- how to list all running services in linux from command line
- Systemd or SysV Init/OpenRC
- How to List all Services
- Gentoo
- CentOS / Red Hat Linux / Ubuntu and Related Variations
- Fedora
- How to List Running Services in Linux
- Detecting the System Manger
- Listing Services in the systemd Service Manager
- Using the systemctl Command
- Listing the ACTIVE Services using the systemctl Command
- Listing the FAILED Services using the systemctl Command
- Listing the running Services using the systemctl Command
- Listing the exited Services using the systemctl Command
- Listing Services in the SysV Service Manager
- Listing the Services with service Command
- Listing Services with the ls Command
- Conclusion
This post and this website contains affiliate links. See my disclosure about affiliate links.
how to list all running services in linux from command line
In operating system talk, a service is an application that can be run in the background, usually in perpetuity in order to perform some task or waiting for service requests from other applications to perform tasks. All operating systems, including Linux has some kind of support for these type of applications. Services are also sometimes referred to as daemons.
There are different services that are required for the functioning of an operating system, while others are used by the user. Some common examples of user services are web servers such as Apache or Nginx and database servers such as Oracle or MySql. Some examples of OS specific services are dbus, xdm, network etc.
Most Linux systems have a similar implementation when it comes to running services, but there are still some differences between distros. Many distros also comes with some easy to use GUI applications that allow you to view and manage system services, but not all. We will look at how this can be done from the command prompt.
I should confess that I have exclusively used and worked on Gentoo and have not been keeping up much with the other distros. So, it is quite possible that this post will skew more towards Gentoo but i will try to keep it as generic as possible.
This post solely deals with how to list all services that you are installed or are running on your system. It does not deal with how add, delete or manage the services. I will probably write another post to deal with those functions. I will however describe how to find the status of the service as well, as that somehow corresponds to the reason you might be listing them in the first place.
Systemd or SysV Init/OpenRC
Despite some difference with the commands used to manage the service, most Linux systems have one thing in common. It stores the service related files in the /etc/ folder. The startup scripts for the services are usually in the /etc/init.d/ folder. You might also want to check the /etc/rc.d folder if you do not find the init.d/ folder.
As your system starts up, there needs to be a program or application that finds and launches appropriate drivers and start services. The old and tried system has been SysV init which mainly loaded and ran the startup scripts from /etc/init.d folder. Systemd is a modern day replacement for init and is being adopted by many distros.
It is important that you be aware of what boot system you have, which will help you with finding the startup scripts. A detailed discussion on that topic is probably not for this post.
How to List all Services
As mentioned earlier, most systems keep the startup scripts for the services in the /etc/init.d/ folder. So, a simple listing of the directory contents should show you the list of services that are installed and available to you.
the file names in the folder usually match the name of the service.
One of the most widely used commands to list services and its status is the service command. It could actually be a symlink to the openrc command in some distros, such as Gentoo. So, this could differ between Linux distros, which means you will need to use a command that is specific to your distro or install another utility for it.
Gentoo
In Gentoo, the rc-status command can be used to list the running services. The rc-status command has several useful command line options.
–all or -a: This will list all the running or stopped services from all run levels, organized by run level.
–servicelist or -s: This option will list all available services, in a long list
–unused or -u: This will print out the list of services that has not been assigned a run level.
You can use the complementary commands: rc-update, rc-config and rc-service to manage the services in the system.
CentOS / Red Hat Linux / Ubuntu and Related Variations
The Ubuntu distribution and the various other related distros such as Kubuntu, Mint, Xubuntu etc uses Upstart by default instead of the traditional init system, and you can use the service command to list the services. Upstart is a event based system, so the output might vary depending on the state of the system and fired events.
You can also check the status of a single service, if you know the service name as shown below.
bash$ service mysql status
where mysql is the name of the service.
You can also use the initctl command, which is equivalent to the service command.
Fedora
Fedora does have support for the service utility that was described above, but they recommend the systemctl utility to manage services. The following command will list all the services that running in the system.
bash$ systemctl list-units —type=service
You can check the status of a single service with the same command and different command line arguments.
bash$ systemctl status httpd.service
where httpd.service is the name of the service.
