- What support does Ubuntu have for the Apple Magic Mouse? [closed]
- 2 Answers 2
- Ubuntu Wiki
- Pairing the Magic Mouse
- Problem: Pairing does not persist between reboots on Maverick (10.10)
- Multitouch status
- Finding your input device
- Installing PyMT and configuring it
- Related links
- Saved searches
- Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
- 0xABAD/magic-mouse-2
- Name already in use
- Sign In Required
- Launching GitHub Desktop
- Launching GitHub Desktop
- Launching Xcode
- Launching Visual Studio Code
- Latest commit
- Git stats
- Files
- README.md
- About
What support does Ubuntu have for the Apple Magic Mouse? [closed]
This question is unlikely to help any future visitors; it is only relevant to a small geographic area, a specific moment in time, or an extraordinarily narrow situation that is not generally applicable to the worldwide audience of the internet. For help making this question more broadly applicable, visit the help center.
Does Ubuntu support the full functionality of the Apple Magic Mouse? What bluetooth adapters work best? What are the caveats?
This question appears to be abandoned, if you are experiencing a similar issue please ask a new question with details pertaining to your problem. If you feel this question is not abandoned, please flag the question explaining that. 🙂
2 Answers 2
Please see this to get help with MultiTouch in Ubuntu: https://wiki.ubuntu.com/Multitouch#Community%20Help
There is a section dedicated to the Apple Magic Mouse, I also have that device and am interested in documenting any multitouch information there.
The above page also includes information on testing and using demos for multitouch.
If you want to see the current gestures available in Ubuntu 10.10 you will need to install the Netbook edition (Unity). On a standard desktop you don’t need to reinstall, just add the ubuntu-netbook package, logout, and login again making sure you choose Ubuntu Netbook Edition at the bottom of the login screen (after choosing your user).
Ubuntu Wiki

The Magic Mouse is a multi-touch mouse produced by Apple Inc.
It can be used as a single-touch or multi-touch device in Ubuntu by pairing it using the Bluetooth utilities in Ubuntu. The following setup instructions only need to be followed once, then Ubuntu will recognize the Magic Mouse without further configuration.
Note: This has been tested in Ubuntu Maverick (10.10) only.
Pairing the Magic Mouse
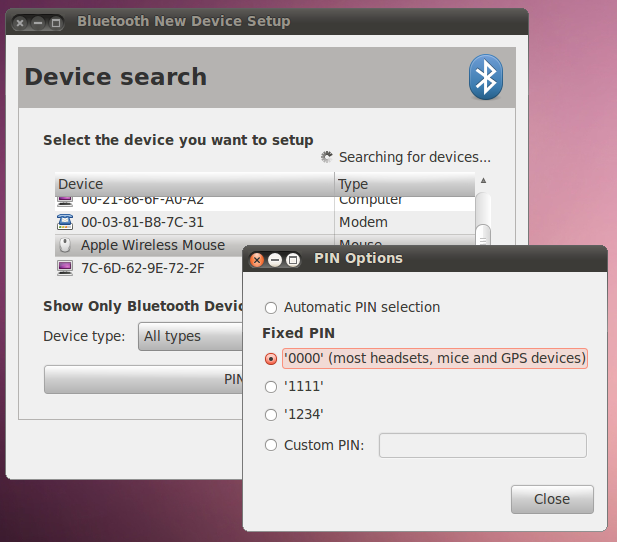
Once you have inserted batteries in your Magic Mouse, if your system is Bluetooth-capable and its radio is enabled, go to System > Preferences > Bluetooth and click on Setup new device. . Once the Bluetooth setup dialog opens, you should see you mouse listed. Click once on it, then choose «PIN options..». Make sure «0000» is selected under «Fixed PIN»:
Clicking Forward should then complete the pairing, which Ubuntu will remember.
The Magic Mouse can be forced in pairing mode by turning it off and on again (the «on» position will show green color in the switch position).
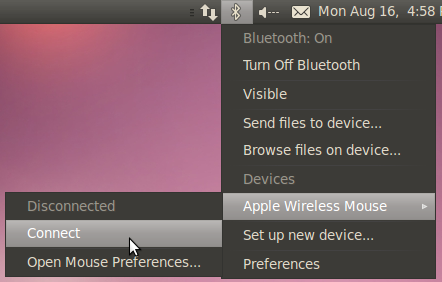
Once the device has been connected once or moved from another system, you can force pairing again by going to the Bluetooth applet and choosing Apple Wireless Mouse > Connect (if a PIN is asked, you can provide 0000 as the PIN code and press Enter to pair the mouse):
Once these steps have been completed the mouse will remain available in Ubuntu.
