- CentOS: How to Set Date, Time, TimeZone and NTP Synchronization
- Hwclock: Hardware Time Configuration
- Manual Time Configuration in CentOS
- How to Set TimeZone in CentOS?
- Configure CentOS to Sync Time with NTP Time Servers
- How to Sync Time in CentOS 8 using Chronyd?
- Common Time Syn Issues in CentOS
- Установка и настройка NTP-сервера на Linux CentOS 8
- Установка сервера
- Настройка NTP
- Тестирование
- Настройка клиента Linux
- Chrony
- Настройка даты и времени в CentOS
- Узнать текущее системное время
- Узнать текущее время BIOS
- Исправить текущее время
- Синхронизация с ntp
- Заставить систему синхронизовать время с ntp
- Timezone
CentOS: How to Set Date, Time, TimeZone and NTP Synchronization
In this article, we’ll show you how to set time, date, timezone, synchronize time with an NTP server and fix typical issues in CentOS Linux.
There are two types of clocks on the servers: hardware one (real-time clock) that are working even if a server is off and the operating system software clock. The time on these clocks may differ. After starting the operating system, the software clock is based on a hardware one and may be adjusted by the OS.
Most applications use software clock time in their operation.
Hwclock: Hardware Time Configuration
Hwclock is used to check the hardware time in Linux:
- hwclock —localtime — check hardware time without correction
- hwclock —utc – displays time if the hardware clock shows UTC time
2020-10-12 06:12:02.912866-04:00
2020-10-12 02:12:18.915319-04:00
To set hardware time according to the system time, run this command:
# hwclock —systohc
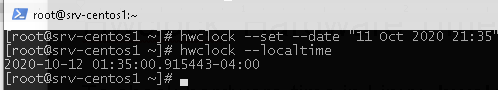
To set the hardware time you want, run the following:
# hwclock —set —date «11 Oct 2020 17:30»
Manual Time Configuration in CentOS
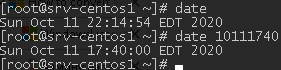
In Linux, date or timedatectl tools are used to check and set software time. If you call date without any parameters, it will show the current time on your server:
Sun Oct 11 22:14:54 EDT 2020
If you want to set time manually, you can use date with additional parameters:
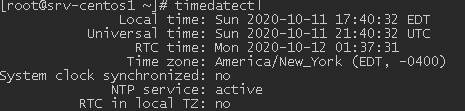
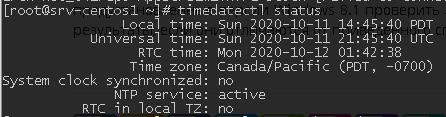
To get extended information about the date, time, timezone, synchronization settings, day-light saving time settings (DST), timedatectl is used. It gives more detailed information about time settings on a server.
Timedatectl also allows to change time:
# timedatectl set-time ‘2020-10-11 17:51:00’
How to Set TimeZone in CentOS?
To set the time according to your timezone on a CentOS Linux, you can change it manually. To do it, you can use two tools:
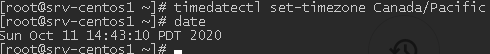
To change a time zone using timedatectl, run this command:
# timedatectl set-timezone Canada/Pacific
# date
Or you can use tzdata. To use this method, replace the file /etc/localtime with the one you need. The entire list of time zones is located in /usr/share/zoneinfo/ directory. Let’s change a timezone to Canada/Pacific. Back up the current locatime file:
# mv /etc/localtime /etc/localtime.bak
Create a symlink to the timezone you want to set:
# ln -s /usr/share/zoneinfo/Canada/Pacific /etc/localtime
Configure CentOS to Sync Time with NTP Time Servers
You can configure automatic time synchronization on your host with an external NTP (Network Time Protocol) server. To do it, you must install the ntp service. For example, you can install it using yum in CentOS 7:
After the installation, start the ntpd service and add it to startup:
# systemctl start ntpd.service
# systemctl enable ntpd.service
Make sure that the service is running:
Redirecting to /bin/systemctl status ntpd.service ● ntpd.service - Network Time Service Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/ntpd.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled) Active: active (running) since Thu 2020-10-11 15:37:33 +06; 5min ago Main PID: 3057 (ntpd) CGroup: /system.slice/ntpd.service └─3057 /usr/sbin/ntpd -u ntp:ntp -g
Specify the NTP servers to synchronize time with in /etc/ntp.conf:
server 0.pool.ntp.org server 1.pool.ntp.org server 2.pool.ntp.org
Time is synchronized in turn. If the first NTP server is not available, the second one is used, etc.
