- How to Change Kernel Version in Manjaro
- Can I change my kernel version?
- How do I check my manjaro kernel version?
- How do I switch back to old kernel?
- How do I downgrade manjaro kernel?
- Which kernel should I use manjaro?
- How do I change the default Linux kernel?
- How do I find my kernel version?
- How do I open kernel version?
- What is the latest manjaro kernel?
- What is a realtime kernel?
- What is the latest Linux kernel?
- Manjaro Kernels
- Identifying the Kernel Being Used
- Adding New Kernels
- Removing Kernels
- Don’t forget the mhwd-kernel -h command
How to Change Kernel Version in Manjaro
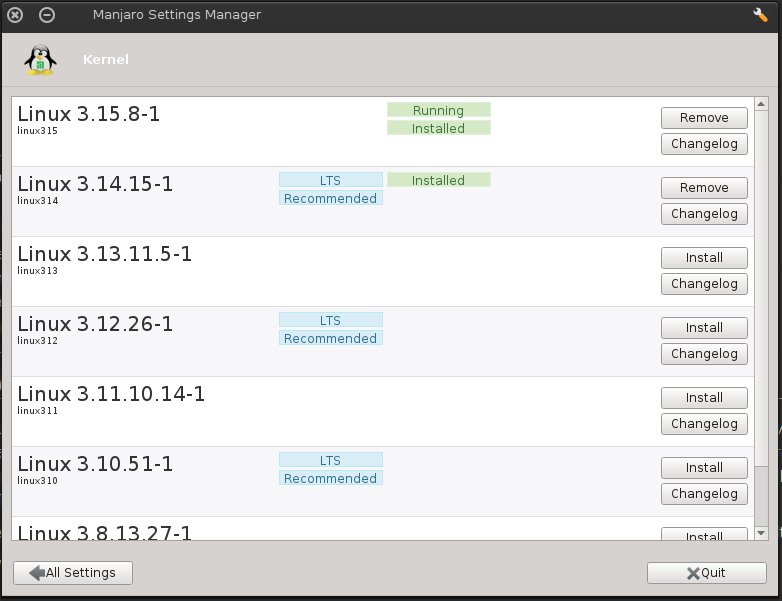
GUI Tool. Manjaro Settings Manager offers an easy way to add and remove kernel (including the necessary kernel modules). New kernels can be installed by pressing the «Install» button. All necessary kernel modules will be installed automatically with a new kernel as well.
Can I change my kernel version?
Need to update the system. first check current version of kernel use uname -r command. . once system upgraded after that system need to reboot. some time after reboot system new kernel version not coming.
How do I check my manjaro kernel version?
On default xfce4 desktop press ALT+F2 , type xfce4-terminal and press ENTER . The above command will reveal the Manjaro system release version and well as the Manjaro code name.
How do I switch back to old kernel?
- Hold the shift key when you see the Grub screen, to get to the grub options.
- you may have better luck holding the shift key all the time through the boot if you have a fast system.
- Choose Advanced options for Ubuntu.
How do I downgrade manjaro kernel?
Removing an old kernel from Manjaro works the same way as installing a new one. To start off, open up the Manjaro Settings Manager, and click on the penguin icon. From here, scroll down and select the installed Linux kernel that you want to uninstall. Click the “uninstall” button to start the removal process.
Which kernel should I use manjaro?
Kernel 5.10 is the latest release. It’s also an LTS release. So I’d generally recommend it. LTS stans for Long Term Support, and is generally the best to choose if you do not want to live on the edge and aren’t looking for a specific feature.
How do I change the default Linux kernel?
As mentioned in the comments, you can set the default kernel to boot into using the grub-set-default X command, where X is the number of the kernel you want to boot into. In some distributions you can also set this number by editing the /etc/default/grub file and setting GRUB_DEFAULT=X , and then running update-grub .
How do I find my kernel version?
- uname Command.
- hostnamectl Command.
- Display the /proc/version File.
- dmesg Command.
How do I open kernel version?
Scroll down and find the Kernel version box.
This box displays your Android’s kernel version. If you don’t see Kernel version on the Software information menu, tap More. This will bring up more options, including your kernel version.
What is the latest manjaro kernel?
