file
- Conclusion
List files over a specific size in current directory and all subdirectories
How can I display all files greater than 10k bytes in my current directory and it’s subdirectories. Tried ls -size +10k but that didn’t work.
could you please expand on this question, or at least explain why the two solutions that were posted — and work, are not appropriate to your assignment. (edit: added please)
ls doesn’t have any options to filter output by size. It does have a —size option (with no arguments) which prints the size of each file in blocks. By the way, -size +10k seems like a syntax that is used with find .
Stack Overflow is a site for programming and development questions. This question appears to be off-topic because it is not about programming or development. See What topics can I ask about here in the Help Center. Perhaps Super User or Unix & Linux Stack Exchange would be a better place to ask. Also see Where do I post questions about Dev Ops?
5 Answers 5
find . -size +10k -exec ls -lh <> \+
the first part of this is identical to @sputnicks answer, and sucesffully finds all files in the directory over 10k (don’t confuse k with K), my addition, the second part then executes ls -lh or ls that lists(-l) the files by human readable size(-h). negate the h if you prefer. of course the <> is the file itself, and the \+ is simply an alternative to \;
which in practice \; would repeat or:
ls -l found.file; ls -l found.file.2; ls -l found.file.3
where \+ display it as one statement or:
ls -l found.file found.file.2 found.file.3
Additionaly, you may want the listing ordered by size. Which is relatively easy to accomplish. I would at the -s option to ls , so ls -ls and then pipe it to sort -n to sort numerically
find . -size +10k -exec ls -ls <> \+ | sort -n
or in reverse order add an -r :
find . -size +10k -exec ls -ls <> \+ | sort -nr
finally, your title says find biggest file in directory. You can do that by then piping the code to tail
find . -size +10k -exec ls -ls <> \+ | sort -n | tail -1 would find you the largest file in the directory and its sub directories.
note you could also sort files by size by using -S, and negate the need for sort. but to find the largest file you would need to use head so
find . -size +10k -exec ls -lS <> \+ | head -1
the benefit of doing it with -S and not sort is one, you don’t have to type sort -n and two you can also use -h the human readable size option. which is one of my favorite to use, but is not available with older versisions of ls , for example we have an old centOs 4 server at work that doesn’t have -h
How to List or Sort All Files by Size in Linux
The Linux ls command is a handy tool for listing files inside a directory. In the past, we have covered how to list and sort files by last modification time using the ls command.
In this article, we will go a step further and explore ways that you can list all the files in a specific directory and sort them by file size.
List or Sort All Files by Size in Linux
To list all files contained in a directory, launch your terminal and run the following command. When invoked without any arguments, the ls command simply lists the files and folders inside a directory.
In the following command the -l flag means long listing and -a tells ls to list all files including hidden files – which are prefixed by a period (.) . To avoid displaying the . and .. files, use the -A option instead of -a .
List All Files Ordered by Size
To list all the files and sort them by size, use the -S flag. By default, it displays output in descending order (biggest to smallest in size).
You can display the output in a human-readable format by appending the -h option as shown.
In addition, you can sort in reverse order (from the smallest to the largest) by adding the -r option as shown.
List or Sort Files by Size According to a Specific File Type
You can list or sort out files by size by applying file type as a filter. For example, to list or sort zipped files by size, use the wildcard symbol as shown.
Exclude Directories When Listing or Sorting Files by Size
To exclude directories in listing or sorting files by size, use the following syntax:
List or Sort All Files Using a Common Unit Size
In the above examples, the file sizes have been printed in different unit sizes, i.e Kilobytes (k) and Megabytes (M).
To print or display all file sizes in a specific unit, for example in Megabytes, add the —block-size= option specifying Megabytes as M as shown below.
From the output, you can see the file sizes are now in MB only.
NOTE: For files less than the specified size (in this case MB), the size will be rounded off to the nearest MB. This implies files in Kilobytes and bytes will appear as 1MB. The same will hold true for any specified size.
You can also print the size in KB units by replacing M with k:
This time around, the file sizes are accurately displayed in kilobytes since no file is less than a kilobyte, and hence no rounding off to the nearest kilobyte is done.
Conclusion
And that’s it for this lecture. In this article, we have demonstrated how to list or sort files by size in Linux. We hope you found this information insightful.
How to List All Files Ordered by Size in Linux
In one of our several articles about listing files using the popular ls command, we covered how to list and sort files by last modification time (date and time) in Linux. In this short handy article, we will present a number of useful ls command options to list all of the files in a certain directory and sort them by file size in Linux.
To list all files in a directory, open a terminal window and run the following command. Note that when ls invoked without any arguments, it will list the files in the current working directory.
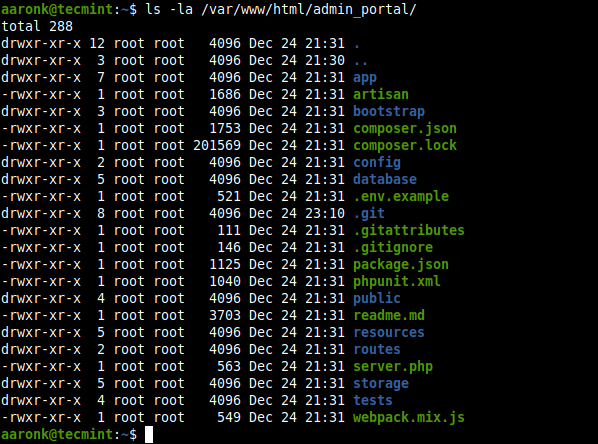
In the following command the -l flag means long listing and -a tells ls to list all files including (.) or hidden files. To avoid showing the . and .. files, use the -A option instead of -a .
$ ls -la OR $ ls -la /var/www/html/admin_portal/
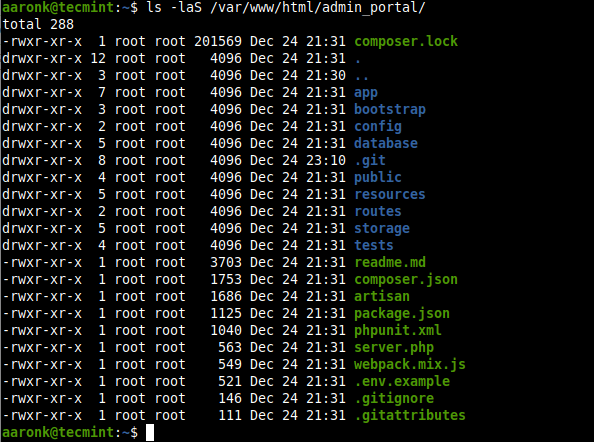
To list all files and sort them by size, use the -S option. By default, it displays output in descending order (biggest to smallest in size).
$ ls -laS /var/www/html/admin_portal/
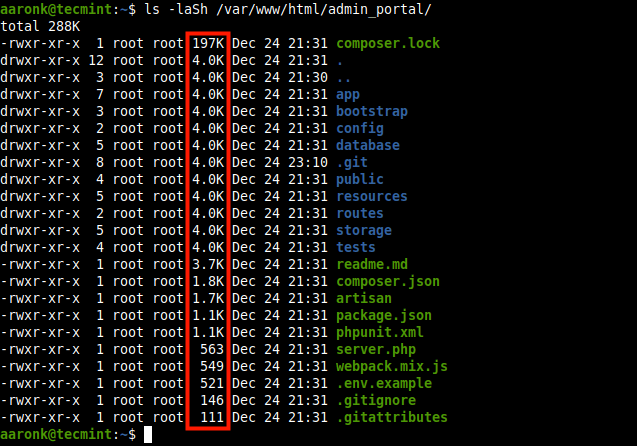
You can output the file sizes in human-readable format by adding the -h option as shown.