You can synchronize time with the specified NTP server manually using this command:
By default, ntpd enables “11 minute mode”. It means that time will be synchronized every 11 minutes. If you cannot use the ntpd daemon, you can configure time synchronization using cron. Add the following command to cron:
How to Sync Time in CentOS 8 using Chronyd?
In CentOS 8 you will have to use chrony to synchronize time, since ntp and ntpdate have been removed from the official repositories.
The main benefits of chrony are:
- High speed and accuracy of time synchronization;
- Proper operation if you don’t have access to master clock (ntpd requires regular requests);
- By default, time is not modified right after the synchronization to prevent any problems for running programs;
- Uses less resources.
By default, chrony is already installed in CentOS Linux, but if you don’t have it on some reason, install it:
Like any other service, chrony needs to be started and added to startup after installation:
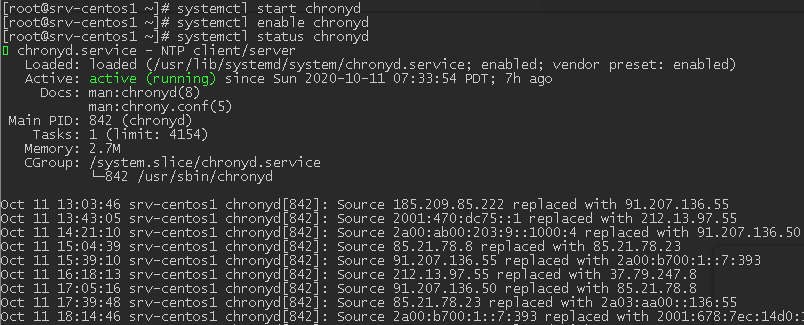
# systemctl start chronyd
# systemctl enable chronyd
Check the chronyd service status:
To make sure that the time synchronization is working, run this command:
Chrony configuration file is /etc/chrony.conf. Specify the list of NTP servers you want to use for synchronization. Like ntp, chrony has a command-line interface: chronyc. To view the information about the current time synchronization options, run this command:
To view the information about sync servers:
If you want to set the specific date and time manually, you can use date, but previously disable the chronyd daemon.
Common Time Syn Issues in CentOS
In this section, I will describe typical errors that appear when working with timedatectl, ntp.
During the manual time synchronization you may come across this error:
ntpdate [26214]: the NTP socket is in use, exiting
This means that the ntpd daemon is running and is preventing manual time synchronization. To manually synchronize the time, stop the ntpd daemon:
And run the synchronization again.
The same error may occur when working with timedatectl:
Failed to set time: Automatic time synchronization is enabled.
You must disable automatic sync in timedatectl:
And run this command to set the time and date you want:
# timedatectl set-time ‘2020-11-12 17:41:00’
When working with time zones, it may occur that they are not installed on your server and you are not able to create a symlink for localtime. To make time zones available on your host, install the tzdata tool:
Also, you may face some errors during manual synchronization like the following one:
11 Oct 21:11:19 ntpdate[897482]: sendto(xx.xx.xx.98): Operation not permitted
In this case, check your firewalld/iptables rules and make sure that the UDP Port 123 is open on your server. Also, some NTP hosts may not be available during validation.
Установка и настройка NTP-сервера на Linux CentOS 8
Опубликовано: 17.12.2020
Тематические термины: NTP, CentOS. Сервер синхронизации времени NTP помогает актуализировать время на всех узлах сети. В инструкции рассказано о его установке и настройке на Linux CentOS 8.
Установка сервера
В CentOS 8 пакетом для синхронизации времени является chrony — он пришел на смену ntpd. Устанавливаем его командой:
Настройка NTP
#pool 2.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
server 192.168.0.100 iburst prefer
server 192.168.0.110 iburst
server 127.127.1.0
- pool — указывает на выполнение синхронизации с пулом серверов.
- server — указывает на выполнение синхронизации с сервером.
- iburst — отправлять несколько пакетов (повышает точность).
- prefer — указывает на предпочитаемый сервер.
- server 127.127.1.0 — позволит в случае отказа сети Интернет брать время из своих системных часов.
* в данном примере мы закомментировали указанный пул по умолчанию и добавили свои серверы 192.168.0.100 и 192.168.0.110.
