- List files by last edited date
- 4 Answers 4
- Mac OS X
- Linux: List Files by Date
- Listing Files by Date Using the ls Command
- 1. Listing Files by Last Modification Date
- 2. List Files by Last Access Date
- 3. List Files by Exact Date
- 4. List Specific Month Modified Files
- Listing Files by Date Using the find Command
- 1. How to List Files by Time Interval Using the find Command
- 2. List All Modified Files After or Before a Specific Date
- 3. Listing After Certain Minutes Modified Files
- What Are mtime, atime and ctime Timestamps
- Conclusion
- About the author
- David Adams
- How to Sort Output of ‘ls’ Command By Last Modified Date and Time
- Linux Basic ls Commands
- Sort Files Based on Time and Date
List files by last edited date
I have a directory: /home/user/ How can I list every file in this directory (including those in sub directories) and order them by the date that they were last modified?
4 Answers 4
where -R means recursive (include subdirectories) and -t means «sort by last modification date».
To see a list of files sorted by date modified, use:
An alias can also be created to achieve this:
Where -h gives a more readable output.
Thanks, that’s perfect. I added a -l in there too so I can actually see the dates so for anyone who searches this out later, it’s- $ ls -lRt
If you’re doing this at the prompt and want to see the most recently modified files, consider ls -lrt[RhA] . the -r reverses the sort order, leaving recently edited stuff at the bottom of the list.
I have expanded on this answer because using ll -Rt was the perfect solution for me as I needed to see the files by date most recently modified. This might be helpful to others.
@MusTheDataGuy ll is does not exists and is not a command. It is mostly an alias in the bash shell, but not defined in most/some/? linux distributions. Some define it as an alias ll=’ls -l’ in /etc/bash.bashrc or /etc/.bashrc. Thus it may not work and it may not exists on OPs system. Use ls -l -Rt at least, as ls is a standard command as defined by posix. Or specify you meant alias ll=’ls -l’; ll -Rt .
If you’d like a master list in which all the files are sorted together by modification date, showing the directory they’re in, but not grouped by directory, you can use this:
find . -type f -printf "%-.22T+ %M %n %-8u %-8g %8s %Tx %.8TX %p\n" | sort | cut -f 2- -d ' ' The result looks a lot like ls -l :
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3892 08/11/2009 11:03:36 /usr/share/man/man1/xmllint.1.gz -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 22946 08/13/2009 11:59:20 /usr/share/man/man1/curl.1.gz -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 728 08/17/2009 12:06:33 /usr/share/man/man1/thunderbird.1.gz -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 873 08/18/2009 10:52:47 /usr/share/man/man1/libgnutls-config.1.gz -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2552 08/19/2009 02:00:34 /usr/share/man/man3/Purple.3pm.gz -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 9546 08/19/2009 02:02:00 /usr/share/man/man1/pidgin.1.gz -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2201 08/19/2009 02:02:46 /usr/share/man/man3/Pidgin.3pm.gz -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 926 08/19/2009 02:03:05 /usr/share/man/man1/purple-remote.1.gz -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 18052 08/19/2009 04:11:47 /usr/share/man/man1/mono.1.gz -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1845 08/19/2009 04:11:47 /usr/share/man/man5/mono-config.5.gz
Mac OS X
For those of you using Mac OS X, option -printf is not available on BSD find (you will get this error: find: -printf: unknown primary or operator ). Fortunately you can Install GNU find through Homebrew (there should be an option to Fink and Macports as well):
After install it the GNU find should be available to you as gfind . So, all you need to do is change the line above to:
gfind . -type f -printf "%-.22T+ %M %n %-8u %-8g %8s %Tx %.8TX %p\n" | sort | cut -f 2- -d ' ' Linux: List Files by Date
Previously, we published a tutorial explaining how to list files by size in Linux. After reading the current tutorial, you will be able to list files by both last and first date modification, by a specific date, and last or first access on the current directory or the entire system.
The knowledge provided in this document is mandatory for all the Linux user levels.
All the steps shown in this article include screenshots to make it easy for all the Linux users to follow and apply them.
