Лучшие сетевые утилиты Linux
Очень часто на серверах или обычных компьютерах с операционной системой Linux приходится настраивать сеть. Пользователям домашнего компьютера вряд ли понадобятся все эти утилиты. Но вот для администраторов серверов или даже сетей, это вещь незаменимая. Особенно когда нужно понять почему не работает сеть или выяснить на каком сетевом узле прерывается передача пакетов.
В этой статье мы рассмотрим полезные сетевые утилиты Linux, это самые основные команды, которые можно использовать для администрирования сети в Linux. Эта статья не научит вас всем тонкостями использования таких команд, это всего лишь небольшой список с кратким описанием.
Лучшие сетевые утилиты Linux
ping хост — позволяет отправить ICMP запрос на удалённый хост. Пакеты будут отправляется непрерывно, пока вы не нажмете Ctrl+C. Когда пакет будет отправлен, хост должен отправить ответное ICMP сообщение, это и будет означать, что другой хост работает. Подробнее про ping читайте тут.
telnet хост порт — позволяет проверить доступность определенного порта на хосте. По умолчанию telnet использует порт 23, но также можно использовать и другие. Нажмите Ctrl+] чтобы завершить работу telnet. Подробнее читайте в статье команда telnet linux.
arp — протокол ARP используется для преобразования IP адресов интернет в физические адреса используемой сети. Эта команда, если передать ей опцию -a позволяет вывести таблицу маршрутизации на вашем устройстве. С помощью опции -d можно удалить все записи. Так или иначе все записи удаляются по истечении 20 минут после добавления.
route — с помощью маршрутизации операционная система определяет к какому узлу надо передать тот или иной пакет. Без параметров эта утилита выводит текущую таблицу маршрутизации. Параметр flush позволяет удалить все маршруты, а add добавить новый маршрут. Подробнее читайте тут.
traceroute ip_адрес — очень полезная утилита, для отслеживания маршрута пакетов. Чаще всего с помощью этой команды выполняется проверка сети linux. Пакет отправляет сообщение на компьютер-отправитель со всех шлюзов между источником и пунктом назначения. Подробнее в статье Команда traceroute.
nslookup домен — отправить запрос DNS серверу, на преобразование доменного имени в IP. Например, nslookup ya.ru вернет IP адрес сервера ya.ru. Подробнее тут.
ip — популярная современная утилита для просмотра сетевых подключений в системе Linux. Позволяет посмотреть сетевые интерфейсы, IP адреса, маску сети, таблицу маршрутизации и многое другое. Подробнее в статье Команда ip в Linux.
iw — позволяет управлять беспроводными интерфейсами, просматривать список подключённых или доступных беспроводных сетей.
ifconfig интерфейс — устаревший аналог утилиты ip. Позволяет посмотреть информацию о сетевых подключениях, IP адрес, маску сети и другие параметры. Без параметров выводит список всех интерфейсов в системе, в параметрах можно передать конкретный интерфейс, по которому надо получить данные. Кроме того, можно поднимать или отключать сетевые интерфейсы. Подробнее тут.
tcpdump — консольный сетевой анализатор, позволяющий посмотреть трафик, проходящий через сетевой интерфейс. Можно анализировать содержимое сетевых пакетов и их тип. Подробнее читайте здесь.
ethtool — позволяет смотреть и изменять параметры сетевой карты.
ss — позволяет вывести все открытые локальные сокеты и проанализировать какие программы их используют. Можно отдельно выводить UDP, TCP и Unix сокеты, а также смотреть к каким удалённым сокетам подключены программы компьютера. Подробнее тут.
netstat — устаревший аналог ss, вместо подсистемы ядра здесь используется файловая система proc, а также данные выводятся немного в другом формате.
nc — утилита позволяет создавать новые сетевые сокеты и подключаться к существующим по сети. Это может понадобиться для тестирования работы сети или приложений. Подробнее тут.
iperf — программа позволяет проверить скорость и стабильность сетевого подключения.
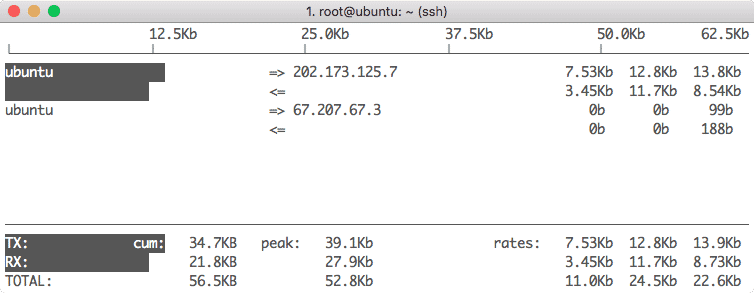
iptraf — позволяет смотреть статистику о сетевых подключениях в реальном времени. С помощью этой утилиты вы можете оценить с какой скоростью передаются данные на ваших сетевых интерфейсах.
