- Роутер на Ubuntu Server 21.04
- Похожие посты:
- Роутер на Ubuntu Server 21.04: 4 комментария
- Configure Ubuntu 20.04 as Linux Router
- Configure Ubuntu 20.04 as Linux Router
- Assign Static IP Addresses to the Linux Router
- IP Address details on the router
- Enable Kernel IP forwarding on Ubuntu Linux Router
- Configure NATing and Forwarding on Linux Router
- Configure Packet Forwarding
- Configure NATing
- Save iptables rules Permanently in Linux
- Other Tutorials
- SUPPORT US VIA A VIRTUAL CUP OF COFFEE
Роутер на Ubuntu Server 21.04
Краткое руководство по настройке роутера в связке iptables + dnsmasq на ОС Ubuntu Server 21.04, а также проброс портов по IP-адресам машин в локальной сети.
Исходные данные
Имеем на машине 2 сетевых интерфейса:
enp0s3 — для внешней сети 192.168.1.0/24
enp0s8 — для внутренней сети 192.168.53.0/24
Также у нас есть шлюз во внешней сети. Это маршрутизатор с IP-адресом 192.168.1.1
Наша задача — настроить доступ в Интернет для внутренней сети.
В первую очередь нам необходимо настроить сетевые интерфейсы. Для этих целей Ubuntu Server 21.04 использует netplan.
Открываем файл /etc/netplan/00-installer-config.yaml
# sudo nano /etc/netplan/00-installer-config.yaml
и приводим его к такому виду:
# This is the network config written by 'subiquity' network: ethernets: enp0s3: addresses: - 192.168.1.53/24 gateway4: 192.168.1.1 nameservers: addresses: - 192.168.1.1 search: [] enp0s8: addresses: - 192.168.53.1/24 nameservers: addresses: [] search: [] version: 2
# sudo netplan generate # sudo netplan apply
Переходим к настройке файрволла (правил iptables).
Создадим каталог /etc/firewall, в нём скрипт iptables.sh и открываем его
# sudo mkdir /etc/firewall # sudo touch /etc/firewall/iptables.sh # sudo nano /etc/firewall/iptables.sh
#!/bin/sh sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 iptables -F iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o enp0s+ -j MASQUERADE iptables -t filter -A INPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT iptables -t filter -A INPUT -p icmp -j ACCEPT iptables -t filter -A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT iptables -t filter -A INPUT -i enp0s+ -j ACCEPT iptables -t filter -A FORWARD -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT iptables -t filter -A FORWARD -p icmp -j ACCEPT iptables -t filter -A FORWARD -i lo -j ACCEPT iptables -t filter -A FORWARD -i enp0s+ -j ACCEPT iptables -t filter -A FORWARD -o enp0s+ -j ACCEPT iptables -t filter -A INPUT -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-host-prohibited iptables -t filter -A FORWARD -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
и сделаем скрипт исполняемым
# sudo chmod +x /etc/firewall/iptables.sh
Теперь создадим службу rc-local. Для этого создадим файл /etc/systemd/system/rc-local.service
# sudo touch /etc/systemd/system/rc-local.service
# sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/rc-local.service
[Unit] Description=/etc/rc.local ConditionPathExists=/etc/rc.local [Service] Type=forking ExecStart=/etc/rc.local start TimeoutSec=0 StandardOutput=tty RemainAfterExit=yes SysVStartPriority=99 [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Затем создадим файл /etc/rc.local и откроем его
# sudo touch /etc/rc.local # sudo nano /etc/rc.local
пропишем в него такой код:
#!/bin/sh -e /etc/firewall/iptables.sh exit 0
и сделаем его исполняемым
Далее перезагрузим машину
Проверим, работают ли созданные правила. Для этого выполним команду
и, если iptables работает корректно, получим примерно такой ответ
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere state RELATED,ESTABLISHED ACCEPT icmp -- anywhere anywhere ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere REJECT all -- anywhere anywhere reject-with icmp-host-prohibited Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere state RELATED,ESTABLISHED ACCEPT icmp -- anywhere anywhere ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere REJECT all -- anywhere anywhere reject-with icmp-host-prohibited Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination
После этого переходим к настройке dnsmasq.
