- Configure Ubuntu 20.04 as Linux Router
- Configure Ubuntu 20.04 as Linux Router
- Assign Static IP Addresses to the Linux Router
- IP Address details on the router
- Enable Kernel IP forwarding on Ubuntu Linux Router
- Configure NATing and Forwarding on Linux Router
- Configure Packet Forwarding
- Configure NATing
- Save iptables rules Permanently in Linux
- Other Tutorials
- SUPPORT US VIA A VIRTUAL CUP OF COFFEE
- How to build Linux Router with Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS
- How to build Linux Router with Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS
Configure Ubuntu 20.04 as Linux Router
Follow through this tutorial to learn how to configure Ubuntu 20.04 as Linux router. Linux is awesome, It can function as “anything”, -:). Just like how you can use any other router to route your traffic between local networks and even to the internet.
Configure Ubuntu 20.04 as Linux Router
There is more to configuring a Linux system to function as a router. However, in this tutorial, we will be covering how to configure Linux router to route traffic to Internet via WAN interface as well as route traffic between LAN via LAN interfaces.
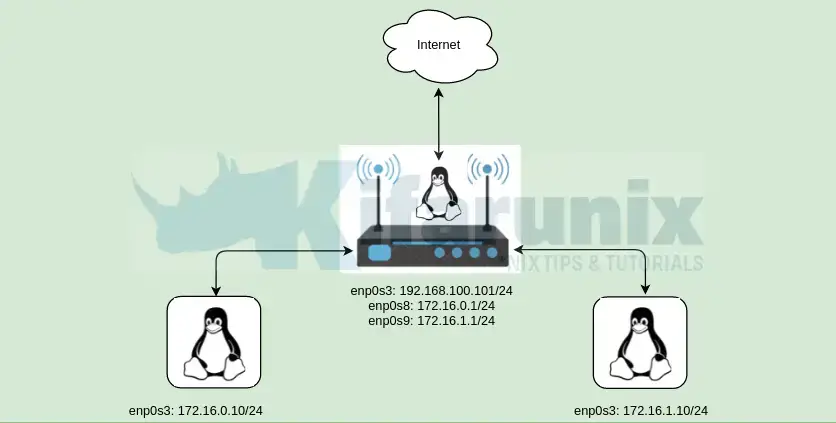
Assign Static IP Addresses to the Linux Router
As per our setup, our Linux router has three interfaces attached:
- enp0s3: WAN Interface with IP 192.168.100.101 (bidged, static)
- enp0s8: LAN, 172.16.0.1/24, (static)
- enp0s9: LAN 172.16.1.1/24, (static)
IP Address details on the router
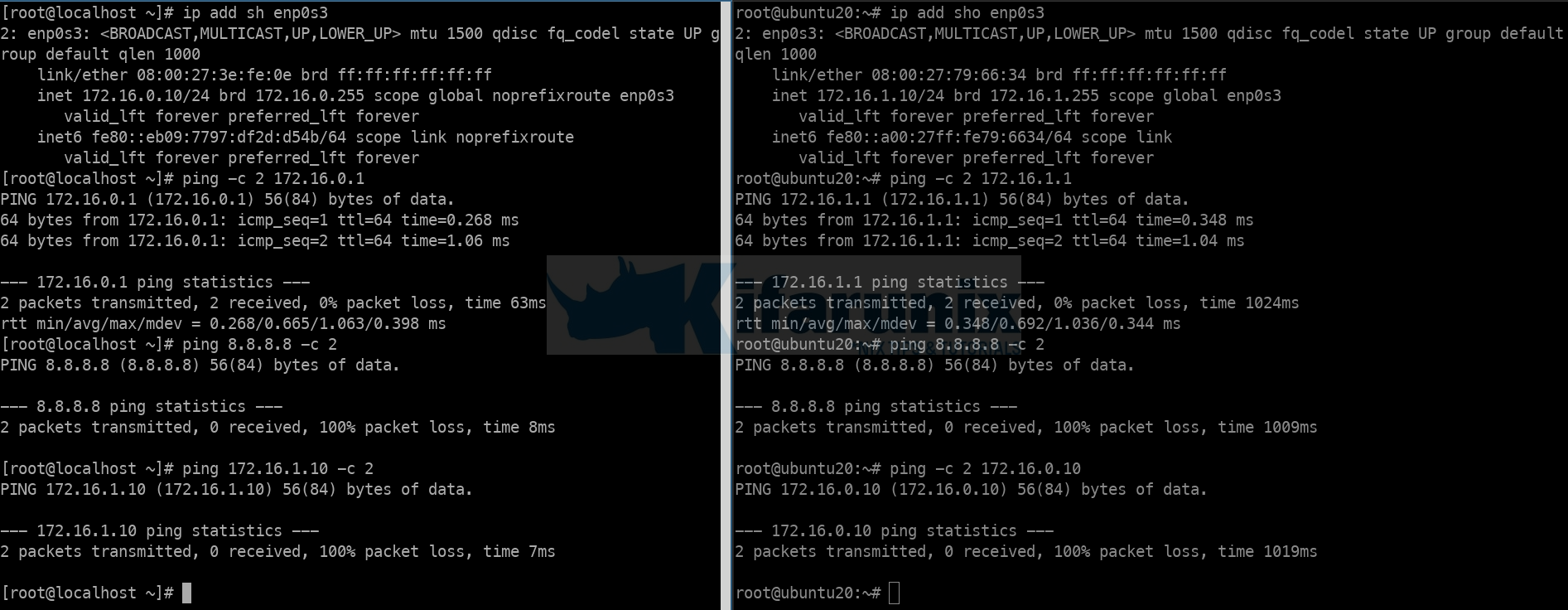
1: lo: mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000 link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: enp0s3: mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 08:00:27:df:2c:b4 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 192.168.100.101/24 brd 192.168.100.255 scope global dynamic enp0s3 valid_lft 86100sec preferred_lft 86100sec inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fedf:2cb4/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 3: enp0s8: mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 08:00:27:12:62:bf brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 172.168.0.1/24 brd 172.168.0.255 scope global enp0s8 valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fe12:62bf/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 4: enp0s9: mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 08:00:27:66:4b:4f brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 172.16.1.1/24 brd 172.16.1.255 scope global enp0s9 valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fe66:4b4f/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever cat /etc/netplan/00-installer-config.yamlnetwork: version: 2 renderer: networkd ethernets: enp0s3: dhcp4: no addresses: [192.168.100.101/24] gateway4: 192.168.100.1 nameservers: addresses: - 192.168.100.1 - 8.8.8.8 enp0s8: dhcp4: no addresses: [172.16.0.1/24] enp0s9: dhcp4: no addresses: [172.16.1.1/24] IP Address details on Other LAN Servers;
Host on 172.16.1.0/24 Network:
1: lo: mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000 link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: enp0s3: mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 08:00:27:79:66:34 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 172.16.1.10/24 brd 172.16.1.255 scope global enp0s3 valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fe79:6634/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever cat /etc/netplan/00-installer-config.yamlnetwork: version: 2 renderer: networkd ethernets: enp0s3: dhcp4: no addresses: - 172.16.1.10/24 gateway4: 172.16.1.1 nameservers: addresses: - 172.16.1.1 - 8.8.8.8 Host on 172.16.1.0/24 Network:
1: lo: mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000 link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: enp0s3: mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 08:00:27:3e:fe:0e brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 172.16.0.10/24 brd 172.16.0.255 scope global noprefixroute enp0s3 valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 fe80::eb09:7797:df2d:d54b/64 scope link noprefixroute valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s3TYPE=Ethernet PROXY_METHOD=none BROWSER_ONLY=no BOOTPROTO=none IPADDR=172.16.0.10 PREFIX=24 GATEWAY=172.16.0.1 DEFROUTE=yes IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPV6INIT=yes IPV6_AUTOCONF=yes IPV6_DEFROUTE=yes IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPV6_ADDR_GEN_MODE=stable-privacy NAME=enp0s3 UUID=ea93c07b-a40e-4e1f-a850-f97e2a762f9a DEVICE=enp0s3 ONBOOT=yes DNS1=172.16.0.1 DNS2=8.8.8.8 NM_CONTROLLED=no - no LAN device has Internet access
- only devices on same LAN can access each other
- No device can access devices on different LAN
Enable Kernel IP forwarding on Ubuntu Linux Router
Next, you need to enable IP forwarding in order for the Linux router box for it to function as a router, receive and forward packets.
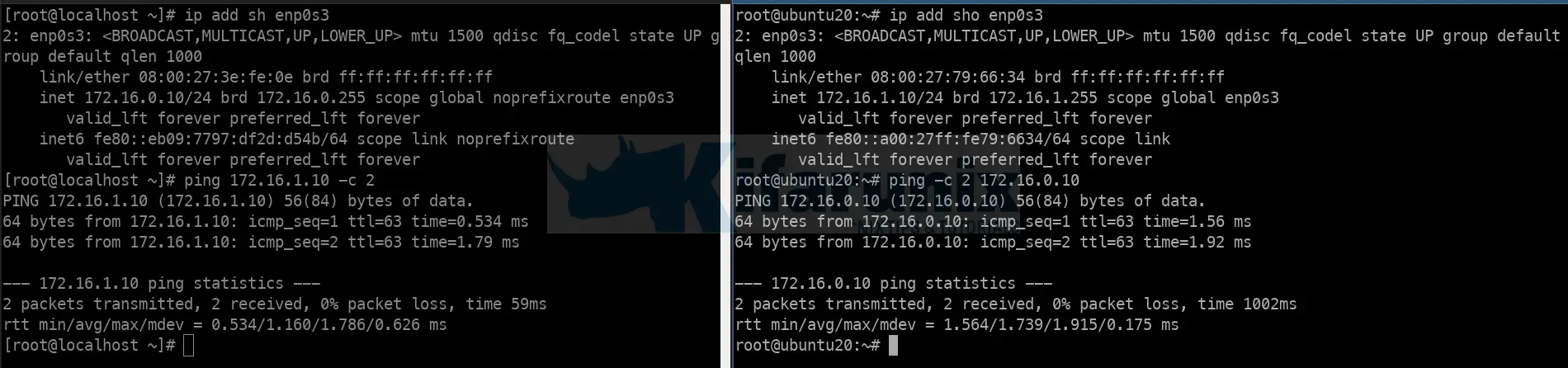
Once this is done, devices on both 172.16.0.0/24 and 172.16.1.0/24 should be able to communicate.