$ ls -laSh /var/www/html/admin_portal/
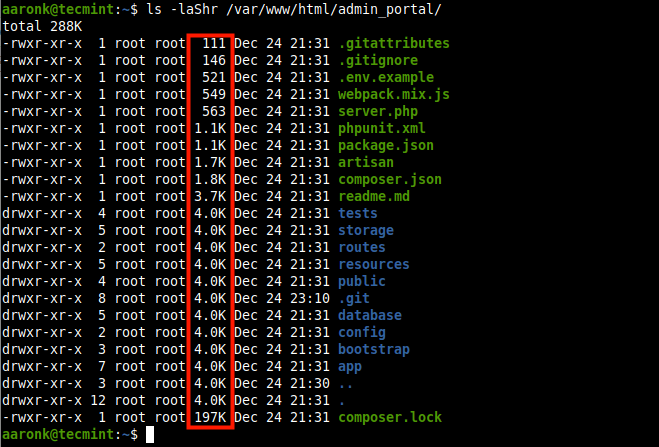
And to sort in reverse order, add the -r flag as follows.
$ ls -laShr /var/www/html/admin_portal/
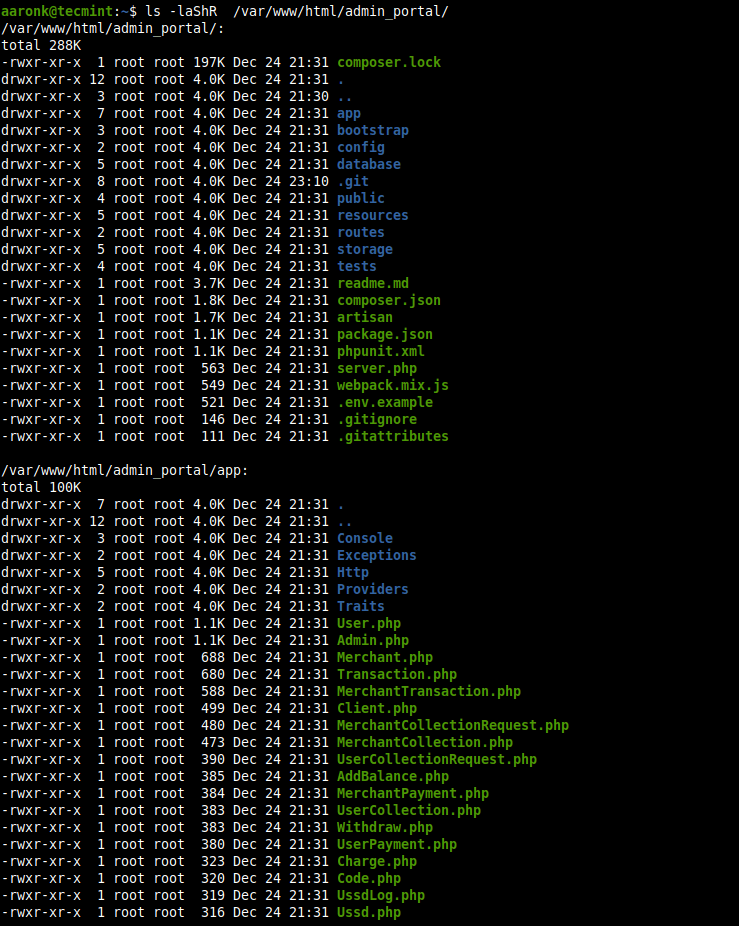
Besides, you can list subdirectories recursively using the -R option.
$ ls -laShR /var/www/html/admin_portal/
You will also find the following related articles useful:
If you any other way to list the files ordered by sizes in Linux, do share with us or do you have questions or thoughts to share about this guide? If yes, reach us via the feedback form below.
The Linux LS Command – How to List Files in a Directory + Option Flags
Bolaji Ayodeji
Since the creation of Unix in the 1970s, a lot of operating systems have used it as their foundation. Many of these operating systems failed, while others succeeded.
Linux is one of the most popular Unix based operating systems. It’s open source, and is used all over the world across many industries.
One amazing feature of the Linux operating system is the Command Line Interface (CLI) which allows users to interact with their computer from a shell. The Linux shell is a REPL (Read, Evaluate, Print, Loop) environment where users can enter a command and the shell runs it and returns a result.
The ls command is one of the many Linux commands that allow a user to list files or directories from the CLI.
In this article, we’ll go in depth on the ls command and some of the most important flags you’ll need day-to-day.
Prerequisites
- A computer with directories and files
- Have one of the Linux distros installed
- Basic knowledge of navigating around the CLI
- A smile on your face 🙂
The Linux ls Command
The ls command is used to list files or directories in Linux and other Unix-based operating systems.
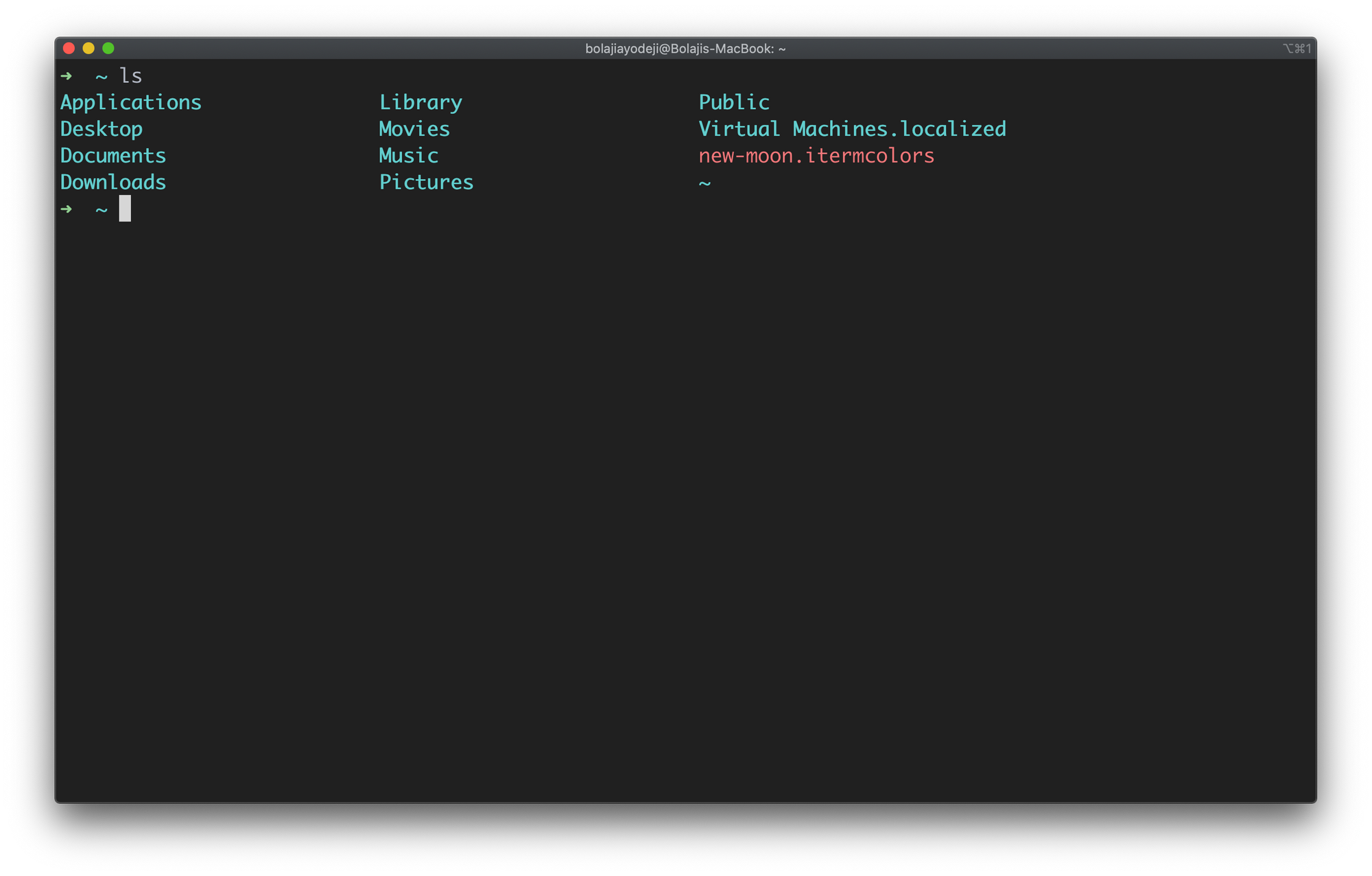
Just like you navigate in your File explorer or Finder with a GUI, the ls command allows you to list all files or directories in the current directory by default, and further interact with them via the command line.