и в самом конце файла добавляем:
bind-interfaces domain-needed bogus-priv interface=enp0s8 resolv-file=/etc/resolv.conf dhcp-range=192.168.53.31,192.168.53.130,24h cache-size=150
# sudo systemctl start dnsmasq
или лучше вообще перезагрузим машину
После этого на других машинах в сети проверяем сетевые настройки и выход в Интернет.
При необходимости в пробросе портов по IP-адресам для доступа из внешней сети, например, необходимо пробросить порт RDP 3389/TCP на IP-адрес машины 192.168.53.25, выполним такие команды:
# sudo iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -i enp0s3 -p tcp --dport 3389 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.53.25:3389 # sudo iptables -t filter -A INPUT -p tcp -m state --state NEW -m tcp --dport 3389 -j ACCEPT
Для того, чтобы эти правила срабатывали после каждой загрузки системы, их необходимо прописать в файл /etc/firewall/iptables.sh
Проброс других портов осуществляется аналогичным образом.
Похожие посты:
Роутер на Ubuntu Server 21.04: 4 комментария
У меня enp2s0 = wan , enp3s1 = Lan очен неясно iptables.sh куда поставит Лан куда ван интерфейс. у тебе всегда enp0s+
enp0s+ означает любой интерфейс, который начинается с enp0s, то есть, если по статье, то это enp0s3 и enp0s8. В вашем случае наверное будет лучше прописать enp+, или перечислить их через запятую, чтобы не писать одно и то же правило два раза.
Раборает. Единствено не работает iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -i enp0s3 -p tcp —dport 3389 -j DNAT —to-destination 192.168.53.25:3389 «iptables v1.8.7 (nf_tables): unknown option «—port»»
вы писали, что у вас интерфейс enp2s0 смотрит в Интернет, а прописываете enp0s3… исправьте, и всё должно получиться.
Configure Ubuntu 20.04 as Linux Router
Follow through this tutorial to learn how to configure Ubuntu 20.04 as Linux router. Linux is awesome, It can function as “anything”, -:). Just like how you can use any other router to route your traffic between local networks and even to the internet.
Configure Ubuntu 20.04 as Linux Router
There is more to configuring a Linux system to function as a router. However, in this tutorial, we will be covering how to configure Linux router to route traffic to Internet via WAN interface as well as route traffic between LAN via LAN interfaces.
