- Linux Directory Structure Explained for Beginners
- Linux directory structure
- / – The root directory
- /bin – Binaries
- /dev – Device files
- /etc – Configuration files
- /usr – User binaries and program data
- /home – User personal data
- /lib – Shared libraries
- /sbin – System binaries
- /tmp – Temporary files
- /var – Variable data files
- /boot – Boot files
- /proc – Process and kernel files
- /opt – Optional software
- /root – The home directory of the root
- /media – Mount point for removable media
- /mnt – Mount directory
- /srv – Service data
- LinuxFilesystemTreeOverview
- Examples
- Main directories
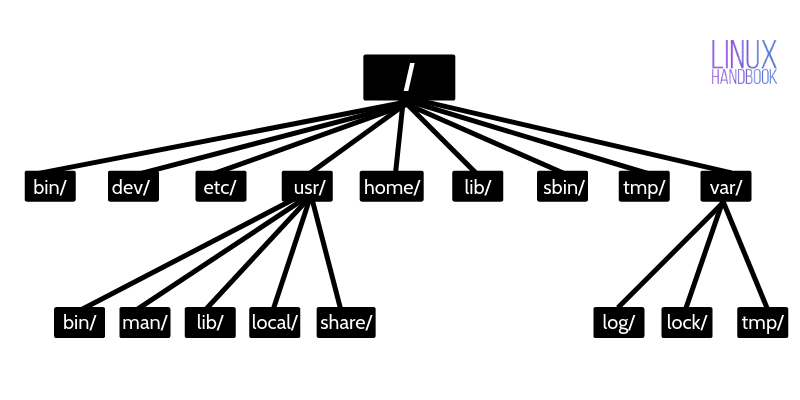
Linux Directory Structure Explained for Beginners
This tutorial explains the Linux directory structure. You’ll learn the Linux filesystem hierarchy along with the purpose of the various directories on a Linux system.
If you are even faintly acquainted with Linux, you might have heard the terms root, lib, bin etc. These are various directories that you’ll find in all Linux distributions.
In fact, the Linux Foundation maintains a Filesystem Hierarchy Standard (FHS). This FHS defines the directory structure and the content/purpose of the directories in Linux distributions. Thanks to this FHS, you’ll find the same directory structure in (almost) all the Linux distributions.
Let’s see the Linux directory structure in detail.
Linux directory structure
Linux is based on UNIX and hence it borrows its filesystem hierarchy from UNIX. You’ll fine a similar directory structure in UNIX-like operating systems such as BSD and macOS. I’ll be using the term Linux hereafter instead of UNIX though.
/ – The root directory
Everything, all the files and directories, in Linux are located under ‘root’ represented by ‘/’. If you look at the directory structure, you’ll realize that it is similar to a plant’s root.
Since all other directories or files are descended from root, the absolute path of any file is traversed through root. For example, if you have a file in /home/user/documents, you can guess that the directory structure goes from root->home->user->documents.
The cruel rm -rf / joke
You may have come across some jokes on internet that mentions “rm -rf /” . rm command is used for removing files and directories in Linux.
With rm -rf /, you ask your system to forcefully and recursively delete the contents of the root directory. Since root directory has everything underneath, you end up deleting everything and your Linux system just vanishes (theoretically).
Most Linux distribution won’t run this command unless you provide –no-preserve-root. In any case, don’t be curious to run this command. Curiosity killed the cat, after all.
/bin – Binaries
The ‘/bin’ directly contains the executable files of many basic shell commands like ls, cp, cd etc. Mostly the programs are in binary format here and accessible by all the users in the Linux system.
/dev – Device files
This directory only contains special files, including those relating to the devices. These are virtual files, not physically on the disk.
Some interesting examples of these files are:
- /dev/null: can be sent to destroy any file or string
- /dev/zero: contains an infinite sequence of 0
- /dev/random: contains an infinite sequence of random values
/etc – Configuration files
The /etc directory contains the core configuration files of the system, use primarily by the administrator and services, such as the password file and networking files.
If you need to make changes in system configuration (for example, changing the hostname), this is where you’ll find the respective files.
/usr – User binaries and program data
in ‘/usr’ go all the executable files, libraries, source of most of the system programs. For this reason, most of the files contained therein is readonly (for the normal user)
- ‘/usr/bin’ contains basic user commands
- ‘/usr/sbin’ contains additional commands for the administrator
- ‘/usr/lib’ contains the system libraries
- ‘/usr/share’ contains documentation or common to all libraries, for example ‘/usr/share/man’ contains the text of the manpage
/home – User personal data
Home directory contains personal directories for the users. The home directory contains the user data and user-specific configuration files. As a user, you’ll put your personal files, notes, programs etc in your home directory.
When you create a user on your Linux system, it’s a general practice to create a home directory for the user. Suppose your Linux system has two users, Alice and Bob. They’ll have a home directory of their own at locations /home/alice and /home/bob.
Do note that Bob won’t have access to /home/alice and vice versa. That makes sense because only the user should have access to his/her home. You may read about file permissions in Linux to know more on this topic.
/lib – Shared libraries
Libraries are basically codes that can be used by the executable binaries. The /lib directory holds the libraries needed by the binaries in /bin and /sbin directories.
Libraries needed by the binaries in the /usr/bin and /usr/sbin are located in the directory /usr/lib.
/sbin – System binaries
This is similar to the /bin directory. The only difference is that is contains the binaries that can only be run by root or a sudo user. You can think of the ‘s’ in ‘sbin’ as super or sudo.
/tmp – Temporary files
As the name suggests, this directory holds temporary files. Many applications use this directory to store temporary files. Even you can use directory to store temporary files.
But do note that the contains of the /tmp directories are deleted when your system restarts. Some Linux system also delete files old files automatically so don’ store anything important here.
