- Mirrors
- Official mirrors
- IPv6-ready mirrors
- Enabling a specific mirror
- Force pacman to refresh the package lists
- Sorting mirrors
- List by speed
- Ranking an existing mirror list
- Fetching and ranking a live mirror list
- Server-side ranking
- Troubleshooting
- Missing mirrorlist
- Misbehaving mirrors
- See also
- Setup Pacman Mirrors on Arch Linux
- The Pacman Mirror Configuration File
- Generating a mirrorlist File for Specific Geographical Location
- Finding the Fastest Arch Linux Mirror
- About the author
- Shahriar Shovon
Mirrors
This page is a guide to selecting and configuring your mirrors, and a listing of current available mirrors.
Official mirrors
The official Arch Linux mirror list is available from the pacman-mirrorlist package. To get an even more up-to-date list of mirrors, use the Pacman Mirrorlist Generator page.
Check the status of the mirrors by visiting the Mirror Status page. It is recommended to only use mirrors that are up to date, i.e. not out of sync.
If you want your mirror to be added to the official list, see DeveloperWiki:NewMirrors. In the meantime, add it to the Unofficial mirrors article.
IPv6-ready mirrors
The Pacman Mirrorlist Generator can also be used to find a list of current IPv6 mirrors.
Enabling a specific mirror
To enable mirrors, edit /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist and locate your geographic region. Uncomment mirrors you would like to use.
## Worldwide #Server = https://geo.mirror.pkgbuild.com/$repo/os/$arch #Server = http://mirror.rackspace.com/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch Server = https://mirror.rackspace.com/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch
See #Sorting mirrors for tools that help choosing mirrors.
Tip: Uncomment 5 favorite mirrors and place them at the top of the mirrorlist file. That way it is easy to find them and move them around if the first mirror on the list has problems. It also makes merging mirrorlist updates easier.
It is also possible to specify mirrors in /etc/pacman.conf . For the core repository, the default setup is:
[core] Include = /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist
To use the kernel.org mirror as a default mirror, add it before the Include line:
[core] Server = https://mirrors.kernel.org/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch Include = /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist
pacman will now try to connect to this mirror first. Proceed to do the same for core-testing, extra, and extra-testing, if applicable.
Warning: If mirrors have been stated directly in pacman.conf , remember to use the same mirror for all repositories. Otherwise this would result in a partial upgrade as packages that are incompatible with each other may be installed, like linux from core and an older kernel module from extra.
Force pacman to refresh the package lists
Mirrors can be out of sync and the package list from the old mirror may not correspond to the package list of the new mirror, even though the dates of the lists may suggest that they do.
After creating/editing /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist , issue the following command:
Passing two —refresh / -y flags forces pacman to refresh all package lists even if they are considered to be up to date.
Note: Issuing pacman -Syyu is an unnecessary waste of bandwidth in most cases, but can sometimes fix issues when switching from a broken mirror to a working mirror. See also Is -Syy safe?.
Warning: In most cases if you force refresh the pacman database, you will want to force downgrade any potentially too-new packages to correspond to the versions offered by the new mirror. This prevents issues where packages are inconsistently upgraded, leading to a partial update.
This is not necessary when using successfully syncing mirrors or checking timestamp of mirror’s lastsync file to ensure package lists are up to date.
Sorting mirrors
When downloading packages, pacman uses the mirrors in the order they are listed in /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist . The order servers appear in the list sets their priority.
It is not optimal to only rank mirrors based on speed since the fastest servers might be out-of-sync. Instead, make a list of mirrors sorted by their speed, then remove those from the list that are out of sync according to their status.
It is recommended to regularly repeat this process to keep the list of mirrors up-to-date.
List by speed
Ranking an existing mirror list
The pacman-contrib package provides a Bash script, /usr/bin/rankmirrors , which can be used to rank the mirrors according to their connection and opening speeds to take advantage of using the fastest local mirror.
Back up the existing /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist :
# cp /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist.backup
To prepare mirrorlist.backup for ranking with rankmirrors, the following actions can be carried out:
- Edit mirrorlist.backup and uncomment the servers to be tested
- If the servers in the file are grouped by country, one can extract all the servers of a specific country by using:
$ awk '/^## Country Name$/f==0/^$/' /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist.backup
# sed -i 's/^#Server/Server/' /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist.backup
# rankmirrors -n 6 /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist.backup > /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist
Fetching and ranking a live mirror list
In order to start with a shortlist of up-to-date mirrors based in some countries and feed it to rankmirrors one can fetch the list from the Pacman Mirrorlist Generator. The command below pulls the up-to-date mirrors in either France or the United Kingdom which support the https protocol, it uncomments the servers in the list and then ranks them and outputs the 5 fastest.
