- Update Python 3 on Debian
- Prerequisites
- 1. Check the Installed Version
- 2. Update Python3
- 2. Update Pip
- Conclusion
- Want to contribute?
- How to Update/Upgrade Python in Linux [Ubuntu/RedHat]
- Updating From Python 2 to Python 3
- Install the Latest Version of Python on Ubuntu/Debian
- Install the Latest Version of Python on Fedora/RHEL
- Checking What Version of Python is Currently Installed
- Using a Package Manager to Upgrade Python Version
- Updating Minor/Major Versions
- How to Upgrade Python to 3.9
- Upgrading Python on Windows OS
- Upgrade to Python 3 with the Installer
- Install Python 3.9 from the Microsoft Store
- Upgrading Python on macOS
- Upgrade Python using Homebrew
- Upgrade Python with the Installer
- Upgrading Python in Linux
- Why Should You Upgrade Python?
- How Do I Upgrade my Python on Debian
- Updating your Python Version
- Update your PIP
Update Python 3 on Debian
This article explains how to install the latest version of Python3 from source code on Debian 10.
Prerequisites
1. Check the Installed Version
Check the installed Python3 version.
You will see something like this.
If your version is older than your application requires, proceed with this guide.
2. Update Python3
# apt-get install wget build-essential libreadline-gplv2-dev libncursesw5-dev libssl-dev libsqlite3-dev tk-dev libgdbm-dev libc6-dev libbz2-dev libffi-dev zlib1g-dev liblzma-dev -y # wget https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.9.6/Python-3.9.6.tgz # cd Python-3.9.6 && ./configure --enable-optimizations # update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/python python /usr/local/bin/python3.9 1 2. Update Pip
# /usr/local/bin/python3.9 -m pip install --upgrade pip # update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/pip pip /usr/local/bin/pip3.9 1 Python 3.9.6 pip 21.2.3 from /usr/local/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pip (python 3.9) Conclusion
Keeping your Python up-to-date is an important part of the development process. It provides bug fixes compared to older versions, and more importantly, it introduces new features and optimizations.
Want to contribute?
You could earn up to $600 by adding new articles.
How to Update/Upgrade Python in Linux [Ubuntu/RedHat]
This article will show you how to update Python to the latest version on your Linux Operating system.
Python is updated yearly with new features and big upgrades – these are called major updates. In addition to this, monthly updates are released which fix small issues and improve security – these are called minor updates.
Major updates change how Python works a bit and may break compatibility with some code as features are added or removed, whereas minor updates are solely there to fix problems without altering any functionality.
Updating From Python 2 to Python 3
Python 3 is still actively developed, receiving both minor and major updates. Python 2 is obsolete – it’s no longer developed, and you shouldn’t be using it for any new projects or to learn.
If you’re upgrading from Python 2 to Python 3, you will need to check your code is compatible – the syntax differs slightly between the two.
Python 2 and Python 3 are treated as separate software packages by most Linux package managers. To upgrade to version 3, simply install it.
The rest of this article will focus on the actively developed Python 3 only.
Install the Latest Version of Python on Ubuntu/Debian
On Ubuntu/Debian based distributions (including Mint, PopOS, etc) – run the following command:
This will install the default Python 3 version currently available on Ubuntu.
To install a specific version of Python 3, specify the full version:
sudo apt install python3.9
Install the Latest Version of Python on Fedora/RHEL
To install Python on RedHat based operating systems, run the following:
sudo dnf install python39
Note that the major version of Python 3 is always specified when installing using the dnf package manager – in this case, Python 3.9
Checking What Version of Python is Currently Installed
To check which version of Python you have installed, run:
Using a Package Manager to Upgrade Python Version
If Python 3 is already installed on your system, it will be updated along with the rest of your system when a software update is run.
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade
Updating Minor/Major Versions
On Ubuntu/Debian based systems, Python will update to the default version available via the package manager. This is usually a bit behind the official release but is considered stable. This may include major releases if you have installed via the python3 package rather than a specific version.
On Fedora, only minor updates will be applied – you’ll need to install the next major release manually when it is available.
How to Upgrade Python to 3.9
Every fresh Python release comes with bug fixes and new features. Python 3.9, the latest point release at the time of writing, comes with features such as improved time zone support, dictionary updates, and more flexible decorators.
This tutorial shows you how to upgrade Python to version 3.9 on all the major operating systems — Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- Administrative rights on the operating system you are using.
- Knowledge of which Python version is currently on your system. If you need help finding out the version of your Python installation, check out How to Check Python Version.
Note: If you are upgrading from a Python 2 release and do not have Python 3 installed, read our comprehensive guides on how to install it on:
Upgrading Python on Windows OS
To upgrade Python on Windows, download the installer or search for the app in the Microsoft Store.
