- 8 ways to fix your Mac when it won’t connect to Wi-Fi or internet
- 1. Verify that the Wi-Fi connection is the one you want
- 2. Check Wireless Diagnostics
- 3. Check your System Updates
- 4. Check your physical hardware
- 5. Change your DNS settings
- 6. Check VPN and security software
- 7. Reset NVRAM/PRAM and the SMC
- Подключение Mac к интернету через Wi‑Fi
- Подключение к открытой сети Wi‑Fi
- Подключение к скрытой сети Wi-Fi
- If your Mac isn’t connecting to the internet over Wi-Fi
- Restart your Mac
- Check date and time and update macOS
- Check VPN or other security software
- Use the built-in diagnostic tools
- Update the Wi-Fi router
- Try a different network or contact your ISP
- Connect to the internet with your Mac
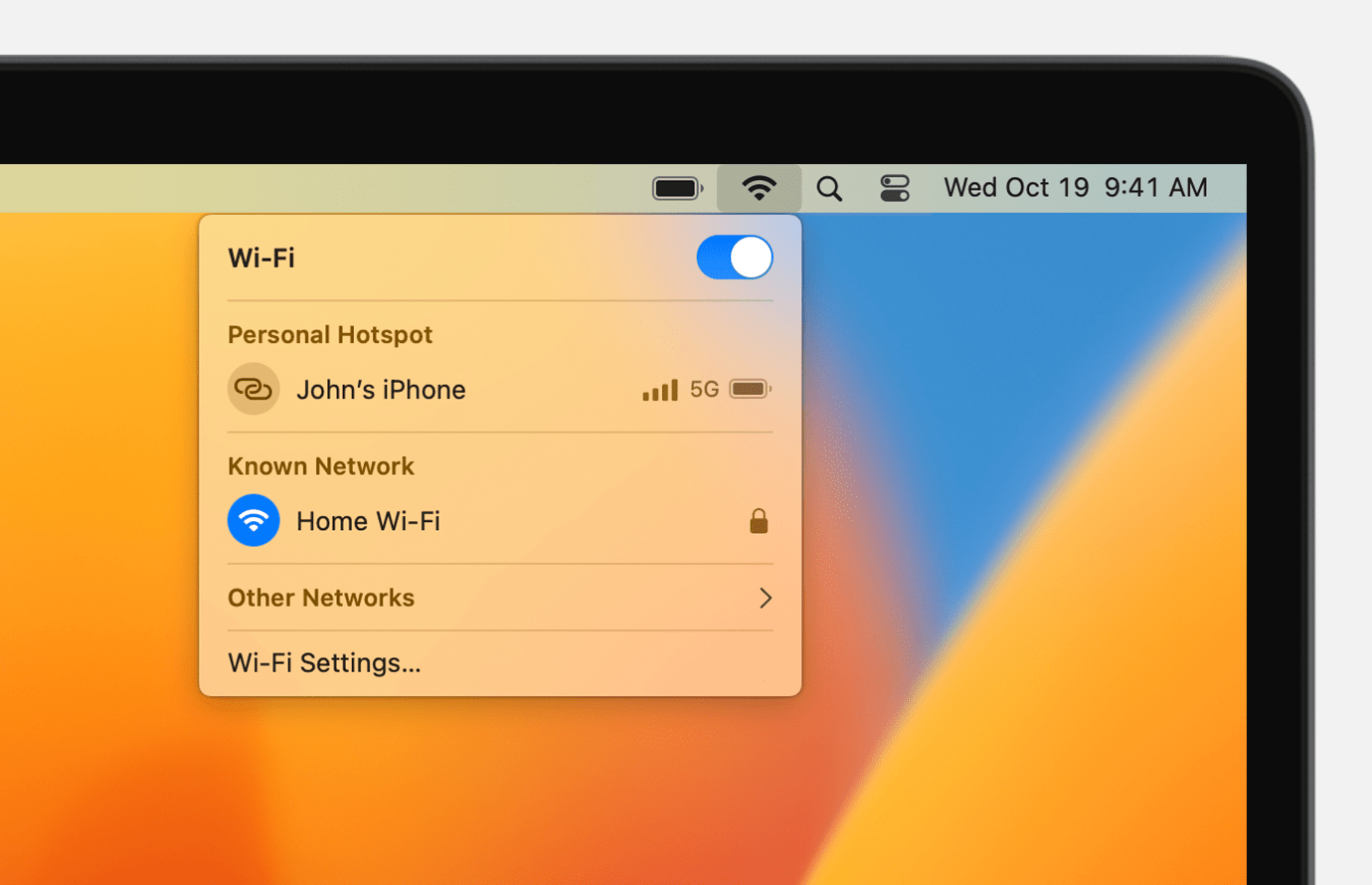
- Connect to a Wi-Fi network
- Connect using Personal Hotspot
- Connect using Ethernet
8 ways to fix your Mac when it won’t connect to Wi-Fi or internet
Email icon An envelope. It indicates the ability to send an email.