$ curl -s "https://archlinux.org/mirrorlist/?country=FR&country=GB&protocol=https&use_mirror_status=on" | sed -e 's/^#Server/Server/' -e '/^#/d' | rankmirrors -n 5 -
Tip: This procedure can be done interactively by navigating to https://archlinux.org/mirrorlist with any text-based browser, for example elinks(1) .
Rate Mirrors — It fetches mirrors, skips outdated/syncing mirrors, then uses info about submarine cables and internet exchanges to jump between countries and find fast mirrors. And it is fast enough to run it before each update. It also supports custom mirror lists fed via stdin.
Server-side ranking
The official Pacman Mirrorlist Generator provides an easy way to obtain a ranked list of mirrors. Because all ranking is done on a single server that takes multiple factors into account, the amount of load on the mirrors and the clients is significantly lower compared to ranking on each individual client.
Another popular alternative is the following tool:
Reflector — Retrieves the latest mirrorlist from the MirrorStatus page, filters and sorts them by speed and overwrites /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist . Provides automation with a systemd service and timer.
Troubleshooting
Missing mirrorlist
This article or section needs expansion.
Reason: Mirror list is also distributed via pacman-mirrorlist , therefore there should be mirrorlist.pacnew within the directory and if not, you can just reinstall the package again, and the mirrorlist be installed because it no longer exists, this is more simple than using curl. (Discuss in Talk:Mirrors)
In case you encounter the following error:
error: config file /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist could not be read: No such file or directory
Get the mirrorlist directly from the website:
# curl -o /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist https://archlinux.org/mirrorlist/all/
Be sure to uncomment a preferred mirror as described in #Enabling a specific mirror, then:
# pacman -Syu pacman-mirrorlist
Misbehaving mirrors
If you are certain a mirror is not operating properly and that is not reflected on the mirrors status page, change the mirror and consider opening a bug report. For mirrors the issue should be opened in the «Arch Linux» project (see the list just below the log-in box, or search for «switch» on the page), with task type «Bug report», category «Mirrors».
See also
Setup Pacman Mirrors on Arch Linux
Like all the other Linux distributions such as Ubuntu, Arch Linux also has an official package repository. It is hosted on the official Arch Linux server. To save bandwidth and reduce the cost, to increase the download speed and response time, the official package repository is copied to different server in different parts of the world. So people close to certain geographical location can use that server instead the official Arch Linux server as they are synced with the official Arch Linux package repository.
Each of these servers that keeps a copy of the official Arch Linux package repository is called a mirror.
The Pacman Mirror Configuration File
Arch Linux package manager Pacman keeps it’s mirror list in /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist file. To change Pacman mirrors, you must modify this file.