Upgrade to Python 3 with the Installer
1. In your browser, visit the Python Releases for Windows section on the official Python website.
2. Click the Download Python button to download the installation file on your computer.
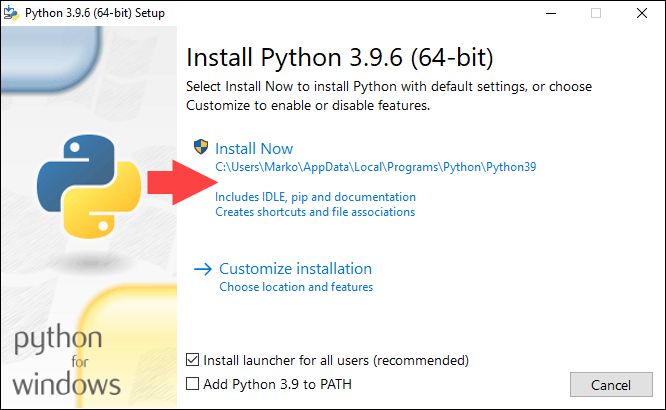
3. Next, run the Python installer. If you are upgrading from another point release of Python 3 (for example, 3.8.10), the installer suggests to install Python 3.9. Select Install Now to install Python with recommended options, or select Customize Installation to pick the install location and features.
If you already have an older version of the same Python release (for example, 3.9.1), the installer offers to upgrade your Python installation. Proceed by selecting Upgrade Now.
4. When the installation finishes, check whether the new version of Python has been installed successfully. Open Windows PowerShell and type:
The output should show the latest version of Python, as in the image below.
Install Python 3.9 from the Microsoft Store
If you want to use Python 3.9 to learn the basics or test some simple concepts, find and install the Python 3.9 app from the Microsoft Store.
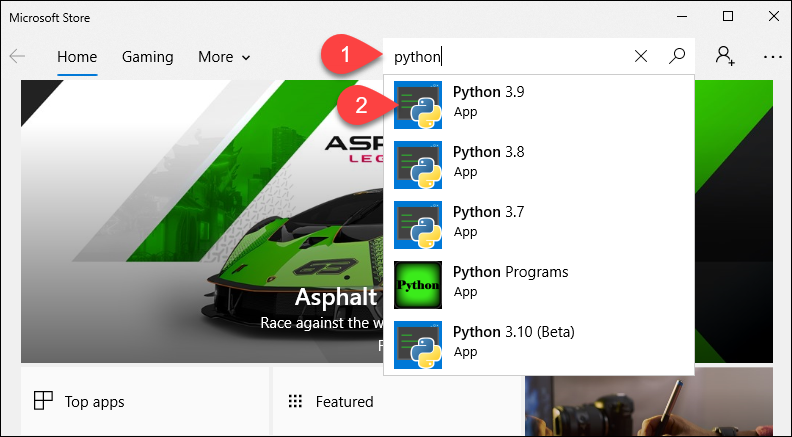
1. Go to Microsoft Store and type Python in the search field.
2. Select Python 3.9 from the search results that appear.
3. Click the Get button to start the installation.
Start the interactive Python 3.9 experience by finding the app in the Start Menu.
Upgrading Python on macOS
On macOS, Python can be installed, upgraded, and maintained using the command line interface or the GUI.
Upgrade Python using Homebrew
Install Python in the macOS terminal using the Homebrew package manager. If you do not have Homebrew, install it by typing the following script in the terminal:
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install.sh)"Then, proceed with the steps:
1. Update Homebrew by running:
2. If you are upgrading from Python 2, install Python 3 with the command:
If you already have a version of Python 3 installed, upgrade the package with the brew upgrade command:
Upgrade Python with the Installer
1. In your browser, navigate to the Python Releases for macOS page, on Python’s official website.
2. Click the link to download the latest Python 3 release on your computer.
3. Run the installer. Go through the installation steps by clicking Continue, agreeing to the License, and confirming the installation location and type.
4. Once the installation is complete, select Close.
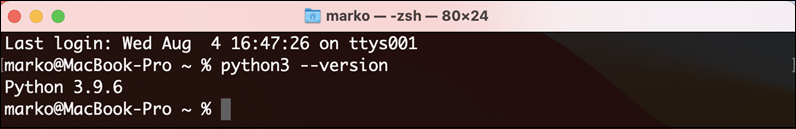
5. Finally, confirm that the new Python version has been successfully installed by typing the following in terminal:
The output should display the latest version of Python.
Upgrading Python in Linux
This article uses Ubuntu and its APT package manager to upgrade Python. If you are using a different Linux distribution, replace the apt Linux command with the appropriate command featured for your package manager.