Topics explained in this document include:
Listing Files by Date Using the ls Command
The first command explained in this tutorial is the ls (list) command available in all the Linux distributions. In this section, you will learn the different tips to show files based on the different time/date related conditions.
1. Listing Files by Last Modification Date
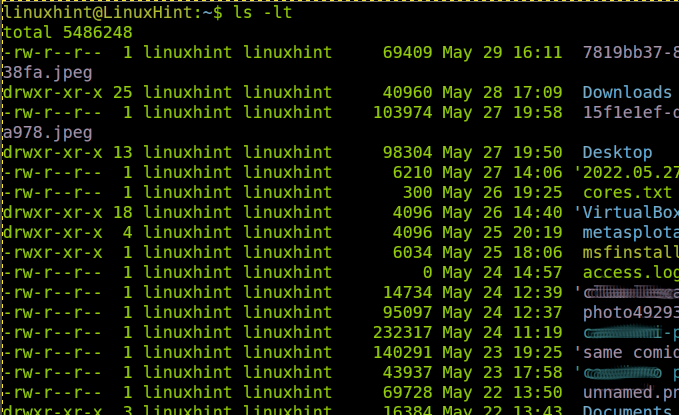
In the first example, we list the files sorted by modification date within a directory. To achieve it, we execute the ls command followed by the -lt flag.
As you can see, the last modified files appear on top of the list.
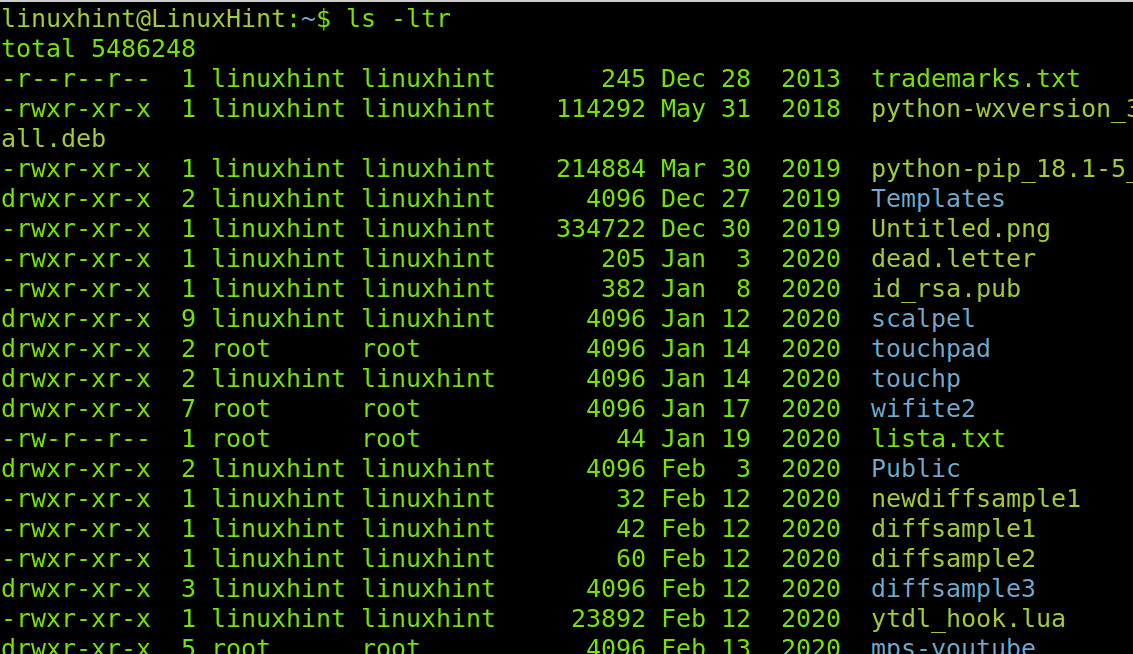
You can get the inverse result, showing the last modified files within a directory at the bottom of the list. This can be done by adding an r to the previous flag, which means using the -ltr flag as shown in the following figure:
That’s how you can use the ls command to list the files by last modification time.
