- How to Mount Linux Drive on Windows
- What file systems can be on Linux?
- How to mount a Linux partition in Windows
- Step-by-step guide to mounting a Linux partition on Windows
- Related articles
- Mount a Linux disk in WSL 2
- Prerequisites
- Mounting an unpartitioned disk
- Mounting a partitioned disk
- Identifying the filesystem type
- Mount the selected partitions
- Access the disk content
- Unmount the disk
- Mount a VHD in WSL
- Command line reference
- Mounting a specific filesystem
- Mounting a specific partition
- Specifying mount options
- Attaching the disk without mounting it
- Specifying the mount name
- Detaching a disk
- Limitations
- Feedback
How to Mount Linux Drive on Windows
If the Linux distribution on your PC coexists with Windows, then accessing the Windows partition will be no problem. NTFS is the default Windows file system and is well supported. Most Linux distributions can easily mount NTFS drives.
However, Windows users cannot do this. Common Linux file systems such as Ext4 are not supported. If you want to access a Linux partition in Windows, you need to install some additional software in order to mount a Linux drive on Windows.
For some people, it can be difficult to mount a Linux drive on Windows. However, there is a most convenient and user-friendly software tool that will help make the process a whole lot easier.
In order to mount a Linux drive in Windows, you need software help, and we’ll help you with that.
What file systems can be on Linux?
There are a lot of file systems on Linux that can be accessed by Windows indirectly; the first step in doing so is to mount the Linux drive on Windows 10.
The following file systems are available and are easy to access on Windows. There are a bunch of file systems on Linux; here is a list:
In order to mount a Linux partition on Windows, the software is available to help you out.
How to mount a Linux partition in Windows
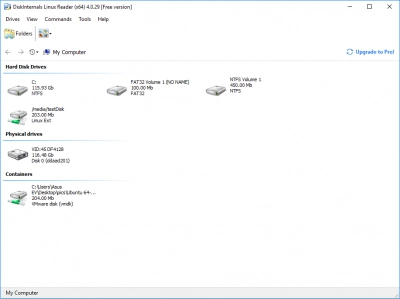
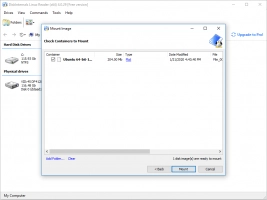
DiskInternals Linux Reader™ is a state-of-the-art software tool that allows file systems to be easily mounted in Windows. This software is easy to follow, easy to install and download, and most importantly, supports a wide array of Linux file systems.
With free and premium options available, you will get tons of features, get your drive mounted and read easily, regardless of the option you choose.
It is effective and easy. Using this software, you will be in control. You’ll be able to follow the steps of the process and not get lost because of its powerful UI.
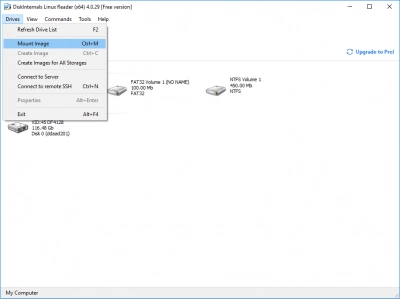
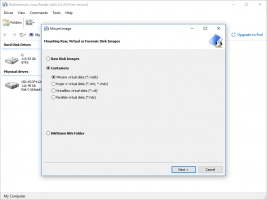
Step-by-step guide to mounting a Linux partition on Windows
DiskInternals Linux Reader™ is one of the most groundbreaking pieces of software to be released to the public. If you’re someone that wants to get your Linux partition mounted on Windows, this is a step-by-step guide to the whole process:
There is a slew of reasons why you should use DiskInternals Linux Reader™ for your Linux mounting and reading needs.
In conclusion, this article talked about the best software for your mounting and reading needs with all the relevant information regarding the available file systems and a lot more. If you want the best software for this kind of task, DiskInternals Linux Reader™ is the way to go.