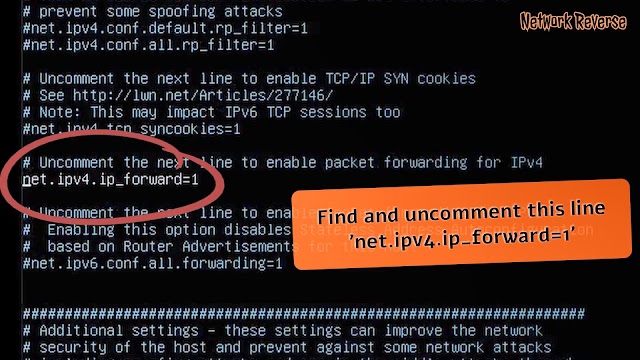
To enable IP forwarding, you need to uncomment the line net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 on the /etc/sysctl.conf configuration file.
So, first check if the said line is already defined on the configuration file;
grep net.ipv4.ip_forward /etc/sysctl.confif the line is present in the config file and comment, simply uncomment by running the command below;
sed -i '/net.ipv4.ip_forward/s/^#//' /etc/sysctl.confOtherwise, just insert the line;
echo 'net.ipv4.ip_forward=1' >> /etc/sysctl.confCheck the status by running the command below;
Verify IP forwarding between the two LANs.
Configure NATing and Forwarding on Linux Router
NATing and Forwarding can be handled using iptables or via the iptables front-end utility like UFW .
Configure Packet Forwarding
Configure the packets received from router LAN interfaces (enp0s8 and enp0s9) to be forwarded through the WAN interface, which in our case is enp0s3 .
iptables -A FORWARD -i enp0s8 -o enp0s3 -j ACCEPTiptables -A FORWARD -i enp0s9 -o enp0s3 -j ACCEPTSimilarly, configure packets that are associated with existing connections received on a WAN interface to be forwarded to the LAN interfaces;
iptables -A FORWARD -i enp0s3 -o enp0s8 -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPTiptables -A FORWARD -i enp0s3 -o enp0s9 -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPTConfigure NATing
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o enp0s3 -j MASQUERADETo ensure that the two local networks can also communicate, run the commands below;
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o enp0s8 -j MASQUERADEiptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o enp0s9 -j MASQUERADEConsult man iptables for more information.
Save iptables rules Permanently in Linux
In order to permanently save iptables rules, simply install the iptables-persistent package and run the iptables-save command as follows.
apt install iptables-persistentThe current rules will be saved during package installation but can still save them thereafter by running the command;
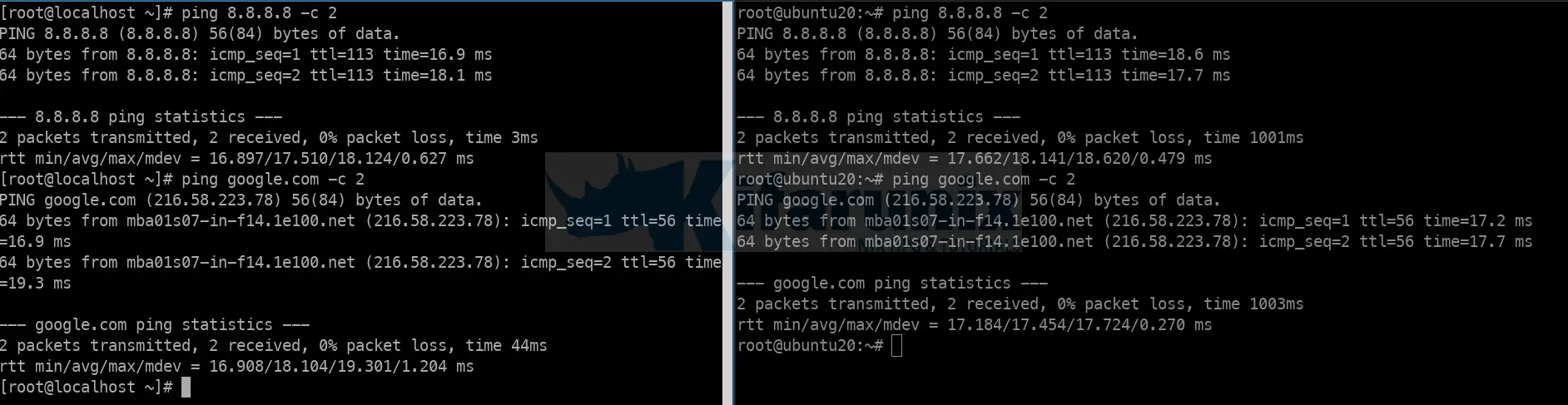
iptables-save > /etc/iptables/rules.v4Your LAN systems should be now be able to connect to internet via the Linux router;
And there you go. You vms can now route traffic through your Linux router.