If you have a different distribution that the ones mentioned and the above commands do not work for you then refer to the documentation that is specific to the distro. Also, be sure to execute the above commands with the superuser permissions by using sudo or equivalent.
Ideally, you should disable the services that are not required or being used. You should remove them from the run level as well. It is usually a waste of hardware resources if it running all the time even if it has a small footprint. There is also a possibility of it being a security risk, especially if it has an open port and is listening on it.
How to List Running Services in Linux
In simpler terms, a Linux service is a server’s response to a request that performs a specific task. It is an application or a program that generally executes in the background.
As a user, you are mostly unaware of all the services running in the background because there are plenty of them.
You might have run through the term daemon most probably while working or learning about services. Daemon is a non-interactive program that runs in the background and strictly does not provide any interfaces for the user to control it.
Some of the common characteristics of a Linux service are:
- There is no GUI(Graphical User Interface).
- Most of the native services start along with the start of the OS.
- Some services wait for an interrupt or a signal to get started.
Some common examples of Linux services are mysql, apparmor, httpd and nfs.
Table of Contents
Detecting the System Manger
Detecting the system manager of your Linux system is the elementary step to listing the running services. This step is essential as the commands for listing the services are based on the system manager.
The system manager is the first process that starts in your system. So, you can use the following command to list the first process in the system.
The output looks like this if the system manager is systemd.
PID TTY TIME CMD 1 ? 00:00:02 systemd
systemd is used in the newer Linux distributions.
If the system manager used is SysV , the output looks like this.
PID TTY TIME CMD 1 ? 00:00:02 init
SysV is also known as init or initialization. It was used in early Linux distributions, and lately, it has been replaced by systemd .
Thus, you can find the system manager from the CMD column of the outputs above. According to the service manager present, you can use the respective methods.
Listing Services in the systemd Service Manager
There are a couple of ways to list the running services when the system manager is systemd , and let’s explore each of them.