Twitter LinkedIn icon The word «in».
LinkedIn Fliboard icon A stylized letter F.
Flipboard Facebook Icon The letter F.
Facebook Email icon An envelope. It indicates the ability to send an email.
Email Link icon An image of a chain link. It symobilizes a website link url.
- If your Mac won’t connect to the Wi-Fi, first verify that you’re using the right Wi-Fi connection.
- You can also try checking Wireless Diagnostics, available updates, physical hardware, and DNS settings.
- If those don’t work, resetting the PRAM and SMC or restarting your Mac might do the trick.
There are a lot of variables that influence why your Wi-Fi connection might drop out, from the hardware in your home or computer, to software on your computer, to issues totally out of your hands originating from your service provider.
Here’s what you can do to narrow down the list of possible culprits and get back up and running again.
1. Verify that the Wi-Fi connection is the one you want
Macs sometimes skip from your expected Wi-Fi connection to a different network. If there are other «open» networks available that don’t actually provide an internet connection, that could be the source of your problem right there.
If you see the Wi-Fi symbol with the exclamation point in the middle, this means you are connected to your wireless router but you’re not getting the proper DNS handshake from your internet provider.
Quick tip: Now’s also a good time to switch between your regular and 5Ghz network if you have both set up. Sometimes a simple switch from one to the other will restore your Wi-Fi connection.
Finally, before escalating to other tactics, try forgetting the WiFi connection and then connecting to it again and see if that clears things up.
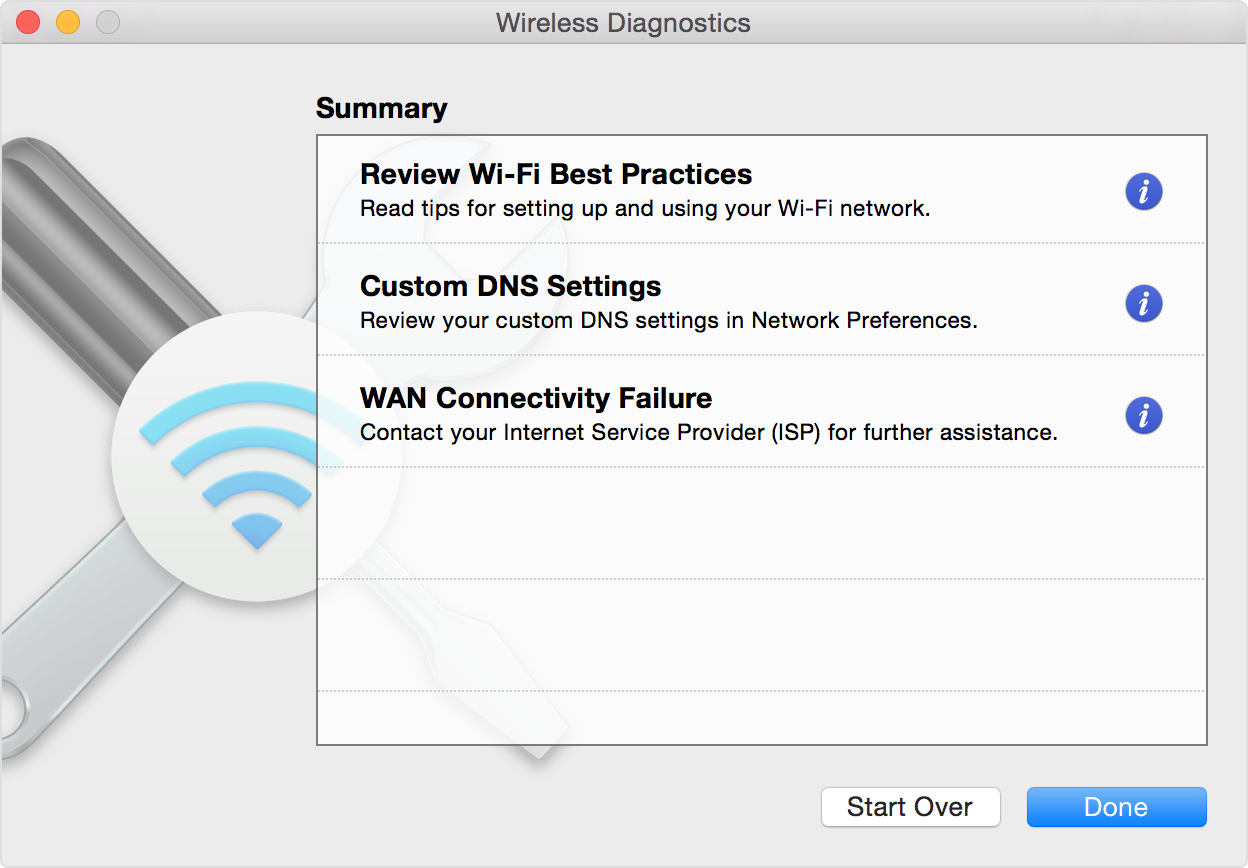
2. Check Wireless Diagnostics
Wireless Diagnostics is Mac OS X’s built-in Wi-Fi troubleshooting tool. I’ve personally never had it solve a single Wi-Fi problem, but hey – maybe it will work for you – and Apple has improved the tool over the years.
