- How to Switch Users in Ubuntu 22.04
- Method 1: Switch User Using CLI
- Method 2: Switch User Using GUI
- Conclusion
- How to Switch Users in Ubuntu and Other Linux Distributions [Quick Beginner Tip]
- Change user in Linux command line
- Change users in Linux graphically (for desktop Linux)
- Как сменить пользователя Ubuntu
- Как сменить пользователя в Ubuntu
- How to Change Users in Linux Command Line
- Various user types in Linux
- 1. System Users
- 2. Regular Users
- 3. Super Users
- Switch users in the command line
- Switch to root user
How to Switch Users in Ubuntu 22.04
Linux operating system allows multiple users to perform tasks on a system without affecting the other users. Every user has a separate home directory and login name, which is not accessible to other users. The administrator can manage and create multiple users to grant them specific privileges. Somehow, the administrator may have to switch between numerous users to have some specific privileges. So, it’s an essential administrative task to switch users in Ubuntu 22.04.
This post will demonstrate multiple ways to switch users in Ubuntu 22.04. The post’s content is as follows:
Method 1: Switch User Using CLI
In this section, we will switch the user via the terminal. The “su” command is used to switch users in Ubuntu, To switch users in Ubuntu, the “su” command is used. The general syntax of the “su” command is as follows:
Example: Switch a User
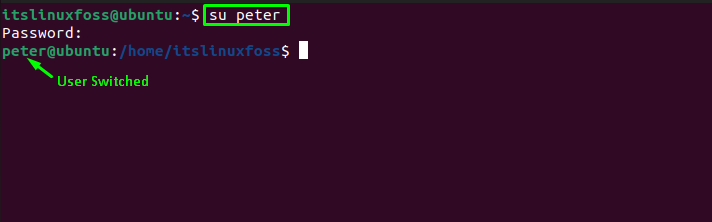
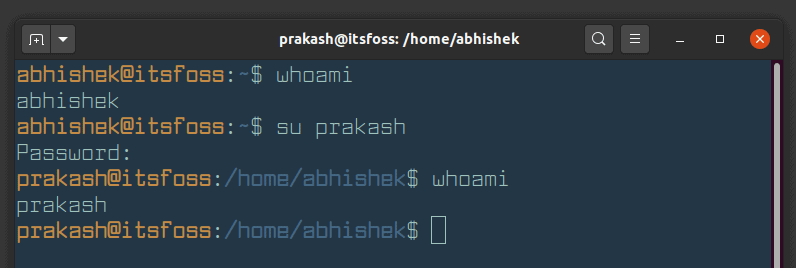
There can be multiple users in a system; we can switch the user within the system with the “su”command. To change the current user to a user named “Peter”, run the below-mentioned command:
The output shows that the user is immediately switched to the new user after executing the command.
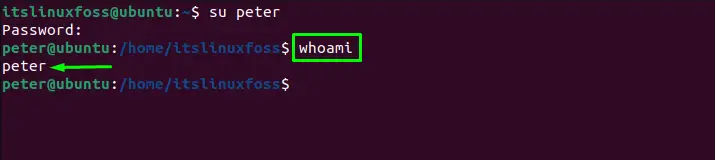
To verify whether the user is switched or not, the “whoami” command may be used:
Example: Switch to a Different User as Login User
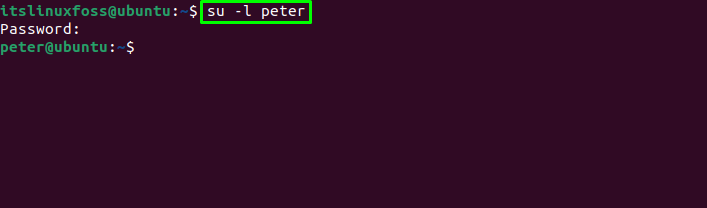
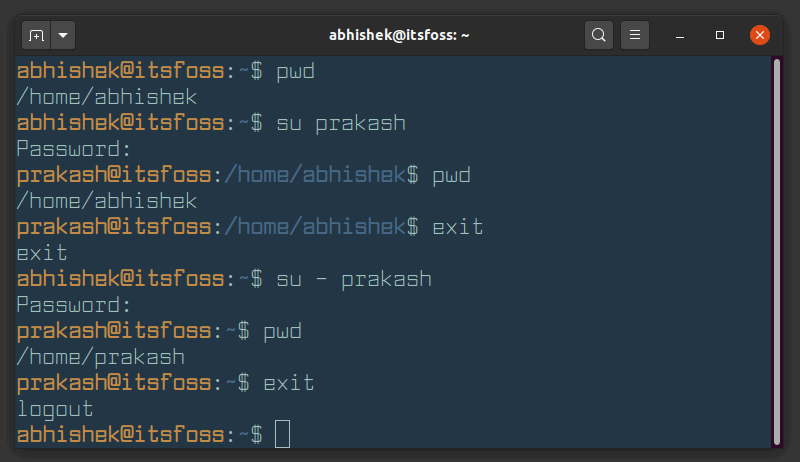
If you want to start a shell as a login shell, that means you will log in as another user but uses the rights (sudo, etc..…) of the login user. It will change the Home directory of the new user and also initializes the environment variables. The command provided below will switch the user to “peter”:
The above screenshot shows the switching has been successfully performed.