Выводы
В этой статье мы рассмотрели самые полезные сетевые утилиты Linux, с помощью них вы можете выполнять тестирование сети, проверить сеть на работоспособность и обнаружить неполадки. Более подробную информацию по каждой из них вы можете найти в официальной документации или в отдельных статьях на сайте.
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
Top 10 Ubuntu Network Tools
Ubuntu is the most popular choice for underlying Operating System due to its ease of use and powerful shell system. Due to more and more network access needed in most of the distributed applications today, the restrictions which need to be applied for network access and monitoring has only increased. In this lesson, we will study the ten most popular Network Tools for Ubuntu OS which can be used to monitor network usage with visualization as well.
Top 10 Ubuntu Network Tools
1. Iftop
This is one of the easiest tools to use for network usage and DNS operations. When it is started on Ubuntu, we get a simple screen like:
We can press “h” and we will be shown help screen for more features:
It is very similar to top utility but specialises in network monitoring and knowing which process is using the network at what IP and what bandwidth are they consuming.
2. Vnstat
Vnstat is another network monitoring utility which is usually included in most of the Linux distributions or can be installed very easily. Like the last utility, it allows us to control the network packets sent and received in a given interval of time which is chosen by the user itself. With vnstat help screen, we can see the following features:
$ vnstat —help
vnStat 1.18 by Teemu Toivola
-q, —query query database
-h, —hours show hours
-d, —days show days
-m, —months show months
-w, —weeks show weeks
-t, —top10 show top10
-s, —short use short output
-u, —update update database
-i, —iface select interface ( default: eth0 )
-?, —help short help
-v, —version show version
-tr, —traffic calculate traffic
-ru, —rateunit swap configured rate unit
-l, —live show transfer rate in real time
See also «—longhelp» for complete options list and «man vnstat» .
As it doesn’t have a fancy GUI, we are showing the console output here:
$ vnstat
Database updated: Mon Sep 10 09: 52 :01 2018
rx: 3.32 TiB tx: 2.81 TiB total: 6.13 TiB
monthly
rx | tx | total | avg. rate
————————+————-+————-+—————
Aug ’18 609.40 GiB | 282.21 GiB | 891.61 GiB | 2.79 Mbit/s
Sep ‘ 18 16.95 GiB | 10.46 GiB | 27.40 GiB | 2.80 Mbit / s
————————+————-+————-+—————
estimated 552.14 GiB | 340.70 GiB | 892.83 GiB |
daily
rx | tx | total | avg. rate
————————+————-+————-+—————
yesterday 19.19 GiB | 8.63 GiB | 27.82 GiB | 2.70 Mbit / s
today 16.95 GiB | 10.46 GiB | 27.40 GiB | 2.80 Mbit / s
————————+————-+————-+—————
estimated 17.81 GiB | 10.99 GiB | 28.80 GiB |
Clearly, it also provides an estimate of the data which will be used at a same rate for the month.
3. Iptraf
Iptraf is another great console-based network monitoring tool for Ubuntu or Linux in general which collects a huge amount of data in terms of IPs which passes through the network with a deep dive in detail like their ICMP flags, TCP faults and byte count. Even a basic interface for the same will look like:
Apart from the packet tracking byte count, we have many more features like:
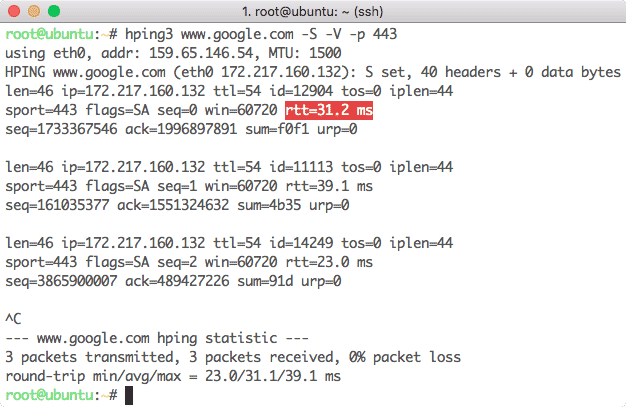
4. Hping3
Hping3 is a command line utility which is similar to Ping command with a small addition that it can use TCP, UDP, and RAW-IP as transport protocols. The main feature is that it doesn’t only check if a Port or an IP is open but it also measures the round trip time the packet took to come back. For instance, if we need to check if www.google.com has an open port 443 and calculate the round-trip time, we can use the following command:
Here is what we get back with this command:
5. Dstat
Dstat is comparatively a less known network monitoring tool in Linux family. Dstat allows us to display all of our system resources in near real-time, we can eg. compare disk utilization in combination with interrupts from our IDE controller, or compare the network bandwidth numbers directly with the disk throughput (in the same interval).
Find more information here for this tool.
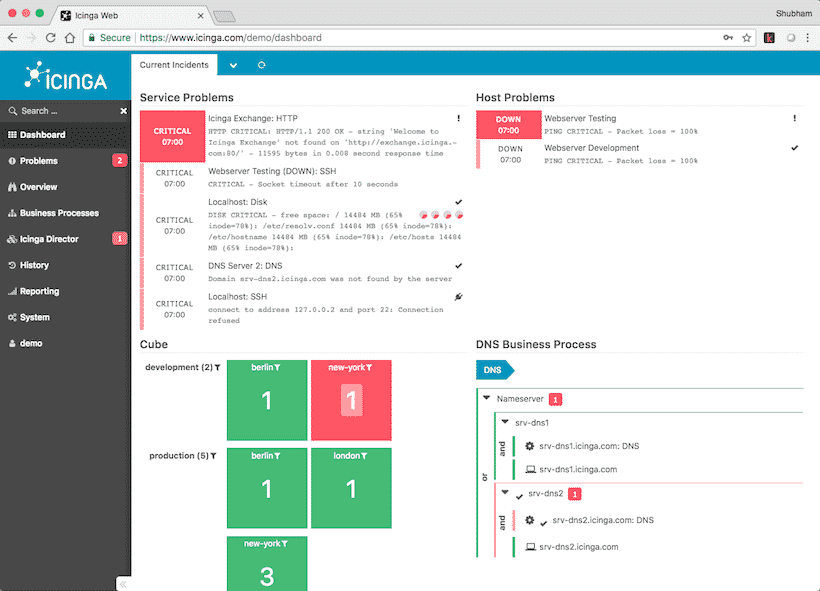
6. Icinga
Icinga is an enterprise-grade tool for network monitoring which also takes care of any suspicious activity on the server and informs configured users like admin about such activities. It has a very nice interactive dashboard which looks like:
It is even possible to try a demo dashboard for this tool. Visit this page for more information.
7. slurm
slurm is a smart and simple network load monitoring tool. It has the following features:
- It provides real-time traffic statistics
- It has three graph modes: combined RX and TX and two split views
- It can monitor any network device
- It curses ASCII graphics
- It has an ASCII theme support
It is an open-source networking tool (look here for the source code). It has a basic interface like:
8. bmon
bmon, which stands for Bandwidth Monitor, is another network monitoring tool with a speciality that it can monitor multiple interface traffic. It also provides information about packets, errors and much more data critical for monitoring. Once installed, here is the list of features it provides for monitoring:
When we start it with a network interface, we will see a simple interface like:
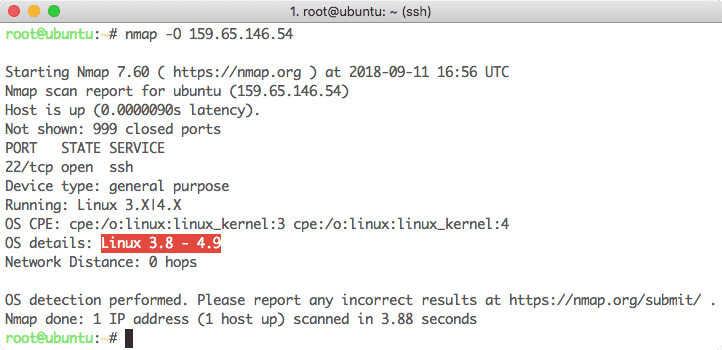
9. Nmap
Nmap is one of the most popular network scanners for common use. The information it can provide includes (but not limited to):
- It can tell what’s running on a given network hosts
- Scan and identify open TCP Ports
- Which OS is running on given IP
- Ping sweeps on an IP subnet
We can -O option for OS detection. Let’s look at an example command we used:
10. Tcpdump
Tcpdump is an excellent tool which goes beyond its scope to provide features like sniffing as well. It can analyze data which is going out of the host and also the data which is arriving on the host. It is possible to intercept the traffic between two hosts with this tool as well (of course you need to have access to those hosts). We first try a command to see what data is going out of our host:
Next, we can also try to sniff traffic going out of a particular port:
Conclusion
In this lesson, we looked at some most popular networking tools in the Ubuntu ecosystem. Even though we might have missed some good tools, please mention them to my Twitter handle which you think should have made the cut @sbmaggarwal or @linuxhint.
About the author
Shubham Aggarwal
I’m a Java EE Engineer with about 4 years of experience in building quality products. I have excellent problem-solving skills in Spring Boot, Hibernate ORM, AWS, Git, Python and I am an emerging Data Scientist.