2. List Files by Last Access Date
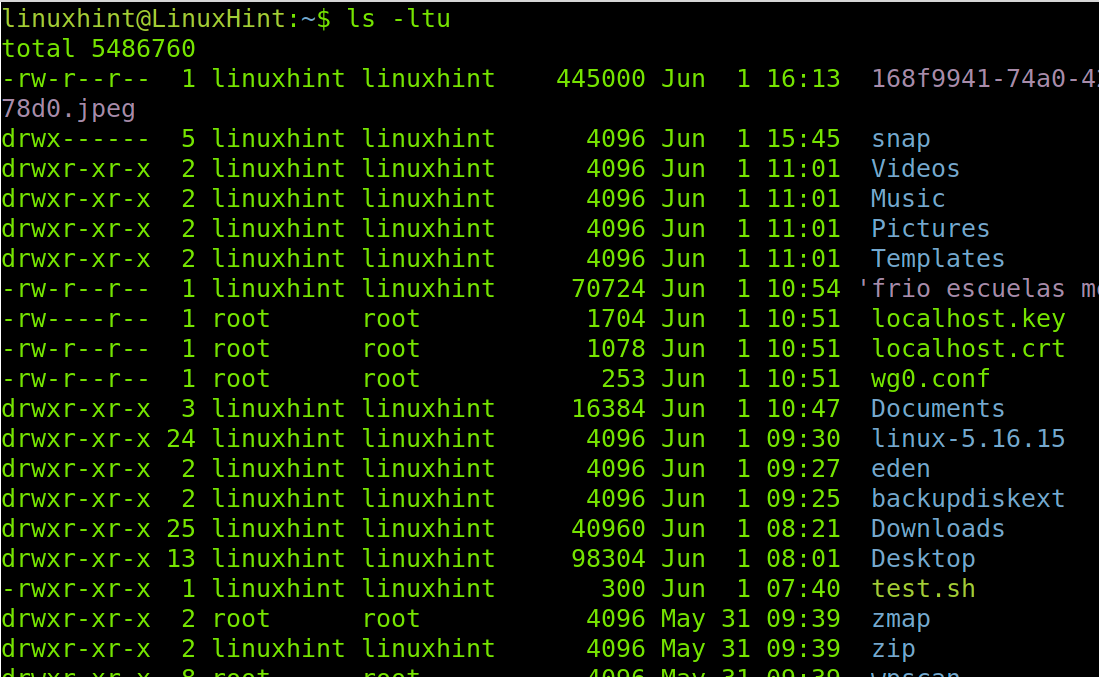
To list the files by last access time, use the previous command adding a “u” in the flag as shown in the following example:
As you can see in the previous figure, the last accessed files show up on top of the list.
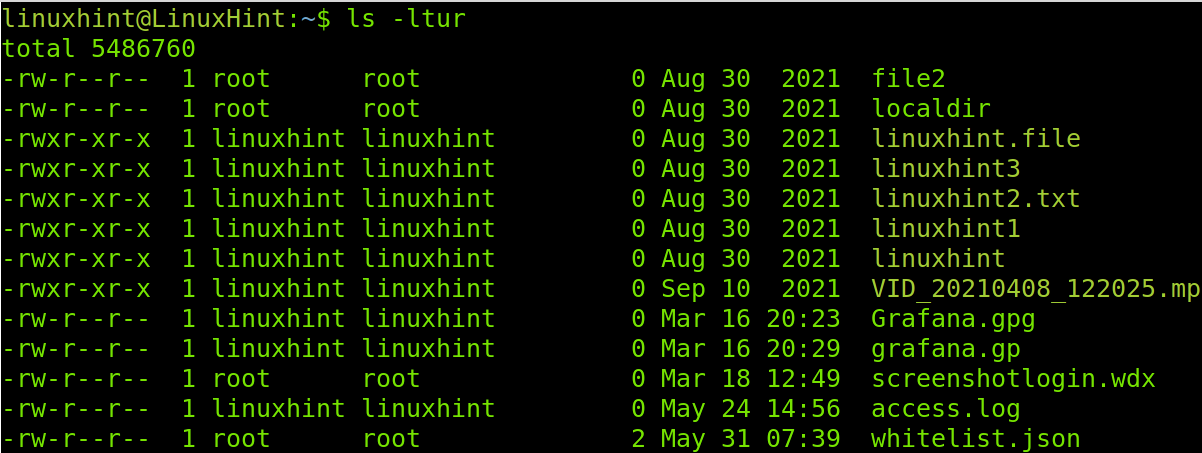
To print the last accessed files first, run the following command, adding an “r”.
