- MongoDB: Create Database and User – Mongo Shell
- Create Database in MongoDB
- Create user for MongoDB database
- Delete MongoBD database
- How to create Database in MongoDB
- How to create a Database in MongoDB
- Step 1: Access the MongoDB Shell
- Step 2: Look for existing Databases
- Step 3: Create a new database
- Step 4: Activate the database.the
- How to drop a database in MongoDB using Ubuntu
- Conclusion
- How to Create and Drop Database in MongoDB: A Comprehensive Guide
- Table of Contents
- 1. Prerequisites
- 2. Understanding MongoDB Structure
- 3. Creating a MongoDB Database
- MongoDB create database | Complete tutorial in 2022
- How to create a database in mongodb
- Why show dbs does not show the database in mongodb
- Create database in mongodb compass
- Mongodb create a database with username and password
- Mongodb create database script
- MongoDB create user
- Conclusion
MongoDB: Create Database and User – Mongo Shell
In MongoDB, in the opposite to traditional SQL databases, there is no need, as well as possibility, to create an empty database.
To create a new database in MongoDB, it needs to insert at least one document into it.
In this article i will show how to create a new database and a user for this database in MongoDB from the command line, using mongo shell.
I will also show how to list collections, get all documents and delete a MongoBD database.
Cool Tip: How to connect to remote MongoDB server from the command line using mongo shell! Read More →
Create Database in MongoDB
MongoDB-Lend: A database holds a set of collections. A collection holds a set of documents. Document is a set of fields (key-value pairs).
To create a new_database in MongoDB, firstly it needs to select this database to use:
> use new_database
To check the currently selected database, run:
However, if you list all databases in MangoDB you won’t find a new_database there:
> show dbs local 0.000GB test 0.000GB
Create MongoDB Database: A new database in MongoDB won’t be created until you insert at lest one document into it.
Create a new_collection and insert a document with some_key and some_value pair:
> db.new_collection.insert(< some_key: "some_value" >)
The new_database has been created as only the first document was inserted:
> show dbs local 0.000GB new_database 0.000GB test 0.000GB
Create user for MongoDB database
To create a new_user for new_database with readWrite permissions in MongoDB, run:
Cool Tip: How to enable auth in MongoDB and create admin / root users! Read More →
To list all collections in the selected MangoDB database, run:
> show collections new_collection
To get all documents from new_collection , run:
> db.new_collection.find()
Delete MongoBD database
To delete selected MongoBD database, run:
How to create Database in MongoDB
MongoDB is a NoSQL type of database that acts differently as compared to traditional relational databases and is suitable to be used for large data sets. MongoDB replaces the concept of traditional databases (that work on rows and columns) with documents. As MongoDB is documents based it allows embedded documents arrays and represent complex hierarchy’s relationships using a single record.MongoDB is widely used because of its flexibility and supports a flexible query model. MongoDB stores data with the help of key value pairs; it converts the JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) data into a binary format known as BSON (it is also derived from JSON). MongoDB also makes provision for nested data; for instance, it stores data in collections that contain multiple documents and interestingly the documents need not be similar in a single collection. These multiple collections collectively are stored in an entire MongoDB.
In this descriptive post, we will guide you to create a database using MongoDB in Ubuntu. For this you must have following list of Prerequisites before creating a database:
Prerequisites
The list of prerequisites is quite simple, and it contains the packages required to create database in MongoDB:
- MongoDB must be installed on your system to perform any operation associated with MongoDB.
- The MongoDB shell provides a powerful command line support to perform database operations, specifically most used CRUD (Create, Retrieve, Update, Delete) operations.