Related articles
- About a bash date command
- Bash and sh: is there any difference
- About Bash Language
- Guide in Pictures
- Shell script usage
- Bash: A Script For User Input
- Here is everything you need to know about Bash for Windows
- Bash Script SSH: How to Use It
- How to use bash get script directory in Linux
- Copy command in shell scripts
- Learn about a bash error code
- 5 Basic Shell Script Examples for Your First Script
- How to Check Bash String Equality
- How to Use Linux Wait Command
- Bash: How to Loop Through Files in Directory
- 20 Examples of Bash Find Command
- Bash Cat Command in Examples
- Linux ZSH: the basic you need to know
- Shell Script Cut: Basic You Need to Know
- Bash: How to Check if String Not Empty in Linux
- Basic of Grep in Linux Shell Script
- Bash: how to split strings in Linux
- An Algorithm: How to Create Bash While Loop
- Bash Time Command on Linux
- Bash: How to Check if the File Does Not Exist
- How to Use Shell Script Sleep Command
- Linux Shell: What You Need to Know at First
- Bash Script: All You Need to Know
- How to Mount Ext4 on Windows for Free
- How to Access Ext4 from Windows
- How to Access Linux Ext2 or Ext3 on Windows
- Linux: Sudo in Bash Scripts
- A Linux bin/bash Shell
- Linux: Bash Printf Examples
- Linux: Bash First Line
- Linux: Write a Shell Script
- Linux: A Bash Source Command
- A Bash to Loop through Lines in File
- A Bash Test Command
- A Bash Status of Last Command
- Linux: New Line in Shell Script
- Linux: $0 in a Shell Script
- Linux: A Bash Startup Script
- A Bash Multiline Command
- A Bash Dirname Command
- Linux: A Bash Linter
- A Bash Nested Loop
- Use a Shell Script to Send an Email
- Hello World Script in Bash
- A crontab service shell script
- Linux: A Bash Basename Command
- Using Bash to Write to a File
- AWK in a Bash Script
- Learn about systemd startup script
- About chaining bash commands
- Using a bash tee command
- Learn about useful bash scripts
- Bash for Loop in One Line
- Learn about a bash wait command
- Arch Linux install script
- About advanced bash scripting
- To run a shell script in Dockerfile
- About a bash export command
- About a bash UNTIL loop
- Using /usr/bin/env command
- Learn about Korn shell scripting
- Shell Script: Replace String in File
- Linux: Bash String Ends With
- Whether bash waits for command to finish
- Using bash if 0
- Using && in an IF statement in bash
- If you want to run shell script in background
- The disk you inserted was not readable by this computer error
- Learn about C shell script
- Learn about SFTP in bash scripting
- Install Oracle Database
- Examples of using the Expect
- Learn to run Perl script in Linux
