How to Move a File to Another Directory in Linux?
In Linux, the basic administrative task consists of creating, removing, and moving a file commonly used by the users. Several methods are used to move files to another directory, like using the “mv” command or with the help of GUI (easy for windows users).
This article will explain all the possible methods to move a file to another directory by following this timeline:
- Method 1: Move File to Another Directory Using CLI
- Example 1: Move a File to Another Directory
- Example 2: Move Multiple Files to Another Directory
- Example 3: Move Specific Type of Files to Another Directory
- Example 4: Move the Unique Files to Another Directory
- Method 2: Move File to Another Directory Using GUI
Method 1: Move File to Another Directory Using CLI
In this section, we will discuss moving the file to another directory with the command line. Files can be moved from one directory to another using the “mv” command. Let’s check its syntax:
$ mv [options] source-file destination-directory
The components of the “mv” command are as follows:
- mv: This represents the “move” command to transfer files.
- options: Replace it with mv command available options.
- source-file: Replace with the source file’s name, which will be moved.
- destination-directory: Replace it with your destination directory name.
Example 1: Move a File to Another Directory
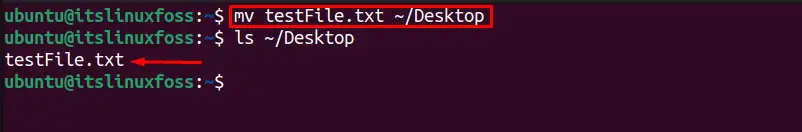
The “mv” command allows the user to move a file to another directory. For instance, to move the “testFile.txt” to the desired directory “~/Desktop”, execute this command:
The “testFile.txt” is moved to the “Desktop” directory, which can be verified using the “ls” command as shown in the above output.
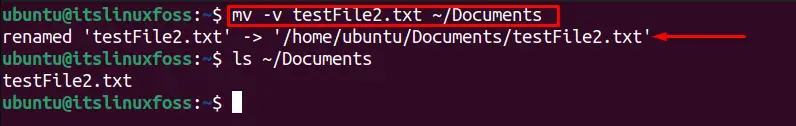
If you want to check the status of every moving file, the “v” verbose option is utilized. For example, to move the “testFile2.txt” to the “Documents” directory to show its status, this command is used:
$ mv -v testFile2.txt ~/Documents
Example 2: Move Multiple Files to Another Directory
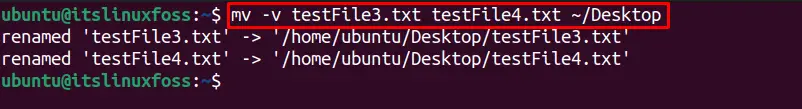
The “mv” command allows the user to move the multiple files to another directory with a single command. To move several files (for example, testFile3.txt and testFile4.txt) to another directory, use the below-mentioned command:
$ mv -v testFile3.txt testFile4.txt ~/Desktop
Both the files are moved to the destination folder “Desktop” as seen in the output.
Example 3: Move Specific Type of Files to Another Directory
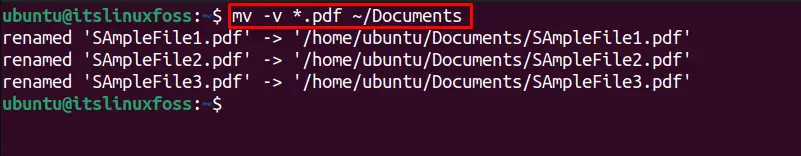
The “mv” can be used to move a specific type of files to a new directory. For instance, to transfer all the “pdf” files to the “Documents” directory, the below command is utilized:
The output verifies the three “pdf” files moved to the “Documents” directory.
Example 4: Move the Unique Files to Another Directory
Sometimes, the file is already present in that directory, and try to move the file again, which duplicates the file in that directory. To avoid the duplication of the files, the “n” option is used, which ignores the already existing files. For instance, to move the “testFile1.txt” to the “Desktop” directory by avoiding the file if already present, the following command is used:
$ mv -n testFile1.txt ~/Desktop
The file “testFile1.txt” is not moved to another directory as the file already exists in the system.