Using the systemctl Command
You can use the systemctl command to list the services in your Linux system.
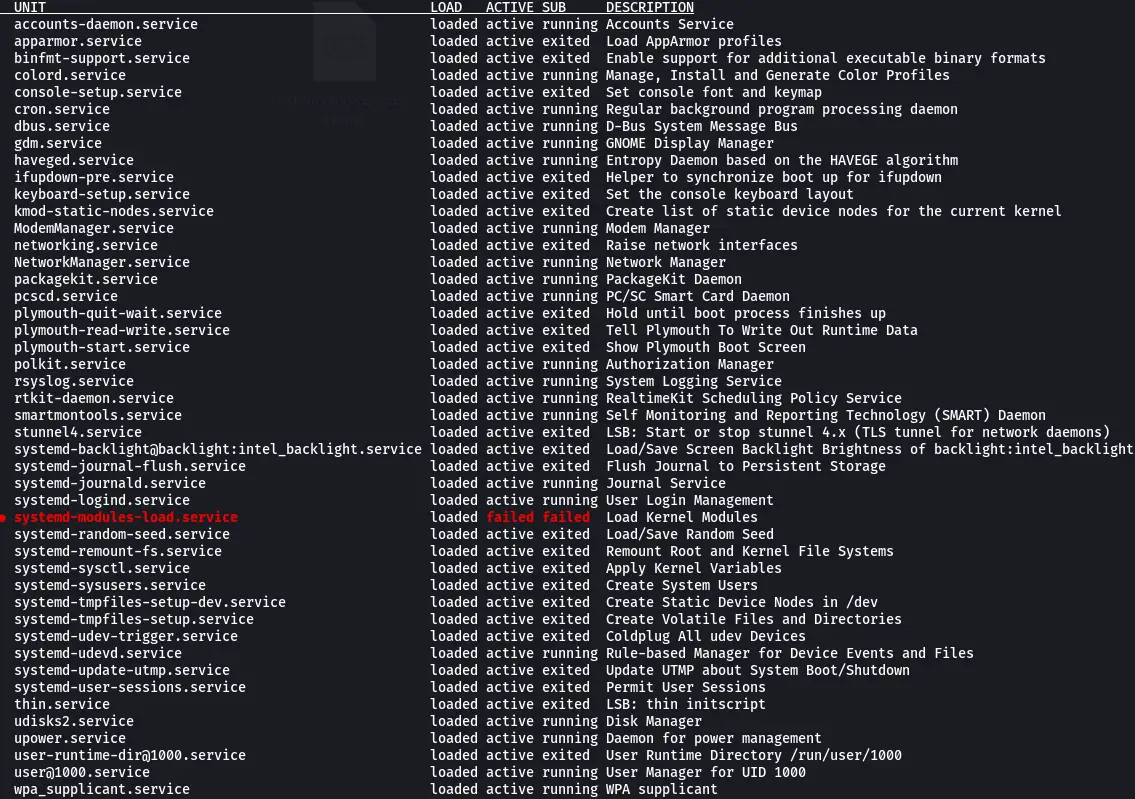
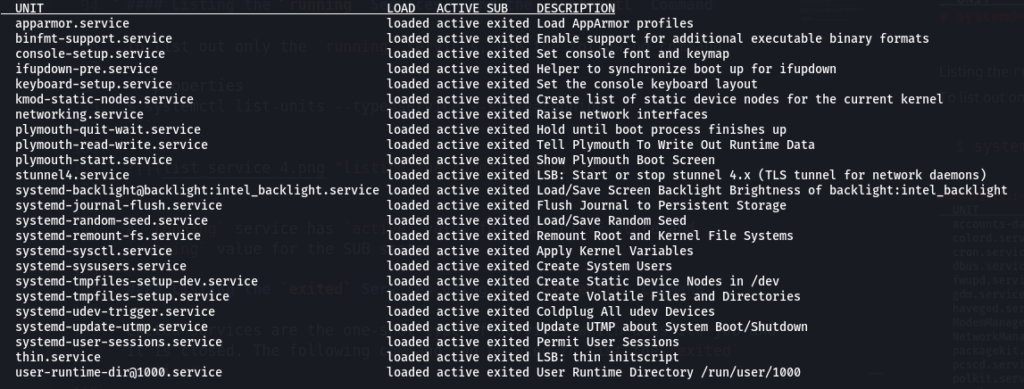
Using the list-units subcommand with the —type=service option will list all the services. It includes active, failed, active (exited), and active (running) services.
systemctl list-units --type=service
The output of the above command is shown below.
In the output above, you can notice several columns. Let’s get to know what they represent.
UNIT: It is an object that starts, stops and manages the services.
LOAD: It states whether the particular unit is correctly loaded.
ACTIVE: It is a high-level state that determines whether the unit is active.
SUB: It represents the low-level activation state of the unit.
DESCRIPTION: It describes the task that the unit performs.
In the sections below, you will learn to list the services according to their states. Some of the systemd states are active, inactive, activating, deactivating, failed, not-found, dead, etc.
Listing the ACTIVE Services using the systemctl Command
You can use specific options and the systemctl command to filter the services. With the —state option, you can set the state of the services. For example, if you want only the active services listed, you can use the following command.
systemctl list-units --type=service --state=active
We have used the —state option with the value active to denote only the active services. In the output below, you can see the active status of all the units.
Listing the FAILED Services using the systemctl Command
Similarly, you can list only the failed services with the following command.
systemctl list-units --type=service --state=failed
Listing the running Services using the systemctl Command
To list only the running services, use the following command.
systemctl list-units --type=service --state=running
A running service has an active value for the ACTIVE state and a running value for the SUB state.
Listing the exited Services using the systemctl Command
Exited services are the one-shot type of services which does their job and are closed. The following command can be used to list the exited services.
systemctl list-units --type=service --state=exited
The ACTIVE state holds the value active for exited service, while the SUB state has the value exited.
Listing Services in the SysV Service Manager
In this section, you will learn a few ways of listing the system’s services that use the SysV service manager.