Assign Static IP Addresses to the Linux Router
As per our setup, our Linux router has three interfaces attached:
- enp0s3: WAN Interface with IP 192.168.100.101 (bidged, static)
- enp0s8: LAN, 172.16.0.1/24, (static)
- enp0s9: LAN 172.16.1.1/24, (static)
IP Address details on the router
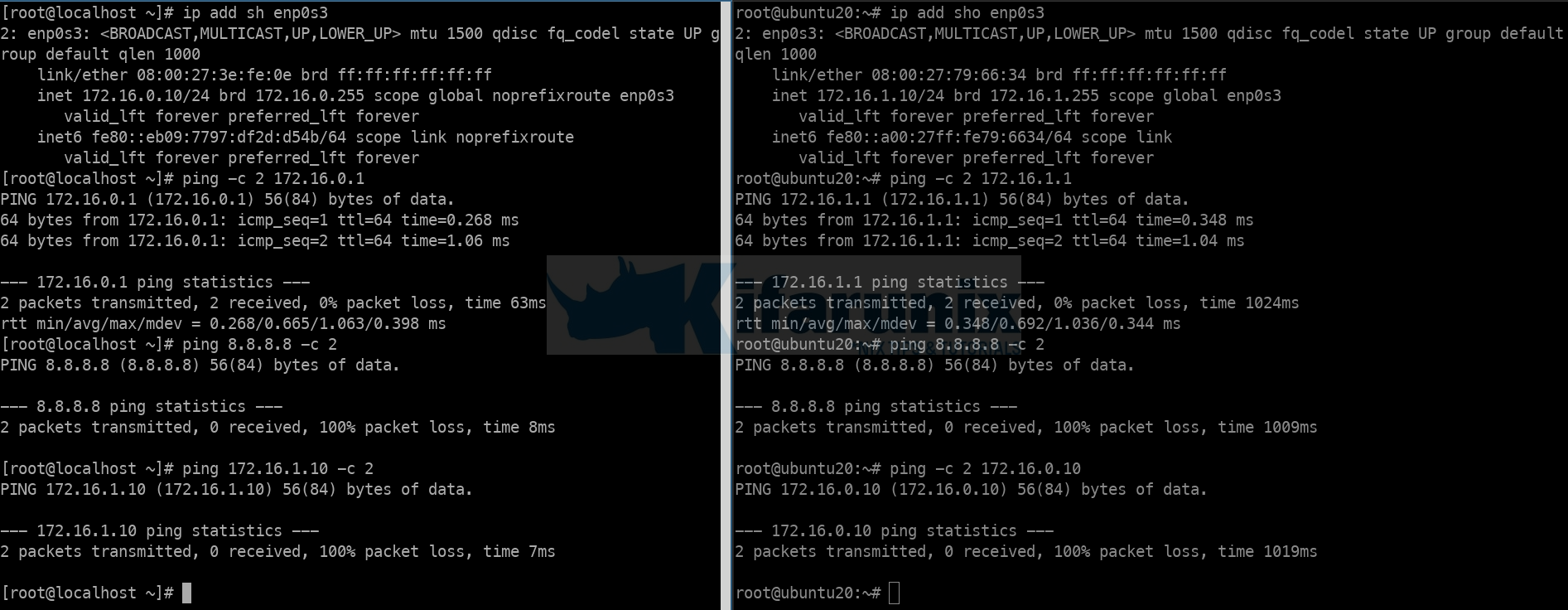
1: lo: mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000 link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: enp0s3: mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 08:00:27:df:2c:b4 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 192.168.100.101/24 brd 192.168.100.255 scope global dynamic enp0s3 valid_lft 86100sec preferred_lft 86100sec inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fedf:2cb4/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 3: enp0s8: mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 08:00:27:12:62:bf brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 172.168.0.1/24 brd 172.168.0.255 scope global enp0s8 valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fe12:62bf/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 4: enp0s9: mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 08:00:27:66:4b:4f brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 172.16.1.1/24 brd 172.16.1.255 scope global enp0s9 valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fe66:4b4f/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever cat /etc/netplan/00-installer-config.yamlnetwork: version: 2 renderer: networkd ethernets: enp0s3: dhcp4: no addresses: [192.168.100.101/24] gateway4: 192.168.100.1 nameservers: addresses: - 192.168.100.1 - 8.8.8.8 enp0s8: dhcp4: no addresses: [172.16.0.1/24] enp0s9: dhcp4: no addresses: [172.16.1.1/24] IP Address details on Other LAN Servers;
Host on 172.16.1.0/24 Network:
1: lo: mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000 link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: enp0s3: mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 08:00:27:79:66:34 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 172.16.1.10/24 brd 172.16.1.255 scope global enp0s3 valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fe79:6634/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever cat /etc/netplan/00-installer-config.yamlnetwork: version: 2 renderer: networkd ethernets: enp0s3: dhcp4: no addresses: - 172.16.1.10/24 gateway4: 172.16.1.1 nameservers: addresses: - 172.16.1.1 - 8.8.8.8 Host on 172.16.1.0/24 Network:
1: lo: mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000 link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: enp0s3: mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 08:00:27:3e:fe:0e brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 172.16.0.10/24 brd 172.16.0.255 scope global noprefixroute enp0s3 valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 fe80::eb09:7797:df2d:d54b/64 scope link noprefixroute valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s3TYPE=Ethernet PROXY_METHOD=none BROWSER_ONLY=no BOOTPROTO=none IPADDR=172.16.0.10 PREFIX=24 GATEWAY=172.16.0.1 DEFROUTE=yes IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPV6INIT=yes IPV6_AUTOCONF=yes IPV6_DEFROUTE=yes IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPV6_ADDR_GEN_MODE=stable-privacy NAME=enp0s3 UUID=ea93c07b-a40e-4e1f-a850-f97e2a762f9a DEVICE=enp0s3 ONBOOT=yes DNS1=172.16.0.1 DNS2=8.8.8.8 NM_CONTROLLED=no - no LAN device has Internet access
- only devices on same LAN can access each other
- No device can access devices on different LAN
Enable Kernel IP forwarding on Ubuntu Linux Router
Next, you need to enable IP forwarding in order for the Linux router box for it to function as a router, receive and forward packets.
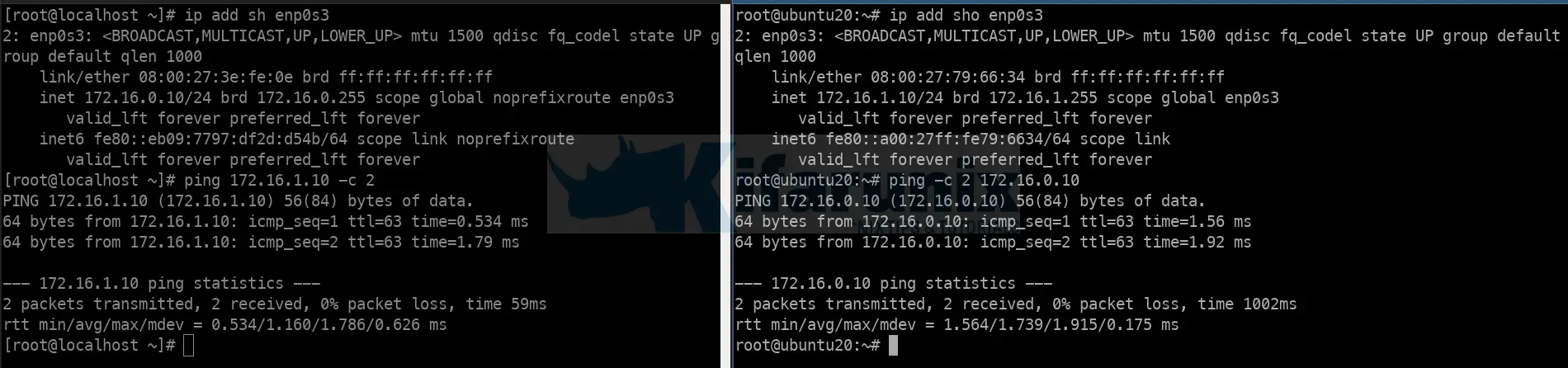
Once this is done, devices on both 172.16.0.0/24 and 172.16.1.0/24 should be able to communicate.
To enable IP forwarding, you need to uncomment the line net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 on the /etc/sysctl.conf configuration file.
So, first check if the said line is already defined on the configuration file;
grep net.ipv4.ip_forward /etc/sysctl.confif the line is present in the config file and comment, simply uncomment by running the command below;
sed -i '/net.ipv4.ip_forward/s/^#//' /etc/sysctl.confOtherwise, just insert the line;
echo 'net.ipv4.ip_forward=1' >> /etc/sysctl.confCheck the status by running the command below;
Verify IP forwarding between the two LANs.