Launch your terminal and type ls to see this in action:
How to list Files in a Directory with Options
The ls command also accepts some flags (also known as options) which are additional information that changes how files or directories are listed in your terminal.
In other words, flags change how the ls command works:
PS: The word contents used in throughout the article refers to the files and directories being listed, not the actual contents of the files/directories ?
List files in the current working directory
Type the ls command to list the contents of the current working directory:
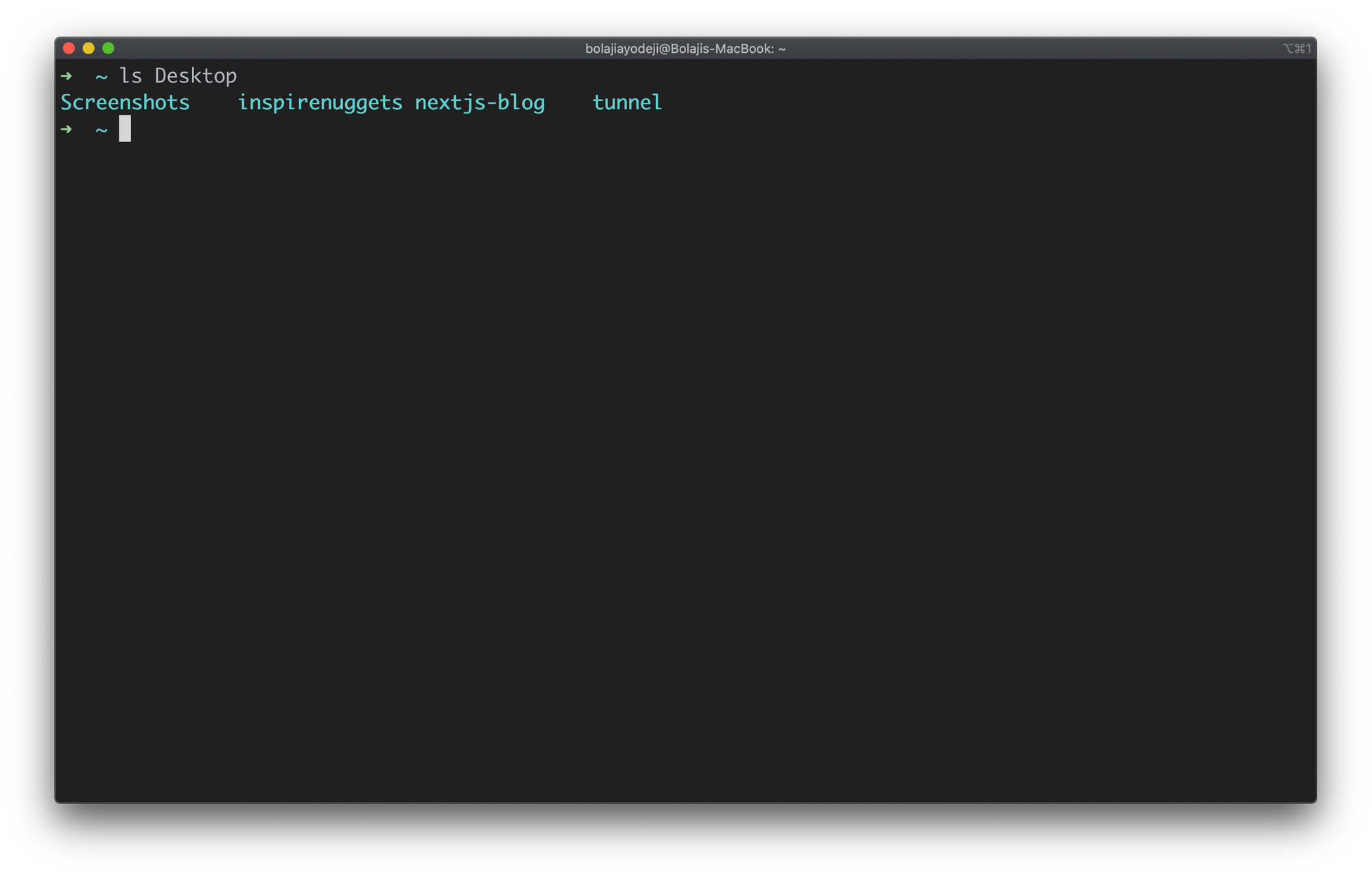
List files in another directory