Method 2: Switch User Using GUI
To switch the user using the GUI approach, we need to log out from the current session and log in with a different user. To do so, the process is described below:
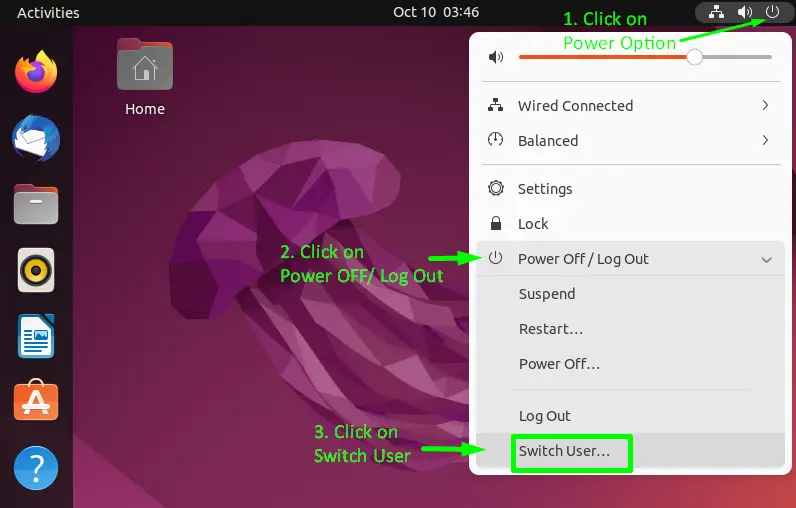
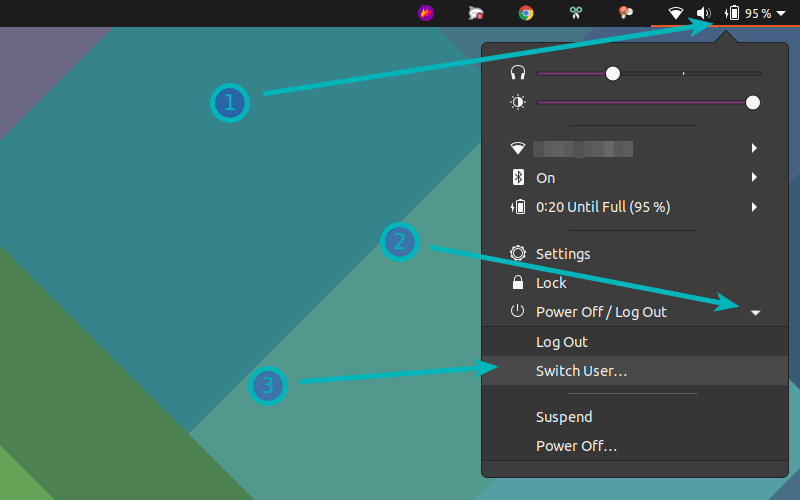
Click on the “Power” icon at the top left (Adjacent to the Volume icon). It will show a list of options; now click on the “Power Off/Log Out” button, which will open a dropdown list. Choose the “Switch User” option to sign out:
It will log you out of the current session and redirect you to the “Start” window of Ubuntu 22.04 where you can find all the users in the system. Click on the desired one and then :
Now, you can switch the user and log in again.
That’s all from this guide!
Conclusion
The GUI and CLI methods are used to switch users in Ubuntu 22.04. In the command line method, use the “su ” command to switch users. Moreover, to switch users as login users, you may use the “su -l ” command. Apart from that, the GUI method is also demonstrated to switch users in Ubuntu 22.04. This post has demonstrated a list of methods to switch users in Ubuntu 22.04.
