- How to cross compile from windows g++ cygwin to get linux executable file [duplicate]
- Compiling C++ application for Windows target under Linux
- Installing MinGW toolchain
- General configuration
- Using pkg-config
- Adding runtime libraries to Wine
- Running with Wine under Clion
- How do I invoke the MinGW cross-compiler on Linux?
- 4 Answers 4
How to cross compile from windows g++ cygwin to get linux executable file [duplicate]
I have an updated cygwin-full install ,mingw ,codeblocks on a windows system. i have a c++ program which performs xml generation based on input. I understand to build an executable file for unix we use makefiles. makefiles being typical project files . Hence i used the plugin cbp2make.exe to get the makefile for the cbp project file. and i tried to execute make in cygwin. hoping to get a linux executable file. but this was clearly wrong. a typical test c++ test program test.c would be compiled in cygwin using gcc cross compile options like.
this would give us the linux executable file test or if no name is specified it would give an a.out This is all well and good for a simple c++ program with no included header files. I understand when we are dealing with c++ files with lot of external library files a simple g++ -o ourprojfile.exe ourprojectfile.cpp does not work hence we would need to use make files. Question 1 : Am i wrong in assuming this ?* Question 2: how can we setup cross compile to get a linux executable file directly from codeblocks. Update : the problem at my end seems to be missing dependent cpp files which i assumed i included in the main file. The solution was to include them in the main file or simply write handle like so
g++-linux myprog_linux main.cpp first.cpp second.cpp third.cpp The problem now is after i get the Linux executable file. when i try to run it on linux machine i get the error of a
/usr/local/folder/myfile/my_prog_nix: error while loading shared libraries: libstdc++.so.5: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory Compiling C++ application for Windows target under Linux
Originally published on 2018-10-14 , updated on 2023-05-26 .
Since forever, I have used Arch Linux for day-to-day computing. Nonetheless, from time to time I need to write some simple code in C++ for Windows. Switching back and forth between operating systems is cumbersome, so compiling under a virtual machine is as well.
The Windows port of GCC is named MinGW (Minimalistic GNU for Windows). Quite surprisingly, it is available in the repositories of major Linux distributions, with a wealth of open-source libraries cross-compiled for the Windows platform.
Leveraging this tool, writing multi-platform software can be almost frictionless. It works well in the IDE CLion too. For demonstration purposes, I provide a sample repository which contains a CMake project of a DLL and Windows executables built with MinGW.
Installing MinGW toolchain
Using Arch Linux, I recommend using the ownstuff unofficial repository. The compiler is packaged in a group named mingw-w64 . You might try compiling it from the AUR, but it can be a real pain. There are also many packages available for various dependency libraries; all package names start with mingw-w64- . For more details, please refer to the Arch Wiki.
MinGW is also available in the official repository under Debian — the meta-package gcc-mingw-w64 . There are numerous precompiled libraries, all having mingw in their package names. There is also an entry on the Debian Wiki about this topic.
General configuration
The most important thing is to define the compiler executables and set CMAKE_SYSTEM_NAME :
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.0) project(mingw-test) set(CMAKE_SYSTEM_NAME Windows) SET(CMAKE_C_COMPILER i686-w64-mingw32-gcc) SET(CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER i686-w64-mingw32-g++) SET(CMAKE_RC_COMPILER i686-w64-mingw32-windres) set(CMAKE_RANLIB i686-w64-mingw32-ranlib) set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "$ -std=c++14") set(CMAKE_SHARED_LIBRARY_LINK_CXX_FLAGS) Then, you simply define the executable. This requires no further comments.
add_executable(example example.cpp) To cross-compile a dynamic loadable library, you use add_library . However, for convenience, it is better to set PREFIX and SUFFIX to empty strings. This way, you can use the whole filename (with the .dll extension) as the target name.
add_library(shared_lib.dll SHARED shared_lib.cpp shared_lib.h) set_target_properties(shared_lib.dll PROPERTIES PREFIX "" SUFFIX "" LINK_FLAGS "-Wl,--add-stdcall-alias" POSITION_INDEPENDENT_CODE 0 # this is to avoid MinGW warning; # MinGW generates position-independent-code for DLL by default ) To link the executable with the aforementioned DLL, you add:
target_link_libraries(example shared_lib.dll) Using pkg-config
The common way of defining library compilation flags and directories under Unix is using the pkg-config tool. This way, your codebase is not dependent on the exact layout of directories of the distribution. Each library provides a .pc file with build parameters such as header locations, compiler flags, etc. Many packages compiled for MinGW also provide .pc files, at least under Debian and Arch Linux.
For example, let’s add zlib as a dependency:
Load PkgConfig package and find zlib:
include(FindPkgConfig) find_package(PkgConfig REQUIRED) pkg_check_modules(ZLIB "zlib") Add dependencies to example executable:
include_directories($ZLIB_INCLUDE_DIRS>) target_link_libraries(example $ZLIB_LIBRARIES>) Adding runtime libraries to Wine
When you try to run your freshly cross-compiled program under Wine, it will probably fail with a message like this:
0009:err:module:import_dll Library libstdc++-6.dll (which is needed by L"your-program.exe") not found It means that Wine cannot find the runtime libraries on which your program depends. They are usually located under /usr/i686-w64-mingw32/bin . You’ll need to add this path to the PATH variable within the Wine subsystem.
