Маршрутизатор cisco разрешить telnet
Как включить telnet в Cisco на примере Cisco 2960+48TC-S
Всем привет, сегодня хочу рассказать, как включить telnet на оборудовании Cisco. Ранее мы рассмотрели, как включить ssh и создали локального пользователя. Я конечно больше предпочитаю ssh, но может кому пригодится, так как ситуации у всех могут быть, абсолютно разными, да и для кругозора ваших знаний, это будет полезно. Все, как обычно у оборудования Cisco, делается до безобразия, очень просто, я бы наверно перефразировал и сказал был дружелюбно, все для людей.
Логинимся через консоль в Cisco, и переходим в режим конфигурирования.
Как включить telnet в Cisco на примере Cisco 2960+48TC-S-02
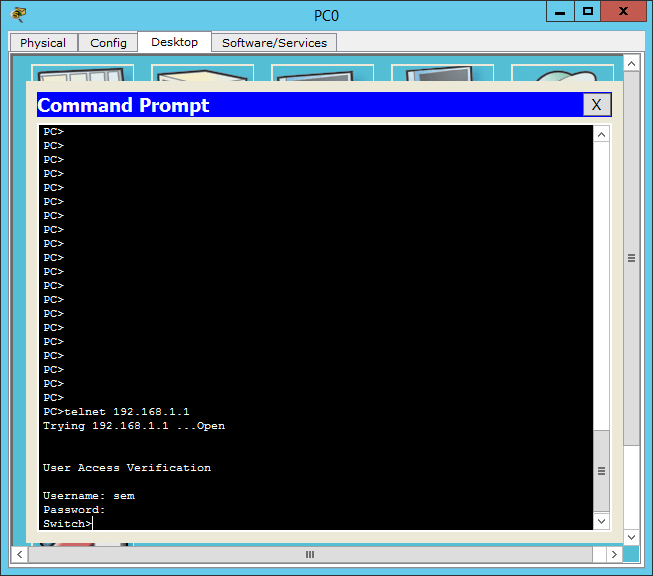
Теперь проверим с какого либо компьютера подключиться по telnet. У меня на коммутаторе настроен ip адрес 192.168.1.1
Как включить telnet в Cisco на примере Cisco 2960+48TC-S-03
как видим я успешно залогинился через telnet. Вот так вот просто включить telnet в Cisco на примере Cisco.
Популярные Похожие записи:
Сброс Digi AnywhereUSB на заводские настройки
Не открывается сайт nic.ru из-за ddos-атаки
- Ошибка someone is currently logged into the APC
Как перезагрузить Digi AnywhereUSB
Настройка пароля на Digi AnywhereUSB
- Сравнение маршрутизаторов Cisco и Juniper, что лучше в 2022 году?
Configure Cisco Routers and Switches for Telnet Access
I wanted to start from the basics as this is the first article under the category Networking. A Tutorial on How to Configure Cisco Routers and Switches for Telnet Access. Lets start with some info about the Telnet protocol – Telnet uses port 23, this protocol is used for remote administration of devices through commands. Take note that Telnet sends commands as plaintext over the network so don’t use telnet this unless you’re on a testing environment or 101% sure your network is safe from intruders.
Configuring Cisco Routers for Telnet access
Assuming you’ve configured the interface IP address settings properly just entering the following commands will configure your cisco router for telnet access.
Router>enable Router#configure terminal Router(config)#enable secret password Router(config)#service password-encryption Router(config)#line vty 0 4 Router(config-line)#password telnetpw Router(config-line)#login
The command enable secret sets a privilege mode password and stores it in an encrypted format so that it isn’t visible when viewing the running configuration. If you already have a privilege mode password set ignore the command. Replace the word password with your strong password. Similarly after the “line vty” command replace telnetpw with your telnet password. The “service password-encryption” stores the telnet password in encrypted format.
Configuring Cisco Switches for Telnet access
To Configure Switches for telnet access we use the same commands as seen above with one addition. Switches being Layer 2 devices do not have any IP addresses assigned by default, so we’ll assign an IP address to a VLAN interface which I’ll show you how. Follow the commands below
Switch>enable Switch#configure terminal Switch(config)#enable secret password Switch(config)#service password-encryption Switch(config)#line vty 0 4 Switch(config-line)#password telnetpw Switch(config-line)#login Switch(config-line)#exit Switch(config)#int vlan 1 Switch(config-if)#ip add 10.0.0.1 255.0.0.0 Switch(config-if)#no shutdown
Replace the word password in the “enable secret” command to your preferred privilege mode password, also replace telnetpw with your telnet password. When you configure the VLAN interface enter the VLAN number in which the TELNET CLIENT (this is the system FROM which you will execute the telnet command) is located. If you haven’t configured VLAN just enter 1, as for the IP address it should be in the same subnet as the Telnet client and the IP address should be unique i.e., it should NOT be assigned to any other host on the network.
Go to your system and telnet to the router/switch
PC>telnet 10.0.0.1 Trying 10.0.0.1 . Open User Access Verification Password: Switch>
Important:- As said earlier Telnet sends commands and passwords in plaintext over the network. The “enable secret” and “service password-encryption” commands only STORE the password in encrypted format