- mkdir command: Create New Directories in Linux
- mkdir command examples
- Create new directories
- Create multiple directories
- Create nested directories
- Create directory with specific permissions
- Linux mkdir Command Examples
- Basic Usage of mkdir Command in Linux
- 1. Create a Directory in Linux
- 2. Create Multiple Directories in Linux
- 3. Create Multiple Directories Using the Brace Expansion
- 4. Create a Nested Sub-Directory Structure
- 5. Create a Directory with Permissions
- 6. Enable Verbose with mkdir Command
mkdir command: Create New Directories in Linux
mkdir is one of the essential Linux commands that every Linux user should know. You can create new directories using mkdir.
One of the essential Linux commands is mkdir. The mkdir allows you to make new directories (folders in common term) in Linux.
In this beginner series, you’ll learn to use the mkdir command.
mkdir command examples
The mkdir command is one of the rare few Linux commands that doesn’t have tons of options. And that makes it really simple to use.
mkdir [option] directory_name_or_pathCreate new directories
To make a new directory, use mkdir command without any option:
This will create a new directory named new_dir in the present directory. You can check it using the ls command.
[email protected]:~/tuts$ ls [email protected]:~/tuts$ mkdir new_dir [email protected]:~/tuts$ ls -l total 4 drwxrwxr-x 2 abhishek abhishek 4096 May 14 16:15 new_dirYou may also specify the path to where you want to create the new directory.
[email protected]:~/tuts$ ls new_dir [email protected]:~/tuts$ mkdir new_dir/another_new_dir [email protected]:~/tuts$ tree . └── new_dir └── another_new_dir 2 directories, 0 filesCreate multiple directories
You may also create several new directories with a single command:
mkdir new_dir_1 new_dir_2 new_dir_3All the new directories are created at the same level. You may also create nested directories which is described in the next section.
Create nested directories
You can use the option -p to create a nested directory structure. If the parent directory doesn’t exist, it will create it for you.
This is particularly helpful when you want to create a directory structure or if you want to make sure that the directory path exists.
This is what the above command created:
[email protected]:~/tuts$ mkdir -p dir1/dir2/dir3/dir4 [email protected]:~/tuts$ tree . ├── dir1 │ └── dir2 │ └── dir3 │ └── dir4 └── new_dir └── another_new_dir 6 directories, 0 filesYou may also use the -p option with a single directory. It won’t create a new directory that already exists, but it won’t throw any errors as well:
[email protected]:~/linuxhandbook$ mkdir new_dir mkdir: cannot create directory ‘new_dir’: File exists [email protected]:~/linuxhandbook$ mkdir -p new_dir [email protected]:~/linuxhandbook$ ls -l total 8 drwxrwxr-x 3 abhishek abhishek 4096 May 14 16:39 dir1 drwxrwxr-x 3 abhishek abhishek 4096 May 14 16:16 new_dirCreate directory with specific permissions
By default, your shell’s umask controls the permission on the newly created directories. If you want different file permissions on the directory, instead of creating the directory first and then changing the permission with the chmod command, you can use the -m option.
Suppose you want permission 766 on the directory you are going to create. You can use:
mkdir -m 766 new_directoryThat’s pretty much what you need to know about the mkdir command. Now that you know how to create directories, maybe you would want to learn about the rmdir command and deleting directories in Linux command line.
Linux mkdir Command Examples
Brief: In this guide, we will take a look at the mkdir command which is used to create a directory. We will also discuss some of the practical examples of it that will help beginners to operate the Linux system confidently.
As Linux users, we use files and directories on a regular basis. Files allow us to store important data whereas directories allow us to organize files in a proper way. In addition to this, we often create a hierarchical directory structure to organize the contents in a better way.
In this beginner-friendly article, we will learn about the mkdir command. As the name suggests, the mkdir command is used to create a named directory at a given path, which also allows us to create single or multiple directories at once with the required file permissions.