Problem: Pairing does not persist between reboots on Maverick (10.10)
If you find that you are not being prompted to «Always grant access» (refer to the Apple Magic Trackpad article) and that the device is not available after a reboot (i.e., you have to reconnect), try adding the pincode for the device (0000) to /var/lib/bluetooth//pincodes, like so:
- Determine the physical (model-specific) and unique device IDs from the output of lsinput (from the «input-tools» package) as shown below.
- Create /lib/bluetooth//pincodes as the root user (or with sudo):
# This folder *should* already exist, create it with 'sudo mkdir' if not. # You can use TAB to complete, if it's the only Bluetooth device on your system: cd /lib/bluetooth/ sudo gedit pincodes
Multitouch status
Finding your input device
Once your mouse has been paired, the hid_magicmouse module should automatically load. To verify this, issue the following command from a terminal:
$ lsmod | grep magic hid_magicmouse 5958 0 hid 67710 3 hid_magicmouse,hidp,usbhid
Here is example output for lsinput (from the «input-tools» package) with a Magic Mouse present (other irrelevant input device removed):
$ sudo lsinput /dev/input/event7 bustype : BUS_BLUETOOTH vendor : 0x5ac product : 0x30d version : 132 name : "Apple Wireless Mouse" phys : "XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX" uniq : "XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX" bits ev : EV_SYN EV_KEY EV_REL EV_ABS
In this case the input device would be /dev/input/event7. The input device number would be 7.
For more information on testing this device for multi-touch support, see Multitouch/Testing.
Installing PyMT and configuring it
To experiment multi-touch capabilities of the Apple Magic Mouse, you can try using PyMT, an open source library for developing multi-touch applications. You will need the device name as ound aboce (in this example, /dev/input/event7). See the Ubuntu PyMT documentation for this.
Related links
- Multitouch — Ubuntu community documentation
- Multitouch/AppleMagicTrackpad — community documentation for the Magic Trackpad, a similar device with some support in Ubuntu 10.10 and later for additional multitouch gestures.
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Magic_Mouse — Wikipedia entry
- http://www.apple.com/magicmouse/ — Apple product page
Multitouch/AppleMagicMouse (последним исправлял пользователь pittsford-216-226-127-122 2013-04-24 12:53:34)
The material on this wiki is available under a free license, see Copyright / License for details.
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session. You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session. You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.
Connect Apple’s Magic Mouse 2 with scrolling on Linux
0xABAD/magic-mouse-2
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
Name already in use
A tag already exists with the provided branch name. Many Git commands accept both tag and branch names, so creating this branch may cause unexpected behavior. Are you sure you want to create this branch?
Sign In Required
Please sign in to use Codespaces.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching Xcode
If nothing happens, download Xcode and try again.
Launching Visual Studio Code
Your codespace will open once ready.
There was a problem preparing your codespace, please try again.
Latest commit
Git stats
Files
Failed to load latest commit information.
README.md
These are my notes for getting Apple’s Magic Mouse 2 with scrolling when connected to work with Linux. While I’m running Ubuntu 19.04 this should work with other distro’s at it only involves udev which is standard with any modern Linux kernel.
DISCLAIMER: While I’ve used Linux off an on over the years, I am by no means an expert. I managed to get the Magic Mouse 2 working for me it might not work for you, and I most likely will not be able to assist you. Finally, while these instructions merely add a configuration file and shell script to your system, I take no responsibility for any damage that may occur on yours. As with anything you find on the internet. USE AT YOUR OWN RISK.
UPDATE: RicardoEPRodrigues has created a one stop shop that builds and installs the driver, necessary udev rules, and load script with a single install script. While this repo remains here for informational purposes your best bet is to checkout his work and not fuss with all these details.