Type the ls [directory path here] command to list the contents of another directory:
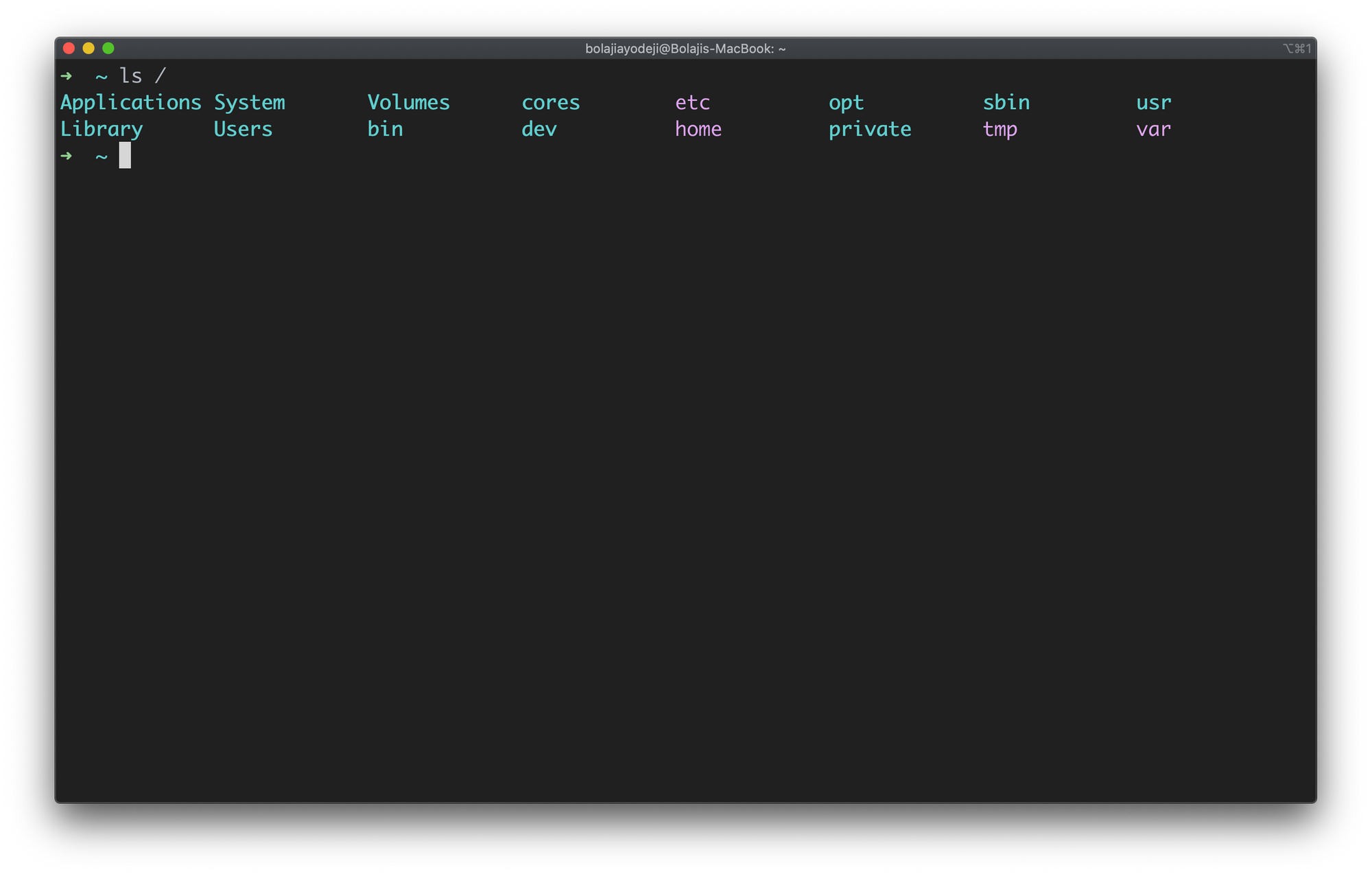
List files in the root directory
Type the ls / command to list the contents of the root directory:
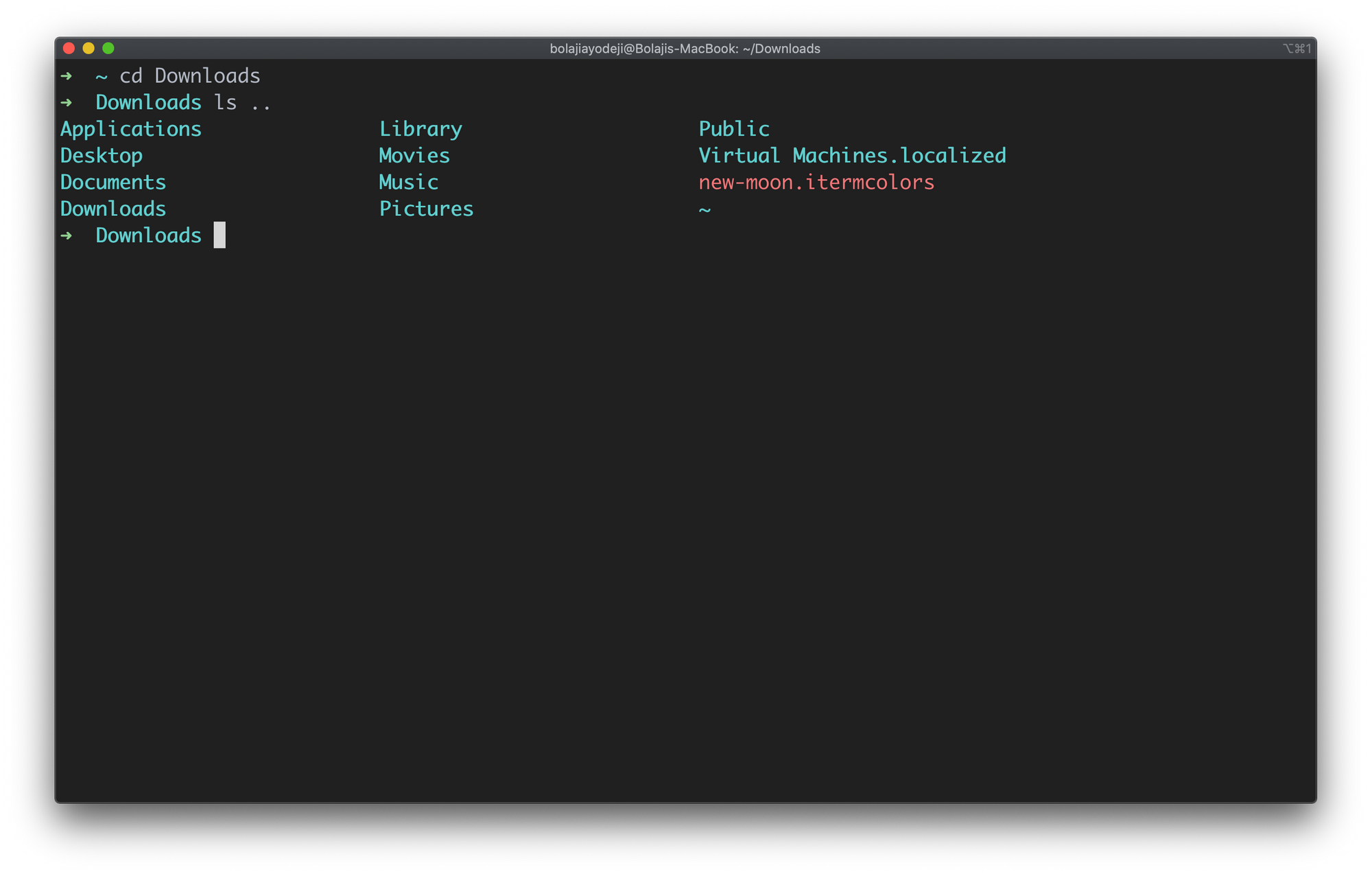
List files in the parent directory
Type the ls .. command to list the contents of the parent directory one level above. Use ls ../.. for contents two levels above:
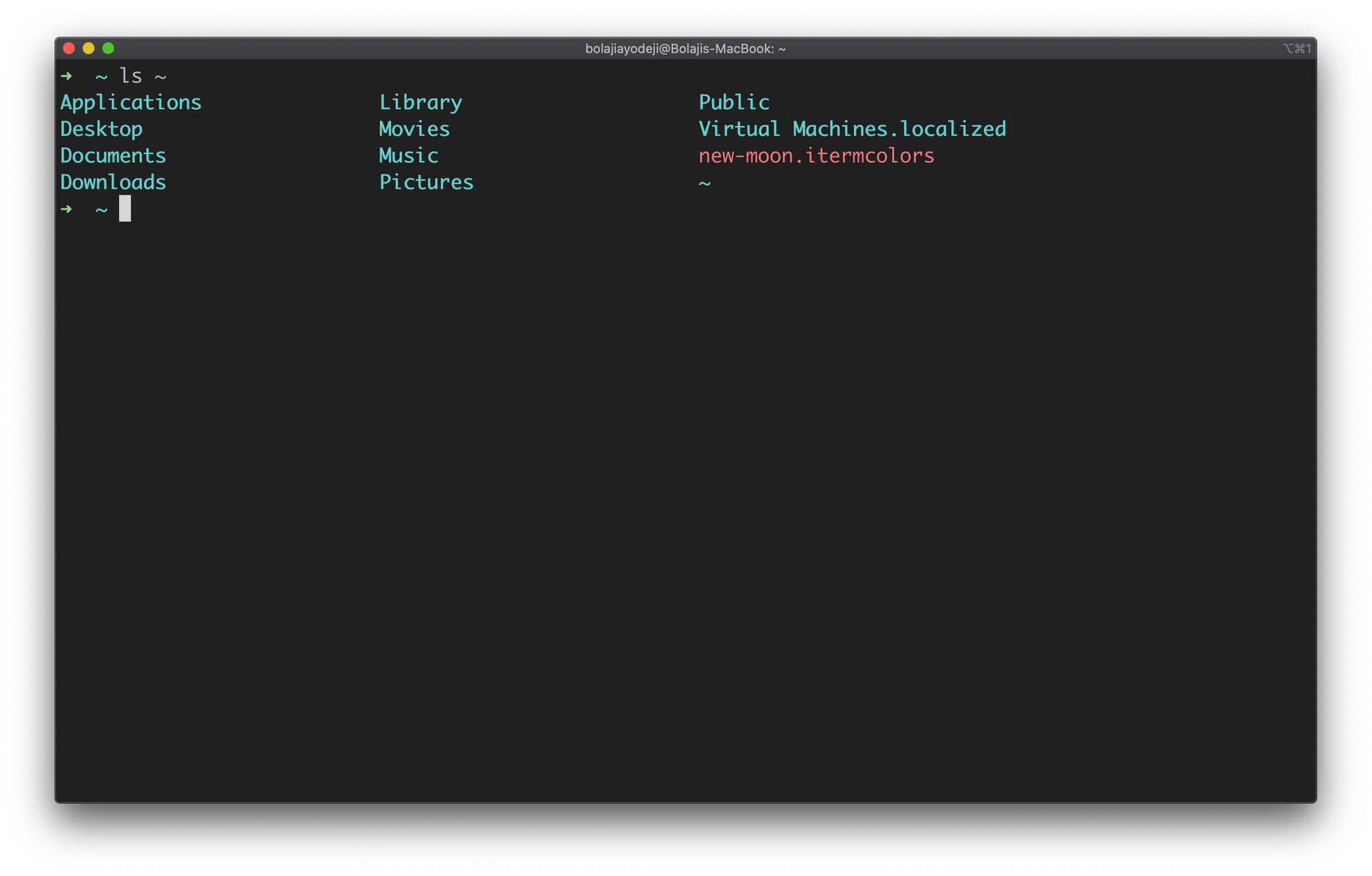
List files in the user’s home directory (/home/user)
Type the ls ~ command to list the contents in the users’s home directory:
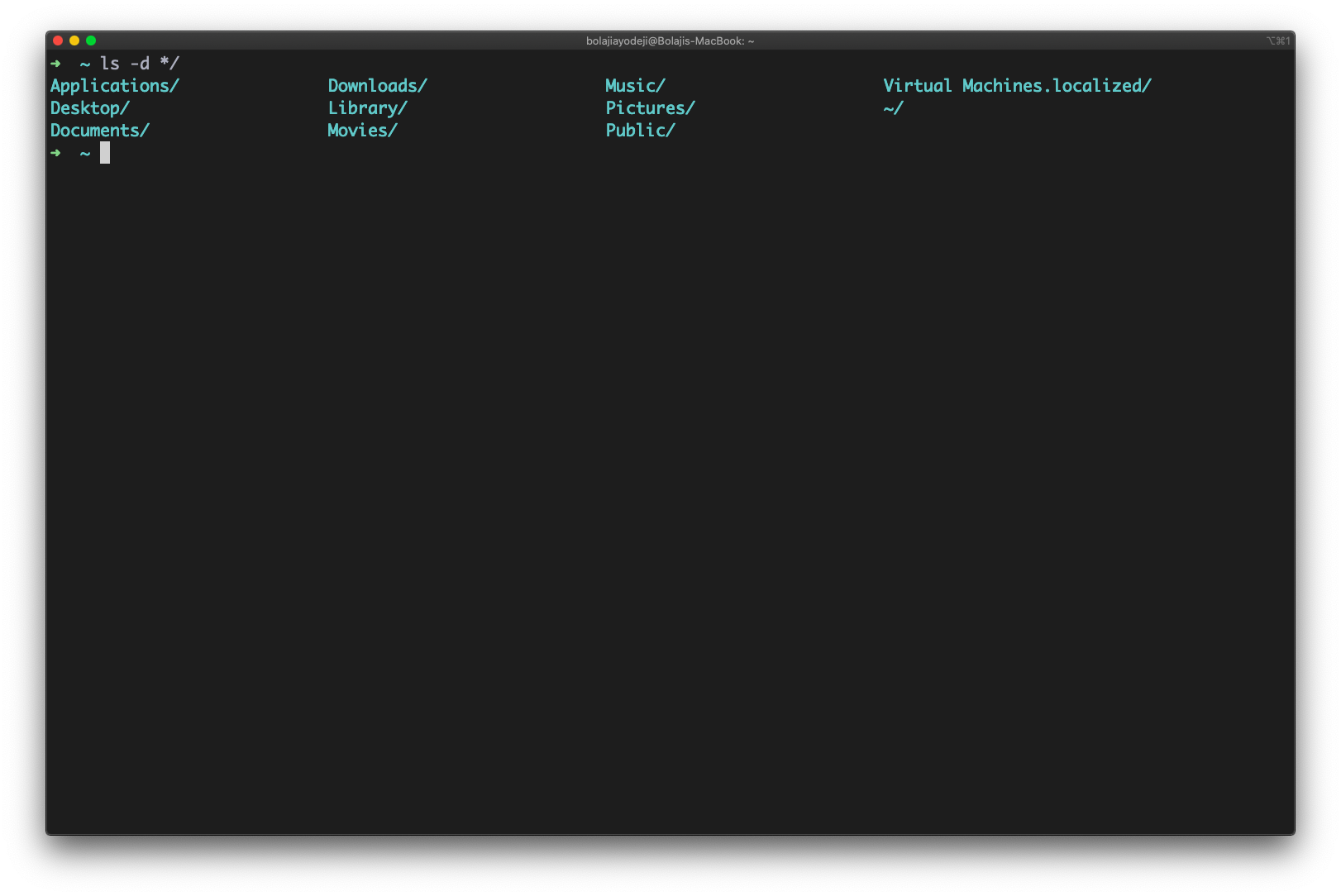
List only directories
Type the ls -d */ command to list only directories:
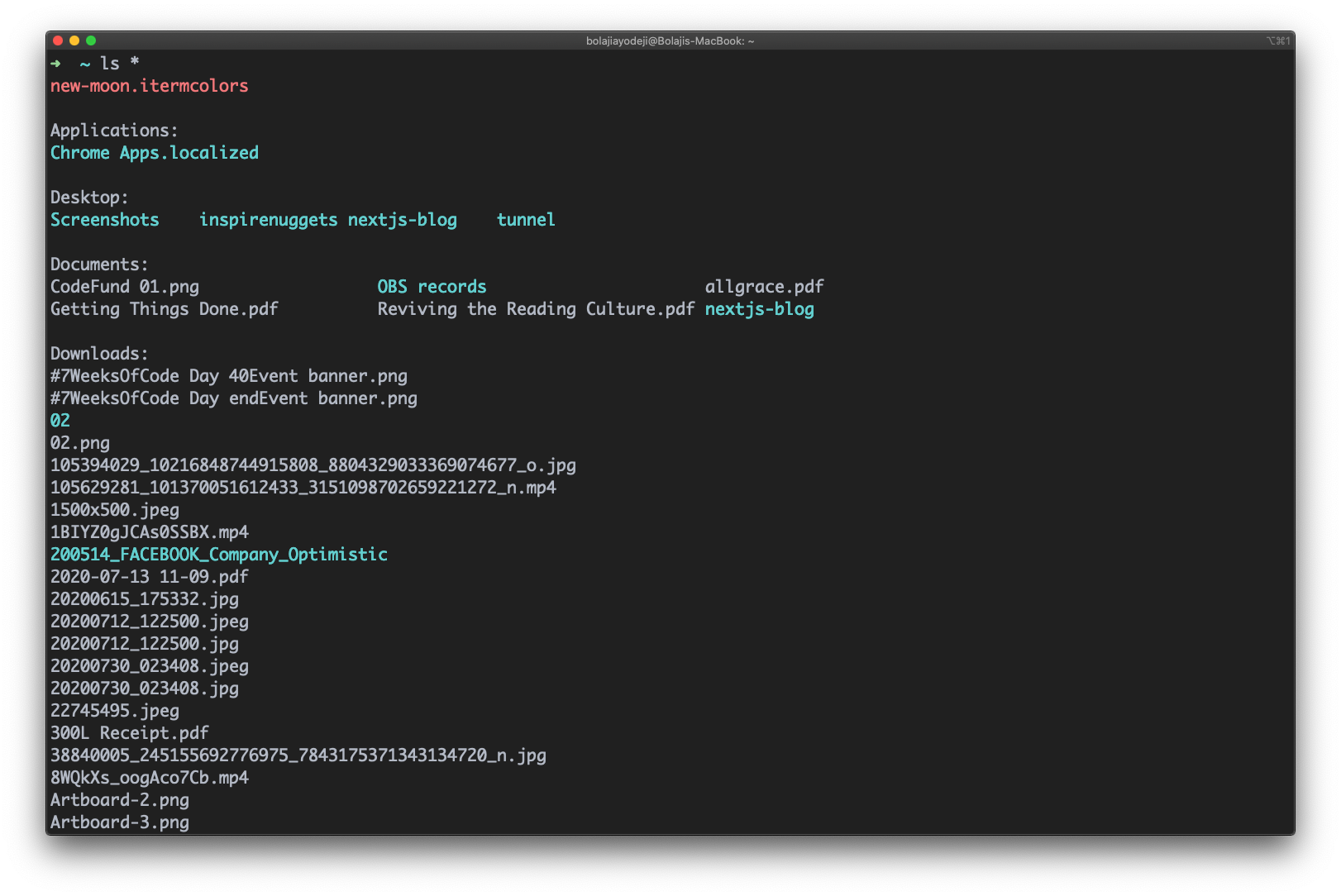
List files with subdirectories
Type the ls * command to list the contents of the directory with it’s subdirectories:
List files recursively
Type the ls -R command to list all files and directories with their corresponding subdirectories down to the last file:
If you have a lot of files, this can take a very long time to complete as every single file in each directory will be printed out. You can instead specify a directory to run this command in, like so: ls Downloads -R
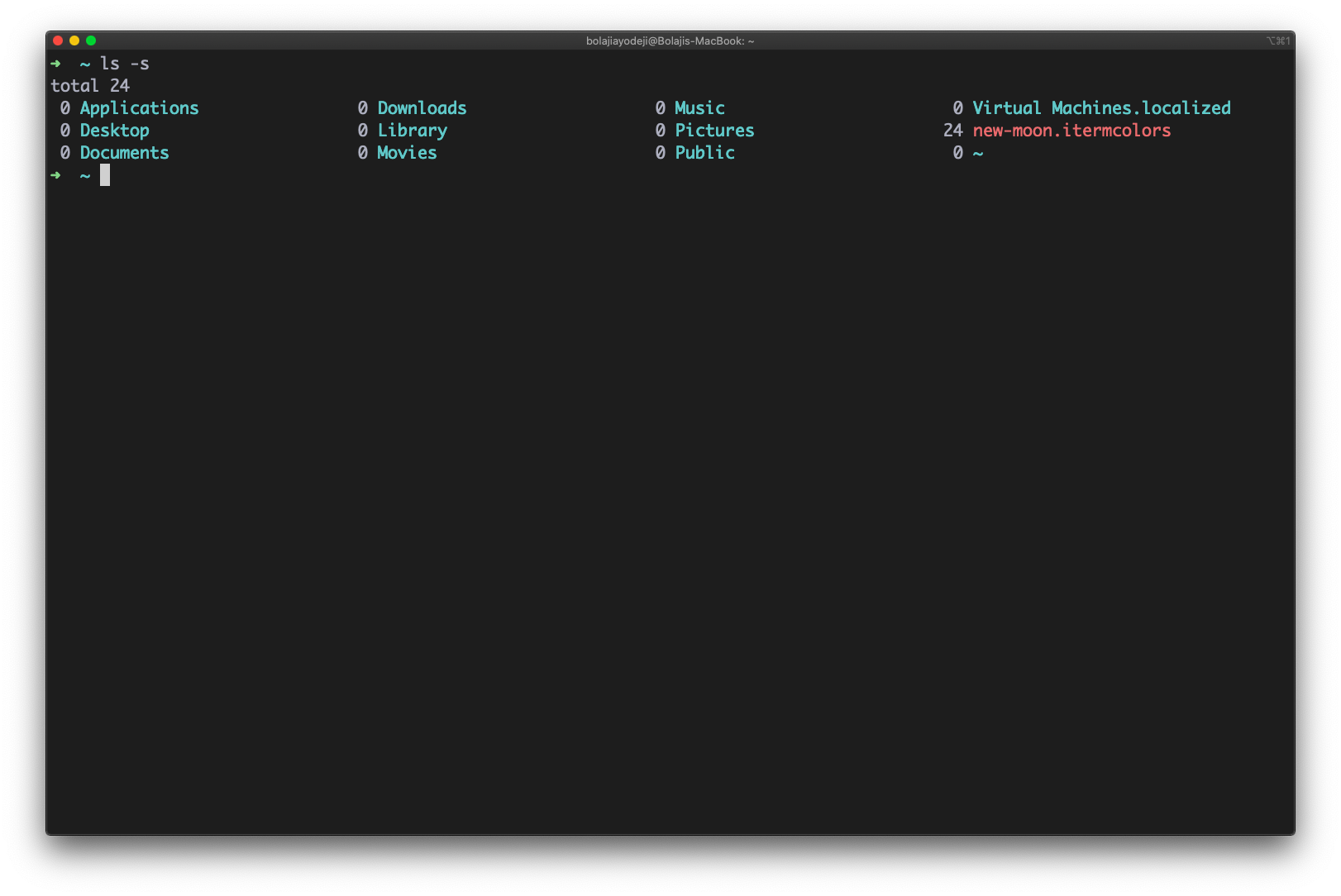
List files with their sizes
Type the ls -s command (the s is lowercase) to list files or directories with their sizes:
List files in long format