* в данном примере мы разрешаем синхронизацию времени с нашим сервером для узлов сети 192.168.0.0/255.255.255.0.
systemctl restart chronyd
Добавляем правило в брандмауэр:
firewall-cmd —permanent —add-service=ntp
Тестирование
Проверить состояние получения эталонного времени можно командой:
Мы должны увидеть, примерно, следующее:
210 Number of sources = 2
MS Name/IP address Stratum Poll Reach LastRx Last sample
===============================================================================
^? 127.127.1.0 0 6 0 — +0ns[ +0ns] +/- 0ns
^* server-01.dmosk.local 2 6 17 55 +629us[+1184us] +/- 152ms
Отобразить текущее время можно командой:
Для настройки часового пояса применяем команду:
timedatectl set-timezone Europe/Moscow
Проверить отдачу времени сервером можно введя команду на другом Linux:
* где 192.168.0.15 — адрес нашего NTP-сервера.
Правильный ответ имеет следующий вид:
ntpdate[3576]: adjust time server 192.168.0.15 offset 0.017657 sec
* время было рассинхронизировано на 0.017657 секунд.
Настройка клиента Linux
Для клиентов можно выбрать несколько стратегий настройки — мы рассмотрим 3:
Chrony
Команда для установки зависит от типа дистрибутива Linux.
После установки открываем /etc/chrony.conf:
. и в качестве сервера оставляем только наш локальный сервер, например:
server 192.168.156.215 iburst
Разрешаем автозапуск сервиса:
systemctl enable chronyd || systemctl enable chrony
systemctl restart chronyd || systemctl restart chrony
Проверить состояние работы можно командой:
Настройка даты и времени в CentOS
При работе в сети синхронизация времени и даты это важный фактор увеличивающий стабильность и безопасность работы всех систем.
В этой статье вы узнаете как настраивать дату и время вручную. И, что более важно — как синхронизировать их с ntp сервером.
Это статьи про дату и время в CentOS 7.
Про дату и вермя в Rocky Linux и CentOS 8 читайте здесь
Узнать текущее системное время
Узнать текущее системное время можно командой date
Узнать текущее время BIOS
Узнать текущее системное время BIOS можно командой hwclock
date и hwclock могут показывать совершенно разное время
Исправить текущее время
Сначала нужно задать время командой date
Также можно вводить «date MMDDhhmmCCYY» без секунд, тогда секунды выставляются на ноль.
После выполнения date нужно внести новое установленное время в BIOS:
Теперь осталось только проверить сохранились ли изменения
Синхронизация с ntp
Проверьте установлен ли ntp командой
Если ntp не установлен выполните
Проверьте запускается ли ntpd автоматически командой
systemctl list-unit-files | grep ntpd.s
Если ntpd неактивен (disabled) выполните
systemctl start ntpd
systemctl enable ntpd
Проверить добавлен ли сервис ntp в зону public в firewall можно командой
sudo firewall-cmd —get-services | grep ntp
Если ещё не добавлен, то чтобы разрешить UDP траффик от ntp выполните
firewall-cmd —permanent —add-service=ntp
firewall-cmd —reload
Отредактируйте файл ntp.conf с настройками сервера
Найдите свою временную зону на сайте www.ntppool.org
Я нашёл зону Helsinki и добавляю строки
server 0.fi.pool.ntp.org server 1.fi.pool.ntp.org server 2.fi.pool.ntp.org server 3.fi.pool.ntp.org
Теперь нужно перезапустить ntpd
Проверить откуда берётся время можно командой
remote refid st t when poll reach delay offset jitter ============================================================================== time.cloudflare 10.79.8.177 3 u 14 64 7 3.987 -0.366 0.016 37.228.129.2 193.66.253.94 2 u 16 64 7 5.301 -1.639 1.908 ivanova.ganneff 237.17.204.95 2 u 13 64 7 5.296 3.850 0.266 ntp23.kashra-se 192.168.100.15 2 u 12 64 5 32.935 -2.213 0.192
Выставить время BIOS по только что полученному времени можно командой
Заставить систему синхронизовать время с ntp
Вместо 0.fi.pool.ntp.org поставьте нужный вам сервер
Timezone
Узнать текущую временную зону
Local time: Fri 2023-07-13 20:37:29 MDT Universal time: Fri 2023-07-13 17:37:29 UTC RTC time: Fri 2021-05-21 07:42:43 Time zone: America/Denver (MDT, -0600) NTP enabled: yes NTP synchronized: yes RTC in local TZ: no DST active: yes Last DST change: DST began at Sun 2021-03-14 01:59:59 MST Sun 2021-03-14 03:00:00 MDT Next DST change: DST ends (the clock jumps one hour backwards) at Sun 2021-11-07 01:59:59 MDT Sun 2021-11-07 01:00:00 MST
Изменить временную зону можно командой set-timezone
timedatectl set-timezone «Europe/Helsinki»
timedatectl | grep «Time zone»
Time zone: Europe/Helsinki (EEST, +0300)