Generating a mirrorlist File for Specific Geographical Location
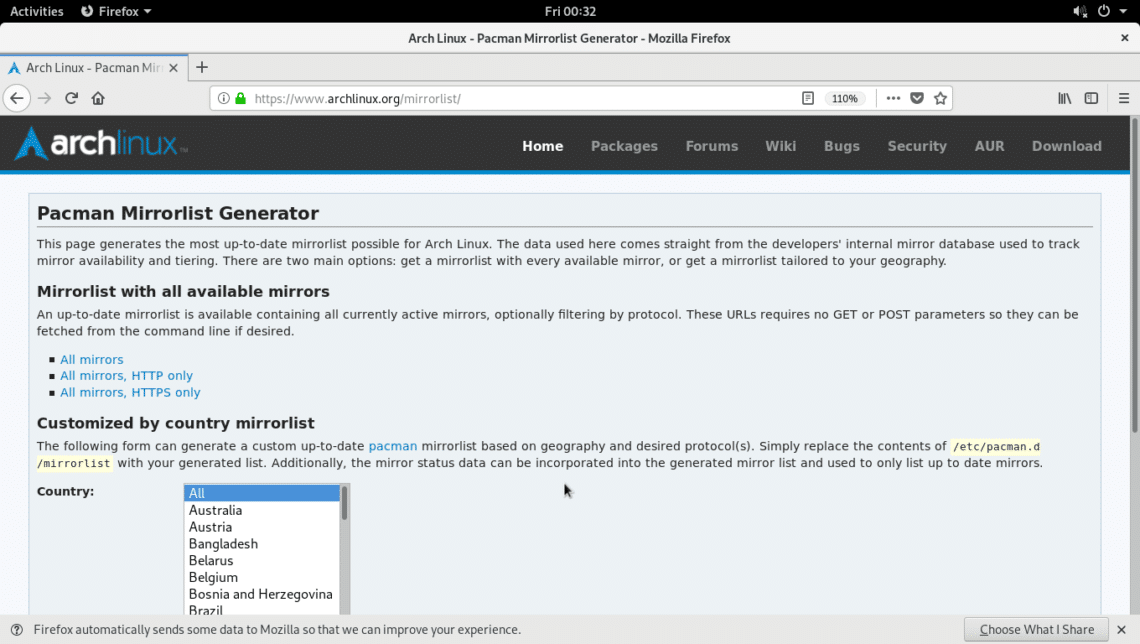
You can generate a mirrorlist file for specific geographical location using the official Arch Linux website.
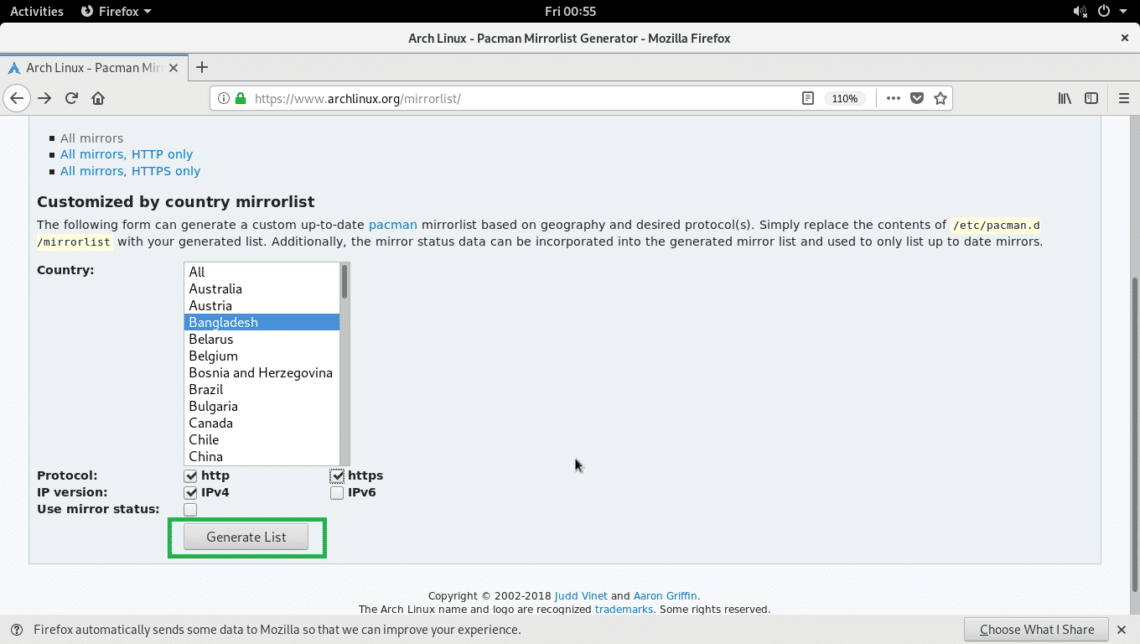
Go to https://www.archlinux.org/mirrorlist/ and you should see the following page as shown in the screenshot below.