That concludes our guide on how to configure Ubuntu 20.04 as Linux Router.
Other Tutorials
SUPPORT US VIA A VIRTUAL CUP OF COFFEE
We’re passionate about sharing our knowledge and experiences with you through our blog. If you appreciate our efforts, consider buying us a virtual coffee. Your support keeps us motivated and enables us to continually improve, ensuring that we can provide you with the best content possible. Thank you for being a coffee-fueled champion of our work!
How to build Linux Router with Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS
Linux router configuration is simple, you just need to make sure the router have two interfaces that connected to the network that will be routed, enable packet forwarding and iptables for NAT if needed. There are more advanced configuration, but in this post we will build Linux router on Ubuntu Server 20.04 to allow LAN traffic through to internet on WAN interface with NAT.
How to build Linux Router with Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS
Ubuntu Server 20.04 comes with netplan as default network interface configuration tool.If you are not familiar with netplan please read the previous post about Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS — Basic Network Configuration with netplan.
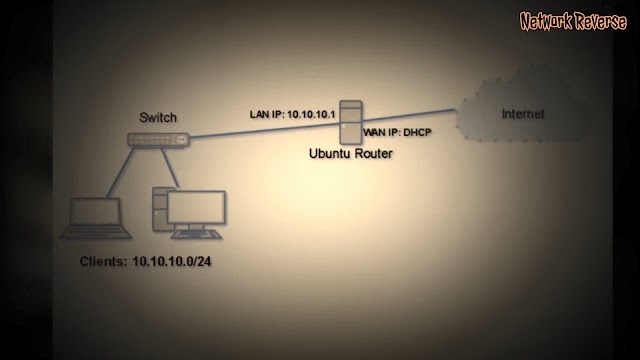
- enp0s3 is the WAN interface, it will be configured to obtain IP address from DHCP server.
- enp0s8 is the LAN interface, it will be configured to use 10.10.10.1/24 IP address.
nano /etc/netplan/anything.yaml
This configuration below addedd interface enp0s3 to obtain dhcp and enp0s8 to use 10.10.10.1/24 IP address. Just add lines that red colored to your configuration file, if it is a newly installed Ubuntu Server.
network: version: 2 renderer: networkd ethernets: enpos3: dhcp4: yes enp0s8 addresses: - 10.10.10.1/24 iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -j MASQUERADE
iptables command line will not be saved after the system reboot, there are many ways to make it persistent after reboot. This time we will use the easiest way to install iptables-persistent package to the Ubuntu server.
apt update -y && apt install iptables-persistent
It will asks you to save the current ipv4 and ipv6 iptables rules, answer yes to save it or no to save it later.
iptables-save > /etc/iptables/rules.v4 This command will save the iptables rules to /etc/iptables/rules.v4 , where later it will be restored by iptables-persistent on every reboot.
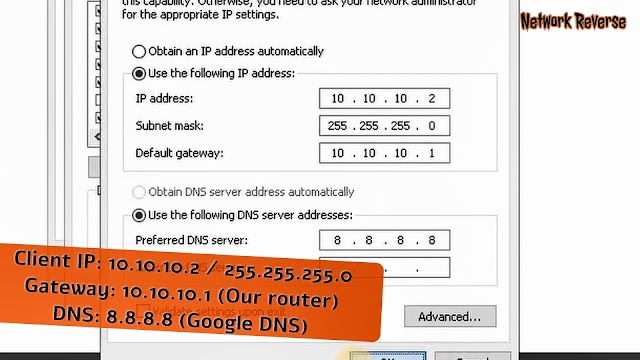
If all going well, we have finished building Linux Router with Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS. According to the topology, the clients use 10.10.10.0/24 network address. So configure the clients accordingly.
You can watch all the activity above on building Linux Router with Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS from this youtube video below. If you still have any problems, please put your comments.