Type the ls -l command to list the contents of the directory in a table format with columns including:
- content permissions
- number of links to the content
- owner of the content
- group owner of the content
- size of the content in bytes
- last modified date / time of the content
- file or directory name
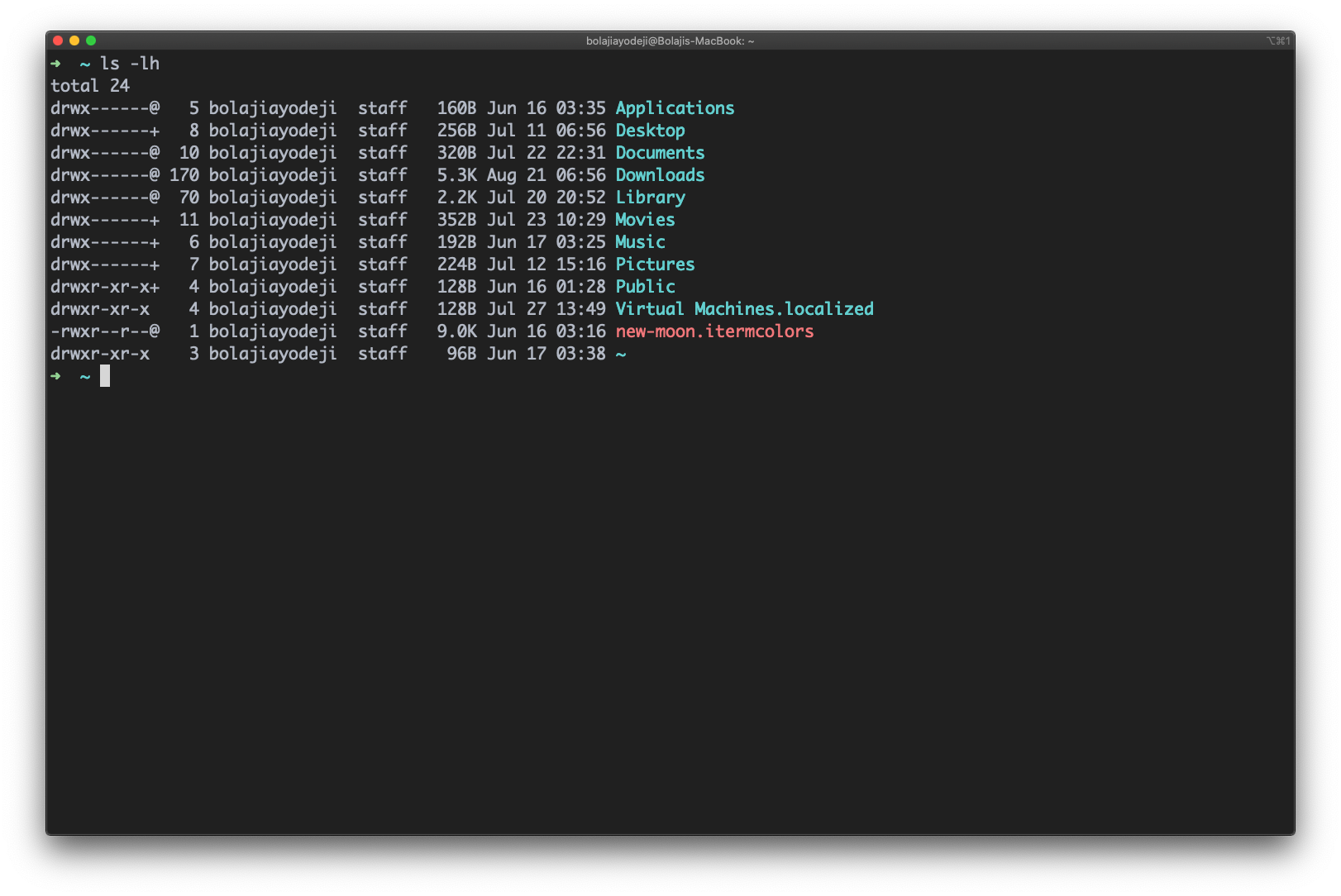
List files in long format with readable file sizes
Type the ls -lh command to list the files or directories in the same table format above, but with another column representing the size of each file/directory:
Note that sizes are listed in bytes (B), megabytes (MB), gigabytes (GB), or terabytes (TB) when the file or directory’s size is larger than 1024 bytes.