Mount a Linux disk in WSL 2
If you want to access a Linux disk format that isn’t supported by Windows, you can use WSL 2 to mount your disk and access its content. This tutorial will cover the steps to identify the disk and partition to attach to WSL2, how to mount them, and how to access them.
If you are looking for guidance on how to connect a USB device (flash drive, SD card reader, etc), see Connect USB devices.
Administrator access is required to attach a disk to WSL 2. The WSL 2 mount command does not support mounting a disk (or partitions that belong to the disk) that is currently in use. wsl —mount always attaches the entire disk even if only a partition is requested. You can’t mount the Windows installation disk.
Prerequisites
You will need to be on Windows 11 Build 22000 or later, or be running the Microsoft Store version of WSL. You can join the Windows Insiders Program to get the latest preview builds.
Mounting an unpartitioned disk
In this simplest case, if you have a disk that doesn’t have any partitions, you can mount it directly using the wsl —mount command. First you need to identify the disk.
- Identify the disk — To list the available disks in Windows, run:
GET-CimInstance -query "SELECT * from Win32_DiskDrive" 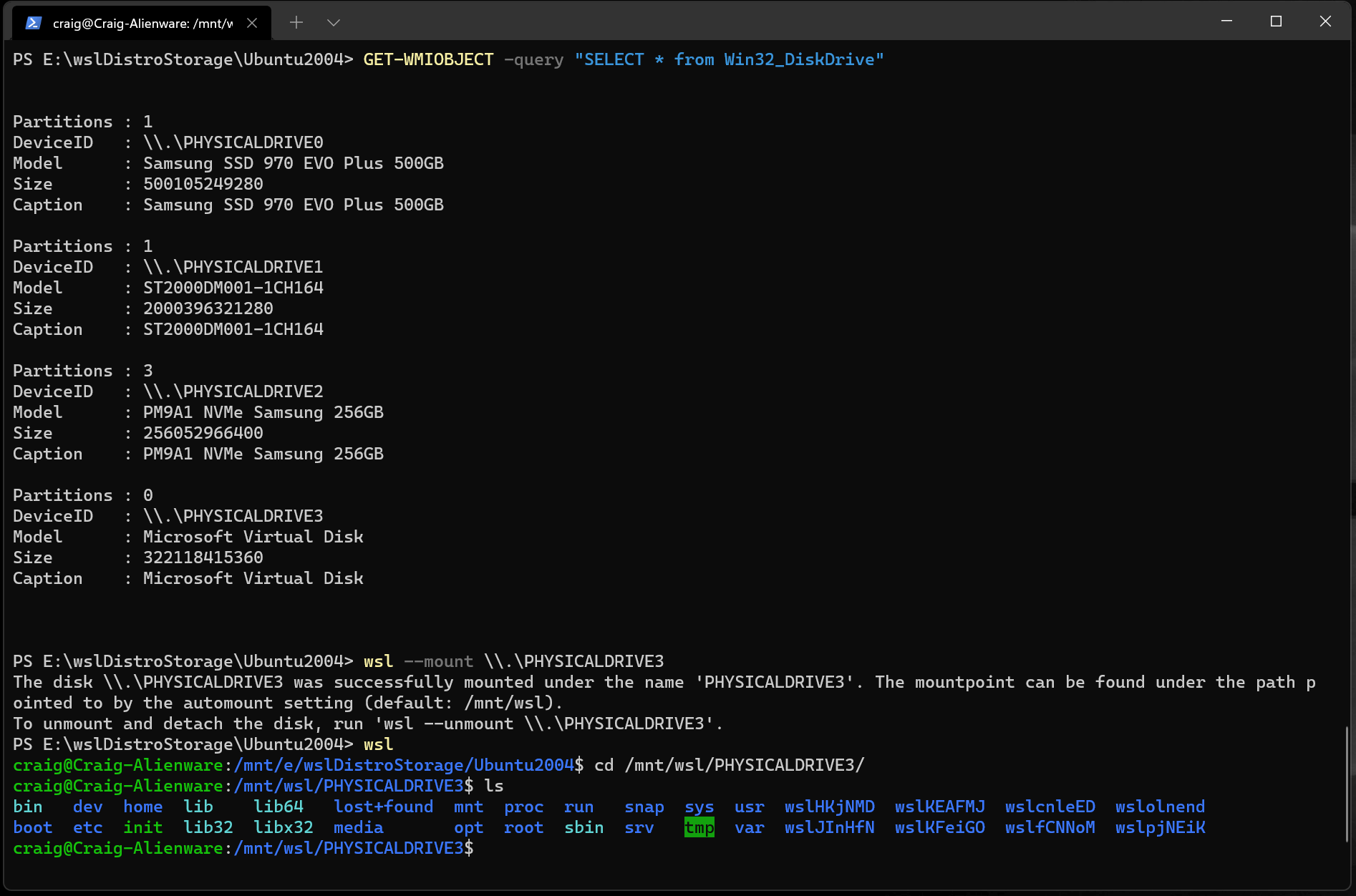
Mounting a partitioned disk
If you have a disk that you aren’t sure what file format it is in, or what partitions it has, you can follow the steps below to mount it.
- Identify the disk — To list the available disks in Windows, run:
GET-CimInstance -query "SELECT * from Win32_DiskDrive" Inside Linux, a block device is identified as /dev/ . For example, /dev/sdb3, is the partition number 3 of disk sdb .
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT sdb 8:16 0 1G 0 disk ├─sdb2 8:18 0 50M 0 part ├─sdb3 8:19 0 873M 0 part └─sdb1 8:17 0 100M 0 part sdc 8:32 0 256G 0 disk / sda 8:0 0 256G 0 disk Identifying the filesystem type
If you don’t know the type of filesystem of a disk or partition, you can use this command:
This will output the detected filesystem type (under the TYPE=»» format).
Mount the selected partitions
Once you have identified the partitions you want to mount, run this command on each partition:
If you wish to mount the entire disk as a single volume (i.e. if the disk isn’t partitioned), —partition can be omitted.
If omitted, the default filesystem type is «ext4».
Access the disk content
Once mounted, the disk can be accessed under the path pointed to by the config value: automount.root . The default value is /mnt/wsl .
From Windows, the disk can be accessed from File Explorer by navigating to: \\wsl$\\\\ (pick any Linux distribution).