Apple’s Magic Mouse 1 works with Ubuntu out of the box (I tried with a co-worker’s), Magic Mouse 2 on the other hand does not work completely (no scrolling) as it speaks a different protocol. Thankfully, someone has written a working driver that you can get from here:
From those instructions, you don’t need DKMS nor do you need to run the install.sh script. Instead just build the kernel module:
cd Link-Magic-Trackpad-2-Driver/linux/drivers/hid make clean make Note that the repository will then have you unload the existing driver and load the one you just built which will cause your Magic Mouse 2 to work as intended. However, if you disconnect the mouse, reboot, reset bluetooth, etc. the driver will not be reloaded. I thought I would be clever and replace the existing driver on my system with this new one but everytime I reconnected the mouse the scrolling would not work and I would still have to manually reload the driver.
The work-around listed here is definitely a kludge and uses udev to run a script when the Magic Mouse 2 is connected via bluetooth. I would recommend checking out this tutorial about udev rules along with reading the man pages. Note that the tutorial is a bit old in internet years and refers to tools udevinfo , udevtest , udevcontrol , and udevtrigger . These should be replaced with udevadm info , udevadm test , udevadm control , and udevadm trigger respectively. The udevadm command is pretty handy and you should definitely check out the man page for it.
The first thing to do is learn how to identify the Magic Mouse when it is connected. We can look at the output of tail -f ~/.local/share/xorg/Xorg.0.log while connecting the Magic Mouse 2 via Bluetooth and look for lines similiar to these:
[ 3821.555] (II) config/udev: Adding input device Magic Mouse 2 (/dev/input/mouse3) [ 3821.555] (II) No input driver specified, ignoring this device. [ 3821.555] (II) This device may have been added with another device file. [ 3821.686] (II) config/udev: Adding input device Magic Mouse 2 (/dev/input/event21) [ 3821.686] (**) Magic Mouse 2: Applying InputClass "libinput pointer catchall" [ 3821.686] (**) Magic Mouse 2: Applying InputClass "Magic Mouse 2" [ 3821.686] (II) Using input driver 'libinput' for 'Magic Mouse 2' The important line here is the config/udev: Adding input device Magic Mouse 2 (/dev/input/event21) or more specifically the /dev/input/event21 part. This acutal location may differ on your system. With this piece of information you can lookup the mouse’s physical ID with udevadm info -a -p $(udevadm info -q path -n /dev/input/event21) . This will print out a lot of info but important part will look similiar to:
looking at parent device '//devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:14.0/usb1/1-6/1-6:1.0/bluetooth/hci0/hci0:2$6/0005:004C:0269.0013/input/input654': KERNELS=="input654" SUBSYSTEMS=="input" DRIVERS=="" ATTRS=="Magic Mouse 2" ATTRS=="d0:c6:37:e4:5f:fb" ATTRS=="98:46:0a:ab:e2:e7" ATTRS=="0" It’s the ATTRS==»d0:c6:37:e4:5f:fb» (your ID may differ) that will be used in a udev rule to identify the mouse inside a rule in the /etc/udev/rules.d directory. In that directory create a 10-magicmouse.rules file and add the following:
SUBSYSTEMS=="input", \ ATTRS=="d0:c6:37:e4:5f:fb", \ ACTION=="add", \ SYMLINK+="input/magicmouse", \ RUN+="/home/user_name/path/to/magic-mouse-2-add.sh" The 10- prefix was picked arbitrarily and could be any number as it is used to determine the lexical ordering of rules in the kernel. The earlier the file is loaded guarantees that the rule will be applied before any others. Ensure that the ATTRS contains the correct ID found from earlier and ensure that the RUN+= portion contains an absolute path to a script on your system. Don’t use a relative path or ~ as the path is not interpreted by a shell and udev processes the path under root. With that place a shell script can be created at that location and should contain the following:
Replace the /home/user_name/path/to with the location of where you downloaded and built the Magic Mouse 2 driver. You can also adjust the scroll_speed to a value of your liking (somewhere between 0 to 63). If you wish to disable scroll acceleration or middle clicking with 3 fingers then set those values to zero. When this script is run it will unload the default Magic Mouse driver and then load the new one built eariler.
Now we need to reload the udev database with:
With that in place the Magic Mouse 2 will now be properly loaded with scrolling when connected via Bluetooth. Note that isn’t perfect and sometimes the kernel will attempt to reload the driver several times every a few seconds. Also, your mouse may randomly disconnect at times but this was happening to me before applying this fix, may be related to a kernel battery power management issue, and something I am looking into.
About
Connect Apple’s Magic Mouse 2 with scrolling on Linux