Keep reading in the following illustrations to learn how to find the files by exact date.
3. List Files by Exact Date
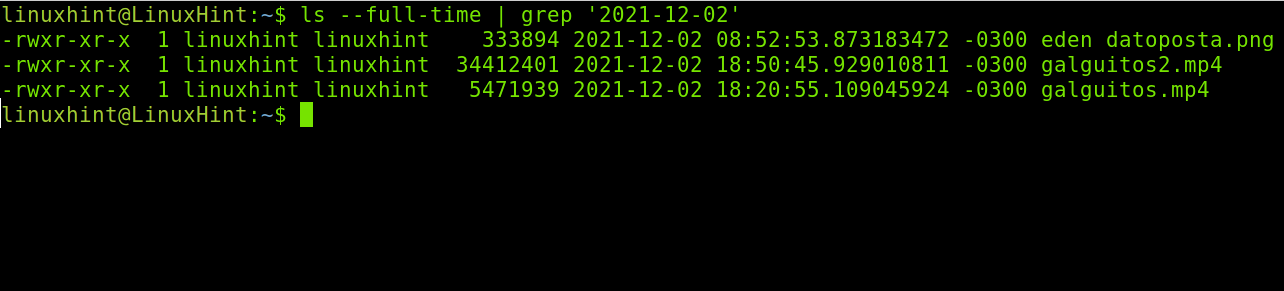
If you want to search the files by the exact date, you can combine the ls with grep as shown in the following example. The following command shows all the modified files on the 2021-12-02 date.
4. List Specific Month Modified Files
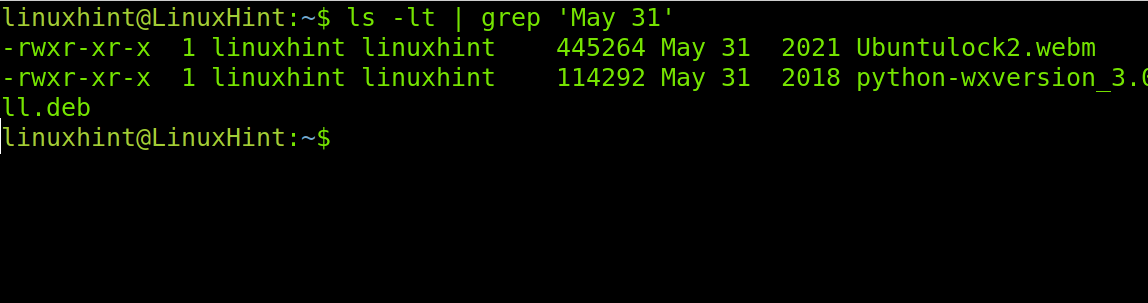
The following example shows how to list the files by month. This shows all the files which were modified on a specific month, but not on a specific year. Therefore, if we search the files from May 31 using the following command, it shows the files modified on May 31 of all years.
Listing Files by Date Using the find Command
This section explains how to list the files by date with the find command, combined with the previous explained ls command.
The following section shows an additional listing time conditions.