Unmount the disk
If you want to unmount and detach the disk from WSL 2, run:
Mount a VHD in WSL
WSL from the Microsoft Store introduces a new argument to directly mount a VHD: wsl —mount —vhd
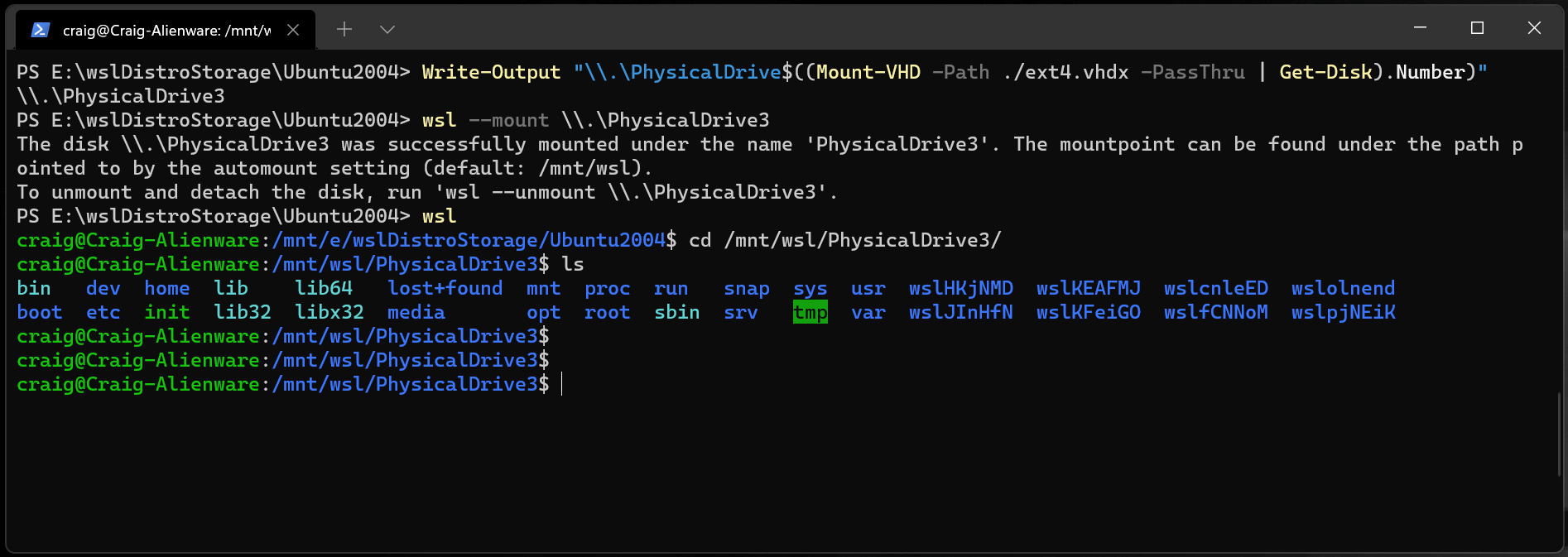
You can also mount virtual hard disk files (VHD) into WSL using wsl —mount . To do this, you first need to mount the VHD into Windows using the Mount-VHD command in Windows. Be sure to run this command with administrator privileges. Below is an example where we use this command, and also output the disk path. Be sure to replace with your actual VHD path.
Write-Output "\\.\PhysicalDrive$((Mount-VHD -Path -PassThru | Get-Disk).Number)" You can use the output above to obtain the disk path for this VHD and mount that into WSL following the instructions in the previous section.
You can also use this technique to mount and interact with the virtual hard disks of other WSL distros, as each WSL 2 distro is stored via a virtual hard disk file called: ext4.vhdx . By default the VHDs for WSL 2 distros are stored in this path: C:\Users\[user]\AppData\Local\Packages\[distro]\LocalState\[distroPackageName] , please exercise caution accessing these system files, this is a power user workflow. Make sure to run wsl —shutdown before interacting with this disk to ensure the disk is not in use.
Command line reference
Mounting a specific filesystem
By default, WSL 2 will attempt to mount the device as ext4. To specify another filesystem, run:
For example, to mount a disk as fat, run:
To list the available filesystems in WSL2, run: cat /proc/filesystems
When a disk has been mounted via WSL2 (Linux file system), it is no longer available to mount via an ext4 driver on the Windows file system.
Mounting a specific partition
By default, WSL 2 attempts to mount the entire disk. To mount a specific partition, run:
This only works if the disk is either MBR (Master Boot Record) or GPT (GUID Partition Table). Read about partition styles — MBR and GPT.
Specifying mount options
To specify mount options, run:
Only filesystem specific options are supported at this time. Generic options such as ro, rw, noatime, . are not supported.
Attaching the disk without mounting it
If the disk scheme isn’t supported by any of the above options, you can attach the disk to WSL 2 without mounting it by running:
This will make the block device available inside WSL 2 so it can be mounted manually from there. Use lsblk to list the available block devices inside WSL 2.
Specifying the mount name
This option is only available with WSL from the Microsoft Store
By default the mountpoint name is generated based on the physical disk or VHD name. This can be overriden with —name . Example:
Detaching a disk
To detach a disk from WSL 2, run:
If Diskpath is omitted, all attached disks are unmounted and detached.
If one disk fails to unmount, WSL 2 can be forced to exit by running wsl —shutdown , which will detach the disk.
Limitations
- At this time, only entire disks can be attached to WSL 2, meaning that it’s not possible to attach only a partition. Concretely, this means that it’s not possible to use wsl —mount to read a partition on the boot device, because that device can’t be detached from Windows.
- Only filesystems that are natively supported in the kernel can be mounted by wsl —mount . This means that it’s not possible to use installed filesystem drivers (such as ntfs-3g for example) by calling wsl —mount .
- Filesystems not directly supported by the kernel can be mounted via a —bare attach and then invoking the relevant FUSE driver.
Feedback
Submit and view feedback for