How to create a Database in MongoDB
This section comprises several steps that must be followed for the creation of a database in MongoDB. Follow the steps carefully:
Step 1: Access the MongoDB Shell
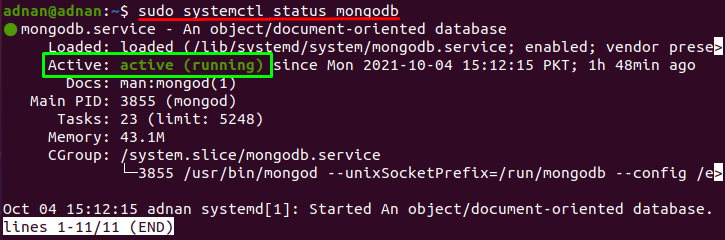
Open the terminal (Ctrl+Alt+T) and first check the MongoDB service status by using the following command:
The output of above command shows that MongoDB service is active and running:
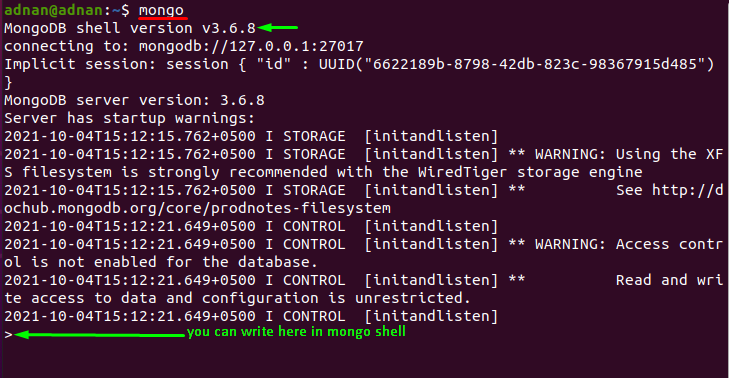
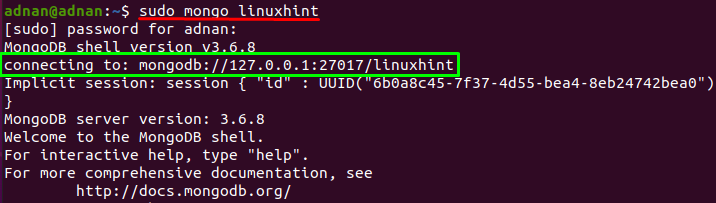
After that, access the mongo shell by using the below mentioned command in your Ubuntu terminal:
Step 2: Look for existing Databases
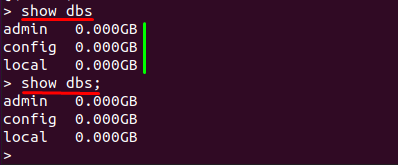
Once you have accessed the mongo shell, you can now check the databases currently listed on your MongoDB server. Use one of the following commands to check the available databases:
As the output shows, there are three databases currently on board: it is noticed that these are built-in databases.
Step 3: Create a new database
To create a new database using mongo shell; you must follow the proper syntax as mentioned below:
Following the above syntax; we have created a new database, “linuxhint,” with the help of following mongo shell command:
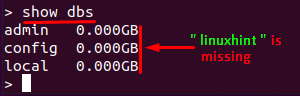
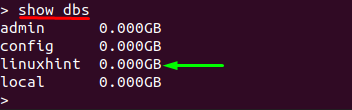
As we have only created an empty database; so, the system will not show it until we insert data into it:
Step 4: Activate the database.the
To activate the “linuxhint” database; we will use the following syntax to do so:
The “db” here refers to the selected database; “collection” is the name of the document you are inserting;
“(< >)” contains the data to be inserted.
Before executing the command, you must ensure that you have selected the correct database; for this, use the following command in the mongo shell:
Or you can connect to the MongoDB database directly from the Ubuntu terminal; use the following command in terminal to connect to the “linuxhint” database:
Following the syntax, we have used the below-mentioned command to create a new user named as “jack”, its designation, and age.
Note: Once the command is executed successfully; it will show the output “WriteResult()”:
After inserting the document in “linuxhint”, verify that “linuxhint” is added to the databases list or not: to do so, execute the following command in the mongo shell:
How to drop a database in MongoDB using Ubuntu
Before executing the drop command, you must ensure that you are in the same database which you want to delete. You can check by using the “db” command in the mongo shell:
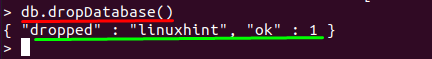
Now, if you will run the following command in your Mongo Shell; the “linuxhint” database will be dropped from MongoDB:
Conclusion
In this technologically rich era, automated management of data is the primary need of every organization. MongoDB is widely used as a DBMS (Database Management System) in IoT (Internet of Things), real-time applications, mobile applications, and content management. MongoDB provides extensive support for famous operating systems like windows, mac, and Linux-based distributions like Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, etc. This article aims at creating a database in MongoDB using Ubuntu as an operating system. The terminal support of Ubuntu is used to access MongoDB shells that are further utilized to create databases. With the help of mongo shell, we have created a database and inserted documents into it. The mongo shell support can also be used to perform other operations on databases like Update, Retrieve and Delete.
How to Create and Drop Database in MongoDB: A Comprehensive Guide
MongoDB is a popular, open-source NoSQL database that provides high performance, high availability, and automatic scaling. As a document-based database, it stores data in flexible, JSON-like documents, making it easy to work with and integrate into various applications. In this article, we’ll cover the fundamentals of creating and dropping databases in MongoDB, allowing you to confidently manage your data.