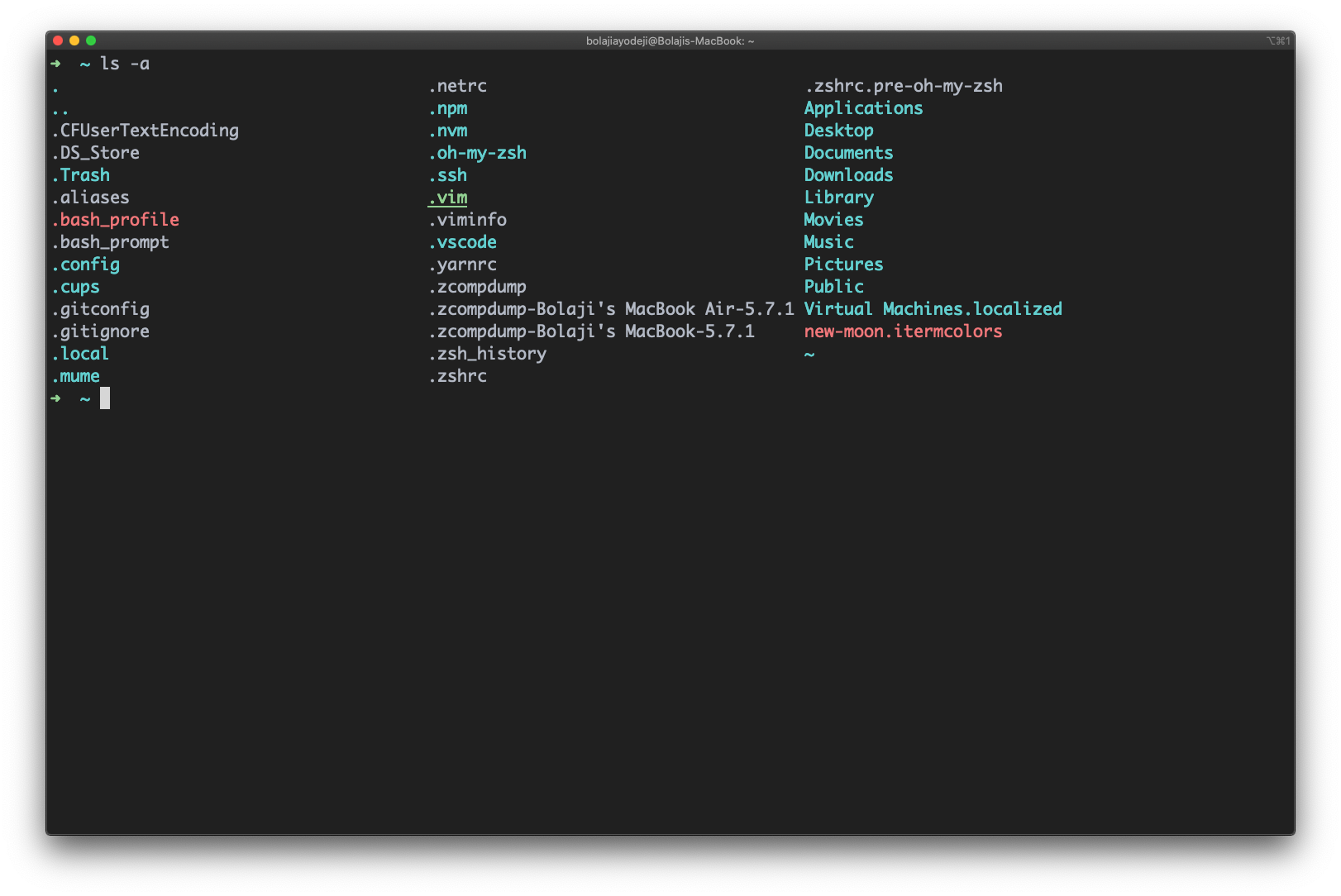
List files including hidden files
Type the ls -a command to list files or directories including hidden files or directories. In Linux, anything that begins with a . is considered a hidden file:
List files in long format including hidden files
Type the ls -l -a or ls -a -l or ls -la or ls -al command to list files or directories in a table format with extra information including hidden files or directories:
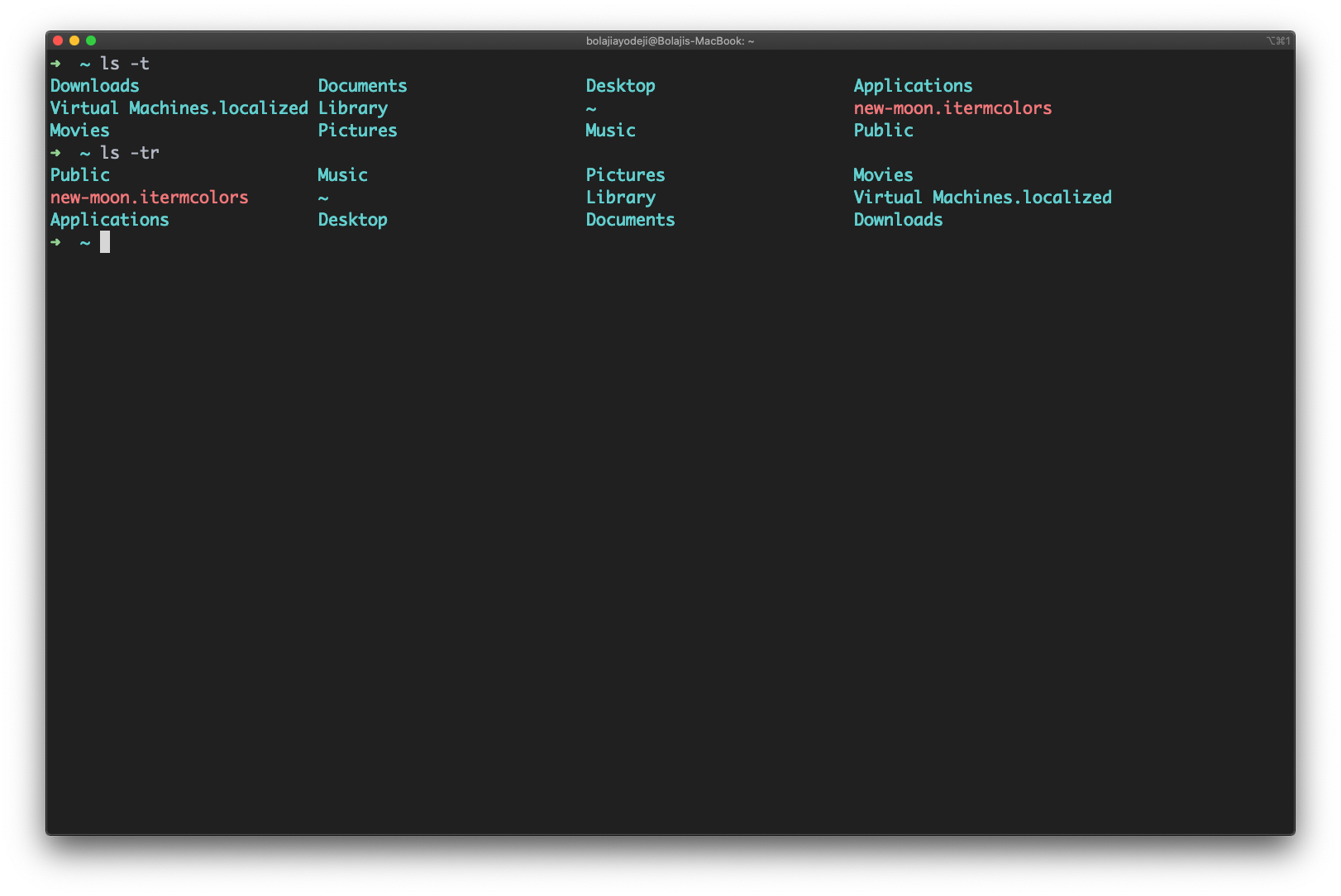
List files and sort by date and time
Type the ls -t command to list files or directories and sort by last modified date in descending order (biggest to smallest).
