The Bluetooth Protocol Architecture
Bluetooth network technology connects mobile devices wirelessly over a short-range to form a personal area network (PAN). The Bluetooth architecture has its own independent model with a stack of protocols, instead of following the standard OSI model or TCP/IP model.
The protocols in the Bluetooth standard can be loosely grouped into the physical layer, data link layer, middleware layer, and application layer as shown in the following diagram −
Protocols in the Bluetooth Protocol Architecture
- Physical Layer − This includes Bluetooth radio and Baseband (also in the data link layer.
- Radio − This is a physical layer equivalent protocol that lays down the physical structure and specifications for transmission of radio waves. It defines air interface, frequency bands, frequency hopping specifications, and modulation techniques.
- Baseband − This protocol takes the services of radio protocol. It defines the addressing scheme, packet frame format, timing, and power control algorithms.
- Link Manager Protocol (LMP) − LMP establishes logical links between Bluetooth devices and maintains the links for enabling communications. The other main functions of LMP are device authentication, message encryption, and negotiation of packet sizes.
- Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol (L2CAP) − L2CAP provides adaption between upper layer frame and baseband layer frame format. L2CAP provides support for both connection-oriented as well as connectionless services.
- RFComm − It is short for Radio Frontend Component. It provides a serial interface with WAP.
- Adopted Protocols − These are the protocols that are adopted from standard models. The commonly adopted protocols used in Bluetooth are Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP), Internet Protocol (IP), User Datagram Protocol (UDP), Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), and Wireless Application Protocol (WAP).
- Service Discovery Protocol (SDP)− SDP takes care of service-related queries like device information so as to establish a connection between contending Bluetooth devices.
- AT Commands − ATtention command set.
What is Bluetooth & How It Work
Bluetooth is the technology that allows electronic devices to communicate with each other directly. It uses radio waves that are both transmitted and received by the devices in connection with each other.
Bluetooth is something that has changed a lot over my years as a network engineer, and what it is today is very different from what it was 10 years ago.
I will now explain what Bluetooth is and how it works, so keep reading.
What is Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a wireless communications technology that allows high-speed, low power, wireless transmissions between electronic devices in short distances using a standardized protocol.
Or in more simple words. Bluetooth is the technology that allows for communication between electronic devices.
Bluetooth is mostly used for connecting things like wireless headphones to your phone or a wireless mouse to a computer. It should also not be confused with a Wi-Fi signal. [1]
The difference between Wi-Fi and Bluetooth is that Wi-Fi is much stronger and comes from your router. And even if devices can connect with each other through Wi-Fi it’s not the same as Bluetooth.
This is because Bluetooth is a direct connection between the devices while Wi-Fi uses the router as an interlink.
How Bluetooth Works
Bluetooth works very similarly to how Wi-Fi signals and radio signals work. Through radio waves.
Bluetooth uses a band of 79 different frequencies (channels) which range from 2,4-2,485 GHz. This frequency interval is shared with industrial, scientific, and medical gadgets. [2]
But this won’t be a problem for you when you use Bluetooth. This is because the class 2 type Bluetooth that exists in consumer devices such as phones and computers only have a range of around 10 m.
Other types of Bluetooth are class 1 and 3. Class 1 is used in industry and has a range of around 100m and class 3 is rarely used because of its short range of 1 m. [3]
Furthermore, the Bluetooth signal is not just one frequency. It can change its frequency, as much as 1600 times every second. This is to keep the signal strength and minimize interference in radio crowded areas.