You can access Wireless Diagnostics by searching for it in the Spotlight search function (as illustrated above), or by doing the following:
1. Hold down your Option key and click the wireless icon (the Wi-Fi symbol) in the status menu at the top of your screen.
2. Select Open Wireless Diagnostics from the dropdown menu.
3. Click on Continue for your Mac to run the diagnostics on your Wi-Fi connection.
You’ll be presented with a detailed look at your network options and the computer will run you through a series of steps to try to identify and fix your Wi-Fi problems.
Quick tip: If Wireless Diagnostics turns up empty, now’s a good time to set up Wireless Monitoring. When the tool finishes, select Monitor my Wi-Fi connection in the pop-up that shows, and then click on Continue. This will produce a log that could help a technician understand your Wi-Fi problems.
3. Check your System Updates
Are there pending system updates you haven’t installed yet? Try upgrading to the latest version of the operating system if the Wi-Fi is giving you fits. There could be bug fixes in there that will clear up your problem.
4. Check your physical hardware
Sometimes, turning the router off and turning it back on again can fix the issue.
Unplug your cable modem and wireless router (if they’re not an all-in-one unit), wait 30 seconds, then plug your cable modem back in and then your wireless router.
If that doesn’t work, you can try updating your router’s firmware. While a few devices do this automatically, if yours doesn’t, you can update it using its accompanying mobile app (if available) or admin panel in a web browser. If that fixes the issue, make sure you keep the firmware updated at all times to prevent problems in the future.
Note: If your router is very old, you might not find any updates available because the manufacturer has stopped providing them for that model. Consider upgrading the device to a newer one.
5. Change your DNS settings
Now we’re getting a little more technical.
It’s possible that your Wi-Fi is working fine but you aren’t getting internet access because your ISP’s Domain Name Server (DNS) isn’t working properly.
In cases like this, try using a free, public DNS instead. Google has a good one.
1. Open Network Preferences from the Wi-Fi icon in the top menu bar or from System Preferences.
2. Click the Advanced button at the bottom.
3. Then select the DNS tab from the menu option.
4. Hit the plus icon and add Google DNS addresses, 8.8.8.8 or 8.8.4.4.
5. Click OK and try browsing the internet again.
6. Check VPN and security software
Sometimes, you might have a VPN installed to protect your network by, for example, hiding your IP address. However, it just might be what’s interfering with your internet connection.
Check the VPN or any other security-related software to ensure that they aren’t the source of the network problems by disabling them and seeing if the issue persists.
7. Reset NVRAM/PRAM and the SMC
NVRAM (Non-Volatile Random-Access-Memory) and PRAM (Parameter Random-Access-Memory) are two internal Mac components that store the memory even when the device is turned off.
This is used in places like your computer’s internal clock and resetting the PRAM/NVRAM can be an effective way to clear out the virtual cobwebs and get your Wi-Fi up and running again.
1. For the PRAM/NVRAM, start the computer and after you hear the startup chime, hold Shift, Control, and Option keys while you press the power button on your Macbook for at least 10 seconds.
2. Immediately after you hear the startup chime, press and hold the Command + Option + P + R keys to reset the PRAM.
Quick tip: On older Macs, release these keys after you hear the startup sound a second time — on a newer Mac, release the keys after the Apple logo appears and disappears twice.
You should also reset the SMC (System Management Controller) while you’re there for the same reason.To reset the SMC, it depends on whether you have a Mac model with a removable battery or not.
If you happen to have a removable battery, all you have to do is remove it and hold down the power button for five seconds.