Method 2: Move File to Another Directory Using GUI
A single or multiple files can be moved to another directory using the GUI approach. The files can be moved to another directory by following these steps:
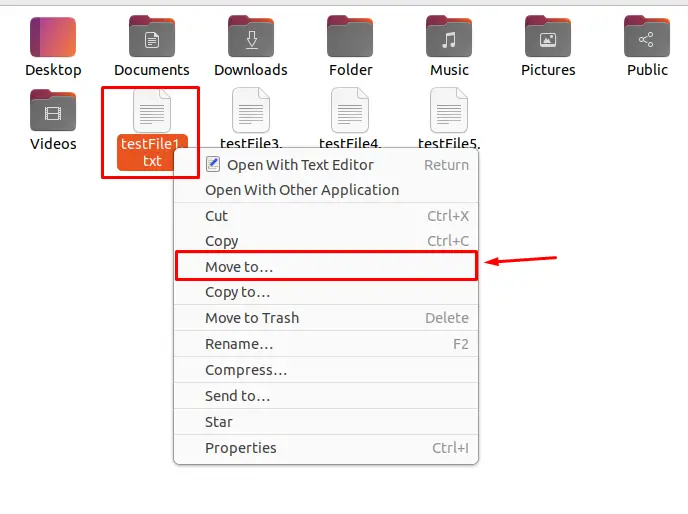
Navigate to the desired folder and right-click on the specific file (which you want to move), then click on the “Move to…” option from the dropdown menu:
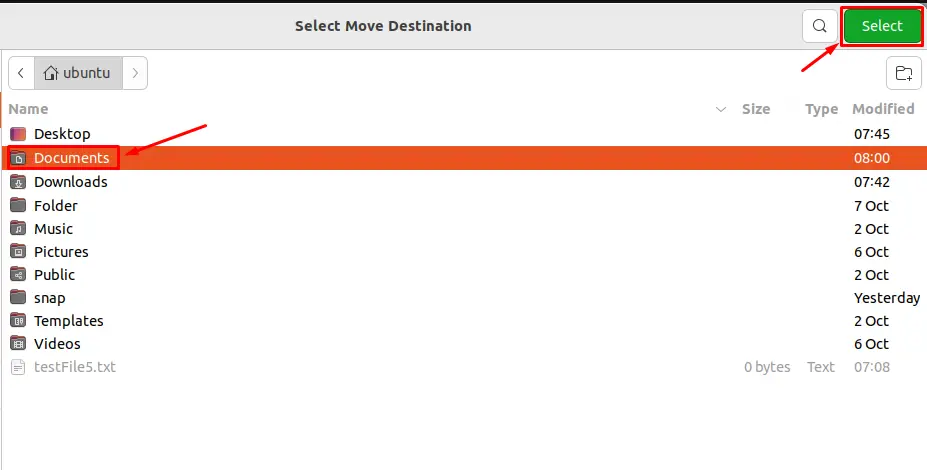
Click on the destination directory (in this case, Documents) and press the “Select” button:
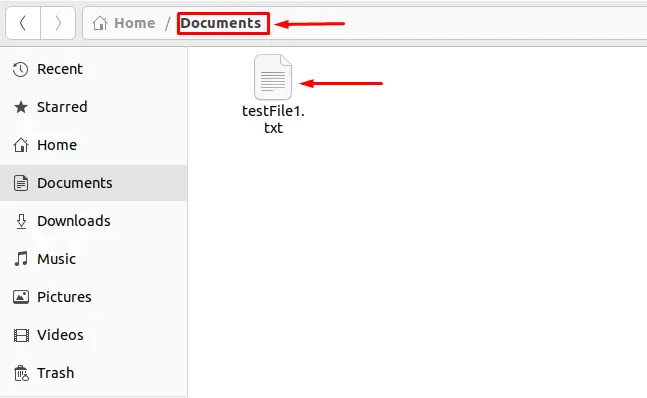
The selected file is moved to the destination (Documents) directory.
Navigate to the destination directory and verify the file has been moved to that directory.
Similarly, multiple files can be moved to another directory by selecting those files, choosing the “Move to… ” option, and clicking on the “Select” button after selecting the destination directory.
Note: Following the GUI method, you can use the shortcut key “CTRL+X” to cut and “CTRL+S” to save the file at the destination.
Conclusion
In Linux, the “mv” command is used to move a file to another directory or choose the “Move to…” option after selecting the file from GUI. A single file or specific files can be moved using the “mv” command, which provides options like moving with confirmation and backup. This guide has explained all possible methods of moving a file to another directory using different options.
Classic SysAdmin: How to Move Files Using Linux Commands or File Managers
There are certain tasks that are done so often, users take for granted just how simple they are. But then, you migrate to a new platform and those same simple tasks begin to require a small portion of your brain’s power to complete. One such task is moving files from one location to another. Sure, it’s most often considered one of the more rudimentary actions to be done on a computer. When you move to the Linux platform, however, you may find yourself asking “Now, how do I move files?”
If you’re familiar with Linux, you know there are always many routes to the same success. Moving files is no exception. You can opt for the power of the command line or the simplicity of the GUI – either way, you will get those files moved.
Let’s examine just how you can move those files about. First, we’ll examine the command line.
Command line moving
One of the issues so many users new to Linux face is the idea of having to use the command line. It can be somewhat daunting at first. Although modern Linux interfaces can help to ensure you rarely have to use this “old school” tool, there is a great deal of power you would be missing if you ignored it altogether. The command for moving files is a perfect illustration of this.