Manjaro
| Manjaro 20.2 | |
|---|---|
| Latest release | 21.0.2 (Ornara) / April 18, 2021 |
| Package manager | pacman, libalpm (back-end) |
| Platforms | x86-64 i686 (unofficial) ARM (unofficial) |
| Kernel type | Monolithic (Linux) |
What is a realtime kernel?
A real-time kernel is software that manages the time of microprocessor to ensure that time-critical events are processed as efficiently as possible. . Most real-time kernels are preemptive. This means that the kernel will always try to execute the highest priority task that is ready to run.
What is the latest Linux kernel?
Linux kernel
| Tux the penguin, mascot of Linux | |
|---|---|
| Linux kernel 3.0.0 booting | |
| Latest release | 5.12.1 (2 May 2021) [±] |
| Latest preview | 5.12-rc8 (18 April 2021) [±] |
| Repository | git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/torvalds/linux.git |
Module
OS Module Common Functionschdir()getcwd()listdir()mkdir()makedirs()rmdir()removedirs()Which module of Python gives methods related to operating system.
Install
Install/Uninstall . deb filesTo install a . deb file, simply Right click on the . deb file, and choose Kubuntu Package Menu->Install Package.Altern.
Mysql
How do I download MySQL on Debian 10?How do I start MySQL on Debian?Where is MySQL installed on Debian?How install MySQL database on Linux?How do I fi.
Latest news, practical advice, detailed reviews and guides. We have everything about the Linux operating system
Manjaro Kernels
As the name would imply, as with the kernel of a seed, the Linux kernel is the core of a Linux operating system. Every other element of a Linux-based operating system is built around the kernel, which acts as an interface between your computer’s hardware and the applications that run on it. As hardware and software applications become more complex and sophisticated, so do the kernels to fully utilise them. As such, Linux kernels are continually under development, with new revisions and versions being regularly released. Further information on the very latest developments in kernel technology can be found at The Linux Kernel Archives
The first Linux kernel was originally developed by Linus Torvalds, the creator of Linux. It is now an open-source project containing millions of lines of code generated by thousands of programmers. However, Linus Torvalds still has the final authority on their development and release.
Manjaro Settings Manager offers an easy way to add and remove kernel (including the necessary kernel modules).
New kernels can be installed by pressing the «Install» button. All necessary kernel modules will be installed automatically with a new kernel as well.
Please consider the «Recommended» tag when choosing a kernel. LTS means Long Term Support, which is safest for most users. «What should I be aware of if I’m not on an LTS kernel?»
The newest installed Kernel will be booted by default, but to run other kernels that are installed, see Selecting Kernels section below.
Instead of using the Manjaro Settings Manager GUI to identify, choose, add, and remove kernels everything can be achieved from a terminal as well.
Identifying the Kernel Being Used
This terminal command will give your system’s kernel information:
The above command not only shows which kernel is being used, it also lists any other kernels that are also installed, as shown in the following example Terminal output:
Currently running: 5.0.17-1-MANJARO (linux50) The following kernels are installed in your system: * linux419 * linux420 * linux50
As seen in the above example, Manjaro is running kernel 5.0.17-1-MANJARO. The information given here is not arbitrary; each part of the kernel name identifies something about that kernel:
- The 5 indicates the version
- The 0 indicates the major revision
- The 17 indicates the minor revision
- The 1 indicates the revision of the Manjaro package
- MANJARO indicates the specific distribution it is used for
Adding New Kernels
Tip mhwd-kernel will automatically update a newly installed kernel with any modules currently used in your existing kernel. For example, if you were to update from kernel 4.14 to 4.19, mhwd-kernel would automatically update 4.19 with any and all modules present in 4.14. How about that!
Manjaro not only supports the use of multiple kernels (selectable from the boot screen), but allows easy access to the very latest bleeding edge kernels as well. This is undertaken through use of Manjaro’s own MHWD-kernel (Manjaro Hard-Ware Detection) command. The syntax of the command is as follows:
sudo mhwd-kernel [-i] [new kernel: linux(version)] [optional - remove the current kernel: rmc]
When listing a new kernel to be installed in the command, it is not necessary to write the entire version number. For example, any version of Kernel 4.19 can be listed simply as ‘linux419’, and any version of Kernel 4.14 can be listed as ‘linux414’, and so on.