To do so, edit the file ~/.wine/system.reg . This file represents the Windows Registry under Wine. Find the PATH variable definition under [System\\CurrentControlSet\\Control\\Session Manager\\Environment] section. Append the library path translated into a Windows-like path: Z:\usr\i686-w64-mingw32\bin so it looks like this:
"PATH"=str(2):"C:\\windows\\system32;C:\\windows;C:\\windows\\system32\\wbem;Z:\\usr\\i686-w64-mingw32\\bin" Running with Wine under Clion
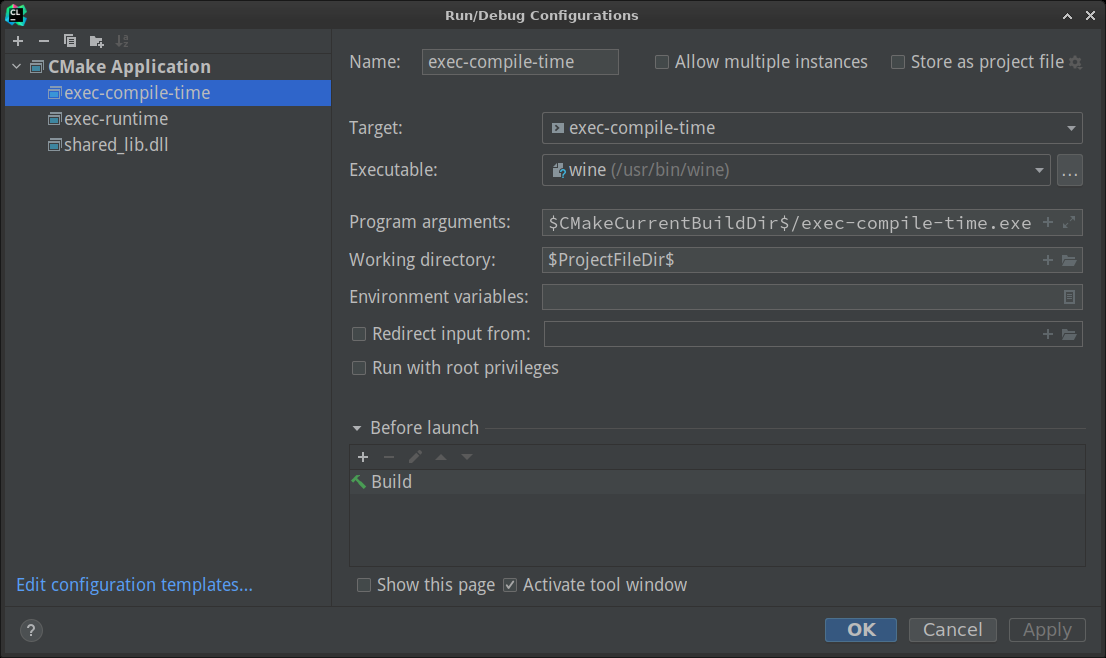
Your CMake project should be loaded by Clion without issues. Windows-specific headers like windows.h are also available. The build will configure itself automatically, but running the target executables will not. Fortunately, you can modify the generated Run/Debug configurations to call Wine, as shown in the picture:

Atom/RSS feed. Copyright by Michał Słomkowski. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. This website is a perpetual work in progress. Last compilation: 2023-07-07 .
Michał Słomkowski — software developer, tinkerer and hardware enthusiast . Based in Poznań, Poland . Feel free to contact me if you have any questions or ideas. If you’re a human being, you can easily decode my e-mail: michal [‘at’ character] domain this site is hosted on. Please inform me about any errors and inaccuracies you stumble upon.
How do I invoke the MinGW cross-compiler on Linux?
and downloaded 500 MB of packages, but I cannot find out how to actually run it. There is no mingw executable, so how do I actually compile with it?
If you run the following command from a terminal it should tell you the executable of the compiler ( g++ in this example case ). You can then edit your makefile appropriately. «locate mingw | grep g++»
@gipi In cmake I just issue a «cmake -G «MinGW Makefiles» for compiling on windows and «cmake -G «Unix Makefiles» when compiling on my linux box to have the Makefile built. Is this what you’re after? If not, you’ll need to elaborate 🙂
4 Answers 4
If you look at the file lists on the Ubuntu package webserver for mingw-w64 ‘s constituent packages:
You can see that mingw-w64 provides a toolchain, i.e. a set of alternative tools (compiler, linker, headers, etc.) used to compile your code for another system.
Assuming you want to compile C++ code for a 64-bit system, you’ll need to use /usr/bin/x86_64-w64-mingw32-g++-win32 . You can use the CXX environment variable to tell most Makefiles to use that compiler to compile code.
There is no variable for toolchain, but you can set variables for C and C++ compilers: CC and CXX respectively.
Another option is to take a look at Mingw Cross Environment (MXE), which is specifically targetting at cross compiling from Linux to Windows (and lately also to Mac). The package has bult-in xupport for a large number of libraries and is actively being developed. Just take a look at the website to find out if it suits your needs.
By the way,it is suggested you use the development rather than the release version. This is because release versions are generally outdated very fast, due to package maintainers (of the libraries) changing URLs resulting in the MXE release version becoming broken. The development version is generally more up-to-date.
There’s no mention about Mac on the website? This seems pretty neat, I’m new to this, so I’m guessing your tool creates the «cross-compiler» first, and then I just have to use your created toolchain to compile things.
Well, it’s not «mine», but that’s pretty much what it does. Not sure about the current state regarding Mac support (I haven’t used mxe in a while). It has been mentioned in the past that they were working on support, but I have no idea if it’s actually been implemented.