1. How to List Files by Time Interval Using the find Command
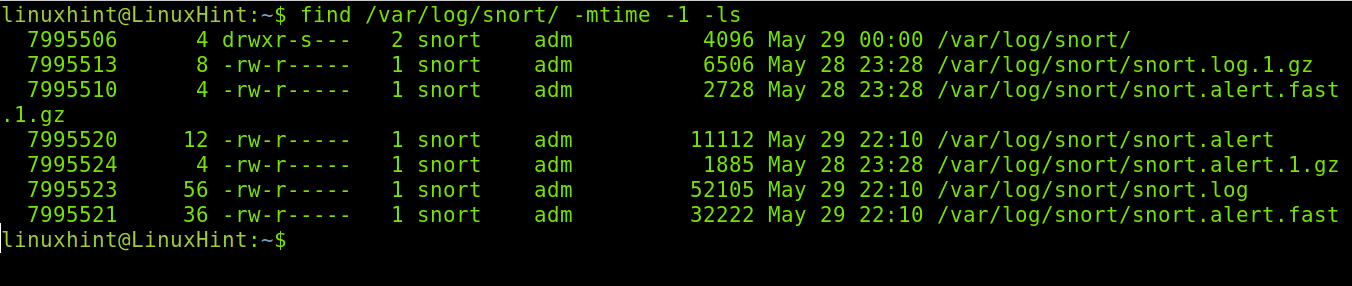
The following example shows how to use the find command followed by the -mtime flag to list the files and directories under the /var/log/snort/ directory which were created or modified in the last 24 hours, where -1 indicates a day.
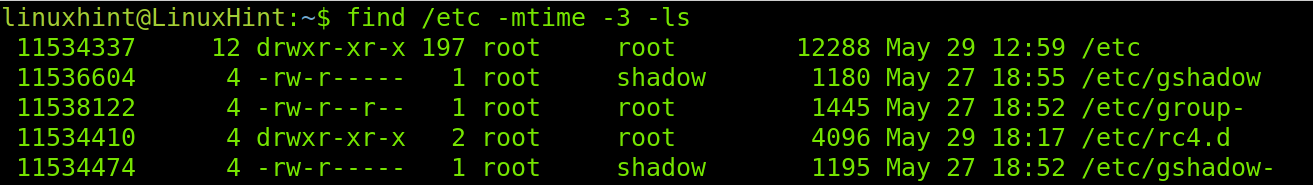
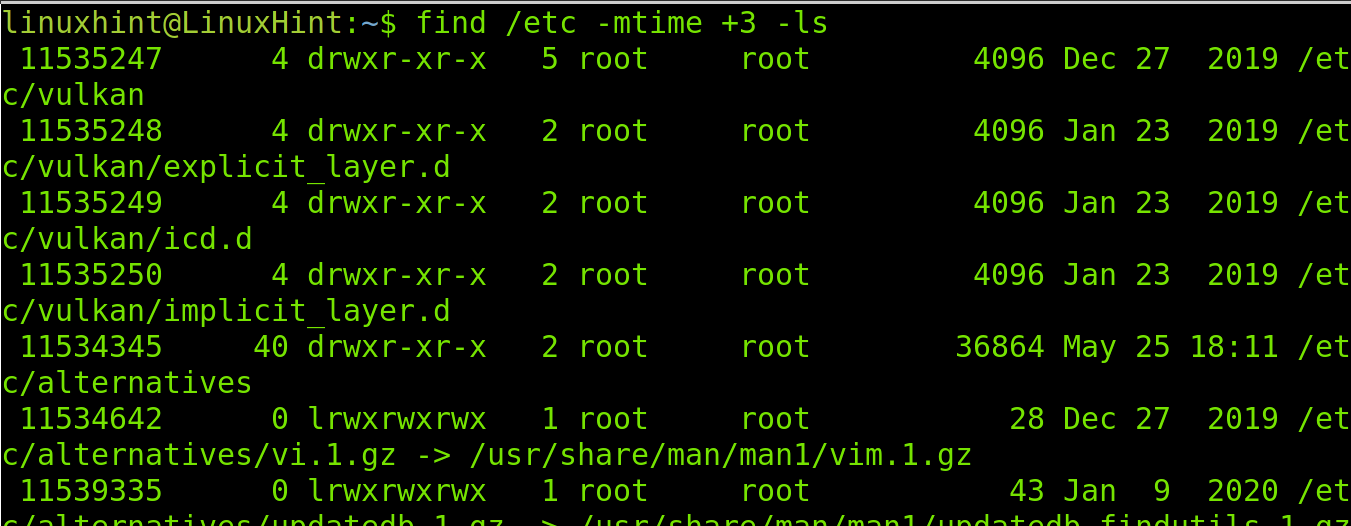
The following example does the same, but the -3 instead of -1 instructs find and ls to show the created or modified files in the last 3 days.