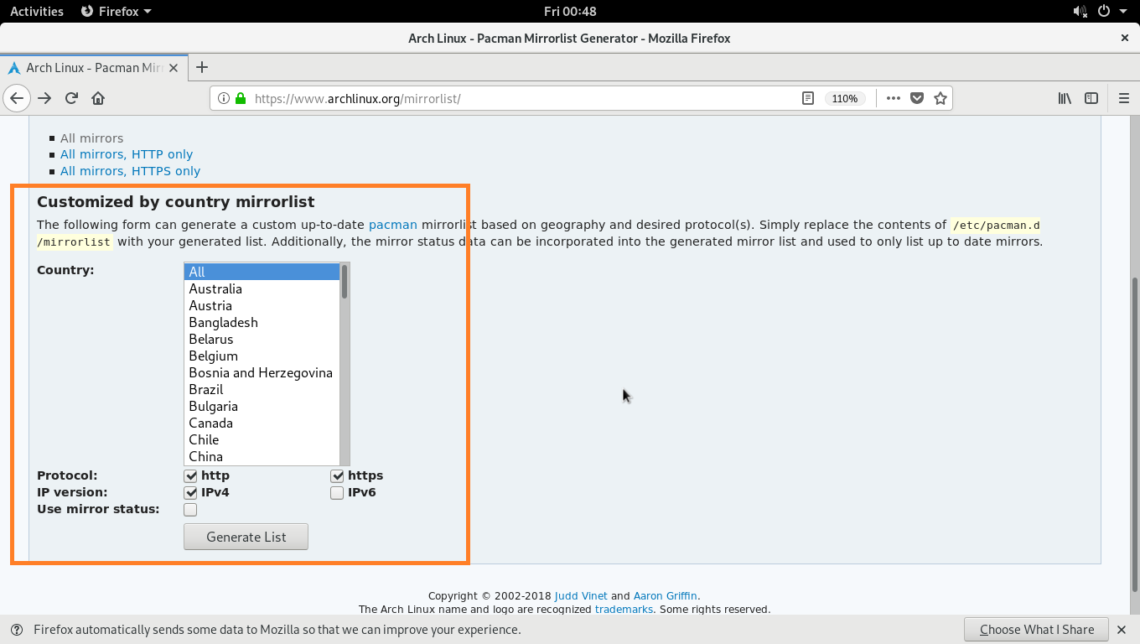
You can also use the mirrorlist generator wizard as marked in the screenshot below.
First select your country.
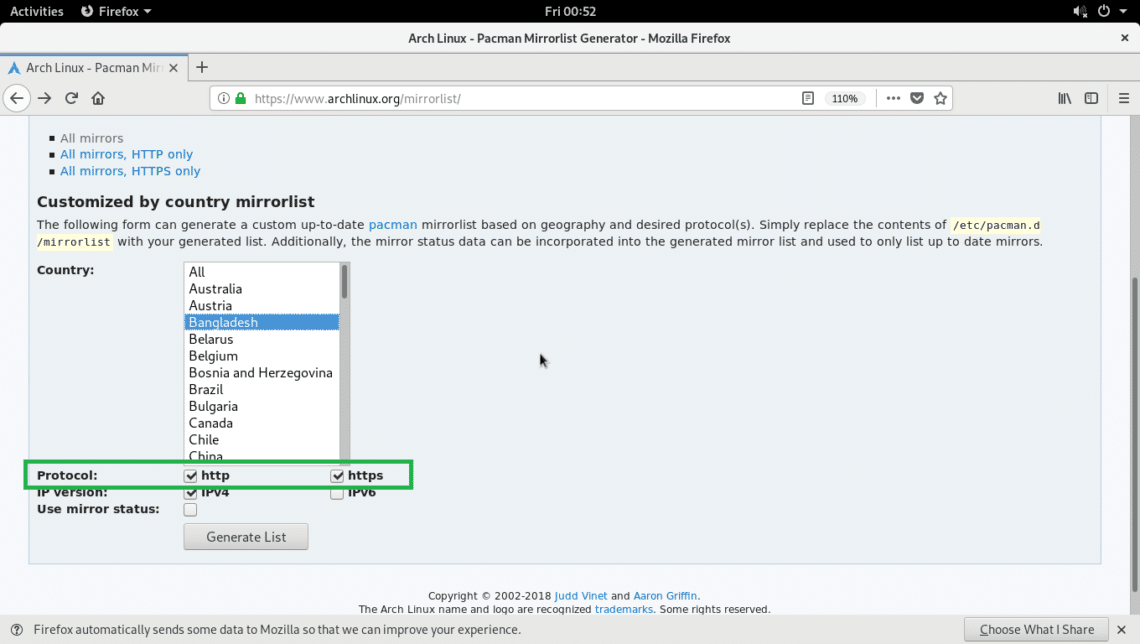
Then check either http or https or both (http and https) in the Protocol section depending on your need.
