- Как очистить apt cache и освободить дисковое пространство
- Что такое apt cache?
- Зачем сохранять кеш после установки пакета?
- Стоит ли очищать apt cache?
- Как правильно очистить apt cache?
- Безопасно ли удалять apt cache?
- How to Clear Apt Cache and Reclaim Precious Disk Space
- What is apt cache? Why is it used?
- Why keep the cache after installing the package?
- Should you clean apt cache?
- How to clean apt cache?
- Is it safe to delete apt cache?
- Conclusion
- How to Clear Apt Cache in Debian, Ubuntu and Linux Mint
- Apt Clean Command
- Apt Autoclean Command
Как очистить apt cache и освободить дисковое пространство
Как очистить кеш apt? Мы просто используем параметр clean команды apt-get:
Но очистка кеша apt — это не просто выполнение указанной выше команды.
В этом руководстве выясним, что такое apt cache, почему он используется, почему вы хотите его очистить и что еще следует знать об очистке apt cache.
Для примера используем Ubuntu, но т.к речь идет об apt, данная информация применима к другим дистрибутивам на основе Debian и Ubuntu, таким как Linux Mint, Deepin и др.
Что такое apt cache?
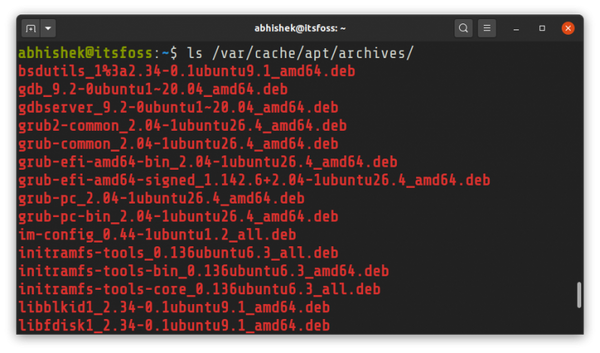
Когда вы устанавливаете пакет с помощью команды apt-get или apt (или пакетов DEB в центре программного обеспечения), менеджер пакетов apt загружает пакет и его зависимости в формате .deb и сохраняет его в папке /var/cache/apt/archives
Во время загрузки apt хранит пакет deb в каталоге /var/cache/apt/archives/partial. Когда пакет deb загружен полностью, он перемещается в каталог /var/cache/apt/archives.
После загрузки файлов требуемого deb пакета и его зависимостей ваша система устанавливает данный пакет. Вот для чего нужен кеш. Системе необходимо место для хранения файлов пакетов перед их установкой.
Зачем сохранять кеш после установки пакета?
Загруженные файлы deb не удаляются из каталога сразу после завершения установки. Если вы удалите пакет и переустановите его, ваша система будет искать пакет в кеше и получать его отсюда, а не загружать его снова (если версия пакета в кеше такая же, как и версия в удаленном репозитории).
Это намного быстрее. Вы можете попробовать это самостоятельно и посмотреть, сколько времени потребуется программе для первой установки, удаления и повторной установки. Вы можете использовать команду time, чтобы узнать, сколько времени требуется для выполнения команды:
time sudo apt install package_nameСтоит ли очищать apt cache?
Если у вас заканчивается дисковое пространство в корневом каталоге, вы можете очистить apt кеш. Это один из нескольких способов освободить дисковое пространство в Ubuntu.
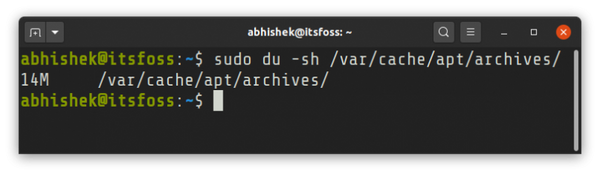
Проверьте, сколько места занимает кеш, с помощью команды du:
sudo du -sh /var/cache/apt/archives/partialКак правильно очистить apt cache?
Если вы хотите очистить кеш apt, воспользуйтесь специальной командой. Не удаляйте каталог кеша вручную.
Используйте команду apt-get с аргументом clean:
Данная команда удалит содержимое каталога /var/cache/apt/archives (кроме файла блокировки).
Есть еще одна команда, которая занимается очисткой кеша apt:
В отличие от clean, autoclean удаляет только те пакеты, которые невозможно загрузить из репозиториев.
Предположим, вы установили пакет xyz. Его файлы deb остаются в кеше. Если теперь в репозитории доступна новая версия пакета xyz, этот существующий пакет xyz в кэше теперь устарел и бесполезен. Опция autoclean удалит такие бесполезные пакеты, которые больше нельзя загрузить.
Безопасно ли удалять apt cache?
Очистка кеша не повлияет отрицательно на производительность системы. Возможно, если вы переустановите пакет, загрузка займет немного больше времени, но это все.
Опять же, используйте команду apt-get clean. Это быстрее и проще, чем вручную удалить каталог кеша.
How to Clear Apt Cache and Reclaim Precious Disk Space
Learn what apt cache is, why it is used, why you would want to clean it and some other things you should know about purging apt cache.
But there is more to cleaning apt cache than just running the above command. In this tutorial, I’ll explain what is apt cache, why is it used, why you would want to clean it and what other things you should know about purging apt cache. I am going to use Ubuntu here for reference but since this is about apt, it is applicable to Debian and other Debian and Ubuntu-based distributions like Linux Mint, Deepin and more.