Contrary to the previous example, you also can use the mtime flag to specify the files before a specific date. For example, if we used the -3 flag to list the modified files in the last 3 days, we can use the +3 file to list the files which were modified before three days ago, older than 72 hours (without including files modified in the last 3 days).
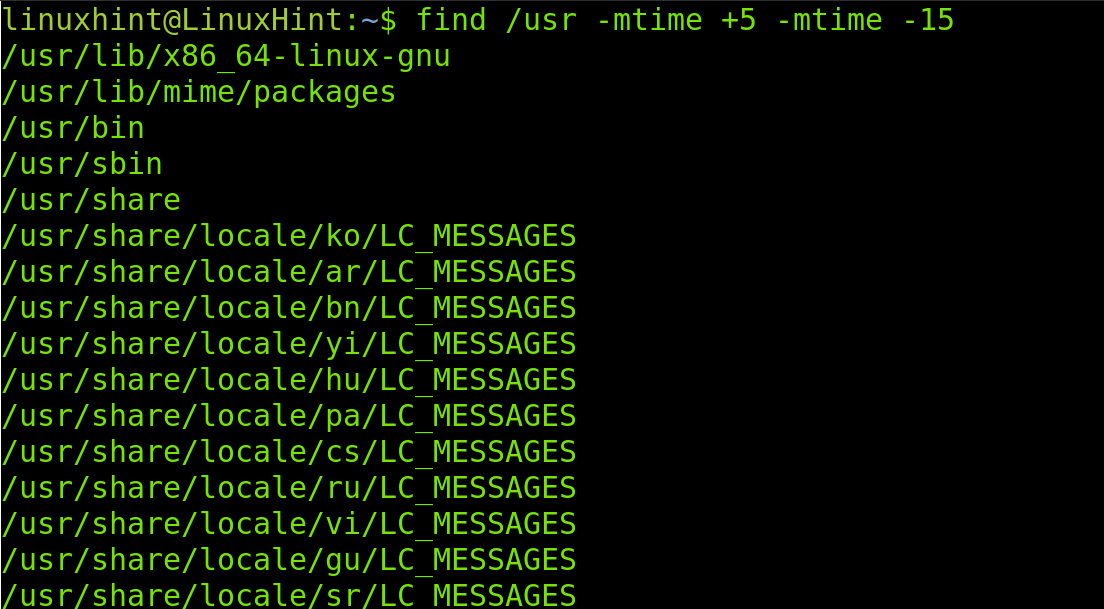
Combining both options is possible like in the following example in which we list the files older than 5 days, but newer than 15 days.
The previously described methods are excellent to easily find the files you know when were created or modified.
2. List All Modified Files After or Before a Specific Date
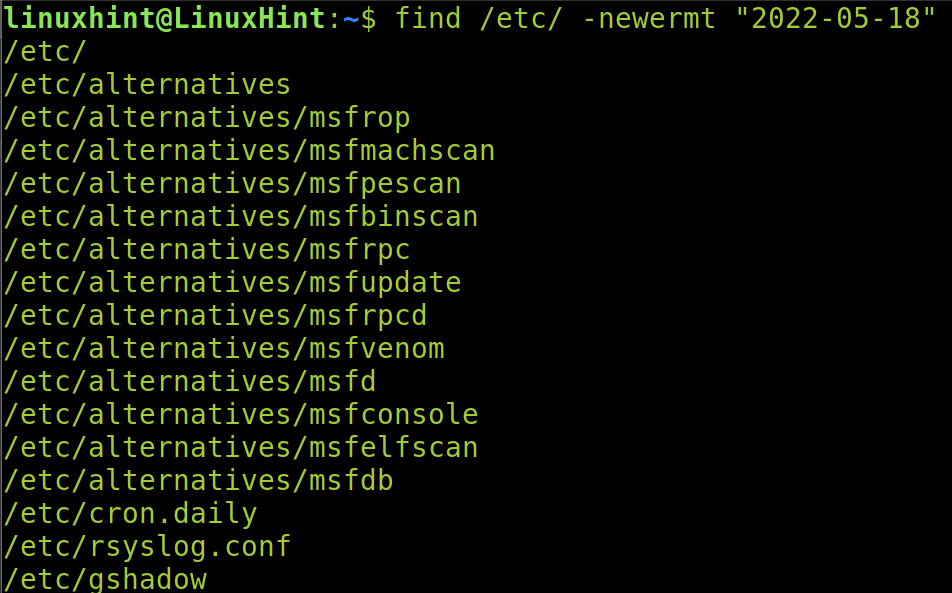
You also can use the find command followed by the -newermt flag to find the files which were modified after or before a specific date.