/var – Variable data files
Var, short for variable, is where programs store runtime information like system logging, user tracking, caches, and other files that system programs create and manage.
The files stored here are NOT cleaned automatically and hence it provides a good place for system administrators to look for information about their system behavior. For example, if you want to check the login history in your Linux system, just check the content of the file in /var/log/wtmp.
/boot – Boot files
The ‘/boot’ directory contains the files of the kernel and boot image, in addition to LILO and Grub. It is often advisable that the directory resides in a partition at the beginning of the disc.
/proc – Process and kernel files
The ‘/proc’ directory contains the information about currently running processes and kernel parameters. The content of the proc directory is used by a number of tools to get runtime system information.
For example, if you want to check processor information in Linux, you can simply refer to the file /proc/cpuinfo. You want to check memory usage of your Linux system, just look at the content of /proc/meminfo file.
/opt – Optional software
Traditionally, the /opt directory is used for installing/storing the files of third-party applications that are not available from the distribution’s repository.
The normal practice is to keep the software code in opt and then link the binary file in the /bin directory so that all the users can run it.
/root – The home directory of the root
There is /root directory as well and it works as the home directory of the root user. So instead of /home/root, the home of root is located at /root. Do not confuse it with the root directory (/).
/media – Mount point for removable media
When you connect a removable media such as USB disk, SD card or DVD, a directory is automatically created under the /media directory for them. You can access the content of the removable media from this directory.
/mnt – Mount directory
This is similar to the /media directory but instead of automatically mounting the removable media, mnt is used by system administrators to manually mount a filesystem.
/srv – Service data
The /srv directory contains data for services provided by the system. For example, if you run a HTTP server, it’s a good practice to store the website data in the /srv directory.
I think this much information is enough for you to understand the Linux directory structure and its usage.
In the end, if you want, you can download and save this image for quick reference to the directory structure in Linux systems.
LinuxFilesystemTreeOverview
Ubuntu (like all UNIX-like systems) organizes files in a hierarchical tree, where relationships are thought of in teams of children and parent. Directories can contain other directories as well as regular files, which are the «leaves» of the tree. Any element of the tree can be referenced by a path name; an absolute path name starts with the character / (identifying the root directory, which contains all other directories and files), then every child directory that must be traversed to reach the element is listed, each separated by a / sign.
A relative path name is one that doesn’t start with /; in that case, the directory tree is traversed starting from a given point, which changes depending on context, called the current directory. In every directory, there are two special directories called . and .., which refer respectively to the directory itself, and to its parent directory.
The fact that all files and directories have a common root means that, even if several different storage devices are present on the system, they are all seen as directories somewhere in the tree, once they are mounted to the desired place.
FilePermissions are another important part of the files organization system: they are superimposed to the directory structure and assign permissions to each element of the tree, ultimately decided by whom it can be accessed and how.
Examples
An absolute path name, pointing to what is normally an executable file on an Ubuntu system:
An absolute path name, but pointing to a directory instead of a regular file:
A relative path name, which will point to /usr/bin/test only if the current directory is /usr/:
A relative path name, which will point to /usr/bin/test if the current directory is any directory in /usr/, for instance /usr/share/:
A path name using the special shortcut ~, which refers to the current user’s home directory:
Path names can contain almost any character, but some characters, such as space, must be escaped in most software, usually by enclosing the name in quotation marks:
"~/Examples/Experience ubuntu.ogg"
or by employing the escape character \:
~/Examples/Experience\ ubuntu.ogg
Main directories
The standard Ubuntu directory structure mostly follows the Filesystem Hierarchy Standard, which can be referred to for more detailed information.
Here, only the most important directories in the system will be presented.
/bin is a place for most commonly used terminal commands, like ls, mount, rm, etc.
/boot contains files needed to start up the system, including the Linux kernel, a RAM disk image and bootloader configuration files.
/dev contains all device files, which are not regular files but instead refer to various hardware devices on the system, including hard drives.
/etc contains system-global configuration files, which affect the system’s behavior for all users.
/home home sweet home, this is the place for users’ home directories.
/lib contains very important dynamic libraries and kernel modules
/media is intended as a mount point for external devices, such as hard drives or removable media (floppies, CDs, DVDs).
/mnt is also a place for mount points, but dedicated specifically to «temporarily mounted» devices, such as network filesystems.
/opt can be used to store additional software for your system, which is not handled by the package manager.
/proc is a virtual filesystem that provides a mechanism for kernel to send information to processes.
/root is the superuser’s home directory, not in /home/ to allow for booting the system even if /home/ is not available.
/run is a tmpfs (temporary file system) available early in the boot process where ephemeral run-time data is stored. Files under this directory are removed or truncated at the beginning of the boot process.
(It deprecates various legacy locations such as /var/run, /var/lock, /lib/init/rw in otherwise non-ephemeral directory trees as well as /dev/.* and /dev/shm which are not device files.)
/sbin contains important administrative commands that should generally only be employed by the superuser.
/srv can contain data directories of services such as HTTP (/srv/www/) or FTP.
/sys is a virtual filesystem that can be accessed to set or obtain information about the kernel’s view of the system.
/tmp is a place for temporary files used by applications.
/usr contains the majority of user utilities and applications, and partly replicates the root directory structure, containing for instance, among others, /usr/bin/ and /usr/lib.
/var is dedicated to variable data, such as logs, databases, websites, and temporary spool (e-mail etc.) files that persist from one boot to the next. A notable directory it contains is /var/log where system log files are kept.
LinuxFilesystemTreeOverview (последним исправлял пользователь sydneypacific-seven-seventeen 2016-01-04 14:38:17)
The material on this wiki is available under a free license, see Copyright / License for details
You can contribute to this wiki, see Wiki Guide for details