Bluetooth Networks
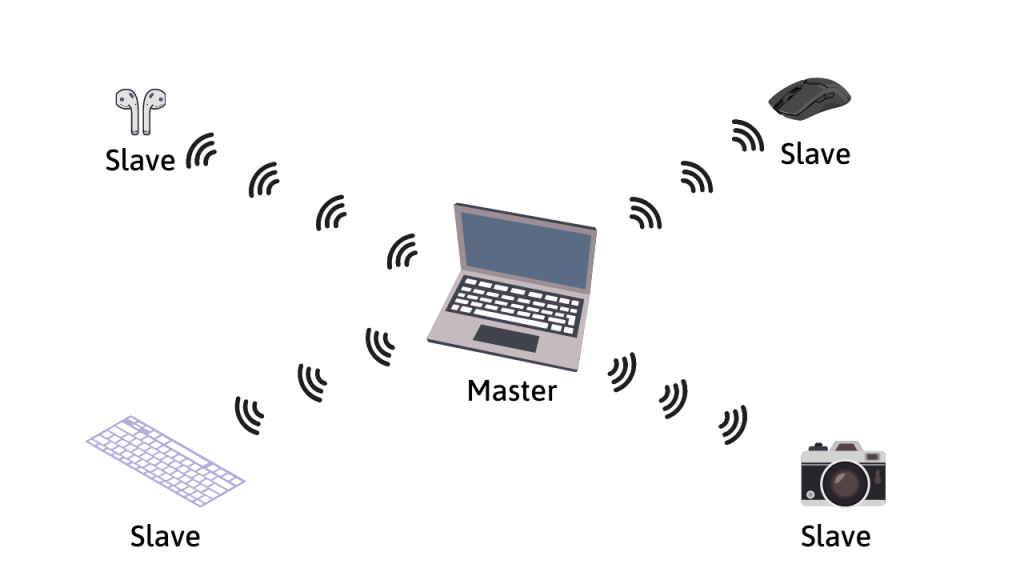
A Bluetooth network is called a piconet and uses a master/slave system to control the data flow.
In this system, one “master” device (often a phone or a computer) can connect to up to seven other devices. These will get the role of slaves (slave devices are often wireless earphones, mice, or keyboards). Slave devices can only connect to one master at a time. [4]
The master’s role is to coordinate data transfer in the piconet (Bluetooth network). It can send or request data from any of its slaves. In addition, slaves are not allowed to communicate with each other in the piconet.
Every electronic device with Bluetooth has a different address. This is important because in a house there are often a lot of devices that use Bluetooth to communicate with each other.
An address makes it possible for the device to know if a Bluetooth signal is meant for it or not.
There are three steps in the connection process between two devices that establish a Bluetooth connection. These steps are:
- Inquiry – If two devices have no information about each other one of them must send an inquiry request. The other device then responds with its address and name and what kind of hardware it is.
- Connecting – Here the two devices form a Bluetooth connection.
- Connection – After the devices have connected they enter a connection state with each other. The device can either be actively connected with each other or passively connected.
An active connection is when the connected devices constantly talk to each other. While passive is when they talk to each other periodically, like once every 1 second.
Device Bonding
Device bonding is when two devices remember each other. Bonded devices automatically establish a connection with each other if they are in range. An example is a car, which often connects with your mobile when you start it.
To create these bonds the devices go through a process called pairing. During pairing the two devices usually follow the normal connection process.
But instead of forgetting the device when they disconnect from each other. The devices’ data gets stored in memory. Furthermore, they also save a shared secret code that allows them to reconnect with each other in the future.
Why It’s Called Bluetooth
The name Bluetooth comes from the Danish king Harald Blåtand. He was king in the 900s and is most known for uniting Denmark and part of Norway into a kingdom. His name Blåtand is directly translated to Bluetooth. The belief is that he got this name from a rotten tooth that appeared blue.
The reason Bluetooth is named after him was that he united Denmark and Norwegian. Just like Bluetooth unites devices with each other. [5]
It is also here it has got its symbol from. The symbol consists of Harald Blåtands initials, H and B. But instead of using normal letters, it uses Nordic runes.
Bluetooth Security
Wireless connections will always be less secure than wired connections. This is because wireless connections are much easier to find and expose. But this makes Bluetooth far from unsecured.
The biggest security feature Bluetooth has is its short range. It makes it much harder for hackers to access it, compared to your internet connection for example. This is why the only real place Bluetooth hacking takes place is in public places with a lot of devices. [6]
In general, Bluetooth security is not something to worry about. And if you want to be extra safe you can set your device on hidden mode. Then will no other Bluetooth device be able to find it.
Pros & Cons With Bluetooth
There are of course some cons with Bluetooth, but they are for the most part overshadowed by the pros. Here they are;
Pros:
- New versions consume little battery.
- Very practical (doesn’t need cables).
- Secure.
- Allows for wireless hardware.
Cons:
Bottom Line
I hope this article has shed some light on how Bluetooth works and what it is. As well as make you realize how often most of us use Bluetooth in our everyday activities.
If you want to learn more about network technology check out my Router vs Modem – What’s the difference.