How to install «make» in ubuntu? [closed]
I’m trying to install «yum» or «apt-get» into my system «ubuntu centOS». I did download the binary files for these two programs from the internet using the command wget. but after decompressing the files using the command «tar -zxvf «filename» ,then configuring the file «./configuring», and then when I want to use the command «make» I get the following error «make: not found». I have searched for a method to download the «make» command but all the methods I found on the net use either the command «yum» or «apt-get» and I don’t have any of them.
You have this slightly wrong. Make is not a program you need to download. it’s a utility that comes integrated into nearly every distribution of linux.
Wait, what? «ubuntu centOS»? Those are two different flavors with their own (often radically different) ways of doing things. It’s almost certainly either one or the other, unless there’s some freakish mashup of the two i haven’t seen or heard of yet. Either way, this is a question about installing software, and seems more suited to Super User.
Just for future reference, there are a couple of major flavors of Linux. I personally count 4: Debian (which includes Ubuntu), RedHat (which includes CentOS), Slackware (including SuSE), and Gentoo. (Some would argue with Gentoo being «major», but IMO it’s popular enough to earn a place, and it’s definitely its own flavor.) Most of the big distros are derived (indirectly or indirectly) from one of those main lines; the ones that aren’t are typically specialized or indie-type stuff. And the main flavors are different enough that you’ll typically only derive from one of them.
Компиляция и установка программ из исходников
Не редко необходимые пакеты можно найти только в виде исходных текстов, в данной статье описывается метод установки пакета из исходных текстов.
Распаковка
Программы обычно распространяются в упакованных архивах, это файлы с расширениями
Нужно понимать отличие между архиватором и упаковщиком.
Для архивации директорий и файлов используется программа tar; результатом её работы является файл с расширением .tar. Грубо говоря, это копия файловой системы — директорий и файлов с их атрибутами и правами доступа, помещённая в один файл.
Данный файл по размеру будет чуть больше, чем суммарный размер файлов, которые были архивированы. Поэтому (а может и по другой причине) используют упаковщики — программы, которые позволяют уменьшить размер файла без потери данных.
Программа tar умеет распаковывать, поэтому не нужно вызывать gunzip, а можно просто указать программе tar, что файл нужно cначала распаковать. Например, команда
tar -xvf some_app_name>.tar.gz
сразу распакует и разархивирует. Отличие файлов с расширениями
лишь в том, что использовались разные упаковщики, программа tar определяет метод сжатия автоматически и дополнительных опций в данном случае не требуется.
После распаковки необходимо перейти в полученный каталог, все описываемые ниже команды выполняются в каталоге с исходными текстами пакета.
Сборка пакета
Для сборки программ в GNU/Linux используется (в основном) программа make, которая запускает инструкции из Makefile, но поскольку дистрибутивов GNU/Linux много, и они все разные, то для того чтобы собрать программу, нужно для каждого дистрибутива отдельно прописывать пути,где какие лежат библиотеки и заголовочные файлы. Программисты не могут изучать каждый дистрибутив и для каждого отдельно создавать Makefile. Поэтому придумали конфигураторы, которые «изучают» систему, и в соответствии с полученными знаниями создают Makefile. Но на конфигураторе они не остановились и придумали конфигураторы конфигураторов …на этом они остановились
Для сборки нам нужны компиляторы: они прописаны в зависимостях пакета build-essential, так что достаточно установить его со всеми зависимостями. Ещё нужны autoconf и automake.
Итак, чтобы собрать что-то из исходников, нужно сначала собрать конфигуратор; как собрать конфигуратор, описано в файле configure.in. Для сборки конфигуратора необходимо выполнить
Если таких скриптов в архиве не оказалось, то можно выполнить последовательно следующие команды:
aclocal autoheader automake --gnu --add-missing --copy --foreign autoconf -f -Wall
Все эти команды используют файл configure.in. После выполнения этих команд создастся файл configure. После этого необходимо запустить конфигуратор для проверки наличия всех зависимостей, а также установки дополнительных опций сборки (если возможно) и просмотра результата установки (опционально- может не быть)
Конфигуратор построит Makefile основываясь на полученных знаниях и файле makefile.am. Можно передать конфигуратору опции, предусмотренные в исходниках программы, которые позволяют включать/отключать те или иные возможности программы, обычно узнать о них можно командой
Также есть набор стандартных опций, вроде
, которая указывает, какой каталог использовать для установки. Для Ubuntu обычно
БЕЗ слеша в конце! Теперь можно запустить процесс сборки самой программы командой
Для сборки достаточно привелегий обычного пользователя. Окончанием сборки можно считать момент, когда команды в консоли перестанут «беспорядочно» выполняться и не будет слова error. Теперь всё скомпилировано и готово для установки.
Установка
Усилия потраченные на Правильную установку в последствии с лихвой окупятся в случае удаления или обновления устанавливаемого программного обеспечения.