We should note that to use the mkdir command the user must have the required permissions on the parent directory, or else the command will fail with the permission denied error.
Just like other Linux commands, the syntax of the mkdir command is mainly divided into two groups – options and arguments:
In the above syntax, the square brackets ([]) represent the optional arguments whereas angular brackets (<>) represent the mandatory arguments.
Basic Usage of mkdir Command in Linux
As the name implies, the mkdir is a short form of the “make directory”. The good thing is that it creates a directory only if a directory or file with the same doesn’t exist at the given path. In this way, this is a very safe command and doesn’t cause any harm to the system.
In this section, we will see the basic usage of the mkdir command with examples.
1. Create a Directory in Linux
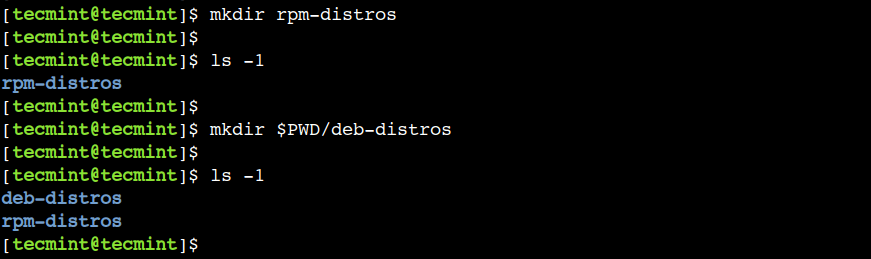
One of the fundamental use of the mkdir command is to create a named directory at a given path. So let’s create a directory with the name rpm-distros in the current working directory:
Now, use the ls command to verify that the directory has been created:
In the first example, we used the relative path with the mkdir command. However, this command also supports the absolute path.
We can use the pwd command or the pwd environment variable to find the absolute path of the current working directory.
So, let’s create the named directory – deb-distros in the current working directory using the absolute path:
Now, verify that the new directory has been created in the current working directory:
2. Create Multiple Directories in Linux
The mkdir command accepts multiple paths as an argument, which allows us to create multiple directories in one go.
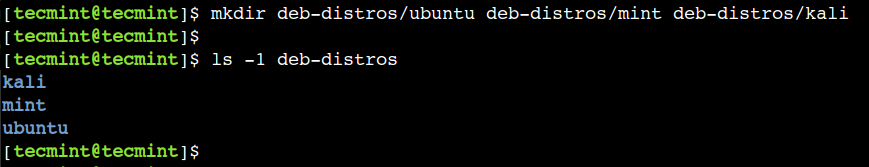
Let’s create three directories inside the deb-distros directory using the single command:
$ mkdir deb-distros/kali deb-distros/mint deb-distros/ubuntu
Now, let’s list the contents of the deb-distros directory:
As we can see, the mkdir command created multiple directories successfully.
3. Create Multiple Directories Using the Brace Expansion
In the previous example, we saw how to create multiple directories inside another directory using a single command. However, that wasn’t the most efficient way because we specified the parent directory name i.e. deb-distros with each sub-directory.
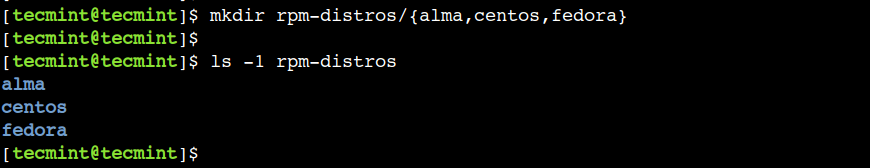
To overcome this limitation, we can specify the sub-directory names in a brace expansion as shown in the following example, where we create three sub-directories inside the rpm-distros directory:
Here, we should note the following two important points:
- There aren’t any spaces on either side of the comma (,) .
- The brace expansion feature is available in the Bash shell only hence this approach is less portable.