How to Switch Users in Ubuntu and Other Linux Distributions [Quick Beginner Tip]
It is really simple to switch users in Ubuntu or any other Linux distribution using the terminal.
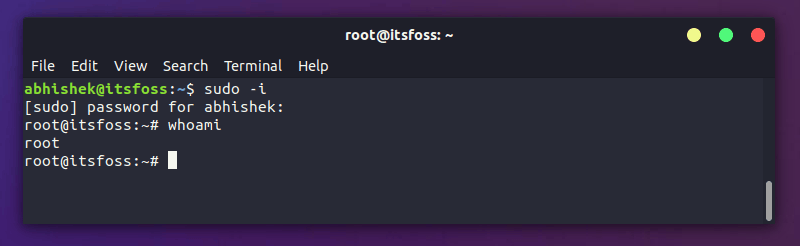
All you need to do is to know the unsername and its account password and you can switch users with su command:
You’ll be asked to enter the password of the user you want to switch to.
As you can see in the screenshot above, I changed to user prakash from user abhishek in the terminal.
There are some minor details with this method that I’ll share with you in a moment. I’ll also share the graphical way of switching users in Linux if you are using desktop Linux.
If you want to switch to the root user in Ubuntu, you can use the following command:
sudo su
You’ll have to enter your own user password here.
Change user in Linux command line
Let’s see things a bit in detail. To switch users, you need to first know the exact username because tab competition doesn’t work here. You can list all the users in Linux command line by viewing the content of the /etc/passwd file.
You’ll also need to know the password of the user account you want to switch to. This is for security reason, of course.
If you are the admin user or have sudo access, you can change account password with passwd command.
You’ll notice that some people use a — between su and the username. There is a specific reason for that.
When you use -, -l or –login option, you start the shell as a login shell. This means that it will initialize the environment variables like PATH and changes to the home directory of the changed user. It will be as if you logged into the terminal as the second user.
Note: though — is more popular, it is advised to use –login option.
Change users in Linux graphically (for desktop Linux)
If you are using desktop Linux, the above method may not be sufficient for you. Why? Because you switch the user in the terminal only. It is confined to the terminal. Nothing is changed outside the terminal.
If you want to switch users so that you can log in as another user and use all the system (browser, applications etc) graphically, you’ll have to log out and then log back in.
Now the screenshots may look different but the steps remain the same. Here’s how to switch users in Ubuntu Linux.
Go to the top right corner and click the Power Off/Log out option to open the dropdown and you can choose either of Switch User or Log Out.
- Switch User: You get to keep your session active (applications keep on running) for current user. Good for temporarily switching users as you won’t lose your work.
- Log out: Current session ends (all applications are closed). Good when you want to switch to the other user for a long time.
You can choose whichever option is more suited for your need.
Now, you’ll be at the login screen with all the available users for your system. Choose the user account of your choice.
Clearly, you need to know the password of the user account you want to use.
That’s it. I hope you find this quick beginner tip helpful in changing users in Ubuntu and other Linux distributions. Questions and suggestions are always welcome.
Как сменить пользователя Ubuntu
Операционная система Ubuntu рассчитана на то, чтобы её использовали от имени одного определенного пользователя. Менять пользователя в процессе работы приходится не так уж часто. Обычно вы вводите логин и пароль при входе в систему, а затем пользуетесь ею пока не придёт пора выключать компьютер.
Если надо выполнить какие-либо действия с административными привилегиями, то для этого есть sudo. Однако иногда надо сменить пользователя Ubuntu. В этой статье мы поговорим о том как сделать это в графическом интерфейсе и в терминале.