Configure NATing and Forwarding on Linux Router
NATing and Forwarding can be handled using iptables or via the iptables front-end utility like UFW .
Configure Packet Forwarding
Configure the packets received from router LAN interfaces (enp0s8 and enp0s9) to be forwarded through the WAN interface, which in our case is enp0s3 .
iptables -A FORWARD -i enp0s8 -o enp0s3 -j ACCEPTiptables -A FORWARD -i enp0s9 -o enp0s3 -j ACCEPTSimilarly, configure packets that are associated with existing connections received on a WAN interface to be forwarded to the LAN interfaces;
iptables -A FORWARD -i enp0s3 -o enp0s8 -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPTiptables -A FORWARD -i enp0s3 -o enp0s9 -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPTConfigure NATing
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o enp0s3 -j MASQUERADETo ensure that the two local networks can also communicate, run the commands below;
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o enp0s8 -j MASQUERADEiptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o enp0s9 -j MASQUERADEConsult man iptables for more information.
Save iptables rules Permanently in Linux
In order to permanently save iptables rules, simply install the iptables-persistent package and run the iptables-save command as follows.
apt install iptables-persistentThe current rules will be saved during package installation but can still save them thereafter by running the command;
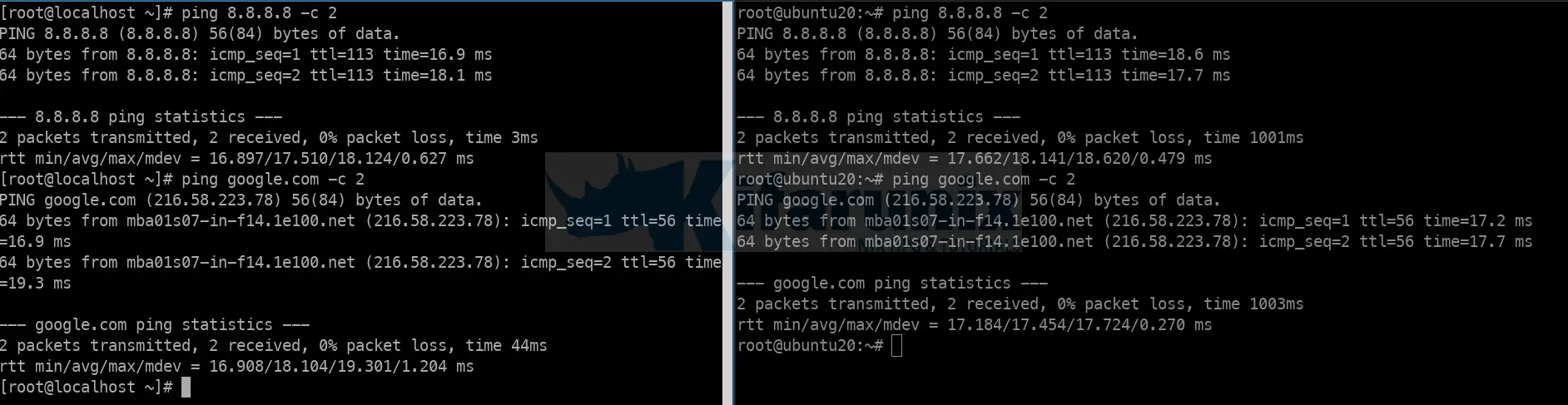
iptables-save > /etc/iptables/rules.v4Your LAN systems should be now be able to connect to internet via the Linux router;
And there you go. You vms can now route traffic through your Linux router.
That concludes our guide on how to configure Ubuntu 20.04 as Linux Router.
Other Tutorials
SUPPORT US VIA A VIRTUAL CUP OF COFFEE
We’re passionate about sharing our knowledge and experiences with you through our blog. If you appreciate our efforts, consider buying us a virtual coffee. Your support keeps us motivated and enables us to continually improve, ensuring that we can provide you with the best content possible. Thank you for being a coffee-fueled champion of our work!