Listing the Services with service Command
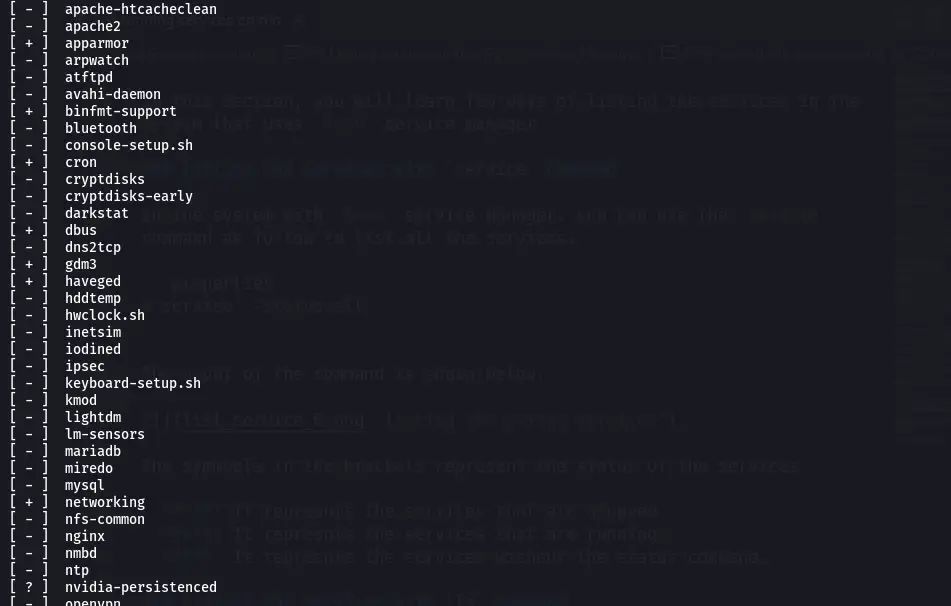
In the system with the SysV service manager, you can use the service command to list all the services.
The output of the command is shown below.
The symbols in the brackets represent the status of the services.
- –: It represents the services that are stopped.
- +: It represents the services that are running.
- ?: It represents the services without the status command.
To list only the running services, you can use the following command.
service --status-all | grep running
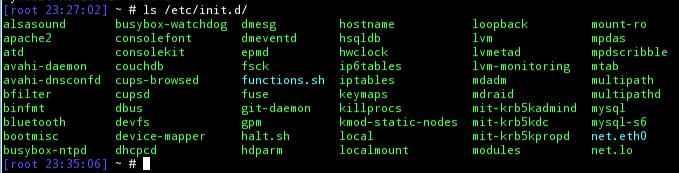
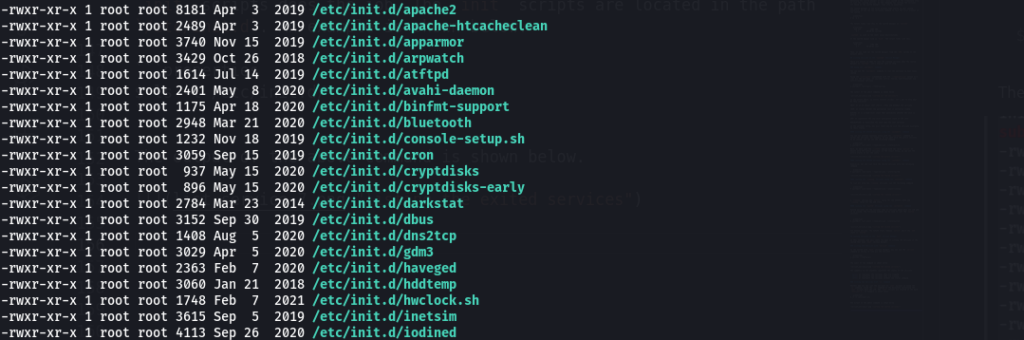
Listing Services with the ls Command
Another way you can list the services of init scripts is using the ls command. Using the ls command on the directory containing the init scripts does the job. The init scripts are located in the path /etc/init.d. An example is shown below.
The output of the above command is shown below.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you learned to identify the system manager used in your Linux system. Thus, you grasped the idea of using the various commands to list the Linux services.