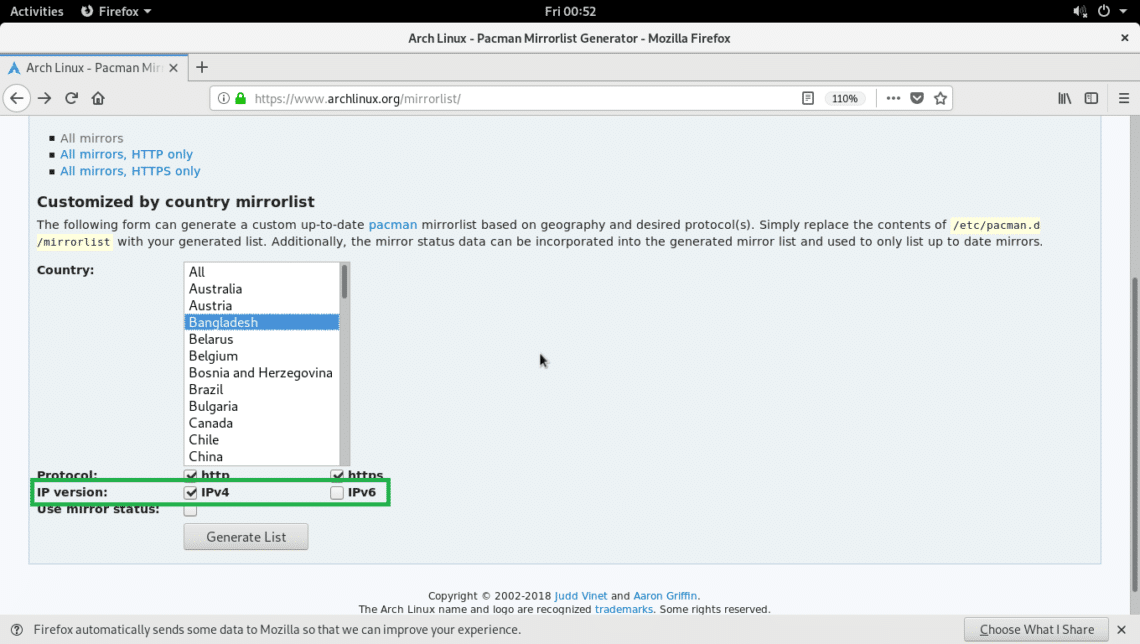
Then select the IP version. IPv4 is available in every country, IPv6 may not be available. You may select both.
Finally click on Generate List button.
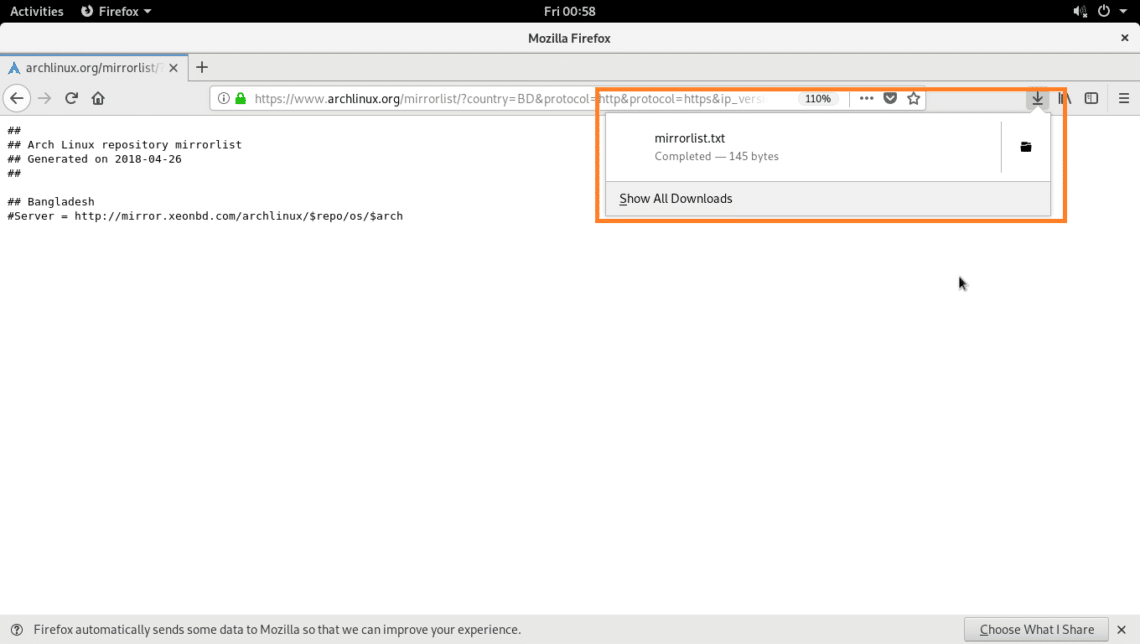
A mirrorlist file should be generate as you can see in the screenshot below.
