- IP Multicast Routing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15.2(7)Ex (Catalyst 1000 Switches)
- Book Title
- Configuring IGMP Snooping
- Results
- Chapter: Configuring IGMP Snooping
- Configuring IGMP Snooping
- Prerequisites for IGMP Snooping
- Restrictions for IGMP Snooping
- Information about IGMP Snooping
- IGMP Snooping
- IGMP Versions
- Joining a Multicast Group
- Leaving a Multicast Group
- Immediate Leave
- IGMP Configurable-Leave Timer
- IGMP Report Suppression
- Default IGMP Snooping Configuration
IP Multicast Routing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15.2(7)Ex (Catalyst 1000 Switches)
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Book Title
IP Multicast Routing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15.2(7)Ex (Catalyst 1000 Switches)
Configuring IGMP Snooping
Results
Chapter: Configuring IGMP Snooping
- Configuring IGMP Snooping
- Prerequisites for IGMP Snooping
- Restrictions for IGMP Snooping
- Information about IGMP Snooping
- IGMP Snooping
- IGMP Versions
- Joining a Multicast Group
- Leaving a Multicast Group
- Immediate Leave
- IGMP Configurable-Leave Timer
- IGMP Report Suppression
- Default IGMP Snooping Configuration
- Default IGMP Filtering and Throttling Configuration
- Enabling or Disabling IGMP Snooping on a Device
- Enabling or Disabling IGMP Snooping on a VLAN Interface
- Configuring a Multicast Router Port
- Configuring a Host Statically to Join a Group
- Enabling IGMP Immediate Leave
- Configuring the IGMP Leave Timer
- Configuring the IGMP Snooping Querier
- Disabling IGMP Report Suppression
- Configuring IGMP Profiles
- Applying IGMP Profiles
- Setting the Maximum Number of IGMP Groups
- Configuring the IGMP Throttling Action
- Monitoring IGMP Snooping Information
- Monitoring IGMP Filtering
- Example: Enabling a Static Connection to a Multicast Router
- Example: Configuring a Host Statically to Join a Group
- Example: Enabling IGMP Immediate Leave
- Example: Setting the IGMP Snooping Querier Source Address
- Example: Setting the IGMP Snooping Querier Maximum Response Time
- Example: Setting the IGMP Snooping Querier Timeout
- Example: Setting the IGMP Snooping Querier Feature
- Example: Configuring IGMP Profiles
- Example: Applying IGMP Profile
- Example: Setting the Maximum Number of IGMP Groups
Configuring IGMP Snooping
Prerequisites for IGMP Snooping
Observe these guidelines when configuring the IGMP snooping querier:
- Configure the VLAN in global configuration mode.
- Configure an IP address on the VLAN interface. When enabled, the IGMP snooping querier uses the IP address as the query source address.
- If there is no IP address configured on the VLAN interface, the IGMP snooping querier tries to use the configured global IP address for the IGMP querier. If there is no global IP address specified, the IGMP querier tries to use the VLAN switch virtual interface (SVI) IP address (if one exists). If there is no SVI IP address, the device uses the first available IP address configured on the device. The first IP address available appears in the output of the show ip interface privileged EXEC command. The IGMP snooping querier does not generate an IGMP general query if it cannot find an available IP address on the device.
- The IGMP snooping querier supports IGMP Versions 1 and 2.
- When administratively enabled, the IGMP snooping querier moves to the nonquerier state if it detects the presence of a multicast router in the network.
- When it is administratively enabled, the IGMP snooping querier moves to the operationally disabled state if IGMP snooping is disabled in the VLAN.
- Layer 3 multicast is not supported.
- MAC based snooping is supported in hardware.
Restrictions for IGMP Snooping
The following are the restrictions for IGMP snooping:
- IGMP report suppression is supported only when the multicast query has IGMPv1 and IGMPv2 reports. This feature is not supported when the query includes IGMPv3 reports.
- The IGMP configurable leave time is only supported on hosts running IGMP Version 2. IGMP version 2 is the default version for the device. The actual leave latency in the network is usually the configured leave time. However, the leave time might vary around the configured time, depending on real-time CPU load conditions, network delays and the amount of traffic sent through the interface.
- The IGMP throttling action restriction can be applied only to Layer 2 ports. You can use ip igmp max-groups action replace interface configuration command on a logical EtherChannel interface but cannot use it on ports that belong to an EtherChannel port group. When the maximum group limitation is set to the default (no maximum), entering the ip igmp max-groups action < deny | replace >command has no effect. If you configure the throttling action and set the maximum group limitation after an interface has added multicast entries to the forwarding table, the forwarding-table entries are either aged out or removed, depending on the throttling action.
- Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) is not supported.
Information about IGMP Snooping
IGMP Snooping
Layer 2 devices can use IGMP snooping to constrain the flooding of multicast traffic by dynamically configuring Layer 2 interfaces so that multicast traffic is forwarded to only those interfaces associated with IP multicast devices. As the name implies, IGMP snooping requires the LAN device to snoop on the IGMP transmissions between the host and the router and to keep track of multicast groups and member ports. When the device receives an IGMP report from a host for a particular multicast group, the device adds the host port number to the forwarding table entry; when it receives an IGMP Leave Group message from a host, it removes the host port from the table entry. It also periodically deletes entries if it does not receive IGMP membership reports from the multicast clients.
For more information on IP multicast and IGMP, see RFC 1112 and RFC 2236.