Now, let’s verify that the required directory structure has been created successfully:
4. Create a Nested Sub-Directory Structure
In the previous sections, we saw how to create multiple directories. However, that approach doesn’t work if we wish to create a nested directory structure. In such a case, we can use the -p option of the command that creates the parent directory if required.
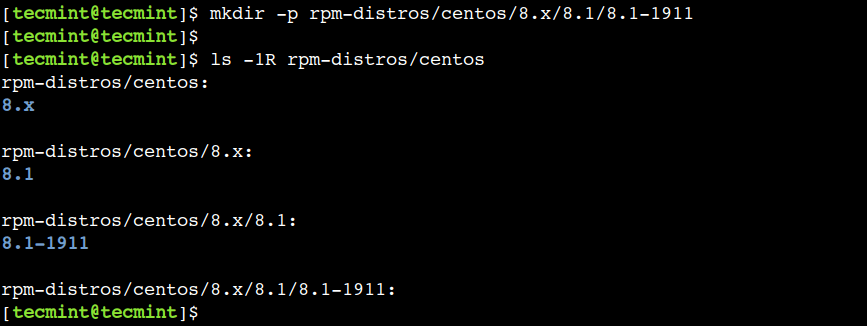
Let’s, create a nested sub-directory structure:
$ mkdir -p rpm-distros/centos/8.x/8.1/8.1-1911
Now, verify the contents of the rpm-distros/centos directory in a recursive way:
As we can see, the command created the required directory structure without reporting the error for the existing parent directories. This option comes in very handy while writing shell scripts. We can use it to suppress the directory creation error which might occur due to the existing directory.
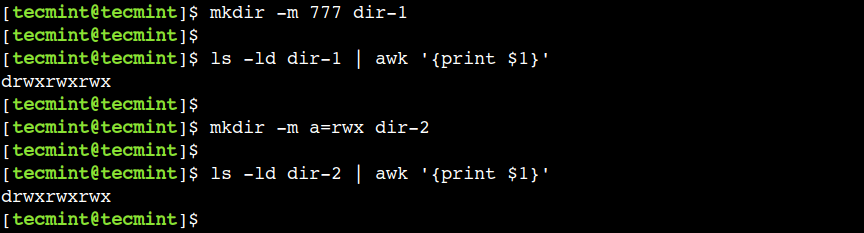
5. Create a Directory with Permissions
Sometimes, we need to modify the access permission of the directory immediately after its creation. In that case, we have to use the two commands – mkdir and chmod. However, we can achieve the same result using a single command.
Let’s use the -m option to set access permissions on a directory while creating it:
In this example, we used the numeric format to set the access permission. In a similar way, we can use the textual format.
For example, we can achieve the same result using the below command:
Now, use the ls command to find out the access permission of the directories:
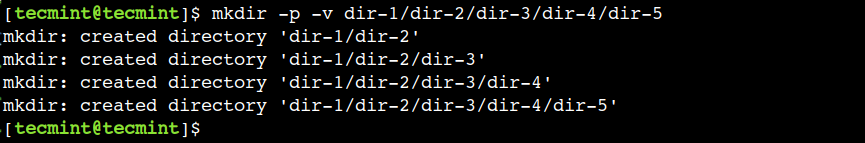
6. Enable Verbose with mkdir Command
By default, the mkdir command doesn’t print anything on the terminal after the directory creation. Hence, so far we have been using the ls command to verify whether or not the directory has been created.
To overcome this limitation, we can use the verbose mode of the command that prints the message for each created directory. This option gives meaningful information when we combine it with the –p option:
Let’s use the -v option with the command to enable the verbose mode:
$ mkdir -p -v dir-1/dir-2/dir-3/dir-4/dir-5
Now, let’s observe the output of the command:
In this article, we saw the basic usage of the mkdir command. First, we saw how to create a single directory as well as multiple directories. Next, we saw how to set permissions on a directory while creating it. Finally, we saw how to verify the directory creation using the verbose mode.
Do you know of any other best example of the mkdir command in Linux? Let us know your views in the comments below.