Правильная установка(Вариант №1)
Установка при помощи утилиты checkinstall. Для установки выполните
sudo apt-get install checkinstall
Минус данного способа: checkinstall понимает не все исходники, поскольку автор программы может написать особые скрипты по установке и checkinstall их не поймёт.
Для создания и установки deb-пакета необходимо выполнить
Правильная установка(Вариант №2)
Быстрое создание deb-пакета «вручную».
Основное отличие от предыдущего способа заключается в том, что в данном случае вы создаете пакет вручную и отслеживаете все вносимые изменения. Так же этот способ подойдет вам, если исходники не поддерживают сборку пакета с checkinstall.
fakeroot make install DESTDIR=`pwd`/tempinstall
Создадим в «корне пакета» директорию DEBIAN и сложим в DEBIAN/conffiles список всех файлов, которые должны попасть в /etc:
сd tempinstall mkdir DEBIAN find etc | sed "s/^/\//" > DEBIAN/conffiles
Package: имя_пакета Version: 1.2.3 Architecture: amd64/i386/armel/all Maintainer: Можете вписать своё имя, можете дребедень, но если оставить пустым, то dpkg будет ругаться Depends: Тут можно вписать список пакетов через запятую. Priority: optional Description: Тоже надо что-нибудь вписать, чтобы не кидало предупреждения
sudo dpkg -i tempinstall.deb
How to install make on Ubuntu
The ”make” command in Linux is used to compile and manage a collection of applications and files from source code. It allows developers to use the terminal to install and collect a variety of programs. It also manages and reduces the amount of time that is required for the compilation. The make command’s primary goal is to break down a huge program into smaller pieces and assess whether or not it needs to be recompiled. It also gives the essential instructions for recompiling them.
The make command is used to execute the makefile which is a unique file that includes the shell commands we write to keep the project running. It includes executable targets and instructions and is not permitted to generate several makefiles. It’s best if you make a separate directory for it. It maintains track of recently updated files, so only update those that are needed. As a result, this article will show you how to install the make package on Ubuntu.
How to install the Make package on Ubuntu
Before installing the make package, it is better to update your already installed packages; otherwise, you may find compatibility issues with some software. You can do that by typing.
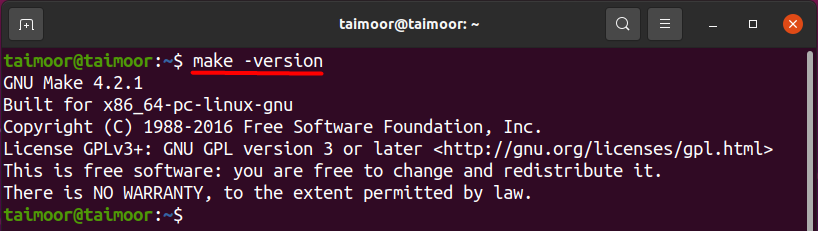
This command will provide you with the information of all outdated packages that can be upgraded to the newer version, so this is highly recommended before installing any new package. Make package comes in default in the Ubuntu OS, so you should verify if it is already installed before considering installing it. You can verify it by typing the below-mentioned command in the terminal.
If the make package is not installed in Ubuntu due to any reason, you will get the error as shown below.
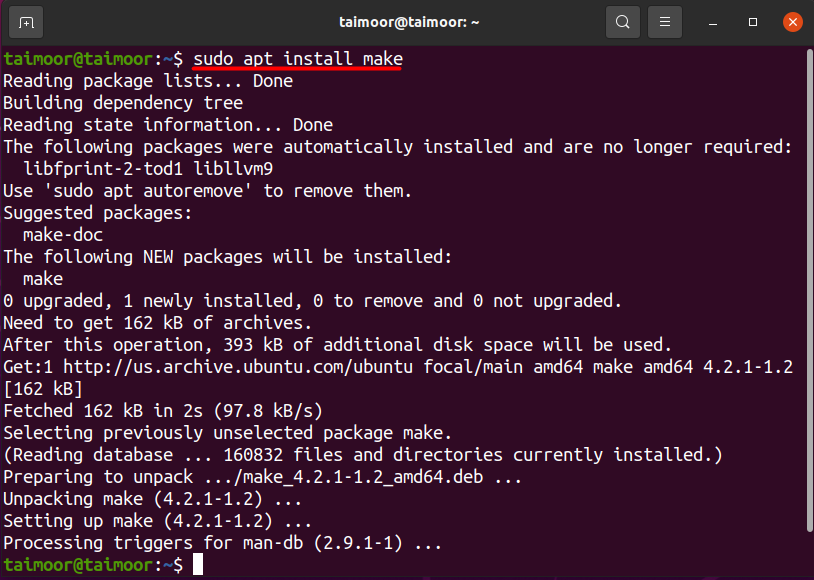
You can install the make package by typing.