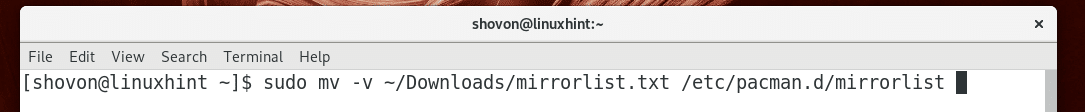
Now press + s and save the file as mirrorlist.txt
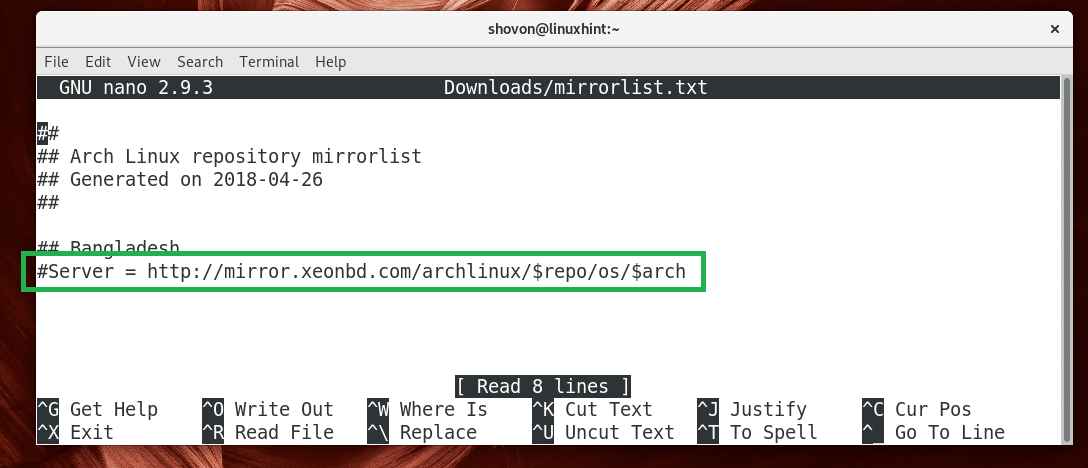
Now open the file with any text editor.
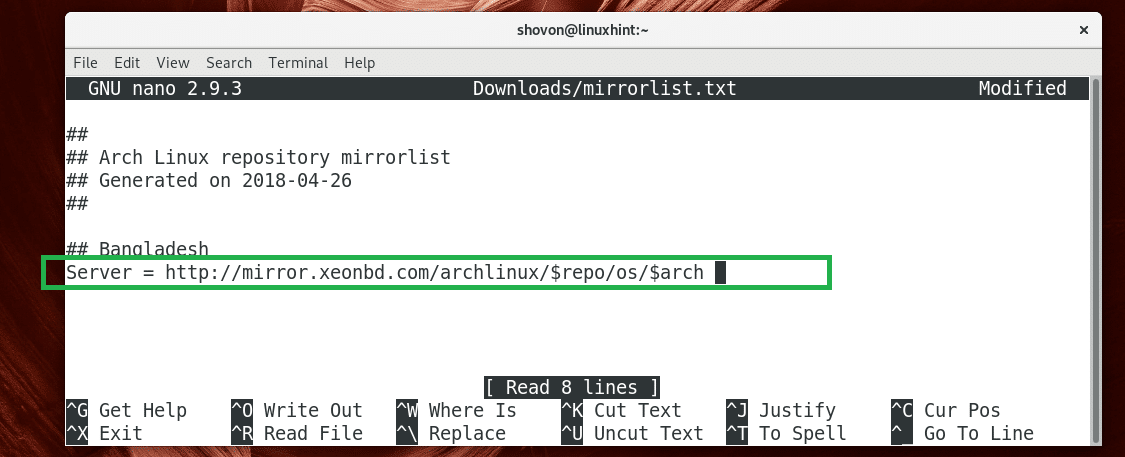
Remove the hash (#) sign from the line that starts with Server =
NOTE: If you have multiple lines starting with Server = , then remove the hash (#) sign from the lines that you want to add as Pacman mirror, leave the rests as it is.