On all other Macs, press and hold Shift + Control + Option and the power button for 10 seconds.
Подключение Mac к интернету через Wi‑Fi
Если Вы находитесь в радиусе действия сети Wi-Fi, можно попробовать подключиться к ней.
Подключение к открытой сети Wi‑Fi
- На компьютере Mac нажмите значок Wi‑Fi в строке меню и выберите сеть, к которой Вы хотите подключиться. Если сеть, к которой нужно подключиться, отсутствует, нажмите «Другие сети», чтобы просмотреть список ближайших сетей.
- При появлении запроса введите пароль для сети, затем нажмите «Подключить».
Подключение к скрытой сети Wi-Fi
Для подключения необходимо знать имя скрытой сети, тип настроек защиты беспроводной сети и пароль сети.
- На компьютере Mac нажмите значок Wi-Fi в строке меню, нажмите «Другие сети», затем в списке сетей нажмите «Другая».
- Введите имя беспроводной сети в поле «Имя сети».
- Нажмите всплывающее меню «Безопасность» и выберите тип защиты беспроводной сети.
- Введите данные в показанные дополнительные поля, например имя пользователя и пароль, затем нажмите «Подключиться».
If your Mac isn’t connecting to the internet over Wi-Fi
If your Mac is connected to a Wi-Fi network but can’t get online to connect to websites, email, and all other internet services, try these solutions.
To connect to the internet over Wi-Fi:
- Your Mac must first be connected to a Wi-Fi network: From the Wi-Fi menu in the menu bar or Control Center, choose a network. You might then be asked to enter the Wi-Fi network’s password or agree to terms and conditions.
- After connecting to a Wi-Fi network, your network must then allow your Mac to connect to the internet. If websites, email, and all other internet services remain unavailable after connecting to Wi-Fi, the following solutions might help.
Restart your Mac
Restarting might help because your Mac then automatically renews the internet address it was assigned when joining the Wi-Fi network. Or you can renew the IP address manually. This is known as renewing the DHCP lease. If the lease expired and the address is already in use by another device, your Mac is assigned a new address.
Check date and time and update macOS
Make sure that the date and time are set correctly on your Mac.
If you can connect to the internet from a different Wi-Fi network, connect to that network and then update macOS on your Mac.
Check VPN or other security software
If you installed VPN or other software that monitors or interacts with your network connections, that software could be affecting access to the internet. Learn about network issues related to VPN and other software.
Use the built-in diagnostic tools
Wi-Fi Recommendations. Click Wi-Fi in Control Center or the menu bar and check for a menu item named Wi-Fi Recommendations. If you see it, your Mac has detected an issue and has recommendations. Choose Wi-Fi Recommendations to learn more.*
Wireless Diagnostics. Press and hold the Option key on your keyboard while clicking Wi-Fi in Control Center or the menu bar, then choose Open Wireless Diagnostics from the menu. Learn more about using Wireless Diagnostics to analyze your wireless environment.
Update the Wi-Fi router
If you manage the network’s Wi-Fi router, install the latest firmware updates for the router, as recommended by its manufacturer. It might also help to simply restart the router and use Apple’s recommended settings for Wi-Fi routers and access points.
Try a different network or contact your ISP
If you can access the internet when connected to a different network, or you’re not sure, check with your internet provider or network administrator to make sure that your network is working properly and there isn’t an internet service outage.
* The Wi-Fi Recommendations feature isn’t available for personal hotspots or networks that use certain enterprise security protocols, such as WPA Enterprise or WPA2 Enterprise.
Connect to the internet with your Mac
Learn how to use Wi-Fi, Personal Hotspot, and Ethernet to connect to the internet.
Connect to a Wi-Fi network
From the Wi-Fi menu in the menu bar, choose a network. You might then be asked to enter the Wi-Fi network’s password or agree to terms and conditions.
Connect using Personal Hotspot
With most carrier plans, you can share the cellular data connection of your iPhone or iPad (Wi-Fi + Cellular) with your Mac. Learn how to set up Personal Hotspot.
Connect using Ethernet
To use a wired connection to the internet, connect an Ethernet cable between your router or modem and the Ethernet port on your Mac. Some Mac models require an Ethernet adapter, such as the Belkin USB-C to Gigabit Ethernet Adapter or the Apple Thunderbolt to Gigabit Ethernet Adapter.
Information about products not manufactured by Apple, or independent websites not controlled or tested by Apple, is provided without recommendation or endorsement. Apple assumes no responsibility with regard to the selection, performance, or use of third-party websites or products. Apple makes no representations regarding third-party website accuracy or reliability. Contact the vendor for additional information.