Therefore, if we want to list the files modified after 22/05/18, we run the command shown in the following figure:
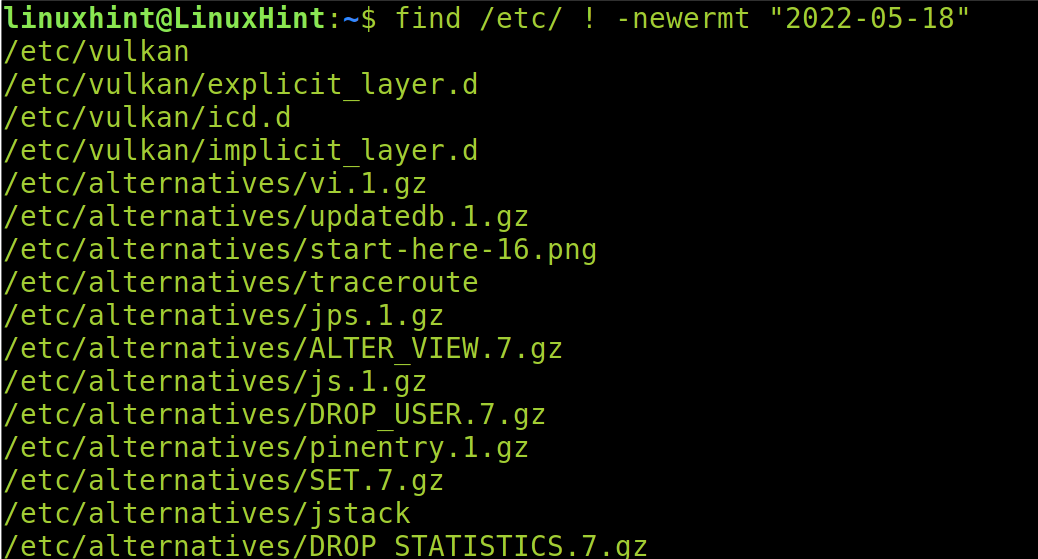
Contrary to the previous example, if we want to list only the files which were modified before 2022/05/18, we run the command shown in the following screenshot. Note that we added a “!” symbol before the -newermt flag.
Keep reading to learn how to do the same with the minute units.
3. Listing After Certain Minutes Modified Files
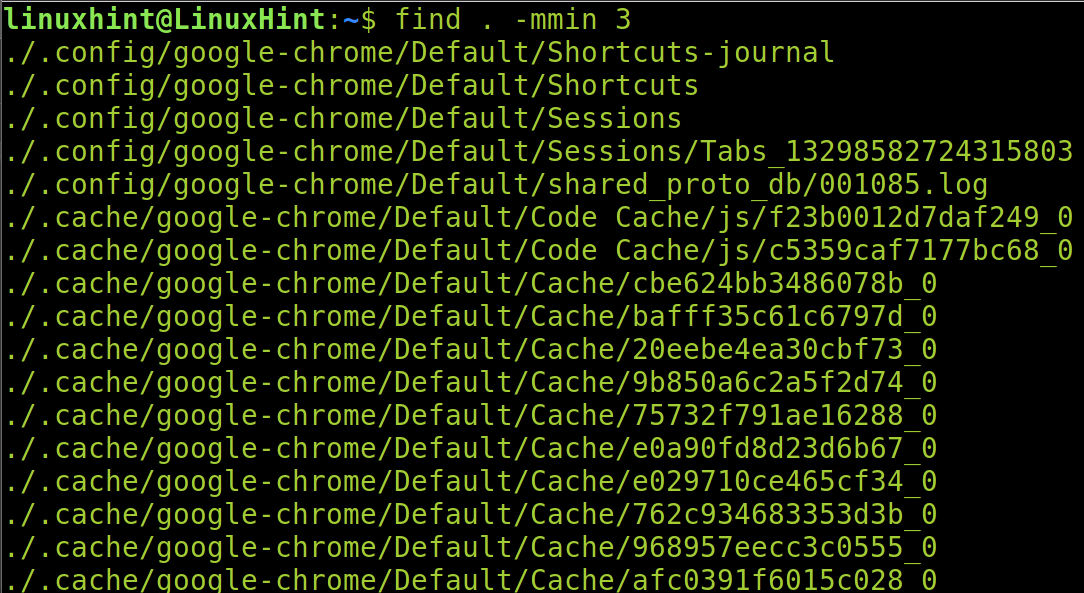
When using the find command, you also can implement the -mmin flag to specify the minute units.