Once you’re done, save the file.
Now replace /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist with this file with the following command:
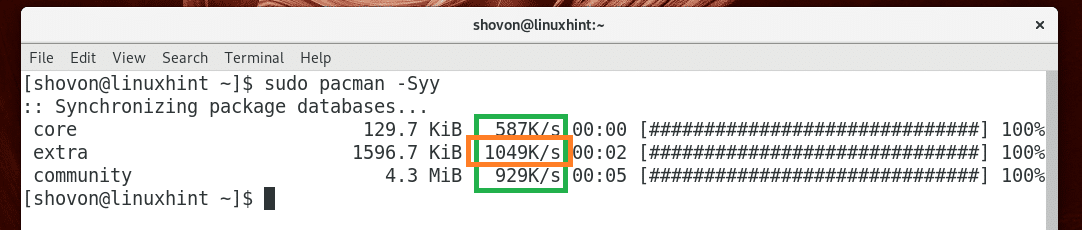
Now update the Pacman package repository cache with the following command:
The Pacman package repository cache should be updated and as you can see from the marked section of the screenshot below, I am getting 10 times more speed than usual. FYI my usual download speed is 128 KBps.
Finding the Fastest Arch Linux Mirror
At times just setting a geographically closer Arch Linux mirror is not enough. So Before you set an Arch Linux mirror, you should check and find out the fastest mirror on your current ISPs network. Thanks to Arch Linux, Pacman has a built in utility rankmirrors to test and find the fastest mirror for you.
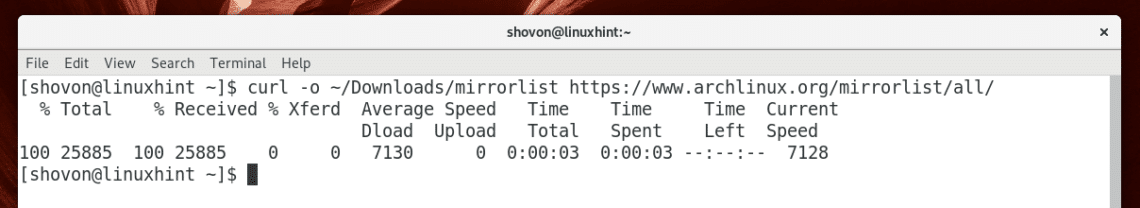
First run the following command to download a mirrorlist file that includes all the available Arch Linux mirrors:
The file should be saved in the Downloads/mirrorlist on your user’s HOME directory.
Now run the following command to uncomment all the mirror lines:
Now start the check with the following command:
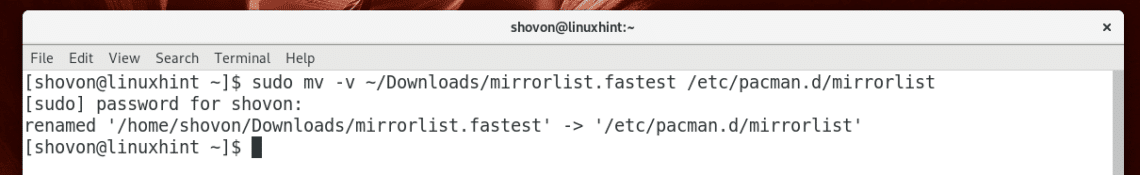
Once the check is complete, the mirrors will be sorted in descending order depending on the download speed in ~/Downloads/mirrorlist.fastest file. It should take a long time to check all the mirrors if your internet connection is slow.
Now replace /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist file with the ~/Downloads/mirrorlist.fastest file with the following command:
Now update the Pacman package repository cache with the following command:
That’s how you setup Pacman mirrors on Arch Linux. Thanks for reading this article.
About the author
Shahriar Shovon
Freelancer & Linux System Administrator. Also loves Web API development with Node.js and JavaScript. I was born in Bangladesh. I am currently studying Electronics and Communication Engineering at Khulna University of Engineering & Technology (KUET), one of the demanding public engineering universities of Bangladesh.