- Get network interface information
- 3 Answers 3
- List network interfaces on Linux
- Show network interfaces
- Linux
- The old way: ifconfig
- Modern version: using the ip command
- Show the default gateway
- AIX and Solaris
- Frequently Asked Questions
- How can I see the MTU of an interface?
- What command can I use to display the default gateway on Linux?
- How can I test if my network configuration is correct?
- Список сетевых интерфейсов Linux
- Список сетевых интерфейсов Linux
- 1. Файловая система
- 2. Утилита ifconfig
- 3. Утилита ip
- 4. Утилита nmcli
- 5. Утилита netstat
- 6. Файл /proc/net/dev
- Выводы
Get network interface information
I tried ifconfig and grep command but can’t get right pattern. There is another command or some trick to do this?
3 Answers 3
Python is good 😀 but let see in bash:
Interfaces=`ifconfig -a \ | grep -o -e "[a-z][a-z]*8*[ ]*Link" \ | perl -pe "s|^([a-z]*1*)[ ]*Link|\1|"` for Interface in $Interfaces; do INET=`ifconfig $Interface | grep -o -e "inet addr:[^ ]*" | grep -o -e "[^:]*$"` MASK=`ifconfig $Interface | grep -o -e "Mask:[^ ]*" | grep -o -e "[^:]*$"` STATUS="up" if [ "$INET" == "" ]; then INET="-" MASK="-" STATUS="down"; fi printf "%-10s %-15s %-16s %-4s\n" "$Interface" "$INET" "$MASK" "$STATUS" done It is quite straightforward.
This is done on an assumption that ‘ ifconfig interface does not show an internet address’ to means that the interface is down.
ifconfig has two output modes — the default one in which it gives a LOT more output, and the short -s one in which it gives less (or, rather, picks different bits of info from what you’d like). So what about taking ifconfig in the default mode and cherry-picking the specific info you want in a script (python, perl, ruby, awk, bash+sed+. whatever floats your boat;-). E.g., w/Python:
import re import subprocess ifc = subprocess.Popen('ifconfig', stdout=subprocess.PIPE) res = [] for x in ifc.stdout: if not x.strip(): print ' '.join(res) del res[:] elif not res: res.append(re.match(r'\w+', x).group()) else: mo = re.match(r'\s+inet addr:(\S+).*Mask:(\S+)', x) if mo: res.extend(mo.groups()) elif re.match(r'\sUP\s', x): res.append('up') elif re.match(r'\sDOWN\s', x): res.append('down') if res: print ' '.join(res) and the output should be as you desire it (easy to translate in any of the other languages I mentioned, I hope).
List network interfaces on Linux
The network configuration is a common place to start during system configuration, security audits, and troubleshooting. It can reveal useful information like MAC and IP addresses. This guide helps you to gather this information on Linux, including listing all available network interfaces and its details.
Show network interfaces
Linux
Every Linux distribution is using its own way of configuring the network configuration details. Therefore, it is good to know which tools can be used to query these details in a generic way. So these commands should be working on the popular distributions like Arch Linux, CentOS, Debian, Gentoo, RHEL, and Ubuntu.
The old way: ifconfig
Previously the most obvious command to obtain the available network interfaces was using the ifconfig command. As some systems no longer have that command installed by default, we will also look at using alternative ip. If you still have ifconfig available, run it with the -a parameter.
Depending on what particular information you need, you can use grep to get you the right lines. The ifconfig command on Linux actually has the most option available, so have a look at the man page for all details.
Modern version: using the ip command
Newer Linux distributions now ship only the ip command. It is advised to start using this command instead of ifconfig, as its output works better with newer machines. Especially when using containerized applications, dynamic routing, and network aliases.
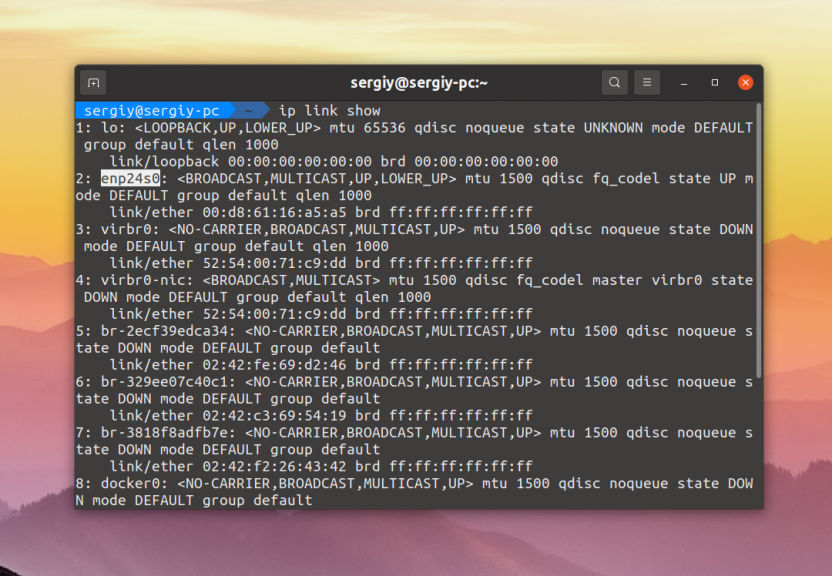
The easiest way to see what network interfaces are available is by showing the available links.
Linux network interfaces with ip link show command
Another option to show available network interfaces is by using netstat.
Note: the column command is optional, but provides a friendlier output for the eye.
Show the default gateway
The default gateway is the system that receives traffic for networks outside your own. On Linux systems, this gateway is typically received via DHCP or manually configured in a text configuration file.
Using the ip command
The output may look like this:
default via 123.12.0.1 dev eth0 onlink 10.17.0.0/16 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 10.17.0.3 123.12.0.0/18 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 123.123.0.3
With netstat
The default gateway can be listed with the netstat command.
The output will be something like this:
Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags MSS Window irtt Iface default 123.12.0.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0 10.17.0.0 * 255.255.0.0 U 0 0 0 eth0 123.12.0.0 * 255.255.192.0 U 0 0 0 eth0
The second column shows the gateway. When it lists an asterisk (*), it means it uses the default gateway.
AIX and Solaris
These two old style platforms have of course ifconfig still available. By using the -a parameter, all interfaces will be displayed.
ifconfig -a | grep «flags ez-toc-section» > DragonBSD, FreeBSD, NetBSD
On the systems running BSD, it is also the ifconfig tool that can be used.
ifconfig -l
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I see the MTU of an interface?
Use the ip show link command.
What command can I use to display the default gateway on Linux?
Use the ip route command to show routing information, including the default gateway and the network interface it uses.
How can I test if my network configuration is correct?
Test if you can reach or access both devices on your network as outside of it. This way you know that your IP address and gateway is correctly set up. If you can only access remote systems by IP address, then check your name server configuration, typically stored in /etc/resolv.conf. Another useful tool to test your system, including your network configuration, is by using auditing tool Lynis. It will test for connectivity of the name servers and retrieves the most important parts of the network settings.
Did this article help you? Become part of the community and share it on your favorite website or social media. Do you have additional tips regarding the network configuration on Linux? Share it in the comments!
One more thing.
Keep learning
So you are interested in Linux security? Join the Linux Security Expert training program, a practical and lab-based training ground. For those who want to become (or stay) a Linux security expert.
Security scanning with Lynis and Lynis Enterprise
Run automated security scans and increase your defenses. Lynis is an open source security tool to perform in-depth audits. It helps with system hardening, vulnerability discovery, and compliance.
Список сетевых интерфейсов Linux
В операционной системе Linux не только жесткие и SSD диски представлены файлами в специальной файловой системе, но и сетевые интерфейсы. Существует несколько способов посмотреть список сетевых интерфейсов Linux, но самый простой из них — это просто посмотреть содержимое папки в файловой системе.
В этой небольшой статье мы рассмотрим все основные способы выполнить эту задачу в терминале или графическом интерфейсе.
Список сетевых интерфейсов Linux
Сетевые интерфейсы проводного интернета Ethernet обычно имеют имя, начинающиеся с символов enp, например, enp3s0. Такое именование используется только если ваш дистрибутив использует systemd, иначе будет применена старая система именования, при которой имена начинаются с символов eth, например eth0. Беспроводные сетевые интерфейсы, обычно называются wlp или wlx при использовании systemd, например, wlp3s0. Без использования systemd имя беспроводного интерфейса будет начинаться с wlan, например wlan0. Все остальные интерфейсы обычно виртуальные. Один из самых основных виртуальных интерфейсов — lo. Это локальный интерфейс, который позволяет программам обращаться к этому компьютеру. А теперь рассмотрим несколько способов посмотреть их список.
1. Файловая система
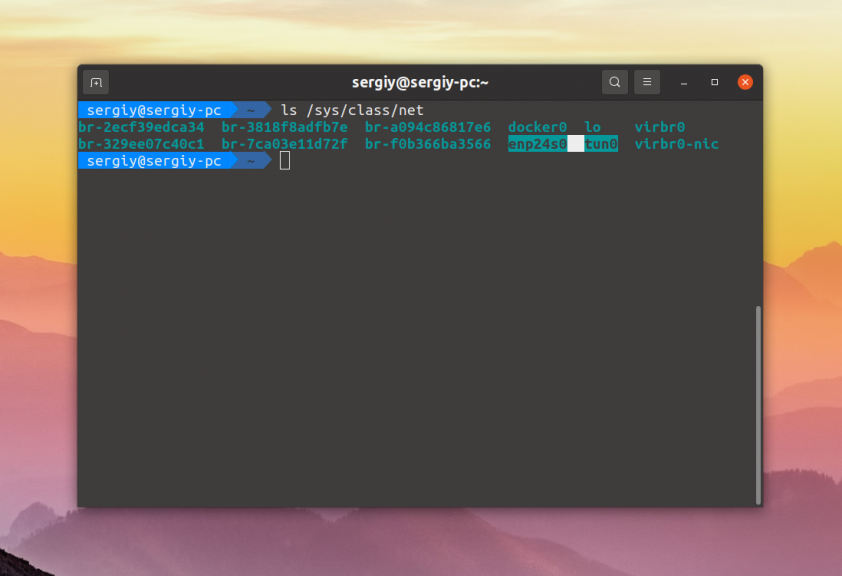
Все файлы устройств сетевых интерфейсов находятся в папке /sys/class/net. Поэтому вы можете посмотреть её содержимое:
2. Утилита ifconfig
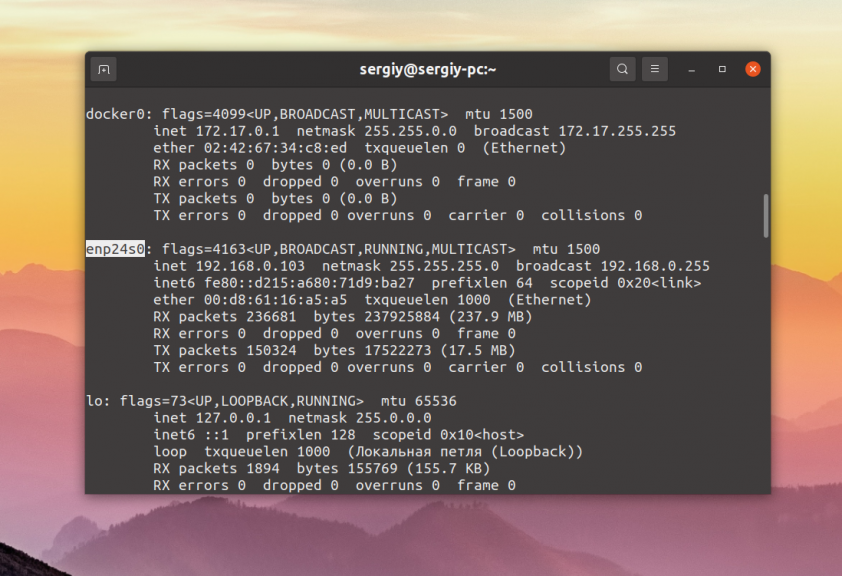
Утилита ifconfig выводит не только список сетевых интерфейсов, но и информацию о них, такую как состояние, IP адрес, MAC адрес и другие параметры. Для отображения всех интерфейсов достаточно выполнить программу без параметров:
3. Утилита ip
Программа ifconfig устарела и ей на смену пришла утилита ip. Она объединяет в себе функции нескольких программ, например ifconfig, route, brctl и других. Посмотреть список устройств с помощью ip можно выполнив команду:
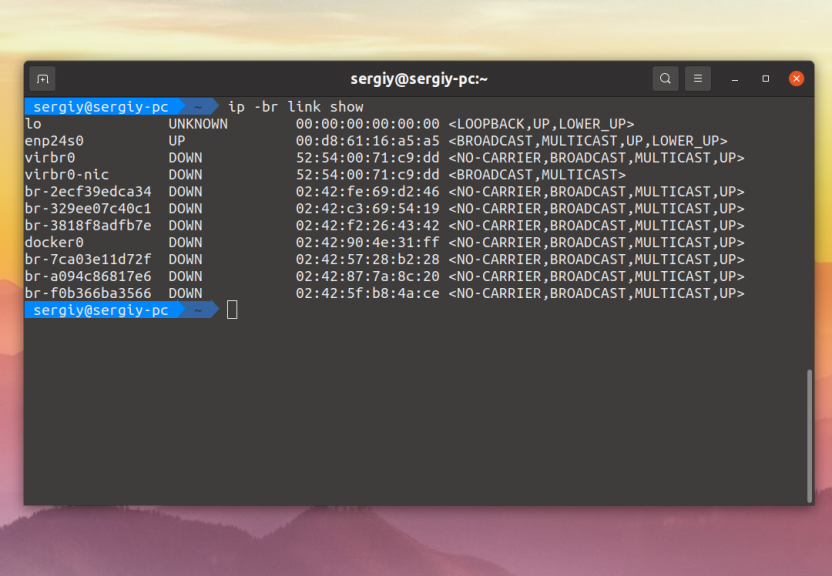
Здесь информации намного меньше, показывается только состояние устройства, MTU и ещё несколько параметров. Можно вывести информацию в более компактном виде, использовав опцию -br:
В таком случае все данные отображаются в одну строчку, выводится состояние, MAC адрес и ещё несколько опций.
4. Утилита nmcli
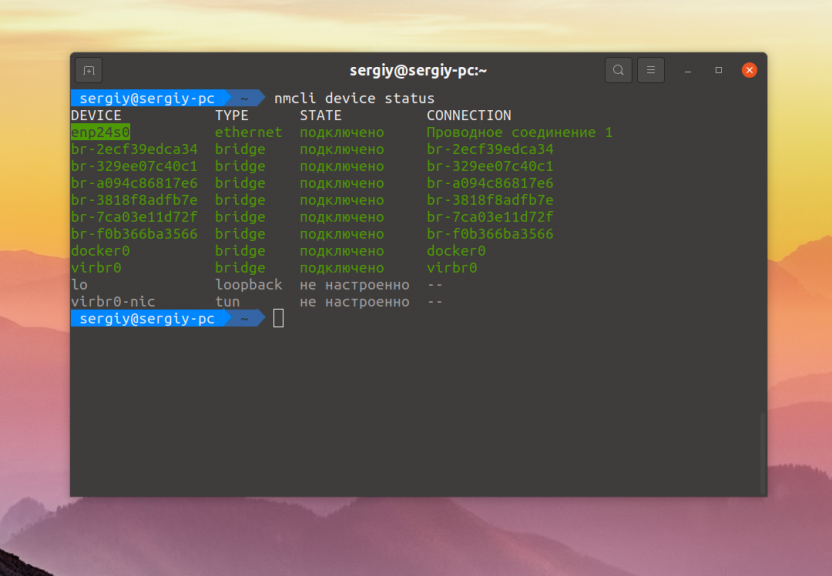
Посмотреть всю нужную информацию можно и с помощью консольной утилиты управлением брандмауэром — nmcli:
Здесь выводится подключение NetworkManager, связанное с конкретным устройством, а также его состояние.
5. Утилита netstat
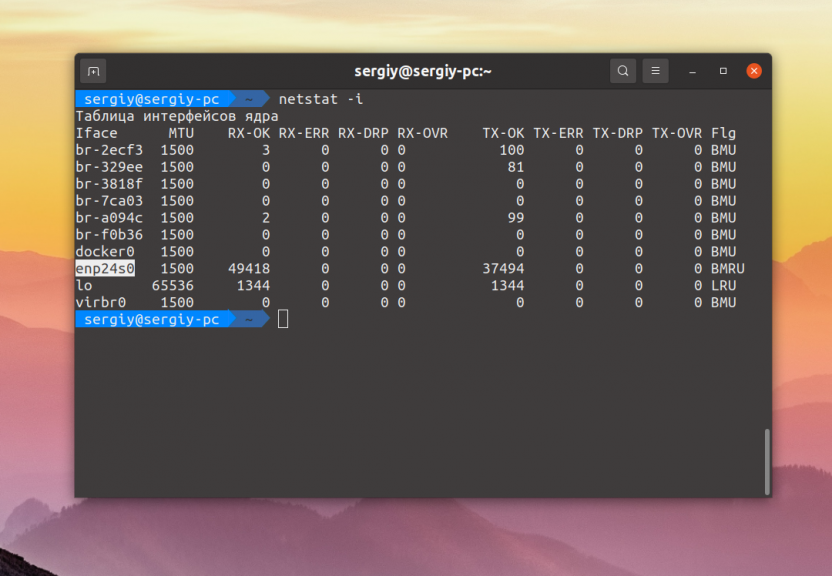
Программа netstat тоже умеет показывать сетевые интерфейсы и статистику по переданным данным если ей передать опцию -i:
6. Файл /proc/net/dev
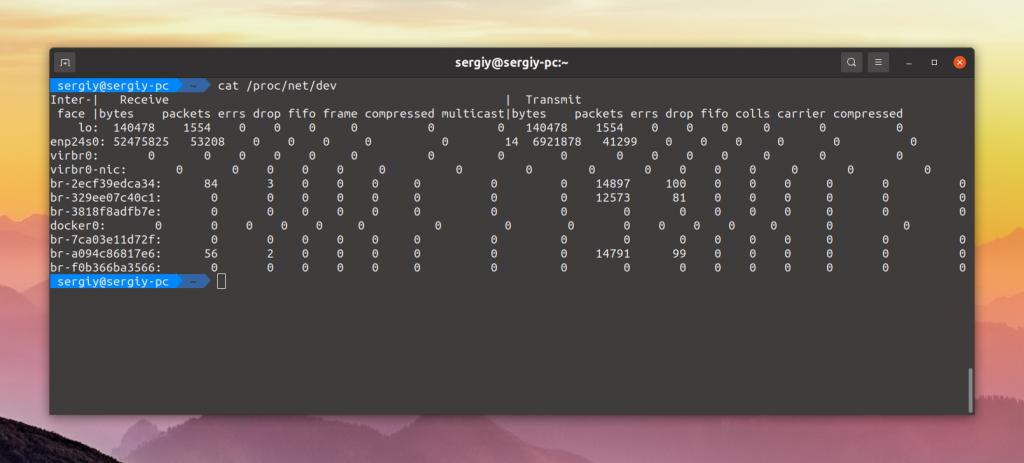
В файле /proc/net/dev тоже содержится список всех сетевых интерфейсов, а также статистика их использования:
Выводы
Теперь вы знаете как посмотреть сетевые интерфейсы в Linux, как видите, это очень просто сделать. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.