The following command instructs the find to show the files which were modified in the last 3 minutes within the current directory (Dot).
We optimized this tutorial for the users looking for a fast solution by showing practical examples first. You can read the explanation on how the previously described commands work in the following illustrations:
What Are mtime, atime and ctime Timestamps
Every Linux file (including directories) has 3 timestamps in its metadata which contain information on file access, file modification, or metadata modification.
The mtime, atime and ctime timestamps are known as MAC Timestamps because of their initials.
- The mtime Timestamp: This timestamp contains information on file creation or modification date. This is the timestamp checked by the previously explained commands when we want to manage or list the files by their creation or modification date.
- The atime Timestamp: This timestamp contains information about the file’s last access. This is the timestamp checked by the previously explained commands when we want to list the last accessed files.
- The ctime Timestamp: This timestamp does not contain information on the file itself, but on its metadata. This timestamp does not inform us about modifications on the file content, but modifications on the metadata like file permissions. If we are looking for files whose permissions were recently edited, we can use the ctime to find these files.
By learning what timestamps are, you can understand how the commands we executed in the previous sections work.
Conclusion
As any user may suppose, knowing how to find and list the files by date or time is a must to know for every Linux user. This can help us for any type of task, from daily tasks to related administration complex tasks. As you can see, all the described steps are pretty easy to learn and implement. In some cases, you can get the same result using the different commands. Here, we only described a way for each listing type to avoid redundancy and prioritize the user understanding.
Any Linux user can incorporate those commands and improve his experience before the Linux terminals. It is highly recommended to practice all the examples shown, at least to remember their existence, by reading the man page for specifications. All instructions in this document are useful for all the Linux distributions.
Thank you for reading this tutorial explaining how to list the files by date in Linux. Keep following us for more professional Linux articles.
About the author
David Adams
David Adams is a System Admin and writer that is focused on open source technologies, security software, and computer systems.
How to Sort Output of ‘ls’ Command By Last Modified Date and Time
One of the commonest things a Linux user will always do on the command line is listing the contents of a directory. As we may already know, ls and dir are the two commands available on Linux for listing directory content, with the former being more popular and in most cases, preferred by users.
When listing directory contents, the results can be sorted based on several criteria such as alphabetical order of filenames, modification time, access time, version and file size. Sorting using each of these file properties can be enabled by using a specific flag.
In this brief ls command guide, we will look at how to sort the output of ls command by last modification time (date and time).
Let us start by executing some basic ls commands.
Linux Basic ls Commands
1. Running ls command without appending any argument will list current working directory contents.
2. To list contents of any directory, for example /etc directory use:
3. A directory always contains a few hidden files (at least two), therefore, to show all files in a directory, use the -a or —all flag:
4. You can as well print detailed information about each file in the ls output, such as the file permissions, number of links, owner’s name and group owner, file size, time of last modification and the file/directory name.
This is activated by the -l option, which means a long listing format as in the next screenshot:
Sort Files Based on Time and Date
5. To list files in a directory and sort them last modified date and time, make use of the -t option as in the command below:
6. If you want a reverse sorting files based on date and time, you can use the -r option to work like so:
We will end here for now, however, there is more usage information and options in the ls command, so make it a point to look through it or any other guides offering ls command tricks every Linux user should know or use sort command. Last but not least, you can reach us via the feedback section below.