The optional rmc (remove current) component is of vital importance. Using this will result in your existing kernel being deleted upon the installation of the new kernel. Otherwise, if it is not used, then the existing kernel will be kept, and will be selectable alongside the new kernel at the boot screen. It is recommended — especially if updating to the latest bleeding edge kernel — to keep your old one, even if only for a short time afterwards. This the safer option, and the old kernel can be easily removed when satisfied with the stability and functionality of the new one.
As an example, once the terminal is opened, the following command will install a new kernel (4.19) without deleting the existing kernel currently being used:
Otherwise, the following command will install a new kernel (5.10) to replace the existing kernel, which will be deleted:
Either way, Manjaro will automatically configure the new kernel for you, ready for immediate use. Once completed, close the terminal and re-boot the system for the change to take effect.
Removing Kernels
Warning DO NOT attempt to delete an existing kernel while it is actually being used by Manjaro at the time. You can first identify what kernel is running on your system by using the command mhwd-kernel -li in the terminal (see above).
Where multiple kernels are present on your system, pacman can be used to remove them in the terminal. It may be necessary to delete a total of three elements of the kernel in total to completely remove it:
Whether or not the headers and extra modules must be deleted depends on whether or not they have been installed.
1. To remove a kernel use the following syntax: sudo mhwd-kernel -r linux[version]
Here is an example for removing kernel 5.0.17-1
2. To delete a kernel’s headers, the syntax is:
For example, to delete the headers of kernel version 5.0.x from the system, the following command would be entered:
3. To delete a kernel’s extra modules, the syntax is:
For example, to delete the extra modules of kernel version 5.0.x from the system, the following command would be entered:
4. To delete all elements of a kernel at the same time — where they are all present on your system — the syntax is:
user $ sudo pacman -R linux[version] linux[version]-headers linux[version]-extramodules COPY TO CLIPBOARD
For example, to completely remove all elements of kernel version 5.0.x, the following command would be entered:
Please note however, that attempting to delete multiple elements at once if they are not present on your system will result in an error message before the operation itself is aborted. It is also worthwhile noting if Manjaro is being run in a virtual machine (e.g. Oracle Virtualbox), you may not be able to delete certain kernels if they contain elements important to the virtualisation process itself.
Don’t forget the mhwd-kernel -h command
As with most Linux commands that can be entered into the Terminal, typing the command followed by either -h or —help will print out the usage & available options to the Terminal for your reference. Here is the output of the mhwd-kernel -h command:
Usage: mhwd-kernel [option] -h --help Show this help message -i --install Install a new kernel [kernel(s)] [optional: rmc = remove current kernel] -l --list List all available kernels -li --listinstalled List installed kernels -r --remove Remove a kernel [kernel(s)]
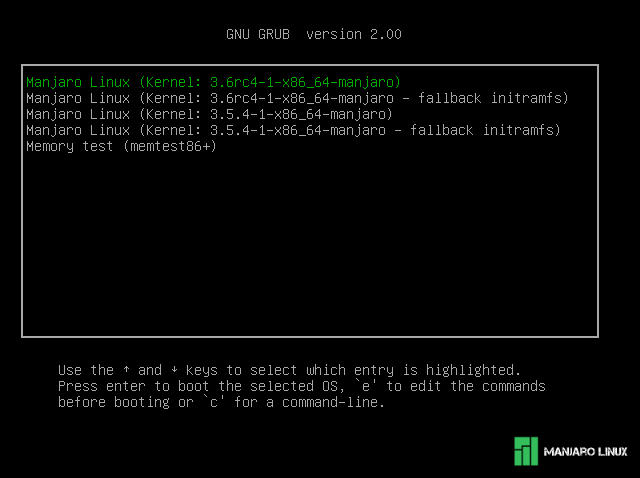
All available kernels installed on your system will be presented upon booting up. GNU GRUB is visible with a couple of options. Choose «Advanced Options for Manjaro Linux» by using the arrow keys ↑ ↓ on your keyboard and then ↵ Enter .
On the next screen (as illustrated) are backup copies of each kernel version installed (which will also be automatically removed if or when a kernel version is deleted). To select a kernel, simply use the arrow keys ↑ ↓ to highlight the desired version, and then press ↵ Enter .
Tip In case you have hidden your grub menu, you can just press Esc during boot to show it and make your changes
Cookie-файлы помогают нам предоставлять наши услуги. Используя наши сервисы, вы соглашаетесь с использованием cookie-файлов.