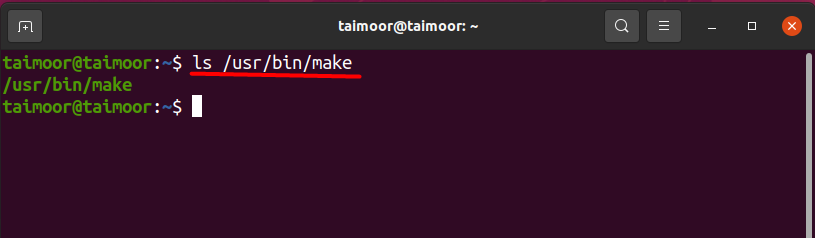
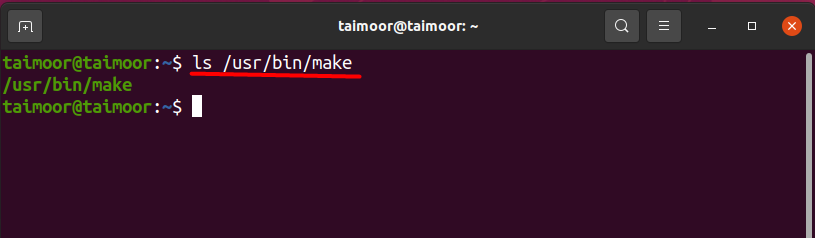
Your system should have a make directory; otherwise, you cannot use the make package. You can verify that by typing.
If the directory is available then you can use the “make” utility; if it displays an error as shown below then there is a way to solve this problem as well:
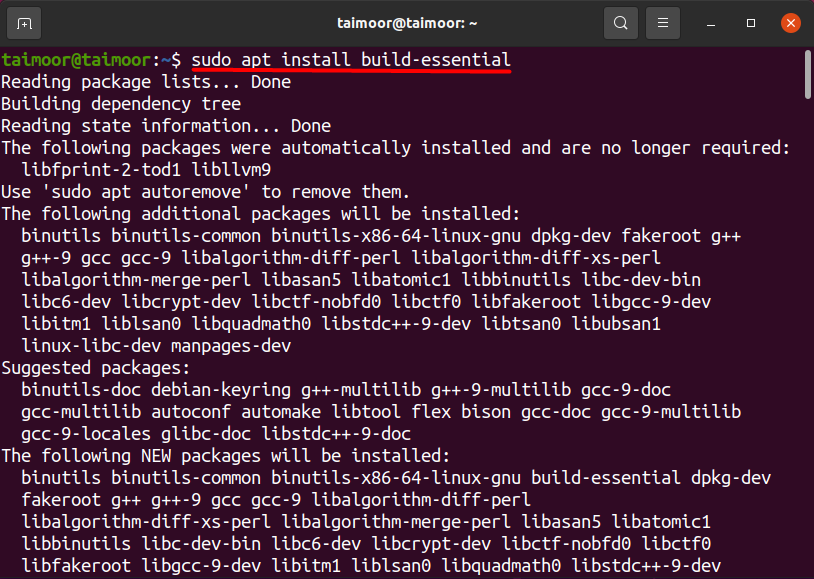
By installing the build-essential package you get rid of this error. It is also known as a meta-package, and you can use it to install a make package and several other packages as well. Many packages are dependent and linked with this package, and you can’t install them without installing the meta-package first. For its installation, you need to type the following command in the terminal.
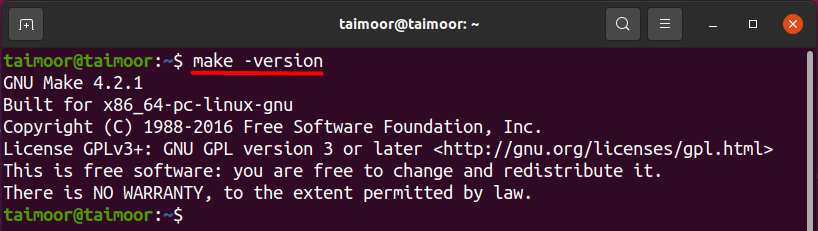
After its installation, you should check the make version to verify if it is properly installed or not. You can also verify the make directory that you won’t see if it is not working correctly before. You can check the version as discussed before by typing the command.
And you can check the make directory, use:
As of now, you can see both the version and the directory, the make package is now correctly installed, and you can use it as per your requirement.
Conclusion
The make command in Linux is used to compile and manage a collection of applications and files from source code. It allows developers to use the terminal to install and collect a variety of programs. It also manages and reduces the time that is required for the compilation process for large projects. In this article, we have shown you how you can install the make package, and some of the solutions have also been discussed if you are not able to install this package
About the author
Taimoor Mohsin
Hi there! I’m an avid writer who loves to help others in finding solutions by writing high-quality content about technology and gaming. In my spare time, I enjoy reading books and watching movies.