Как сменить пользователя в Ubuntu
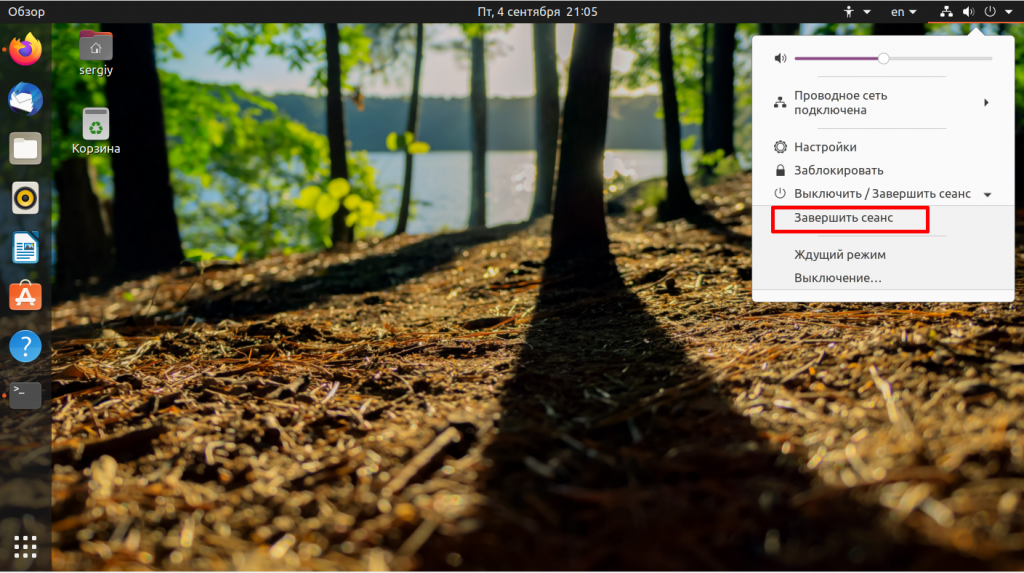
Сначала кликните по значку выключения в правом верхнем углу экрана и выберите там пункт Завершить сеанс или Сменить пользователя:
Затем подтвердите завершение сеанса или смену:
Далее перед вами откроется обычное окно входа, где вы сможете выбрать пользователя из списка или ввести его логин в поле ввода. Затем вы снова окажетесь на рабочем столе Ubuntu.
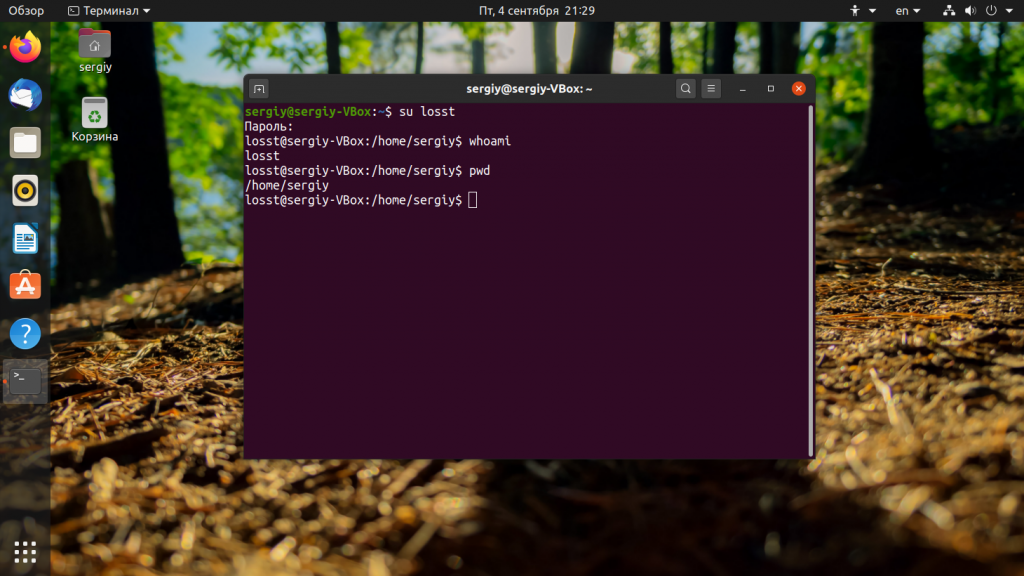
Теперь давайте поговорим как выполняется смена пользователя в терминале. Для этого надо использовать команду su. Например, чтобы сменить пользователя на losst достаточно выполнить:
Утилита запросит пароль пользователя losst после чего откроет командную строку от его имени:
Если вы хотите, чтобы путь к домашней папке и все другие переменные окружения для пользователя обновились используйте опцию -l или —login. Вместо неё также можно просто добавить чёрточку «-«. Например:
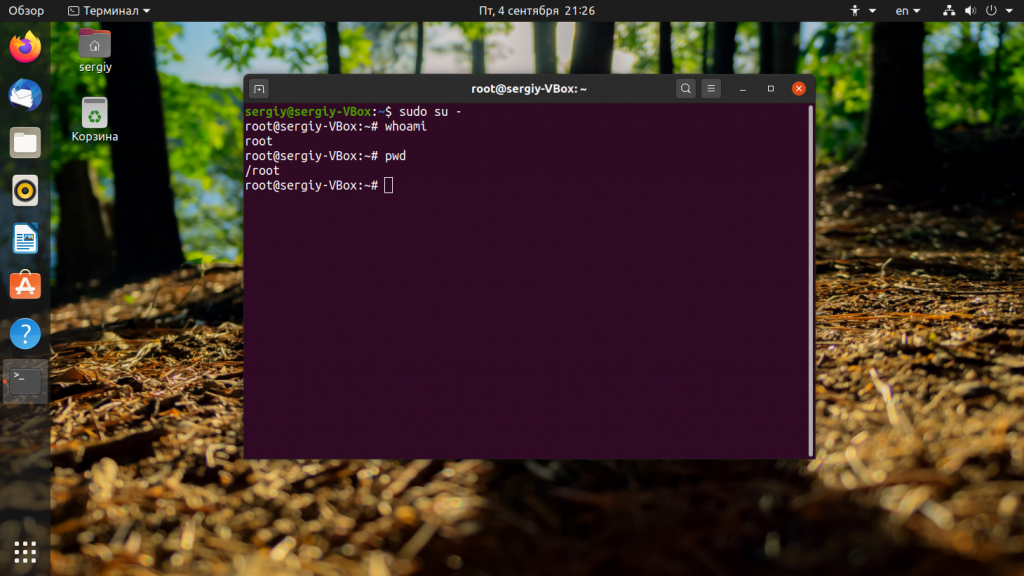
Если выполнить утилиту без параметров, то вы войдете от имени пользователя root. Но поскольку пароль root не задан по умолчанию, то следует добавить перед ней sudo:
В таком случае иногда целесообразнее использовать опцию -i команды sudo:
В этой статье мы рассмотрели как поменять пользователя в Ubuntu, как видите, здесь всё очень просто. Если остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
How to Change Users in Linux Command Line
Linux systems have different users and different types of users. Learn how to switch the users in Linux command line or how to change to the root user in Linux.
Linux systems have different types of users with different types or permissions as well.
Not all users can execute all commands and not all users are allowed to switch to other users neither. This all might sound confusing but, I will try to explain these so it can be easy to understand.
For the moment, here’s a quick summary of how to switch users in Linux command line.
To switch users, you need to know the password of that user. You can switch the users with this command:
To switch to root user in Ubuntu, you can use this command:
Various user types in Linux
If you list all users in Linux, you’ll see a lot of users that you didn’t know about. Who are these users? Where did they come from? I could write an entire article in regards of how users work in Linux, however, this is not the idea for this one.
Basically, there are 3 types of users in Linux:
1. System Users
These are the users that are automatically created in Linux systems to be able to run services or applications and are not intended to log in to the system (in fact you can’t log in as any of these users).
2. Regular Users
These are the (human) users who can log in to a system. Each of these users might have or not different permissions or levels in the system which is given by the groups they belong to.
3. Super Users
These are system administrators or users who can perform high-level tasks that can be considered critical or system dangerous.
Switch users in the command line
When using a Linux system you can log in with a user and then simply “switch” to another user through the same command line session. In order to do this, there is a command “su -“, which allows you to switch to become another user:
[email protected]:~$ su - janedoe Password: [email protected]:~$ In the above example, you need to know the password of janedoe in order to switch to that user. Which makes sense because if you are going to switch to a user, you need to know the password of that user else it will be a security risk.
Switch to root user
For security reasons, some systems have ‘root’ account blocked for direct login, either locally or remotely, so this means it will not accept someone who tries to log in using ‘root’ even with the correct password.
So, how do you perform actions as the ‘root’ user? That’s what the ‘sudo’ command allows you to.
The sudo command will basically execute anything you want in the system as if the ‘root’ was doing it. You don’t need to know the ‘root’ user’s password, in fact, probably nobody knows it or there is no password assigned to ‘root’. You only need to know your own user’s password and that user must be in the ‘sudoers’ group, which is basically the group of users which can use ‘sudo’ in the system.
Normally, it is a good practice to run the commands with sudo that needs to run with root permission like this:
But if you want to change to root user so that all the subsequent commands will be run as root, you can use:
You’ll use your own password here, not the root account’s password.
As a sudo user yourself, you can create sudo user by adding the user to sudo group.
Linux systems allow you to easily switch users or execute high-level commands with the usage of ‘su‘ and ‘sudo’ commands. And remember: with great sudo power comes great responsibility!