Warning: Many Linux systems have Python 2 installed as the system version. Removing Python 2 could cause a system error. If you are planning to install Python 3 on Linux, install it alongside Python 2 and invoke it with the python3 command.
1. Start by updating the repositories:
2. Next, install Python 3.9 by running:
sudo apt install python3.9When prompted, type Y to start the installation.
3. Once Python installs, invoke the 3.9 version by running:
4. However, checking the installation with the python3 —version command still returns the old version. To fix this, you need to create a list of update alternatives. First, add the old version to the list with the command:
sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/python3 python3 /usr/bin/python3.[old-version] 1 5. Now add the new version:
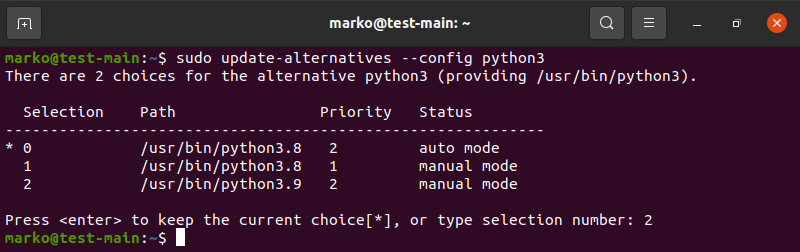
sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/python3 python3 /usr/bin/python3.9 26. Next, type the following command to configure the priority status of the versions:
sudo update-alternatives --config python3The output displays the available choices and their assigned number (in the example below, the numbers are 0, 1, 2). Type the number of the the version you wish to use and press Enter.
7. If you are not planning to use the old version of Python, remove the symlink that contained the previous Python 3 version with:
8. Then, replace the symlink with the new version:
sudo ln -s python3.9 /usr/bin/python39. Now, check the default version:
The output should confirm the successful installation and setup of the latest available version.
Why Should You Upgrade Python?
Since Python 3 was not a backward-compatible release, for a long time Python 2 remained the version of choice for those who wanted a stable development environment. Some services like Google App Engine did not support Python 3 for a long time.
However, given that the official support for the final Python 2.7 release has ended, upgrading to Python 3 is now strongly recommended. Python 3 is faster, and its syntax is more user-friendly.
If you already work with Python 3, upgrading to the latest point release gives you all the security updates and bug fixes.
After reading this tutorial, you should know how to upgrade your Python 3 version on Windows, macOS, and Linux. If you want to learn more about Python, read our article on Python data types.
Marko Aleksić is a Technical Writer at phoenixNAP. His innate curiosity regarding all things IT, combined with over a decade long background in writing, teaching and working in IT-related fields, led him to technical writing, where he has an opportunity to employ his skills and make technology less daunting to everyone.
Windows does not come with the Python programming language by default. However, you can install Python on your Windows server or local machine in just a few easy steps.
Flask is one of the most popular web application frameworks written in Python. This article explains how to install Flask in a virtual testing environment and create a simple Flask application.
Python is a popular programming language often used to write scripts for operating systems. Learn how to install Python 3.8 on Ubuntu 18.04 or 20.04.
NumPy (Numerical Python) is an open-source library for the Python programming language. It is used for scientific computing and working with arrays. Learn how to install it in this tutorial.
How Do I Upgrade my Python on Debian
In order to go to upgrade your python, you need to check its version. This can be done using the following command:
If python is successfully installed on your server, then you should get something like this:
Updating your Python Version
First, you need to install the required dependencies to compile the Python source code. This can be done using a special command, which is presented below:
# apt-get install wget build-essential libreadline-gplv2-dev libncursesw5-dev libssl-dev libsqlite3-dev tk-dev libgdbm-dev libc6-dev libbz2-dev libffi-dev zlib1g-dev liblzma-dev -yAfter that, we recommend going to the Python source download page to find the latest gzip version of the source code. Replace the urls and filenames in this tutorial with the latest version. Then download your python
wget https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.9.6/Python-3.9.6.tgzAfter that, you need to unpack the archive that you just downloaded. You can do it like this:
Next, compile the Python source
cd Python-3.9.6 && ./configure --enable-optimizationsThis is followed by the installation of your Python. Use the following command:
After that, a mandatory step for execution will be to check the name of your new Python executable file
Then Install the new default Python executable. Replace the two instances of /python3.9 in the following command with the name of your new Python executable
update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/python python /usr/local/bin/python3.9 1Update your PIP
An important step for this update is to update your pip.
/usr/local/bin/python3.9 -m pip install --upgrade pipThen you should check the name of your new pip executable
Set the new item as default. Use the name of your new pip executable in the following command:
update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/pip pip /usr/local/bin/pip3.9 1After that, you need to check the current version of your installed Python. You can make sure like this:
After that, you will be able to see the following:
Python-3.9.6 pip 21.2.3 from /usr/local/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pip (python 3.9)