The multicast router sends out periodic general queries to all VLANs. All hosts interested in this multicast traffic send join requests and are added to the forwarding table entry. The device creates one entry per VLAN in the IGMP snooping IP multicast forwarding table for each group from which it receives an IGMP join request.
The device supports IP multicast group-based bridging, instead of MAC-addressed based groups. With multicast MAC address-based groups, if an IP address being configured translates (aliases) to a previously configured MAC address or to any reserved multicast MAC addresses (in the range 224.0.0.xxx), the command fails. Because the device uses IP multicast groups, there are no address aliasing issues.
The IP multicast groups learned through IGMP snooping are dynamic. However, you can statically configure multicast groups by using the ip igmp snooping vlan vlan-id static ip_address interface interface-id global configuration command. If you specify group membership for a multicast group address statically, your setting supersedes any automatic manipulation by IGMP snooping. Multicast group membership lists can consist of both user-defined and IGMP snooping-learned settings.
You can configure an IGMP snooping querier to support IGMP snooping in subnets without multicast interfaces because the multicast traffic does not need to be routed.
If a port spanning-tree, a port group, or a VLAN ID change occurs, the IGMP snooping-learned multicast groups from this port on the VLAN are deleted.
These sections describe IGMP snooping characteristics:
IGMP Versions
The device supports IGMP version 1, IGMP version 2, and IGMP version 3. These versions are interoperable on the device. For example, if IGMP snooping is enabled and the querier’s version is IGMPv2, and the device receives an IGMPv3 report from a host, then the device can forward the IGMPv3 report to the multicast router.
An IGMPv3 device can receive messages from and forward messages to a device running the Source Specific Multicast (SSM) feature.
Joining a Multicast Group
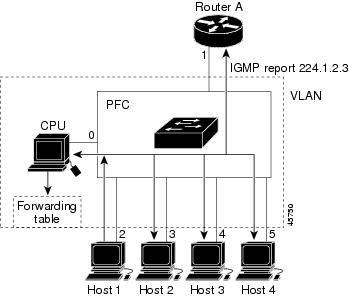
Router A sends a general query to the device, which forwards the query to ports 2 through 5, all of which are members of the same VLAN. Host 1 wants to join multicast group 224.1.2.3 and multicasts an IGMP membership report (IGMP join message) to the group. The device CPU uses the information in the IGMP report to set up a forwarding-table entry that includes the port numbers connected to Host 1 and to the router.
The device hardware can distinguish IGMP information packets from other packets for the multicast group. The information in the table tells the switching engine to send frames addressed to the 224.1.2.3 multicast IP address that are not IGMP packets to the router and to the host that has joined the group.
Leaving a Multicast Group
The router sends periodic multicast general queries, and the device forwards these queries through all ports in the VLAN. Interested hosts respond to the queries. If at least one host in the VLAN wants to receive multicast traffic, the router continues forwarding the multicast traffic to the VLAN. The device forwards multicast group traffic only to those hosts listed in the forwarding table for that IP multicast group maintained by IGMP snooping.
When hosts want to leave a multicast group, they can silently leave, or they can send a leave message. When the device receives a leave message from a host, it sends a group-specific query to learn if any other devices connected to that interface are interested in traffic for the specific multicast group. The device then updates the forwarding table for that MAC group so that only those hosts interested in receiving multicast traffic for the group are listed in the forwarding table. If the router receives no reports from a VLAN, it removes the group for the VLAN from its IGMP cache.
Immediate Leave
The device uses IGMP snooping Immediate Leave to remove from the forwarding table an interface that sends a leave message without the device sending group-specific queries to the interface. The VLAN interface is pruned from the multicast tree for the multicast group specified in the original leave message. Immediate Leave ensures optimal bandwidth management for all hosts on a switched network, even when multiple multicast groups are simultaneously in use.
Immediate Leave is only supported on IGMP version 2 hosts. IGMP version 2 is the default version for the device.
You should use the Immediate Leave feature only on VLANs where a single host is connected to each port. If Immediate Leave is enabled on VLANs where more than one host is connected to a port, some hosts may be dropped inadvertently.
IGMP Configurable-Leave Timer
You can configure the time that the device waits after sending a group-specific query to determine if hosts are still interested in a specific multicast group. The IGMP leave response time can be configured from 100 to 32767 milliseconds.
IGMP Report Suppression
IGMP report suppression is supported only when the multicast query has IGMPv1 and IGMPv2 reports. This feature is not supported when the query includes IGMPv3 reports.
The device uses IGMP report suppression to forward only one IGMP report per multicast router query to multicast devices. When IGMP report suppression is enabled (the default), the device sends the first IGMP report from all hosts for a group to all the multicast routers. The device does not send the remaining IGMP reports for the group to the multicast routers. This feature prevents duplicate reports from being sent to the multicast devices.
If the multicast router query includes requests only for IGMPv1 and IGMPv2 reports, the device forwards only the first IGMPv1 or IGMPv2 report from all hosts for a group to all the multicast routers.
If the multicast router query also includes requests for IGMPv3 reports, the device forwards all IGMPv1, IGMPv2, and IGMPv3 reports for a group to the multicast devices.
If you disable IGMP report suppression, all IGMP reports are forwarded to the multicast routers.
Default IGMP Snooping Configuration
This table displays the default IGMP snooping configuration for the device.
- IGMP Snooping