Table of Contents
- Prerequisites
- Understanding MongoDB Structure
- Creating a MongoDB Database
- Listing Databases
- Dropping a MongoDB Database
- Conclusion
1. Prerequisites
Before diving into creating and dropping databases, ensure that you have MongoDB installed on your system. You can download it from the official MongoDB website. Additionally, it is helpful to have a basic understanding of JSON, JavaScript, and the command line.
2. Understanding MongoDB Structure
MongoDB organizes data into databases, collections, and documents. A database contains multiple collections, which are analogous to tables in a relational database, and each collection holds documents. Documents are BSON (Binary JSON) objects that store data in a flexible, semi-structured format.
3. Creating a MongoDB Database
In MongoDB, you don’t explicitly create a database. Instead, you create a database by switching to a non-existent database, then inserting data into it. The new database is created automatically when you insert the first document.
To create a database, follow these steps:
- Open the MongoDB shell by running the mongo command in your terminal or command prompt.
- Use the use command followed by the desired database name to switch to the new database:
MongoDB create database | Complete tutorial in 2022
MongoDB is the most popular open-source No-SQL database. It is a document-based database that saves the data into a JSON document. In this blog post, I will explain MongoDB create database command and how we can create a database in mongodb using other methods. So let’s get started.
How to create a database in mongodb
Mongodb saves the data into mongo databases, and a single database can hold multiple collections.
Before creating a database in MongoDB, let’s verify what all database is initially present in mongodb by typing the below command
show dbs; admin 0.000GB config 0.000GB local 0.000GB
To create a database in mongodb type, use the command followed by
let’s use the above command and create a database named naiveskill
let’s type the below command to verify the current database in which the user is:
Now let’s again run the show dbs command and verify if the new database is available
show dbs; admin 0.000GB config 0.000GB local 0.000GB
You might be wondering why the database is not displaying.
Why show dbs does not show the database in mongodb
The mongodb show dbs command will not show the databases that do not have any documents. Once you create a document for a collection under a particular database, then only the database will be visible.
Now let’s create a collection in the naiveskill database by typing the below command.
Verify the collection by typing the below command
Let’s insert a document into the mongo test collection
Now again, let’s run the show dbs command and verify if the database is visible now
show dbs; admin 0.000GB config 0.000GB local 0.000GB naiveskill 0.000GB
Excellent, now the database is visible. If can follow this tutorial on mongodb commands to learn more about the mongodb.
Create database in mongodb compass
MongoDB Compass is a UI-based tool for querying, aggregating and analyzing your MongoDB data. Compass is open-source and free to use and can be run on macOS, Windows, and Linux.
You can download the mongodb from here.
Connect to mongodb UI by passing the mongodb connection string.
Once you are connected to the compass, you will get below the screen to create a database in mongodb.
Click on Create Database button and provide the database name to create a new database name naive.
Mongodb create a database with username and password
To create a database in mongodb using username and password, first, you need to connect to mongodb using username and password.
mongo --host “hostname:port” -u user -p password --authenticationDatabase admin test
Once the connection to MongoDB is successful, you can typically use to create the database in mongodb.
Mongodb create database script
We can interact with mongodb programmatically using many languages like C/C++, Java, Python, nodeJS, ruby, shift, scala, etc. In mongodb, this interaction happens via drivers. The complete list of drivers in mongodb can be found here.
One of the most popular drivers is the python driver, which uses the pymongo client to interact with python programmatically.
The pymongo driver can be installed by typing the below command:
Once the pymongo driver installation is complete, connect to the ipython/python shell and import pymongo
Now the next step is to create a MongoClient.The MongoClient takes the MongoDB connection string as a parameter.
Since, in my case, the MongoDB is running locally on port 27017, type the below connection string to connect to MongoDB.
client = pymongo.MongoClient("mongodb://localhost:27017/") You can change the connecting string based on the server and port where mongodb is running.
Now the database can be programmatically created by using mongo client. Type the below command to create the ‘naiveskill’ database
If you wish to learn more about the mongodb python client, you can follow this tutorial on MongoDB with python.
MongoDB create user
We can use mongodb createUser() command to create a user in mongodb
To create a user first, we need to create a database. Let’s create a new admin database
Now type the below command to create a user myUserAdmin and assign the role userAdminAnyDatabase
Now type the below command to verify if the user gets added to the admin database
Verify the user by typing the below command
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we have learned various ways to create a database in mongodb, like using the command line, an atlas, and programmatically.
I hope you have liked this tutorial. Please do let me know in the comment box. I will be more than happy to hear from you.