What is apt cache? Why is it used?
When you install a package using apt-get or apt command (or DEB packages in the software center), the apt package manager downloads the package and its dependencies in .deb format and keeps it in /var/cache/apt/archives folder. While downloading, apt keeps the deb package in /var/cache/apt/archives/partial directory. When the deb package is downloaded completely, it is moved out to /var/cache/apt/archives directory. Once the deb files for the package and its dependencies are downloaded, your system installs the package from these deb files. Now you see the use of cache? The system needs a place to keep the package files somewhere before installing them. If you are aware of the Linux directory structure, you would understand that /var/cache is the appropriate here.
Why keep the cache after installing the package?
The downloaded deb files are not removed from the directory immediately after the installation is completed. If you remove a package and reinstall it, your system will look for the package in the cache and get it from here instead of downloading it again (as long as the package version in the cache is the same as the version in remote repository). This is much quicker. You can try this on your own and see how long a program takes to install the first time, remove it and install it again. You can use the time command to find out how long does it take to complete a command: time sudo apt install package_name. I couldn’t find anything concrete on the cache retention policy so I cannot say how long does Ubuntu keep the downloaded packages in the cache.
Should you clean apt cache?
It depends on you. If you are running out of disk space on root, you could clean apt cache and reclaim the disk space. It is one of the several ways to free up disk space on Ubuntu. Check how much space the cache takes with the du command: Sometime this could go in 100s of MB and this space could be crucial if you are running a server.
How to clean apt cache?
If you want to clear the apt cache, there is a dedicated command to do that. So don’t go about manually deleting the cache directory. You may think it is apt-cache command but that’s deceiving. Simply use the apt-get command with clean as argument:
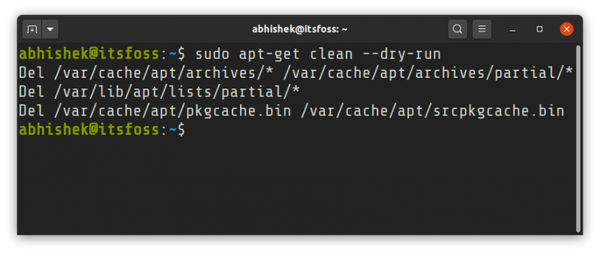
This will remove the content of the /var/cache/apt/archives directory (except the lock file). Here’s a dry run (simulation) of what the apt-get clean command deletes: There is another command that deals with cleaning the apt cache:
Unlike clean, autoclean only removes the packages that are not possible to download from the repositories. Suppose you installed package xyz. Its deb files remain in the cache. If there is now a new version of xyz package available in the repository, this existing xyz package in the cache is now outdated and useless. The autoclean option will delete such useless packages that cannot be downloaded anymore.
Is it safe to delete apt cache?
Yes. It is completely safe to clear the cache created by apt. It won’t negatively impact the performance of the system. Maybe if you reinstall the package it will take a bit longer to download but that’s about it. Again, use the apt-get clean command. It is quicker and easier than manually deleting cache directory. You may also use graphical tools like Stacer or Bleachbit for this purpose.
Conclusion
At the time of writing this article, there is no built-in option with the newer apt command. However, keeping backward compatibility, apt clean can still be run (which should be running apt-get clean underneath it). Please refer to this article to know the difference between apt and apt-get. I hope you find this explanation about apt cache interesting. It is not something essential but knowing this little things make you more knowledgeable about your Linux system. I welcome your feedback and suggestions in the comment section.
How to Clear Apt Cache in Debian, Ubuntu and Linux Mint
apt (Advanced Packaging Tool) is the package installation and dependency management tool in Debian and other Debian-based distributions. It works on top of ‘Dpkg‘ which is nothing but the Debian package installer.
The way apt installs packages is: it downloads the package for the required software, and additionally it downloads the packages for all the dependencies for the required software.
Once the packages are extracted and installation is complete, they are moved to a Cache directory which is located at ‘/var/cache/apt/archives’. Some packages for libraries, etc. are also located in other directories.
The reason why these packages are kept in the cache is that: next time another software has an existing package in the cache (with the required version), Apt will not download the package but instead use it from the Cache itself.
However as the system gets older, a lot of packages get cluttered in the Cache. Hence, it is a good practice to clear Apt Cache from time to time to free up the occupied space.
Today, we will see how to clear the Apt Cache in Debian and other Debian-based distributions.
Apt Clean Command
To delete the apt cache, we can call apt with the ‘clean‘ parameter to remove all the files in the cache directory. The user need not manually delete those files.
You can run ‘apt clean‘ with a parameter called ‘ —dry-run ‘, i.e. the dry run parameter, which will simply show you the directories from which packages will be deleted, and will not actually delete the packages.
To delete all these directories you can run apt clean (without dry run).
Apt Autoclean Command
Similar to apt clean, there is another command called ‘apt autoclean’. This command will remove the packages from Cache, for which a newer version is available in the repository.
apt will check the repository for a newer version of every package in the Cache.
The other packages in the cache, which don’t yet have a newer version in the repository, will remain in the cache and not be deleted with autoclean.
Conclusion
In this article, we learned how to clear the apt cache in Debian and Debian-based distributions. It is a good practice to clear the Cache from time to time. Users can also schedule a cron job (which automatically runs a command at specific intervals of time) to clear the Cache.
If you have any questions, let us know in the comments below!