The command to move files is mv . It’s very simple and one of the first commands you will learn on the platform. Instead of just listing out the syntax and the usual switches for the command – and then allowing you to do the rest – let’s walk through how you can make use of this tool.
The mv command does one thing – it moves a file from one location to another. This can be somewhat misleading because mv is also used to rename files. How? Simple. Here’s an example. Say you have the file testfile in /home/jack/ and you want to rename it to testfile2 (while keeping it in the same location). To do this, you would use the mv command like so:
mv /home/jack/testfile /home/jack/testfile2
or, if you’re already within /home/jack:
The above commands would move /home/jack/testfile to /home/jack/testfile2 – effectively renaming the file. But what if you simply wanted to move the file? Say you want to keep your home directory (in this case /home/jack) free from stray files. You could move that testfile into /home/jack/Documents with the command:
mv /home/jack/testfile /home/jack/Documents/
With the above command, you have relocated the file into a new location, while retaining the original file name.
What if you have a number of files you want to move? Luckily, you don’t have to issue the mv command for every file. You can use wildcards to help you out. Here’s an example:
You have a number of .mp3 files in your ~/Downloads directory (~/ – is an easy way to represent your home directory – in our earlier example, that would be /home/jack/) and you want them in ~/Music. You could quickly move them with a single command, like so:
That command would move every file that ended in .mp3 from the Downloads directory, and move them into the Music directory.
Should you want to move a file into the parent directory of the current working directory, there’s an easy way to do that. Say you have the file testfile located in ~/Downloads and you want it in your home directory. If you are currently in the ~/Downloads directory, you can move it up one folder (to ~/) like so:
The “../” means to move the folder up one level. If you’re buried deeper, say ~/Downloads/today/, you can still easily move that file with:
Just remember, each “../” represents one level up.
As you can see, moving files from the command line isn’t difficult at all.
GUI
There are a lot of GUIs available for the Linux platform. On top of that, there are a lot of file managers you can use. The most popular file managers are Nautilus (GNOME) and Dolphin (KDE). Both are very powerful and flexible. I want to illustrate how files are moved using the Nautilus file manager.
Nautilus has probably the most efficient means of moving files about. Here’s how it’s done:
- Open up the Nautilus file manager.
- Locate the file you want to move and right-click said file.
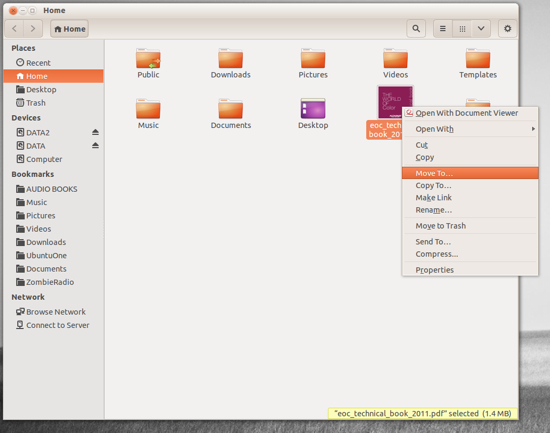
- From the pop-up menu (Figure 1) select the “Move To” option.
- When the Select Destination window opens, navigate to the new location for the file.
- Once you’ve located the destination folder, click Select.
This context menu also allows you to copy the file to a new location, move the file to the Trash, and more.
If you’re more of a drag and drop kind of person, fear not – Nautilus is ready to serve. Let’s say you have a file in your home directory and you want to drag it to Documents. By default, Nautilus will have a few bookmarks in the left pane of the window. You can drag the file into the Document bookmark without having to open a second Nautilus window. Simply click, hold, and drag the file from the main viewing pane to the Documents bookmark.
If, however, the destination for that file is not listed in your bookmarks (or doesn’t appear in the current main viewing pane), you’ll need to open up a second Nautilus window. Side by side, you can then drag the file from the source folder in the original window to the destination folder in the second window.
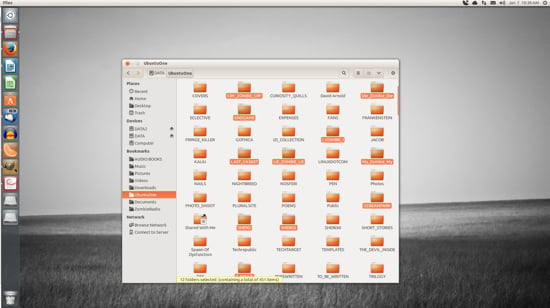
If you need to move multiple files, you’re still in luck. Similar to nearly every modern user interface, you can do a multi-select of files by holding down the Ctrl button as you click each file. After you have selected each file (Figure 2), you can either right-click one of the selected files and then choose the Move To option, or just drag and drop them into a new location.
The selected files (in this case, folders) will each be highlighted.
Moving files on the Linux desktop is incredibly easy. Either with the command line or your desktop of choice, you have numerous routes to success – all of which are user-friendly and quick to master.