You can also add a -r flag to reverse the sorting order like so: ls -tr :
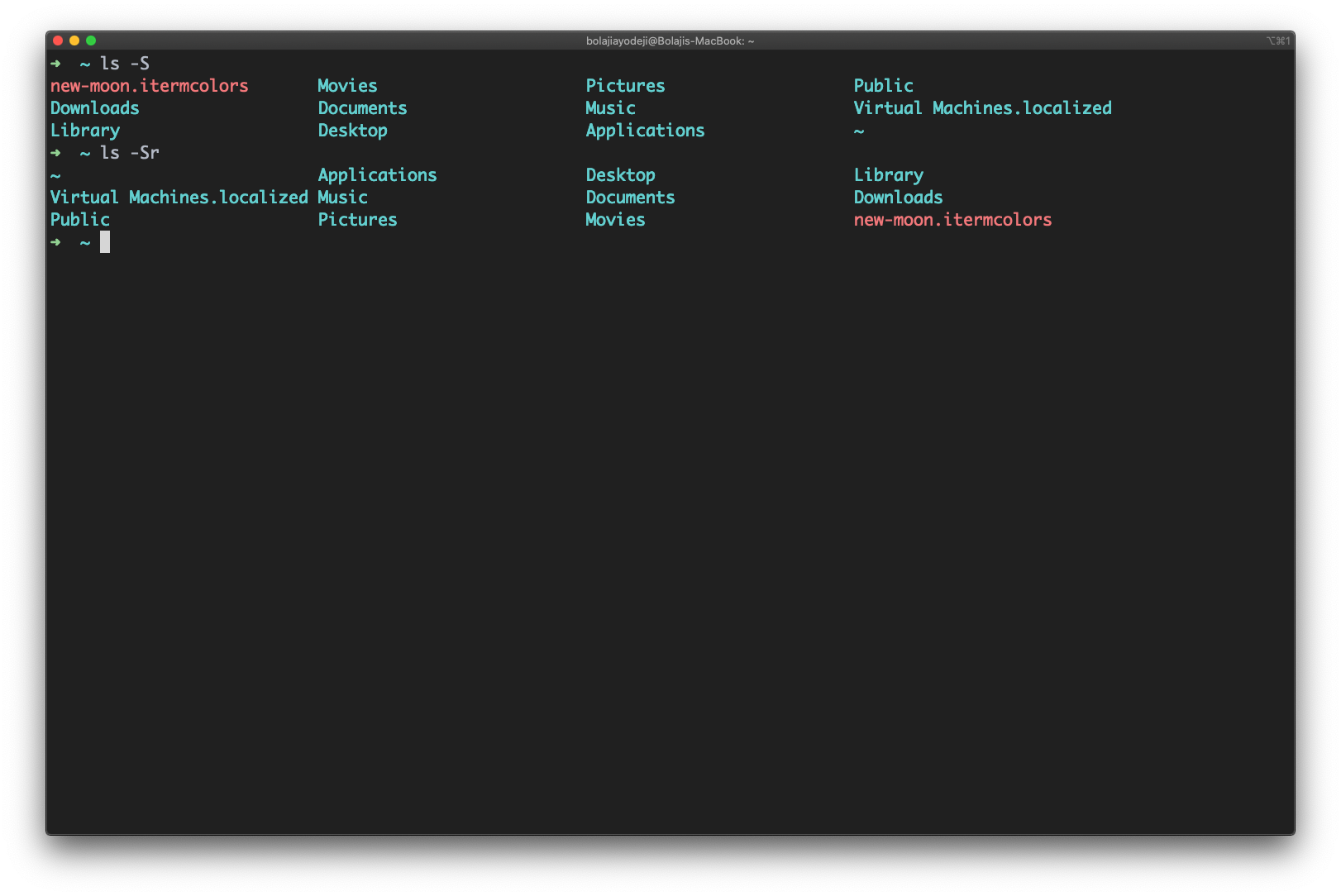
List files and sort by file size
Type the ls -S (the S is uppercase) command to list files or directories and sort by size in descending order (biggest to smallest).
You can also add a -r flag to reverse the sorting order like so: ls -Sr :
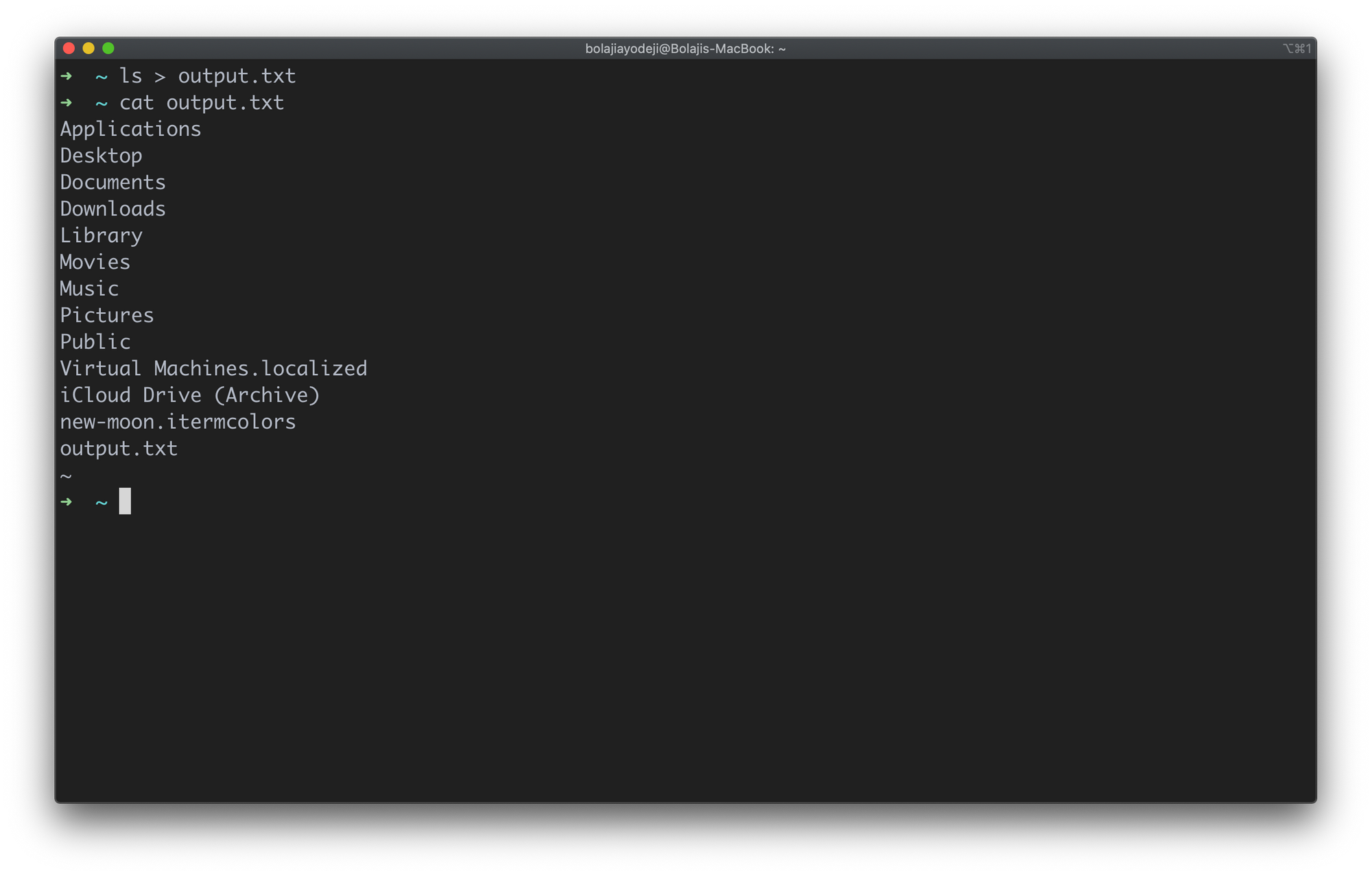
List files and output the result to a file
Type the ls > output.txt command to print the output of the preceding command into an output.txt file. You can use any of the flags discussed before like -la — the key point here is that the result will be outputted into a file and not logged to the command line.
Then you can use the file as you see fit, or log the contents of the file with cat output.txt :
Conclusion
There are tons of other commands and combinations you can explore to list out files and directories based on your needs. One thing to remember is the ability to combine multiple commands together at once.
Imagine you want to list a file in long format, including hidden files, and sort by file size. The command would be ls -alS , which is a combination of ls -l , ls -a , and ls -S .
If you forget any command or are unsure about what to do, you can run ls —help or man ls which will display a manual with all possible options for the ls command: