60 Linux Networking commands and scripts
Recently, I wanted to test network throughput via command line with at least 3 tools. For the life of me, I could not remember iperf . Not being able to remember previously used command line tools is frustrating and something we can all relate to. So I created a go-to list of network tools for myself. Then, I thought, why not turn this list into a blog post? So I spent another hour or two compiling this ongoing list of Linux Networking Commands and Scripts. I look forward mostly to suggestions, because I know there’s always something missing or new scripts out there to try.
Linux Networking commands and scripts
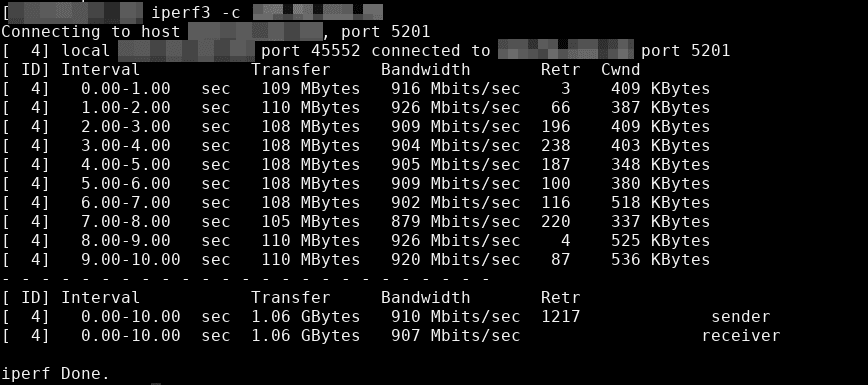
iperf command example/screenshot
This list of Linux Networking commands and scripts will receive ongoing updates:
- aria2 – downloading just about everything. Torrents included.
- arpwatch – Ethernet Activity Monitor.
- bmon – bandwidth monitor and rate estimator.
- bwm-ng – live network bandwidth monitor.
- curl – transferring data with URLs. (or try httpie)
- darkstat – captures network traffic, usage statistics.
- dhclient – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Client
- dig – query DNS servers for information.
- dstat – replacement for vmstat, iostat, mpstat, netstat and ifstat.
- ethtool – utility for controlling network drivers and hardware.
- gated – gateway routing daemon.
- host – DNS lookup utility.
- hping – TCP/IP packet assembler/analyzer.
- ibmonitor – shows bandwidth and total data transferred.
- ifstat – report network interfaces bandwidth.
- iftop – display bandwidth usage.
- ip (PDF file) – a command with more features that ifconfig (net-tools).
- iperf3 – network bandwidth measurement tool. (above screenshot Stacklinux VPS)
- iproute2 – collection of utilities for controlling TCP/IP.
- iptables – take control of network traffic.
- IPTraf – An IP Network Monitor.
- iputils – set of small useful utilities for Linux networking.
- iw – a new nl80211 based CLI configuration utility for wireless devices.
- jwhois (whois) – client for the whois service.
- “lsof -i” – reveal information about your network sockets.
- mtr – network diagnostic tool.
- net-tools – utilities include: arp, hostname, ifconfig, netstat, rarp, route, plipconfig, slattach, mii-tool, iptunnel and ipmaddr.
- ncat – improved re-implementation of the venerable netcat.
- netcat – networking utility for reading/writing network connections.
- nethogs – a small ‘net top’ tool.
- Netperf – Network bandwidth Testing.
- netplan – Netplan is a utility for easily configuring networking on a linux system.
- netsniff-ng – Swiss army knife for daily Linux network plumbing.
- netwatch – monitoring Network Connections.
- ngrep – grep applied to the network layer.
- nload – display network usage.
- nmap – network discovery and security auditing.
- nmcli – a command-line tool for controlling NetworkManager and reporting network status.
- nmtui – provides a text interface to configure networking by controlling NetworkManager .
- nslookup – query Internet name servers interactively.
- ping – send icmp echo_request to network hosts.
- route – show / manipulate the IP routing table.
- slurm – network load monitor.
- snort – Network Intrusion Detection and Prevention System.
- smokeping – keeps track of your network latency.
- socat – establishes two bidirectional byte streams and transfers data between them.
- speedometer – Measure and display the rate of data across a network.
- speedtest-cli – test internet bandwidth using speedtest.net
- ss – utility to investigate sockets.
- ssh – secure system administration and file transfers over insecure networks.
- tcpdump – command-line packet analyzer.
- tcptrack – Displays information about tcp connections on a network interface.
- telnet – user interface to the TELNET protocol.
- tracepath – very similar function to traceroute.
- traceroute – print the route packets trace to network host.
- vnStat – network traffic monitor.
- websocat – Connection forwarder from/to web sockets to/from usual sockets, in style of socat.
- wget – retrieving files using HTTP, HTTPS, FTP and FTPS.
- Wireless Tools for Linux – includes iwconfig, iwlist, iwspy, iwpriv and ifrename.
- Wireshark – network protocol analyzer.
- Suggestions welcomed.
Published: January 31st, 2020 | Last updated: April 13th, 2022
15 Best Linux Networking Commands and Scripts You Should Know
Both servers and software development use Linux. Today, Linux distributions are used by the vast majority of electronics and embedded systems.
Worldwide, Linux servers make up about 90% of all internet servers. Additionally, the Linux kernel is used by around 80% of all smartphones.
Today, every system in the world is linked via a network. Information exchange across systems requires network connectivity.
Computer networking refers to communication over the internet as well as within a network. A network can be as tiny and basic as one in a home or as intricate as one in a space station.
Network configuration and troubleshooting are both parts of networking. We are learning about Linux networking commands in this article.
TL;DR
| Linux Networking Commands | Description |
|---|---|
| aria2 | aria2 is a command line tool for downloading files in Linux. It is a lightweight alternative to wget and curl. |
| ifconfig | Displays information about currently active network interface and is used to configure kernel-resident network interfaces. |
| traceroute | This command is used to determine the route taken by packets to reach a specified host. |
| ping | Measures the round-trip time for messages sent from the originating host to a destination computer that are echoed back to the source. |
| curl | Helps in transferring data from or to a server without user interaction. |
| netstat | It can be used to view information about active network connections, routing tables, port listening and a variety of other networking-related information. |
| nmap | Nmap is a network exploration and security auditing tool. It can be used to identify hosts and services on a network, as well as security issues. |
| dig | dig command can be used to query DNS information. With dig, you can find out a host’s IP address, MX record, and other DNS information. |
| bmon | The bmon command in Linux is a network monitoring tool that can be used to check the status of your network connection. It can be used to monitor bandwidth usage, packet loss, and other network statistics. |
| dhclient | The dhclient command is a network configuration utility that allows you to configure your system to use a dynamic IP address. |
| host | This command allows users to query DNS records and perform other network-related functions. |
| iperf | This command is used to measure the throughput of a network or the performance of a network device. |
| ncat | ncat command is used for a variety of purposes, from port scanning to file transfers. |
| ss | It is a CLI command that shows the network statistics |